SANsurfer iSCSI HBA CLI User’s Guide
Document Revision History
Changes Sections Affected Revision E Changes
SN0054621-00 E
Appendix C Target Parameters Appendix F Using Trace
Table of Contents
Getting Started
SN0054621-00 E
Non-interactive Mode Commands
SN0054621-00 E
HBA Statistics Target Parameters
Port-level Parameters HBA-level Parameters
Glossary Index
Trace Variables Trace Level Trace Data
List of Figures
How This Guide is Organized
Introduction
Intended Audience
Typographic Conventions
Part Number Title Or Name
Related Documents
Related Documents
Supported HBAs
Supported QLogic HBAs
Supported Operating Systems
Ports Media
Availability
License Agreements
Technical Support
Training
Introduction Technical Support SN0054621-00 E
Downloading the Installation Package
Installation and Removal
Installing SANsurfer iSCSI HBA CLI
To download the installation package
„ Microsoft Windows see Installing on Microsoft Windows on
Where
Installation and Removal Installing SANsurfer iSCSI HBA CLI
To install using the GUI installation
Installing on Microsoft Windows
Windows Standard GUI Installation
Read the information, and then click Next
Install Wizard Select Which Users
Select Which Users window appears, as shown in Figure
Install Wizard Ready to Install
To begin installation, click Install
Install Wizard Installing SANsurferiCLI
Install Wizard Complete
Click Finish Restart your computer
Quiet or Unattended Windows Installation
Windows Command Line Installation
Standard Windows Interactive CLI Installation
Passive Windows Installation
Overwrite Previous Windows Installations
Installing on Red Hat/SUSE Linux/PPC
Installing on Solaris SPARC/Solaris
Solaris Attended Installation
Create the noaskpkgadd.txt file with contents
Solaris Silent Installation
To install silently on Solaris
Create the following two files
Control Panel Uninstall
Microsoft Windows Uninstall
Start Menu Uninstall
Command Line Uninstall
To uninstall quietly from the command line
Red Hat/SUSE Linux/PPC Uninstall
Solaris SPARC/Solaris x86 Uninstall
Page
Introduction
Starting Interactive Mode
Getting Started
Starting Non-interactive Mode
Windows system displays the Main Menu. For example
Interactive Mode Commands
Command Line Interface Menu
Level
Port Level Info & Operations see
Port Network Settings Menu see
Ping Target see
Target Level Info & Operations see
List All QLogic iSCSI HBA Ports Detected see
To choose an HBA
Display Program Version Information
Host Level Info & Operations Menu
Import HBA Menu, Multiple Adapters
Save Host Configuration
Display General System Information
CLI Option -g
Select a configuration import option, and then press Enter
Import HBA Configuration
To import a single HBA configuration
Select from the following parameter sets to import
Select HBA Port
Update Firmware, Multiple Adapters
Install HBA Driver, All Adapters
CLI Option -d
CLI Option -ch
HBA Level Info & Operations Menu
HBA Information
HBA Options Menu
Update BIOS/UEFI or FCode Code Image
Update Firmware Image
No CLI Option
HBA Reset
Update ROM Image
Retrieve FW Crash Record
HBA Diagnostic Menu
HBA Diagnostic Menu provides the following options
Retrieve FW Flash & Nvram Record
Retrieve FW Coredump Record
Display HBA Level Statistics
To make changes to the HBA level parameters
HBA Level Parameters Menu
Display HBA Level Parameters
Display VPD Information
Configure HBA Level Parameters
Save Changes and Reset HBA
CLI Option -vpd
Port Level Info & Operations Menu
Port Link Settings Menu
Display Active Link Configuration
Configure Link Configuration
Port Network Settings Menu
Display Configured Link Configuration
Save Changes and Reset HBA if necessary
Configure IP Settings
ISNS Settings
To edit the configured HBA settings
Edit Configured Port Settings Menu
Display Configured Port Settings
Change Port Iscsi Alias Name
Port Firmware Settings Menu
To make changes to the HBA firmware settings
To edit specific HBA settings
Edit a Specific Port Setting
Configure iSCSI Settings
At the following prompt, type the new value
Configure Firmware Settings
Configure Device Settings
„ TaskManagementTimeout
Configure Basic Settings
Configure Advanced Settings
„ Ldrouterauto „ Loclinkauto „ Routableauto
„ VLANUserPriority
Configure IPv6 Settings
„ Vlanid
„ ZIO
Legacy QLA4010 Restore Default Port Settings
Port Restore Factory Defaults
Configure IPv6 TCP Settings
This option is not supported in the QLA4010 HBA
To use port diagnostics
Port Diagnostic Menu
Port Diagnostic Menu contains the following options
Here is an example of a successful ping attempt
Ping Target
To ping a target
Here is an example of a ping on an IPv6 network
To start a loopback test
Perform Loopback Test
Perform Read/Write Buffer Test
To start a read/write buffer test
Display Port Statistics
Reset Statistics
Display Connection Error Log
Display ARP Table
Display Neighbor Cache IPv6
Export Connection Error Log
Display Default Router List IPv6
Display Destination Cache IPv6
BIOS/UEFI or FCode Settings Menu
To edit the HBA BIOS/UEFI or FCode settings
Set Primary Boot Target Information
Display BIOS/UEFI or FCode Information
Set BIOS/UEFI or FCode Mode
Set Secondary Boot Target Information
Target Level Info & Operations
Clear Primary Boot Target Information
Clear Secondary Boot Target Information
Set Alternative Client ID
HBA CLI
List Targets
Display Target Information CLI Option -t
Interactive Mode Commands Port Level Info & Operations Menu
Delete Target
Configure Target Parameters
Bind Target
Configure Target Authentication Menu
Disable a Target
Enable a Target
To configure target authentication Chap
Display Targets Using Chap Entries
Display Chap Table
„ Name Chap name „ Secret Chap secret
Assign a Chap Entry to a Target
Add a Chap Entry
To assign a Chap entry to a target
Edit a Chap Entry
Add a Default Bidi Chap
To add a default Bidi Chap
To edit a Chap entry
Target Discovery Menu
Delete a Chap Entry
Save Target/CHAP Changes
To delete an entry from the Chap table
Add a Send Target
Display Send Targets
Display Discovered Targets
Mark Send Target for Re-discovery
Configure iSNS
Login and Persist a Discovered Target
Display iSNS Settings
Remove a Send Target
List LUN Information
List All QLogic iSCSI HBA Ports Detected
Refresh
Help
Select HBA Port
Exit
Non-Interactive Mode Commands
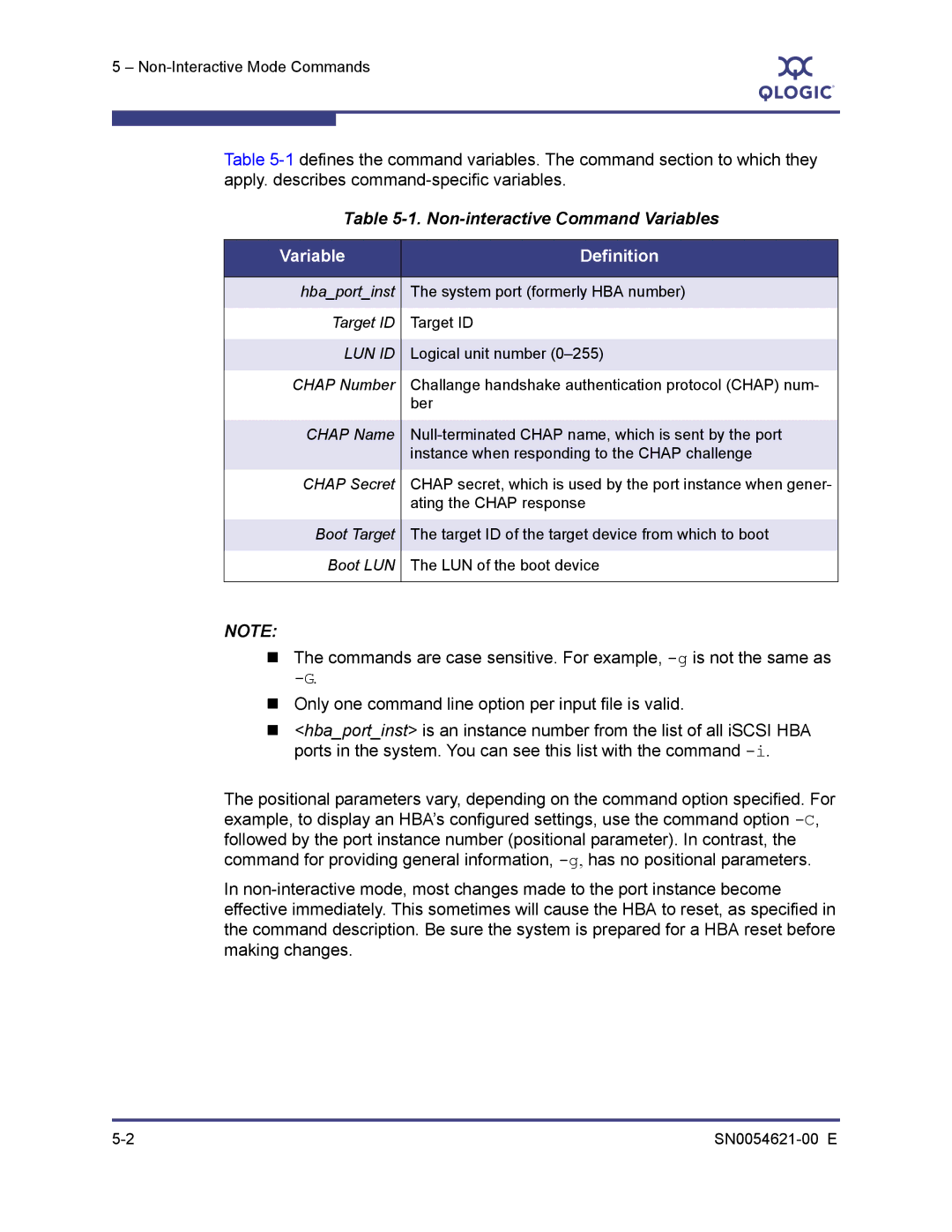
Non-interactive Command Variables
Variable Definition
Acb
Non-interactive Commands
HBA Reset
Addchap
Update BIOS/UEFI or FCode Mode
Bootcode
Bootcodemode
Binfo
HBA Information
For IBM cards, the following modes are available
Install HBA Driver, All Adapters
Cpbootcode
Csbootcode
System reboot may be required see the log file for details
Delchap
Dce
Defbidi
Display Destination Cache IPv6 only
Display Default Router List IPv6 only
Dtdspa
Dspchap
Dtdsp
Dtdupd
Dtrem
Dtli
Dtlia
Dumpnvram
Dtrema
Dumpcore
Edchap
Chap Parameters
Update Firmware Image-Specific HBA
Update Firmware Image-All HBAs
Parameter Parameter Alias Value
Help
Gcr
Display General System Information
List All QLogic iSCSI HBA Ports Detected
Port 0 on this HBA HBA Model Number
Import
Isns
Configure iSNS Settings
Ipdhcp
Isns6
Lcd
Model
Configuration Name Configuration Alias Value
Linkchap
HBA Parameters
Iparp
Afwdt
Afwdack
Ipad
Netconf
Display Neighbor Cache
Where option includes the following
Netconf6
To add persistent targets, enter the -pacommand as follows
To disable the IPv4 network, enter the following
To disables the IPv4 and IPv6 networks
To set only the local link address, enter the following
Pdt
Pbootcode
Pad
Pet
Ping
Following provides the IPv6 source address values
Rdf
Port Restore Factory Defaults
Rdh
Rwt
Save
Sreset
Sbootcode
Sbootcodecid
Sdmrc
Stdsp
Stat
Stathba
Strd
Ver
Display Program Version Information
Vpd
Display VPD Information
Port-level Parameters
Table A-1. Port Settings
Port- and HBA-level Parameters
Parameter Value Alias Description
EIPV4
Afwstm
Iprr
EIPV6
Zioe
IPV4TOS
Enable
TOS
IPV4TTL
IPV6NDRET
TCPV6ND
IPV6NDRT
IPV6STO
IPV6TC
TCPV6TS
IPV6TCPWS
IPV6VLANEN
When on, iSCSi headers with CRC protection
Loclinkauto
Ldrouterauto
Ldra
Locla
Vlan
Tmto
Winscale
Vlanid
Table A-2. HBA Settings
HBA-level Parameters
Statistic Abbreviation Meaning
HBA Statistics
Table B-1. HBA Statistics
HBA Statistics
Table B-1. HBA Statistics
Table B-1. HBA Statistics
Target Parameters
Table C-1. Target Parameters
Parameter Alias Function Value
Tgtmb
Tgtiname
Tgtkato
TGEMOR2T
Tgtidd
Tgttms
Tgtwinscaleen
Tgtlds
Tgttcpn
Tgtisnack
Tgtis
Target Parameters SN0054621-00 E
Table D-1. Interactive-Mode Error Code Descriptions
Error Codes
Interactive Mode Error Codes
Return Name Description
Coreerrhbainv
Coreerrnospace
Coreerrnocount
Coreerrnotgt
Coreerrbootcodeinvalid
Coreerrsetbootcode
Coreerrbootcodeenabled
Coreerrbootcodemode
Coreerrsecuritydescriptor
Coreerrdriverupdatefailed
Coreerrfailuretoinstall
Initializationfailed
Command Error Codes
Non-interactive Mode Error Codes
Table D-2. Non-interactive Mode Error Codes
Chapmap
Coreerrunabletogetinfofromdirverfile
Coreerrfailuretoinstalldrivers
Coreerrunabletounzipdriverfile
Coreerrsecuritydescriptorinitializationfailed
Gcr
Isns6
Corestatusbad
Netconf
Pbootcode
Coreerrinvalidcfgparameter
Stat
Ver Vpd
Error Codes Non-interactive Mode Error Codes SN0054621-00 E
File Type
Downloadable File Names
Table E-1. File Names
File Name Description
Downloadable File Names SN0054621-00 E
Click Properties
Using Trace
To use trace
Table F-1. Trace Parameters
Trace Variables
Trace Level
Variable Character String
Table F-3. Some More Info About Trace Levels
Table F-2. Trace Level Commands
Value Trace Level
Trace Output Value
Table F-4. Trace Data
Trace Data
To continue, press Enter
Amount Data Level
Glossary
Comma separated values CSV file
CoS
CSV file
Device
Fast!UTIL
GPort
Flash Bios
Flash
HBA alias
NPort Node Port
LUN masking
Media
NPort ID Virtualization
Point-to-point
Network adapter
Path
Port
MAC
Bios
Index
ARP
36,5-29
C4-22,5-5cache
41,5-9
Ch4-12,5-5
28,5-27
30,5-25
14,5-26
31,5-28
HBA
Dhcp
TCP Tcpdchp
Core 4-17,5-11firmware core 4-16firmware Flash 4-15NVRAM
Chap
Dr4-33,5-8driver
Dumpnvram 4-15, 5-11-dv
25,4-26,5-20,A-2
26,A-2
26,5-20,A-2,C-2
Version 4-12,4-48,5-14version, HBA
Ldrouterauto A-8
Routableauto A-8
G4-9,5-13
H4-49,5-13
48,5-14
12,5-24
48,4-49
12,4-48,4-49,5-14
25,A-4
Iocb
Address 4-26,4-49,5-20,A-3,C-3HBA port
26,A-4
IPv6 SourceAddFlg, target C-3TCP settings
Alias 4-24,4-26,A-6
Suse
LIP
49,5-14
21,A-8
5-1
N4-18,4-24,5-19
Pa4-40,5-23
Nh4-24,5-23
Nvram
Glossary-6
R2T
PPC
ID, LUN
IP ARP
C-5
35,5-29
Scsi
12,4-49,5-14
Stat4-32,5-30-stathba5-30statistics
Snack
ISCSI 4-24,5-20,A-7target iSCSI I/O C-5
T4-37,5-30
Index-18 SN0054621-00 E
Tcpdhcp
TCP
Dhcp A-8
25,C-2
TCP 4-27,5-20,A-5,A-8time to live, IPv4 4-25,A-4timeouts
25,4-27,A-7,C-3
25,C-4
Vlan
SN0054621-00 E Index-21
Camberley Surrey, GU16 7ER UK +44 0 1276 804