Micro Motion
Page
Contents
Contents
Using a DeviceNet Tool
Optional Configuration
Measurement Performance
Appendix a Default Values and Ranges
Micro Motion Model 2400S Transmitters for DeviceNet
Determining transmitter information
Safety
Before You Begin
Overview
Communication tools
DeviceNet functionality
Determining version information
1Obtaining version information
Planning the configuration
Pre-configuration worksheet
1Configuration overview
2Flowmeter documentation resources
Before You Begin Pre-configuration worksheet
Configuration data
Flowmeter documentation
Micro Motion customer service
KBaud
Setting the DeviceNet node address and baud rate
Flowmeter Startup
Bringing the transmitter online
Flowmeter Startup
User interface without or with display
Using the Transmitter User Interface
1User interface Transmitters without display
Using the Transmitter User Interface
Using the optical switches
Removing and replacing the transmitter housing cover
Using the display
Display language
Viewing process variables
3Entering the display menu system
Using display menus
Entering floating-point values with the display
Display password
Scroll to d
Select
Micro Motion Model 2400S Transmitters for DeviceNet
Connecting with ProLink II or Pocket ProLink Software
Configuration upload/download
Requirements
Connecting via the service port clips
Connecting to a Model 2400S DN transmitter
Service port connection parameters
1Service port auto-detection limits
Protocol Service Port
1Serial port connections to service port clips
Connecting via the IrDA port
Protocol Service Port IrDA Port
ProLink II language
Using a DeviceNet Tool
Connecting to the Model 2400S DN transmitter
Using the DeviceNet device profile
Type B tools
Using a DeviceNet tool
Using a DeviceNet Tool
Type a tools
1Default DeviceNet assemblies
Default assemblies
Micro Motion Model 2400S Transmitters for DeviceNet
Characterization parameters
Required Transmitter Configuration
When to characterize
Characterizing the flowmeter
Sensor type
Required Transmitter Configuration
1Sensor calibration parameters
Flow calibration values
2Characterizing the flowmeter
How to characterize
Configuring the measurement units
3Configuring measurement units
2Mass flow measurement units
Volume flow units
3Volume flow measurement units Liquid
Mass flow units
M3/MIN
4Volume flow measurement units Gas
5Density measurement units
Density units
7Pressure measurement units
Temperature units
6Temperature measurement units
Pressure units
MPA
Recording process variables
Using the Transmitter
Using the Transmitter
With the display
With ProLink
With a DeviceNet tool
1Process data in DeviceNet objects
Attribute Data Class Instance Type Description
Density fixed Baume units
2Summary of input assemblies
Mass flow, mass
API average temperature-corrected density
Using the module LED
Using the LEDs
4Network LED states, definitions, and recommendations
Using the network LED
Using the status LED
3Module LED states, definitions, and recommendations
5Transmitter status LED
Using ProLink
Handling status alarms
Status LED state Alarm priority Definition
6Transmitter responses to status alarms
Status window
1Viewing and acknowledging alarms with the display
Alarm Log window
Click ProLink Alarm Log
Click ProLink Status
Using the totalizers and inventories
208772.63
3Controlling totalizers and inventories with the display
Controlling totalizers and inventories
Object Function Disabled Enabled
Inventory reset
To accomplish this Use this device profile data
To reset an individual totalizer or inventory
Using the Transmitter
Instance ID Data description Size bytes Data type
9Output assemblies used for totalizer and inventory control
Micro Motion Model 2400S Transmitters for DeviceNet
Optional Configuration
1Configuration map
Tool Topic Subtopic ProLink DeviceNet tool Display Section
Optional Configuration
Configuring volume flow measurement for gas
Specific Gravity Compared to Air, or Density
Using the Gas Wizard
Click ProLink Configure Flow
Enable the Enter Other Gas Property radio button
Configuring cutoffs
1Gas standard volume flow measurement DeviceNet tool
Cutoff type Default Comments
2Cutoff default values
Cutoffs and volume flow
Configuring the damping values
Process variable Valid damping values
Damping and volume measurement
Configuring the flow direction parameter
3Valid damping values
Configuring events
4Effect of flow direction on totalizers and flow values
Defining events
DeviceNet ProLink II label Display label Code Description
5Event types
6Event actions
DeviceNet Type Code Description
Start Stop
Example
Sec range is 0.0-60.0 sec
Configuring slug flow limits and duration
Checking and reporting event status
Changing event setpoints from the display
Configuring status alarm severity
Alarm severity levels and fault reporting
Transmitter action if condition occurs
8Status alarms and severity levels
Enabling and disabling display functions
Configuring the display
Update period
Language
Configuring the LCD backlight
Parameter Enabled shown Disabled hidden
9Display functions
Configuring the display variables and display precision
10Example of a display variable configuration
Display variable Process variable
DeviceNet node address
Configuring digital communications
11Baud rate codes
DeviceNet configurable input assembly
Switch position Baud rate
DeviceNet baud rate
Modbus Ascii support
Modbus address
Digital communications fault action
12Digital communications fault action options
IrDA port usage
Parameter Description
Fault timeout
Configuring device settings
13Device settings
Terms and definitions
Configuring sensor parameters
Configuring the petroleum measurement application
About the petroleum measurement application
API reference tables
14API reference temperature tables
Configuration procedure
15API parameters
16Standard curves and associated measurement units
Configuring the enhanced density application
Name Description Density unit Temperature unit
About the enhanced density application
Hfcs
17Derived variables and available process variables
Volume Conc SG
3Configuring the enhanced density application DeviceNet tool
Micro Motion Model 2400S Transmitters for DeviceNet
Pressure Compensation Temperature Compensation
Pressure compensation
Options
Configuration
Pressure Compensation and Temperature Compensation
Pressure correction factors
External temperature compensation
2Configuring pressure compensation with a DeviceNet tool
3Configuring external temperature compensation with ProLink
Section See Section
Obtaining external pressure and temperature data
Micro Motion Model 2400S Transmitters for DeviceNet
Meter validation, meter verification, and calibration
Measurement Performance
Measurement Performance
Meter verification
Meter validation and meter factors
Calibration
Performing meter verification
Comparison and recommendations
1Meter verification procedure ProLink
2Meter verification procedure Display menu
3Meter verification procedure DeviceNet tool
Step number Step description Interface
1DeviceNet interface for meter verification
Uncertainty limit and test results
Performing meter validation
Additional ProLink II tools for meter verification
⋅ ExternalStandard
For DeviceNet Device Profile
Performing zero calibration
Preparing for zero
Zero procedure
4Zero button Flowmeter zero procedure
6ProLink II Flowmeter zero procedure
Performing density calibration
7DeviceNet tool Flowmeter zero procedure
Density calibration fluids
Density calibration procedures
Preparing for density calibration
Sensor requirements
8D1 and D2 density calibration ProLink
9D1 and D2 density calibration DeviceNet tool
10D3 or D3 and D4 density calibration ProLink
11D3 or D3 and D4 density calibration DeviceNet tool
12Temperature calibration ProLink
Performing temperature calibration
110
Section Topic
Troubleshooting
Guide to troubleshooting topics
1Troubleshooting topics and locations
Troubleshooting
Transmitter does not operate
Transmitter does not communicate
ProLink
Diagnosing wiring problems
Checking the DeviceNet cable and connector
Checking the communication device
Fault conditions
Simulation mode for process variables
Zero or calibration failure
Transmitter LEDs
Status alarms
2Status alarms and remedies
Alarm ProLink Code Message Cause Suggested remedy
A012 Zero Too High See A10
PIC UI Eeprom
3Process variables problems and remedies
Symptom Cause Suggested remedy
Checking process variables
120
Checking slug flow
Checking the calibration
Checking the flow measurement configuration
Checking the sensor tubes
Checking the characterization
5Sensor pickoff values
Obtaining the test point values
4Test points with DeviceNet tool
Evaluating the test points
7Low pickoff voltage causes and remedies
Drive gain problems
6Drive gain problems, causes, and remedies
Low pickoff voltage
Checking sensor circuitry
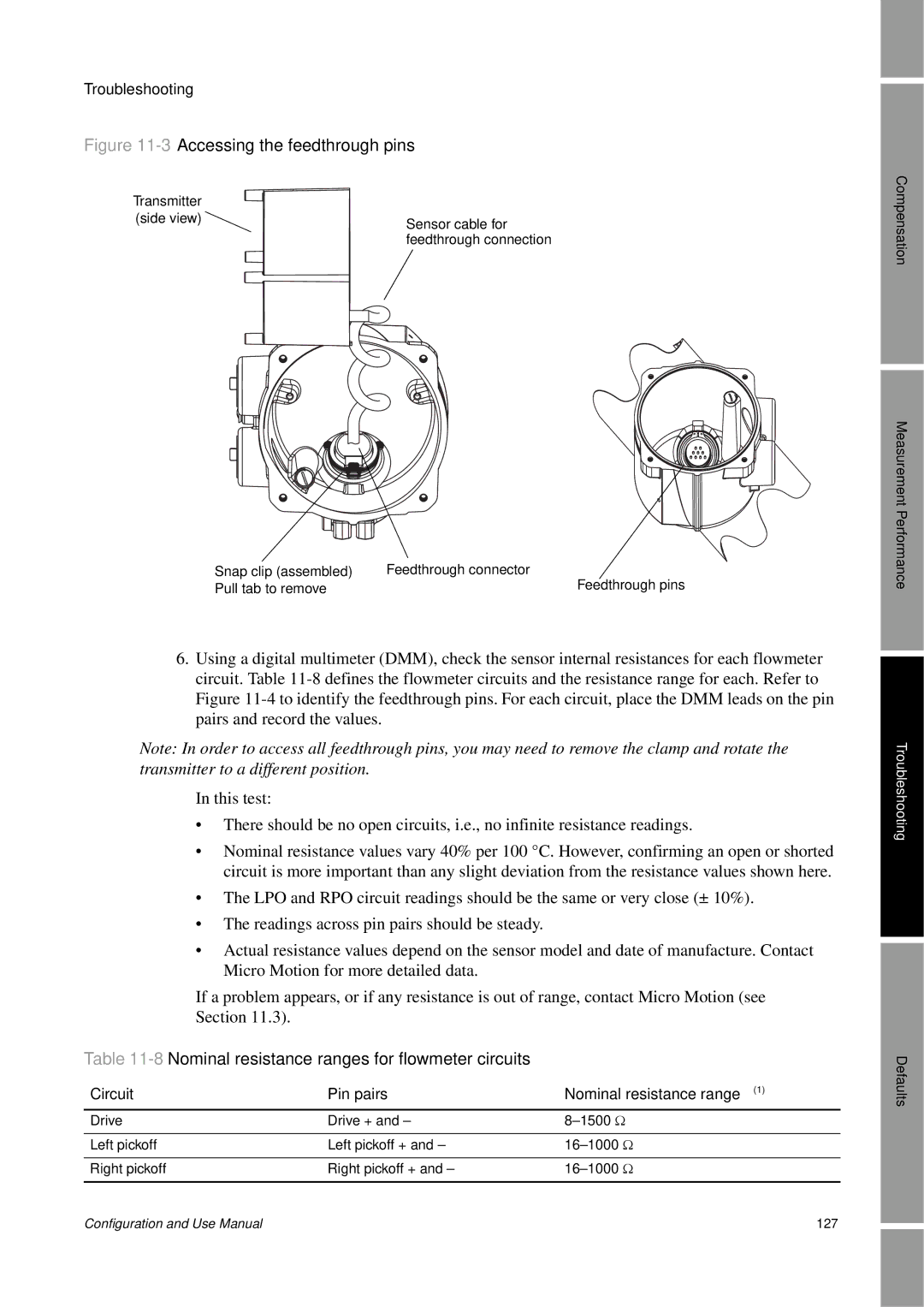
2Exploded view of transmitter and connection to sensor
Circuit Pin pairs Nominal resistance range1
8Nominal resistance ranges for flowmeter circuits
4Feedthrough pins
9Sensor and cable short to case causes and remedies
130
Type Setting Default Range Comments
Default Values and Ranges
Most frequently used defaults and ranges
Table A-1Transmitter default values and ranges
Default Values and Ranges
Configuration and Use Manual 133
134
Version information
Menu Flowcharts
Figure B-1ProLink II main menu
Menu Flowcharts
Figure B-2ProLink II configuration menu
Figure B-3ProLink II configuration menu
Figure B-4Display menu Off-line menu, top level
Figure B-6Display menu Off-line maintenance Configuration
Figure B-7Display menu Off-line maintenance Zero
142
Device Profile
Appendix C
Device Profile
Attrib Name Data type Service Mem Description Comments
Table C-3Analog Input Point Object 0x0A Instance 3 density
Gas Standard Volume Object
Calibration Object
Table C-5Gas Standard Volume Object 0x64 Instance
Table C-6Calibration Object 0x65 Instance
Diagnostics Object
Table C-7Diagnostics Object 0x66 Instance
Configuration and Use Manual 151
0x0200 = D4
Get Collection of status bits
=UI Prom
Set Entry in the alarm Range Index History log Alarm history
156
Configuration and Use Manual 157
158
Sensor Information Object
Local Display Object
Table C-8Sensor Information Object 0x67 Instance
Table C-9Local Display Object 0x68 Instance
API Object
Table C-10API Object 0x69 Instance
CTL Real
Table C-11Enhanced Density Object 0x6A Instance
Code Description
Process variable codes
Measurement unit codes
Alarm index codes
Alarm index codes
Table C-16
Code or abbreviation Definition Comment or reference
Display Codes and Abbreviations
Codes and abbreviations
Table D-1Display codes used for display variables
Display Codes and Abbreviations
Table D-2Display codes used in off-line menu
Enabl
172
Index
Index
See EDS
MAC ID
See also Display
178
Page
MMI-20007739