Architecture
In this document (bit 0 is always the rightmost bit).
Byte addressing is used with the R3900 Processor Core, but there are alignment restrictions for halfword and word access. Halfword access is aligned on an even byte boundary (0, 2, 4...) and word access on a byte boundary divisible by 4 (0, 4, 8...) .
The address of
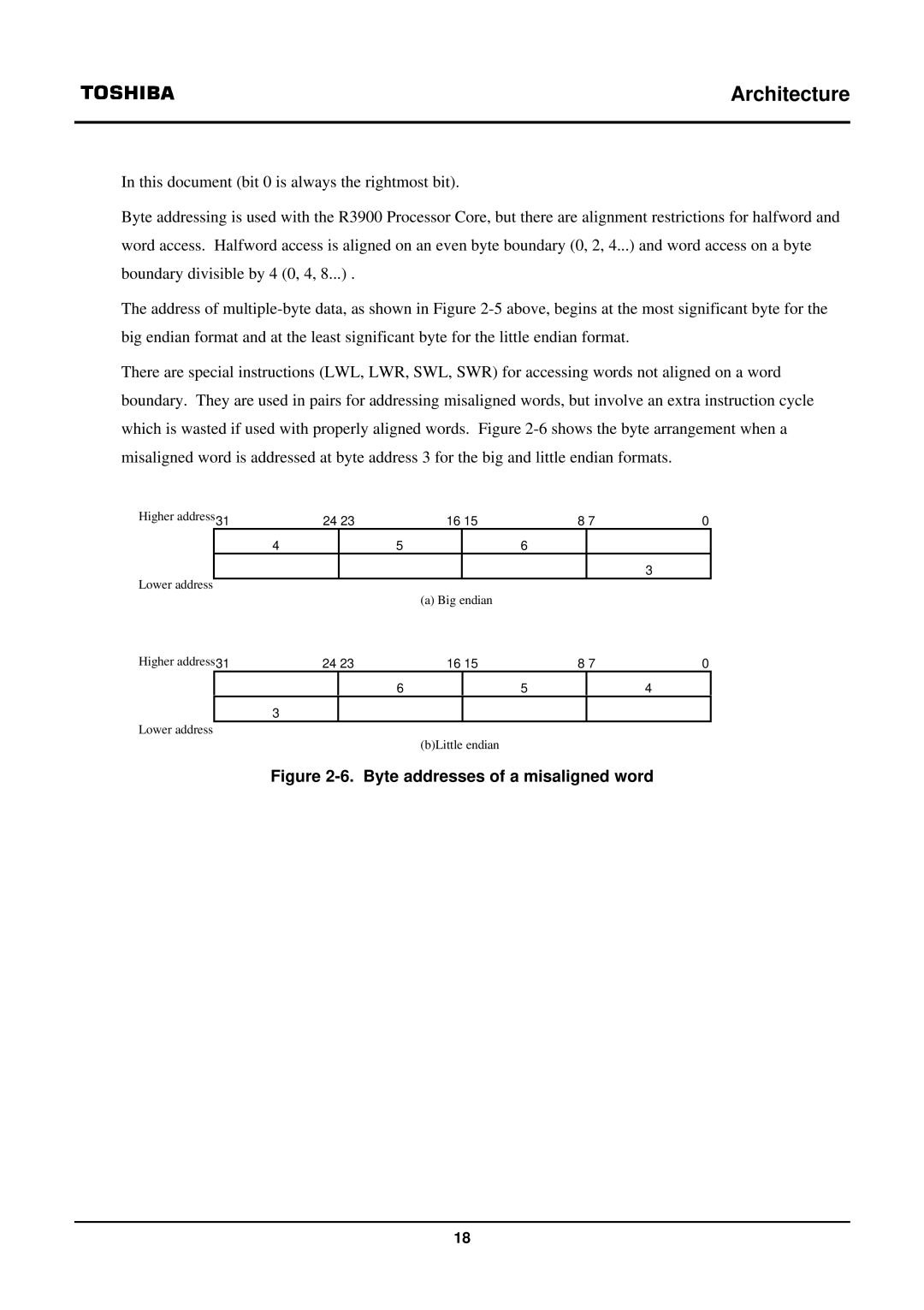
There are special instructions (LWL, LWR, SWL, SWR) for accessing words not aligned on a word boundary. They are used in pairs for addressing misaligned words, but involve an extra instruction cycle which is wasted if used with properly aligned words. Figure
Higher address31 | 24 23 | 16 15 | 8 7 | 0 | |
| 4 |
| 5 | 6 |
|
3
Lower address
(a) Big endian
Higher address31 | 24 23 | 16 15 | 8 7 | 0 | ||||
|
|
|
| 6 |
| 5 |
| 4 |
3
Lower address
(b)Little endian
Figure 2-6. Byte addresses of a misaligned word
18