6 |
▪The number of bytes they can fit into a hop, depending on hop time, is:
Hop time
(MS) FEC Bytes/hop
745
7 FEC 11
14139
14 FEC 59
28324
28 FEC 151
Included in the byte count is 9 bytes of overhead per packet. So, at 7MS without FEC, a 1000 byte packet requires 1009 bytes split into 45 bytes/hop, or 23 hops. 1026 bytes of data also requires 23 hops; however, a
▪If any transceiver in your network is connected to a large LAN, such as may be found in a large office complex, there may be undesired multicast or broadcast traffic over the air.
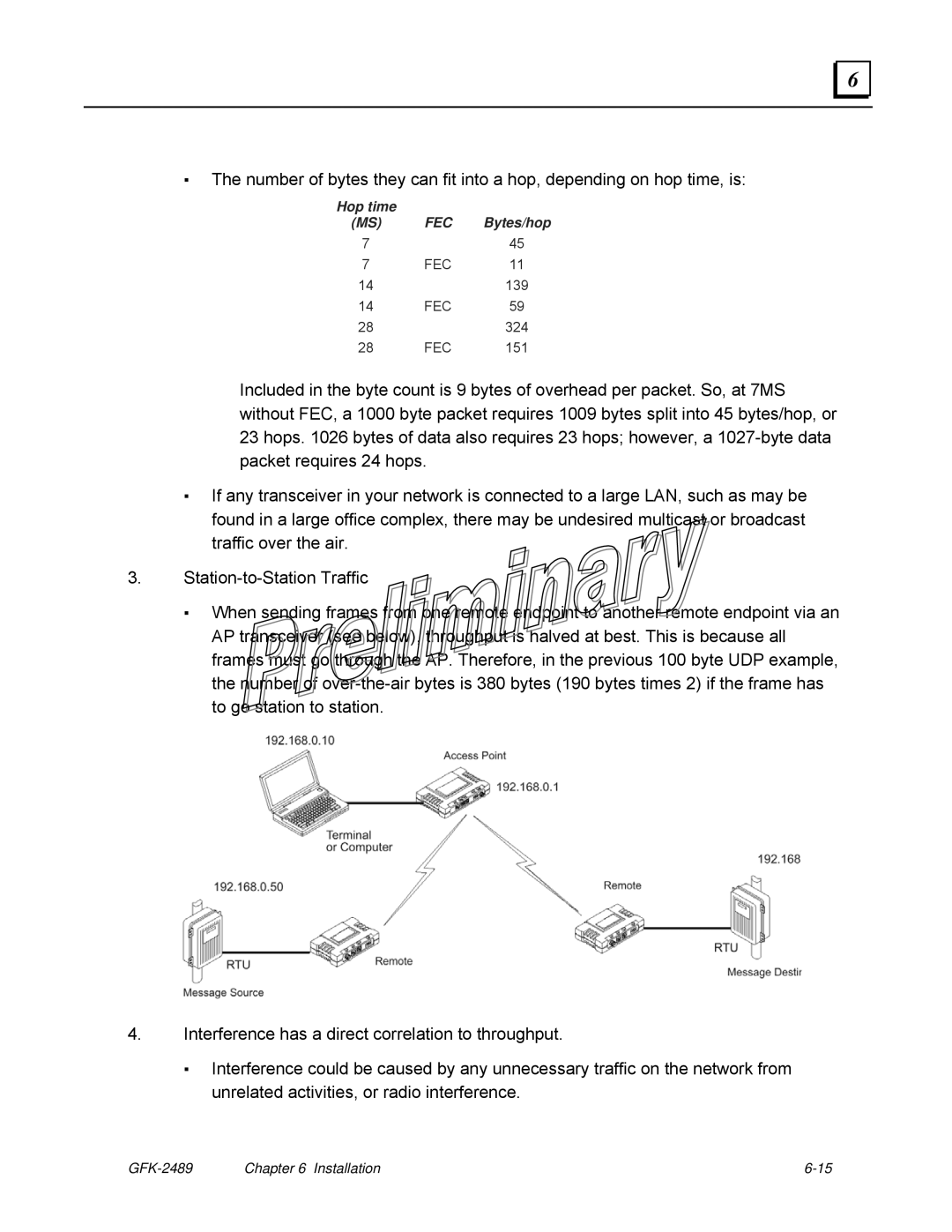
3.
▪When sending frames from one remote endpoint to another remote endpoint via an AP transceiver (see below), throughput is halved at best. This is because all frames must go through the AP. Therefore, in the previous 100 byte UDP example, the number of
4.Interference has a direct correlation to throughput.
▪Interference could be caused by any unnecessary traffic on the network from unrelated activities, or radio interference.
| Chapter 6 Installation |