to Section TOC
to Master TOC
THEORY OF OPERATION
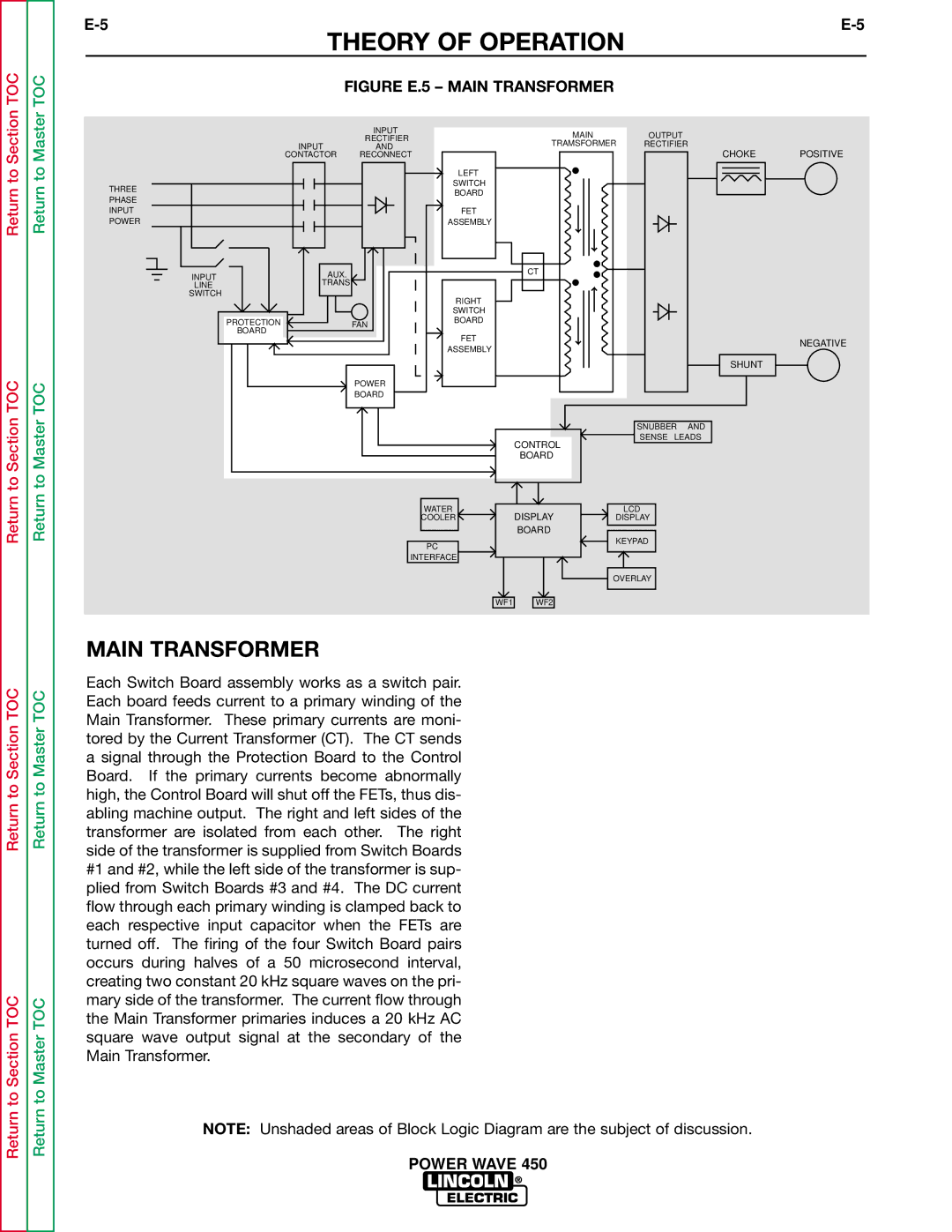
FIGURE E.5 – MAIN TRANSFORMER
| INPUT | MAIN | OUTPUT |
|
| RECTIFIER |
| ||
| TRAMSFORMER | RECTIFIER |
| |
INPUT | AND | POSITIVE | ||
CONTACTOR | RECONNECT |
| CHOKE | |
|
| LEFT |
|
|
THREE |
| SWITCH |
|
|
| BOARD |
|
| |
PHASE |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
Return
Return to Section TOC
Return
Return to Master TOC
INPUT |
| FET |
POWER |
| ASSEMBLY |
INPUT | AUX. | CT |
TRANS |
| |
LINE |
| |
SWITCH |
| RIGHT |
|
| |
|
| SWITCH |
PROTECTION | FAN | BOARD |
BOARD |
|
|
FET
ASSEMBLY
POWER
BOARD
CONTROL
BOARD
WATER
COOLERDISPLAY
BOARD
PC
INTERFACE
NEGATIVE
SHUNT
SNUBBER AND
SENSE LEADS
LCD
DISPLAY
KEYPAD
Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
OVERLAY
WF1 WF2
MAIN TRANSFORMER
Each Switch Board assembly works as a switch pair. Each board feeds current to a primary winding of the Main Transformer. These primary currents are moni- tored by the Current Transformer (CT). The CT sends a signal through the Protection Board to the Control Board. If the primary currents become abnormally high, the Control Board will shut off the FETs, thus dis- abling machine output. The right and left sides of the transformer are isolated from each other. The right side of the transformer is supplied from Switch Boards #1 and #2, while the left side of the transformer is sup- plied from Switch Boards #3 and #4. The DC current flow through each primary winding is clamped back to each respective input capacitor when the FETs are turned off. The firing of the four Switch Board pairs occurs during halves of a 50 microsecond interval, creating two constant 20 kHz square waves on the pri- mary side of the transformer. The current flow through the Main Transformer primaries induces a 20 kHz AC square wave output signal at the secondary of the Main Transformer.
NOTE: Unshaded areas of Block Logic Diagram are the subject of discussion.