to Section TOC
to Master TOC
THEORY OF OPERATION
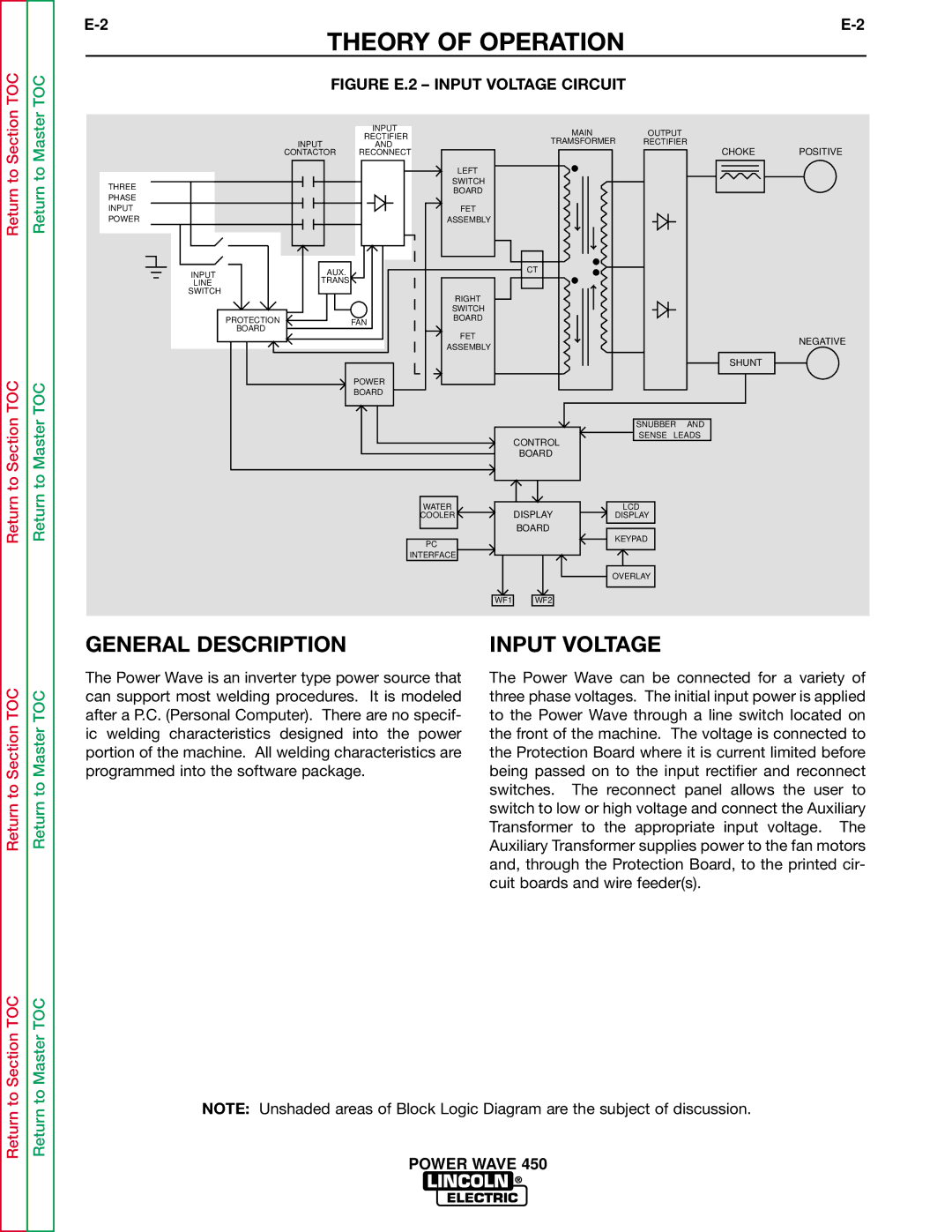
FIGURE E.2 – INPUT VOLTAGE CIRCUIT
| INPUT | MAIN | OUTPUT |
|
| RECTIFIER |
| ||
| TRAMSFORMER | RECTIFIER |
| |
INPUT | AND | POSITIVE | ||
CONTACTOR | RECONNECT |
| CHOKE | |
|
| LEFT |
|
|
THREE |
| SWITCH |
|
|
| BOARD |
|
| |
PHASE |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
Return
Return to Section TOC
Return
Return to Master TOC
INPUT |
| FET |
POWER |
| ASSEMBLY |
INPUT | AUX. | CT |
TRANS |
| |
LINE |
| |
SWITCH |
| RIGHT |
|
| |
|
| SWITCH |
PROTECTION | FAN | BOARD |
BOARD |
|
|
FET
ASSEMBLY
POWER
BOARD
CONTROL
BOARD
WATER
COOLERDISPLAY
BOARD
PC
INTERFACE
NEGATIVE
SHUNT
SNUBBER AND
SENSE LEADS
LCD
DISPLAY
KEYPAD
OVERLAY
WF1 WF2
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Power Wave is an inverter type power source that can support most welding procedures. It is modeled after a P.C. (Personal Computer). There are no specif- ic welding characteristics designed into the power portion of the machine. All welding characteristics are programmed into the software package.
INPUT VOLTAGE
The Power Wave can be connected for a variety of three phase voltages. The initial input power is applied to the Power Wave through a line switch located on the front of the machine. The voltage is connected to the Protection Board where it is current limited before being passed on to the input rectifier and reconnect switches. The reconnect panel allows the user to switch to low or high voltage and connect the Auxiliary Transformer to the appropriate input voltage. The Auxiliary Transformer supplies power to the fan motors and, through the Protection Board, to the printed cir- cuit boards and wire feeder(s).
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
NOTE: Unshaded areas of Block Logic Diagram are the subject of discussion.