Intel 460GX Chipset System Software Developer’s Manual
Intel 460GX Chipset System Software Developer’s Manual
Contents
Coherency
10.1
Latency
10-1
11-8
13.2.4
Figures
Tables
12-11
System Overview
Introduction
Name Function
Component Overview
Intel 460GX Chipset Components
Itanium Processor System Bus Support
Product Features
I/O Support
PXB Features
Dram Interface Support
GXB Features
RAS Features
Programmable Interrupt Device PID
Other Platform Components
Reference Documents
1 I/O & Firmware Bridge IFB
Date Description June Initial release
Revision History
Introduction
Register Descriptions
Access Mechanism
Device
Access Restrictions
Partitioning
Device Mapping on Bus CBN
Reserved or Undefined Register Locations
Default Upon Reset
Register Attributes
Reserved Bits Defined in Registers
Gart Programming Region
Configaddress Configuration Address Register
I/O Mapped Registers
Consistency
1.1
Error Handling Registers
Configdata Configuration Data Register
1 SAC
Valid
Bits Description Disable
1.2
1.3
Ferrsac First Error Status Register
Nerrsac All Error Status Register
Biuitid BIU Itid Register
Saferr System Address on First Error
Address bits
Biudata BIU Data Register
2.3 SEC0TXINFOFERR Txinfo on First Memory Card B SEC
2 SDC
2.1 SEC0DFERR Data on First Memory Card B SEC
2.2 SEC0ECCFERR ECC on First Memory Card B SEC
2.7 SEC1DFERR Data on First Memory Card a SEC
2.4 DED0DFERR Data on First Memory Card B DED
2.5 DED0ECCFERR ECC on First Memory Card B DED
2.6 DED0TXINFOFERR Txinfo on First Memory Card B DED
2.10 DED1DFERR Data on First Memory Card a DED
2.8 SEC1ECCFERR ECC on First Memory Card a SEC
2.9 SEC1TXINFOFERR Txinfo on First Memory Card a SEC
2.12 DED1TXINFOFERR Txinfo on First Memory Card a DED
Sdcferr First Error Status Register
2.11 DED1ECCFERR ECC on First Memory Card a DED
14 ’Forward’ Underflow Card B Left Stack Error FL0
22 ’Forward’ Underflow Card a Right Stack Error FR1
21 ’Forward’ Underflow Card a Left Stack Error FL1
15 ’Forward’ Underflow Card B Right Stack Error FR0
Pitidferr Data on First Pitid Parity Error
Sdcnerr SDC Next Error Status Register
Pcmdferr Command on First Pcmd Parity Error
ECCMSK0 ECC Mask Register Card B
Sdcrspferr Response on First Sdcrsp Error
Dpbrleferr Private Data Bus Receive Length Error
Eccmskf ECC Mask Register
ParMskP PB Parity Mask and IB Correction Enable Register
ECCMSK1 ECC Mask Register Card a
Pvdtxinfoferr Txinfo on First PVD Parity Error
Pvddferr Data on First PVD Parity Error
Pvdparferr Parity on First PVD Parity Error
Dedfdferr Data on First System Bus DED
Secfdferr Data on First System Bus SEC
Secfeccferr ECC on First System Bus SEC
Secftxinfoferr Txinfo on First System Bus SEC
Dedfeccferr ECC on First System Bus DED
Ferrmac First Error Status Register
Que-Overflow Error
3 MAC
4 PXB
Cmndferr Command on First Error
Errsts Error Status Register
Errcmd Error Command Register
Ferrpci
Ferragp First Error Status Register for AGP
5 GXB
5.1
Nerragp Next Errors Status Register for AGP
Ferrgart First Error Status Register for Gart
Nerrgart
Pacerr PCI Address & Cmd First Error
Pderr PCI Data First Error
Bits Description Intrq Asserted Flag
Nepci Register Records an PCI Bus Error Flag
Fepci Register Records an PCI Bus Error Flag
6 WXB
Fepci PCI Bus First Error Status Register
Nepci PCI Bus Next Error Status Register
6764 C/BE30 6332 AD6332 310 AD310
Fepcial PCI First Error Address/Command Log
Fepcidl PCI First Error Data Log
Performance Monitor Registers
Dmask Encodings
Overflow
Count Value
Length Encodings
Event Select
Umask Encodings
Reload Control
Disable Source
Enable Source
2 SDC
FSBDPMD1,0 System Bus Performance Monitor Data Registers
3.2 PMR10 Performance Monitoring Response
3 PXB
3.1 PMD10 Performance Monitoring Data Register
Initiating Agent Selection
Reload Mode
3.3 PME10 Performance Monitoring Event Selection
Count Data Cycles
AGPPMD0,1 AGP Performance Monitor Data Registers
4 GXB
Event 1 Input
Pcipmd PCI Performance Monitor Data Registers
Percon Performance Monitor Control Register
Pipe or Sideband Request Mask
AGPPMC0,1 AGP Performance Monitor Configuration Register
Event 0 Input
Initiating Agent
Pcipmc PCI Performance Monitor Configuration Register
EVENT1 Count Enable
Disable Source
Issuing Agent Qualifier
PCIWXBPMC0 PCI Performance Monitor Configuration Register
5 WXB
Data Transfer and Transaction Qualifier
Xtprs External Task Priority Registers
PCIWXBPMC1 PCI Performance Monitor Configuration Register
Interrupt Related Registers
Memory-Mapped Register Summary
Address Name Access Default Value
PID PCI Memory-mapped Registers
2.1 I/O Register Select Register FEC00000h
I/O Window Register Format
PID Indirect Access Registers
2.2 I/O Window Register FEC00010h
XAPIC EOI Register FEC00040h
RTE
Offset Name Access Default Value
3.1 I/O xAPIC ID Register 00h
Memory-mapped Register Summary Cont’d
I/O xAPIC Version Register Format
3.2 I/O xAPIC Version Register 01h
3.3 I/O xAPIC Arbitration ID Register 02h
I/O Apic ID Register Format
10. I/O xAPIC RTE Format
Bits Sapic Mode Apic Mode Description Name
3.4 I/O xAPIC RTE 10h-8Fh
I/O xAPIC Arbitration ID Register Format
10. I/O xAPIC RTE Format Cont’d
Sapic Mode Apic Mode Description Name
Vector
Destination
Processor Coherency
System Architecture
Coherency
AGP Coherency
Ordering
PCI Coherency
Arbitration for Inbound Transactions
WXB Arbitration
WXB Arbitration at the PCI Bus
Arbitration for Outbound Transactions
Big-endian Support
Indivisible Operations
Processor Locks
Locks with AGP Non-coherent Traffic
Inbound PCI Locks
Atomic Writes
Atomic Reads
WXB PCI Hot-Plug Support
Interrupt Delivery
Slot Power-down and Disable
Slot Power-up and Enable
System Architecture
Compatibility Region
System Address Map
Memory Map
System Memory Address Space
System Firmware
Medium Extended Memory Region
Low Extended Memory Region
Variable GAP
High Extended Memory above 4G
Re-mapped Memory Areas
Itanium Processor and Chipset-specific Memory Space
I/O Address Map
System I/O Address Space
High PXB must ignore GXB must BINIT# after Gart
Devices View of the System Memory Map
Address Range Outbound Inbound Dest. Decision
Legal and Illegal Address Disposition
Address Disposition
Binit
Address Disposition Cont’d
Main memory if present above 4 GB
Above TOM
System Address Map
System
General Memory Characteristics
Memory Subsystem
Organization
Maximum Memory Configuration Using Two Cards
Double Number Memory Size
Minimum/Maximum Memory Size per Configuration
Technology & Configuration Size
Dimm Types
Address Interleaving
Interleaving/Configurations
Bandwidth
Summary of Configuration Rules
Non-uniform Memory Configurations
Removing a Bad Row
Supporting Features
Memory Subsystem Clocking
Auto Detection
Memory Size Time to Scrub
Hardware Initialization
Memory Scrubbing
Scrubbing Time
Memory Subsystem
System Bus
Data Integrity and Error Handling
Integrity
5 AGP
Dram
Expander Buses
PCI Buses
Data Poisoning
Usage of First-error and Next-error
Memory ECC Routing
INTREQ#
Masked Bits
BERR#/BINIT# Generation
XSERR#
SAC/SDC Errors
Data ECC or Parity Errors
XBINIT#
SAC to SDC Interface Errors
System Bus Errors
5 SDC/Memory Card Interface Errors
SAC to MAC Interface Errors
SDC Internal Errors
Error Determination
6 SDC/System Bus Errors
SAC Address on an Error
Special Notes on Usage of SECTID, DEDTID, Fsetid Registers
SDC Logging Registers
1 SAC/SDC Error Clearing
Clearing Errors
Multiple Errors
ERR ERR
SDC Multiple Errors
Error Anomalies
SAC Multiple Errors
Single Errors with Multiple Reporting
SAC Error Flow on Data
Data Flow Errors
Table of Errors
Error Conditions
System Bus ADD/CMND
Error Cases
SAC to SDC Interface Errors
Error Cases Cont’d
Internal SDC Error
Detected as PCI Master
PXB Errors
Master Abort
PCI Integrity
PCI Bus Monitoring
PXB as Master
PXB as Target
Target Abort
GXB Error Flow
Target Retry
GXB Errors
GXB Error Signals
Gart Interface Errors
GXB Error Flow
Multiple Errors
Data Parity Poisoning
WXB Data Integrity and Error Handling
Usage of First Error and Next Error Registers
Integrity
Abbreviation Error
Error Mask Bits
Error Steering/Signaling
Supported Error Escalation to XBINIT#a
Escalation
Supported Error Escalation to SERROUT#a
Supported Error Escalation to PA/BINTRQ#
SERR# Generation
XBINIT# Generation
Error Determination and Logging
INTRQ# Interrupt
WXB as Bus Master
Error Conditions
Other Violations
WXB as Target
Discard Timer Expiration
PCI Interface Errors
System Error Signaled
Graphics Address Relocation Table Gart
AGP Subsystem
14b
12b
24b
22b
Gart Entry Format for 4kB Pages
Gart Implementation
Parity
Programming Gart
Sizes
Gtlb
SE2 ADSC# ADSP# ADV# LBO# SB# SW#
Coherency
SGW#
Addresses Used by the Graphics Card
4.1 3.3V AGP 1X and 2X Mode Compatibility
AGP Traffic
Interrupt Handling
Coherency, Translation and Types of AGP Traffic
Traffic Priority
Coherency for AGP/PCI Streams
Ordering Rules
Processor Locks and AGP Traffic
Inbound Reads
Address Faults
Address Alignment and Transfer Sizes
PCI Semantics Traffic
Inbound Reads Directed To Memory
Inbound Delayed Read Matching Rules
PCI Stream Read Prefetching
Inbound Writes
Delayed Read Matching Criteria
Command Address BEs
Inbound I/O Reads
Outbound Writes
Retry/Disconnect Conditions
Outbound Reads
1st write 2nd write 3rd write Transferred as
Transfer Data Length Combining Supported Used Mode
Fast Back-to-Back Transactions
Burst Write Combining Modes
Bandwidth Estimates for Various Request Sizes
Latency
GXB Address Map
Inbound Read Prefetching
AGP Subsystem
AGP Subsystem
WXB Hot-Plug
Ihpc Configuration Registers
Ihpc Configuration Register Space
Did Device Identification Register
Number List for the Ihpc PCI Register Descriptions
VID Vendor Identification Register
Pcicmd PCI Command Register
RID Revision Identification Register
Pcists PCI Status Register
HDR Header Register
MLT Master Latency Timer Register
Class Class Register
CLS Cache Line Size
Interrupt Line
Base Address
Svid Subsystem Vendor Identification
SID Subsystem ID
Hot-Plug Slot Identifier
Miscellaneous Hot-Plug Configuration
Interrupt Pin
Power Fault Serr Status
Hot-Plug Features
Switch Change Serr Status
Arbiter Serr Status
Memory Access Index
Memory Mapped Register Access Port
Ihpc Memory Mapped Registers
M66EN
Ihpc Memor Mapped Register Space
Number List for Ihpc Memory Mapped Register Descriptions
Slot Enable
LED Control
Hot-Plug Miscellaneous
Hot-Plug Interrupt Input and Clear
Hot-Plug Interrupt Mask
Serial Input Byte Data
Hot-Plug Non-interrupt Inputs
Serial Input Byte Pointer
General Purpose Output
Extended Hot-Plug Miscellaneous
Hot-Plug Switch Interrupt Redirect Enable
Slot Power Control
IFB Register Mapping
PCI / LPC / FWH Configuration
PCI Configuration Registers Function
Mnemonic Register Register Access
Hedt
Biosen
Pcists
Classc
PCI Configuration Registers-Function 1 IDE Interface
IDE Configuration
Configuration Offset Mnemonic Register
Universal Serial Bus USB Configuration
PCI Configuration Registers-Function 2 USB Interface
SMBus Configuration Registers Function
SMBus Controller Configuration
IFB Register Mapping
IFB Usage Considerations
Usage of 1MIN Timer in Power Management
Usage of the SW SMI# Timer
CD-ROM Auto RUN Feature of the OS
SSDE1 SSDE0 PSDE1 PSDE0
Ultra DMA Configuration
Reserved Secondary Primary Drive Ultra DMA Mode Enable
Disabled Enabled
Ultra DMA Fields that Indicate Ultra DMA Drive Capabilities
Determining a Drive’s Transfer Rate Capabilities
Overview
Capability Word Bits Field Offset
PIO
Capability Word Bits
DMA
Capability Word Bits Field
Determining a Drive’s Best Ultra DMA Capability
10-6
Capability Word Offset Bits Field
150 Minimum Multi Word DMA Transfer Cycle Time per
Determining a Drive’s Best PIO Capability
Drives Reported DMA Drive’s Best DMA Mode Cycle Time
Drive PIO Capability as a Function of Cycle Time
Drives Reported PIO Drive’s Best PIO Mode
Mode Yes Disabled Enabled DMA Mode Iordy If fixed disk
IFB Timing Settings
10.5.6.1 DMA/PIO Timing Settings
IFB Drive Mode Based on DMA/PIO Capabilities
DMA Iordy IDE
DMA/PIO Timing Values Based on Piix Cable Mode/System Speed
Drive Configuration for Selected Timings
Ultra DMA Timing Settings
10. Ultra DMA Timing Value Based on Drive Mode
10-12
12. PIO Transfer/Mode Values
Drive’s Selected PIO Speed Capability
13. Drive Capabilities Checklist
Settings Checklist
Register Type Offset Value Comments
Example Configurations
Example #1 Ultra DMA/33 Configuration
14. IFB Settings Checklist
44h 0Bh Ultra DMA Control Register
Example #3 Non Ultra DMA/33 Drive Configuration
40-41h E377h Mode config. for Primary IDE Timing Register
4A-4Bh 0002h Ultra DMA mode config
10-16
Ultra DMA System Software Considerations
4A-4Bh 0000h
Intel 460GX Chipset Software Developer’s Manual 10-17
Completed or halted
Bit Description Reserved. This bit is hardwired to
BMISX-Bus Master IDE Status Register I/O
Bit Description
Bit Type Description
USB Resume Enable Bit
10-20
DID-Device Identification Register Function
LPC/FWH Interface Configuration
VID-Vendor Identification Register Function
PCISTS-PCI Device Status Register Function
PCICMD-PCI Command Register Function
Bit
RID-Revision Identification Register Function
CLASSC-Class Code Register Function
HEDT-Header Type Register Function
SCI IRQ Routing Control
Acpi Enable Function
Acpi Base Address Function
PIRQRCAD-PIRQx Route Control Registers Function
BIOSEN-BIOS Enable Register Function
TOM-Top of Memory Register Function
SerIRQC-Serial IRQ Control Register Function
Deterministic Latency Control Register Function
MSTAT-Miscellaneous Status Register Function
Bits Description
PDMACFG-PCI DMA Configuration Resister Function O
MGPIOC-Muxed Gpio Control Function
Base Offset Channel
RTCCFG-Real Time Clock Configuration Register Function
Bits Decode Range
Gpio Enable Function
Gpio Base Address Function
LPC COM Decode Ranges Function
110
LPC FDD/LPT Decode Ranges Function
000
011
11-12
LPC Sound Decode Ranges Function
LPC Generic Decode Range Function
220 233 240 253 260 273 280 293
1413 Reserved
LPC Enables Function
Firmware Hub FWH Decode Enable Register
Reserved. This bit must be a
Firmware Hub FWH Select Register
DMA Registers
Test Mode Register
Dcom-Dma Command Register I/O
PCI to LPC I/O Space Registers
Dr-Dma Request Register I/O
Dcm-Dma Channel Mode Register I/O
Bit Description Reserved. Must be
WSMB-Write Single Mask Bit I/O
RWAMB-Read / Write All Mask Bits I/O
DBADDR-DMA Base and Current Address Registers I/O
Ds-Dma Status Register I/O
DCBP-Dma Clear Byte Pointer Register I/O
When counting down a DMA transfer
DBCNT-Dma Base and Current Count Registers I/O
DLPAGE-DMA Low Page Registers I/O
Dclm-Dma Clear Mask Register I/O
11.2.2.1 Icw1-Initialization Command Word 1 Register I/O
Interrupt Controller Registers
Dmc-Dma Master Clear Register I/O
Bit Description Reserved. Must be programmed to all 0s
11.2.2.2 Icw2-Initialization Command Word 2 Register I/O
11.2.2.3 Icw3-Initialization Command Word 3 Register I/O
11-22
11.2.2.4 Icw3-Initialization Command Word 3 Register I/O
11.2.2.5 Icw4-Initialization Command Word 4 Register I/O
11.2.2.6 Ocw1-Operational Control Word 1 Register I/O
11.2.2.8 Ocw3-Operational Control Word 3 Register I/O
11.2.2.7 Ocw2-Operational Control Word 2 Register I/O
Elcr1-Edge/Level Control Register I/O
Bit Decription
Counter/Timer Registers
Tcw-Timer Control Word Register I/O
Elcr2-Edge/Level Control Register I/O
5. When bit 1=0, status and/or count will not be latched
Latched. When bit 4=1, the status will not be latched
5. When bit 3=0, status and/or count will not be latched
5. When bit 2=0, status and/or count will not be latched
TMRCNT-Timer Count Registers I/O
TMRSTS-Timer Status Registers I/O
Nmisc-Nmi Status and Control Register I/O
NMI Registers
Used for NMI enabling/disabling. See description in Section
NMI Enable. Used by IFB NMI logic
Real Time Clock Registers
RTCD-Real-time Clock Data Register I/O
RTCED-Real-time Clock Extended Data Register I/O
Advanced Power Management APM Registers
APMC-Advanced Power Management Control Port I/O
RTCEI-Real-time Clock Extended Index Register I/O
Acpi Registers
APMS-Advanced Power Management Status Port I/O
Power Management 1 Status
11-32
Power Management 1 Enable
Power Management 1 Control
States can be supported in external logic
3124 Reserved 230
Power Management 1 Timer
Bit Description Bits Mode
General Purpose 0 Status
CF9 write
General Purpose 0 Enable
Power up, this bit is set to ‘1’
1512 Reserved
General Purpose 1 Status
General Purpose 1 Enable
SMI Registers
Thrmsts bit
Global Control and Enable
Port at B2h in I/O space
Status Register is set
GPIO7
General Purpose I/O Registers
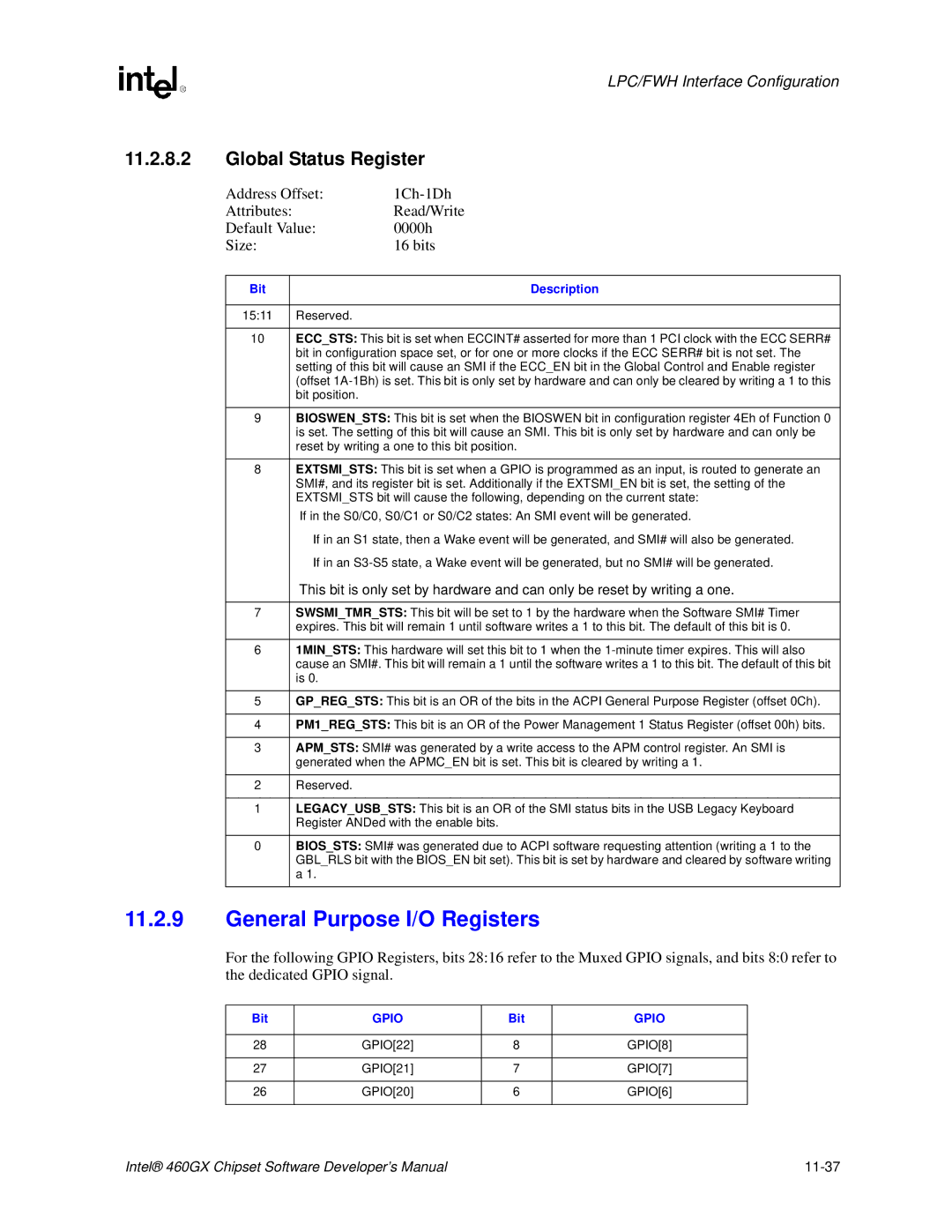
Global Status Register
GPIO8
GP Data
GP Output
Bit is set
GP TTL
1916
159 Reserved
GP Invert
GP Blink
GP Lock
GP Pull-up
GP SMI
GP Pulse
GP Core
11-42
IDE Controller Register Descriptions PCI Function
IDE Configuration
PCI Configuration Registers Function
Configuration Mnemonic Register
VGA Palette Snoop. This bit is hardwired to
SERR# Enable. This bit is hardwired to
Wait Cycle Control. This bit is hardwired to
Parity Error Response. This bit is hardwired to
By writing a 1 to this bit
SERR# Status. Read as
Bus Master interface registers and correspond to AD154
MLT-Master Latency Timer Register Function
BMIBA-Bus Master Interface Base Address Register Function
IDETIM-IDE Timing Register Function
SVID-Subsystem Vendor ID Function
SID-Subsystem ID Function
SIDETIM-Slave IDE Timing Register Function
Bit Description Reserved
DMACTL-Synchronous DMA Control Register Function
SDMATIM-Synchronous DMA Timing Register Function
Ultra DMA/33 Timing Modes
BMICx-Bus Master IDE Command Register I/O
Ultra DMA/33 Timing Mode Settings
IDE Controller I/O Space Registers
BMISx-Bus Master IDE Status Register I/O
312
Interrupt/Activity Status Combinations
Is equal to the IDE device transfer size
12-12
Usbren
Universal Serial Bus USB Configuration
PCI Configuration Registers-Function
Reserved. Read as
USB Host Controller Register Descriptions PCI Function
Bit Description 1510 Reserved. Read
Reserved. Read as 0’s
Resets STA to 0 by writing a 1 to this bit
13-4
This field
Register in Function
INTLN-Interrupt Line Register Function
USBBA-USB I/O Space Base Address Function
LEGSUP-Legacy Support Register Function
INTPN-Interrupt Pin Function
Miscellaneous Control Function
SBRNUM-Serial Bus Release Number Function
Accesses that are part of the sequence
Default to 1 for compatibility with older USB software
Needs to be serviced later
Appropriate enable bits are set
USB Host Controller I/O Space Registers
USBREN-USB Resume Enable
USBCMD-USB Command Register I/O
By Software or Hardware
Run/Stop, Debug Bit Interaction
Swdbg Bit Run/Stop Bit Operation
Stop=0, the Frnum register can be reprogrammed
Register =
USBINTR-USB Interrupt Enable Register I/O
USBSTS-USB Status Register I/O
Interrupt is generated to the system
SOFMOD-Start of Frame SOF Modify Register I/O
Address signals
FRNUM-Frame Number Register I/O
FLBASEADD-Frame List Base Address Register I/O
PORTSC-Port Status and Control Register I/O
Register define the hub states as follows
X0 Disable
Asserted, the corresponding port is disabled
EOF2 time See of the USB Specification
13-14
Base Address Register
SM Bus Controller Configuration
SM Bus Configuration Registers Function
Class Code 0C-1Fh Reserved
14-2
System Management Register Descriptions
Shutdown special cycle
STA to 0 by writing a 1 to this bit
14-4
SMBBA-SMBus Base Address Function
Interrupt pin PIRQB# is used
Host Configuration
Smbshdw2-SMBus Slave Shadow Port 2 Function
Smbslvc-SMBus Slave Command Function
SMBus I/O Space Registers
Smbshdw1-SMBus Slave Shadow Port 1 Function
Position
Transaction errors are caused by
Smbhststs-SMBus Host Status Register I/O
Smbslvsts-SMBus Slave Status Register I/O
Smbhstcnt-SMBus Host Control Register I/O
Smbhstdat0-SMBus Host Data 0 Register I/O
Smbhstcmd-SMBus Host Command Register I/O
Command field of SMBus host transaction
Smbhstadd-SMBus Host Address Register I/O
Smbslvcnt-SMBus Slave Control Register I/O
Smbhstdat1-SMBus Host Data 1 Register I/O
Smbblkdat-SMBus Block Data Register I/O
Address 10h or one of the slave shadow port addresses
14.3.9.1 Smbshdwcmd -SMBus Shadow Command Register I/O
Smbslvdat-SMBus Slave Data Register I/O
14.3.9.2 10.3.11.smbslvevt-SMBus Slave Event Register I/O
14-12
Interrupt Controller
PCI/LPC Bridge Description
PCI Interface
15-2
Initialization Command Words ICWs
Programming the Interrupt Controller
End of Interrupt EOI
Operation Command Words OCWs
Automatic End of Interrupt Aeoi Mode
End of Interrupt Operation
Automatic Rotation Equal Priority Devices
Fully Nested Mode
Special Fully Nested Mode
Modes of Operation
Specific Rotation Specific Priority
Cascade Mode
Poll Command
Masking on an Individual Interrupt Request Basis
Edge and Level Triggered Mode
Special Mask Mode
Interrupt Masks
Interrupt Steering
Reading the Interrupt Controller Status
Protocol
Quiet Active Mode
Continuous Idle Mode
Serial Interrupts
3222
Stop Frame
Serirq Frames
Data Frame Number Usage # Clocks Past Start
15-10
Timer/Counters
Programming the Interval Timer
Write Operations
Interval Timer Control Word Format
15-12
Counter Latch Command
Read Operations
Counter I/O Port Read
Real Time Clock
Read Back Command
Index Address Name
RTC Registers and RAM
RTC Standard RAM Bank
90625 ms 8125 ms
15.5.1.1 Register a
1 Invalid 0 Invalid
RSMRST#
15.5.1.2 Register B
15.5.1.3 Register C
15.5.1.4 Register D
RTC Update Cycle
RTC Interrupts
Lockable RAM Ranges
15-18
Acpi State Description
IFB Power Management
IFB Power States and Consumption
Overview
Causes of SMI#
IFB Power Planes
Power Plane Descriptions
16.2.2 SMI# Generation
SCI Event Comment
SCI Generation
Sleep States
Causes of SCI#
Offset Register Name/Function Comment
Acpi Bits Not Implemented by IFB
Entry/Exit for the S4 and S5 States
Acpi Bits Not Implemented in IFB
S5 Wake Event Comment
Handling of Power Failures in IFB
Action after Power Returns
16-6