6 |
Antenna and Feedline Selection
Antennas
The equipment can be used with a number of antennas. The antenna type used depends on the physical size and layout of a system.
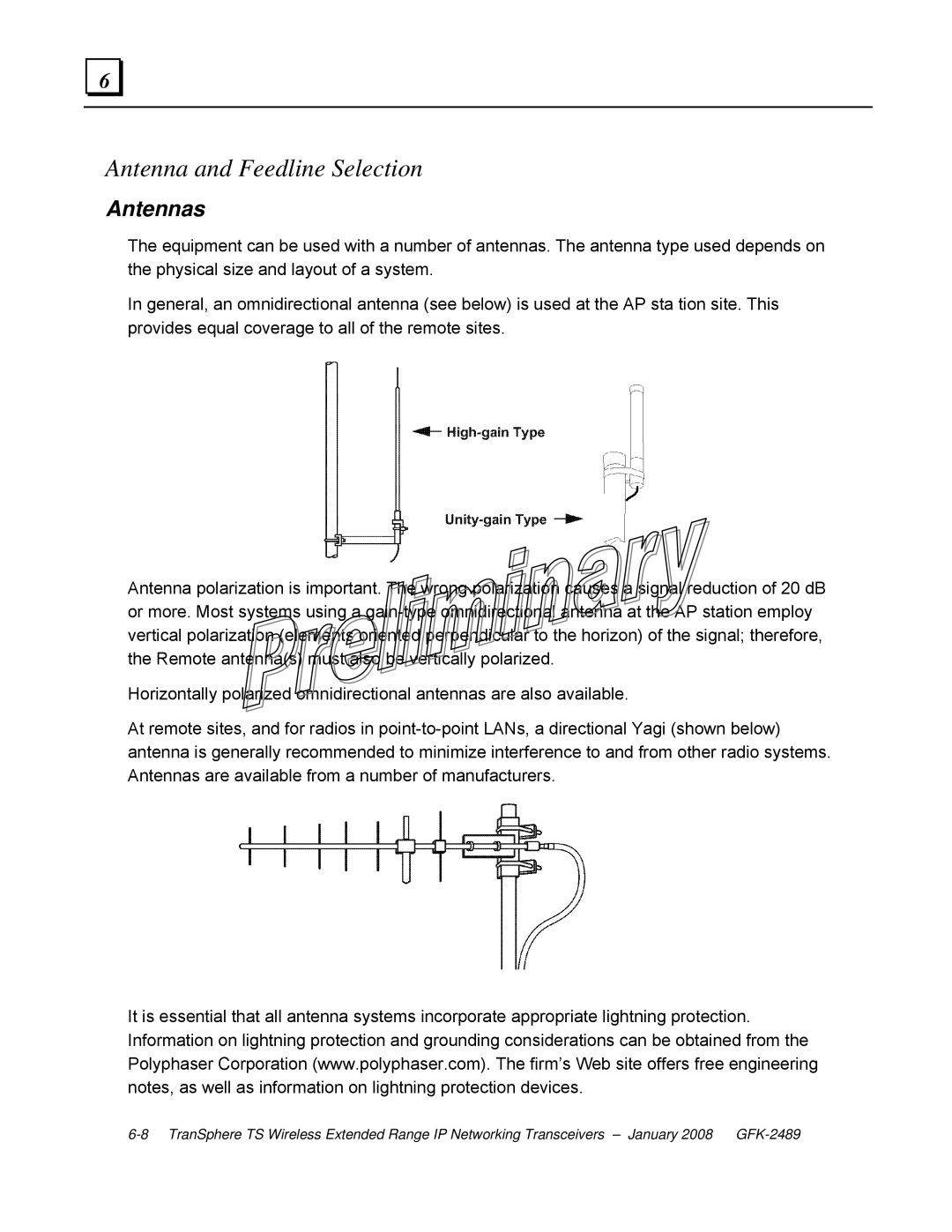
In general, an omnidirectional antenna (see below) is used at the AP sta tion site. This provides equal coverage to all of the remote sites.
Antenna polarization is important. The wrong polarization causes a signal reduction of 20 dB or more. Most systems using a
Horizontally polarized omnidirectional antennas are also available.
At remote sites, and for radios in
It is essential that all antenna systems incorporate appropriate lightning protection. Information on lightning protection and grounding considerations can be obtained from the Polyphaser Corporation (www.polyphaser.com). The firm’s Web site offers free engineering notes, as well as information on lightning protection devices.