3Com Router Configuration Guide
3Com Corporation
Campus Drive
Marlborough, MA
01752-3064
Page
VPN
This guide describes 3Com routers and how to configure them
List conventions that are used throughout this guide
Text Conventions
About this Guide
3Com Router Introduction 3Com Router User Interface
Page
3COM Router Introduction
Features of the 3Com
Following table lists the basic features of the 3Com Router
List of the 3Com Router 1.x features
Router Version
RIP-1/RIP-2
NAT
Quality of service
3Com Router
New Features of the 3Com Router 1.x
3COM Router Introduction
Configuration
Establish
Environment
Port
Establish a new connection
Set port communication parameters
Establish a remote configuration environment
Configuration
Connection
Environment
Router
Workstation Ethernet
Command Line
Interface CLI
3COM Router User Interface
System view Table
Views and their prompts
Async 0 in any
Ethernet 0 in any
Loopback 0 in any
Enter controller
Helps
Full help
Partial help
List of common command line error messages
Common error Message Causes
For example
Routerdisplay ?
Command Line
Features
Display Features
Three options are available for users
Following commands
Please perform the following commands in system view
User Identity
Management
Configure the router name
System
Set the system clock
By default, the system clock is 080000 1 1
Execute the following commands in all views
Reboot the system
Display the System Information Router
System Management
Page
Storage Media and File Types Supported by the System
Softwaresoftware
Input Ctrl+D, and the following prompt information displays
Upgrade Boot ROM Software
Upgrade the 3Com
Router Main Program
Software
Main Program software
XModem Approach
Modify the terminal baud rate
Transfer File dialog box
Preparation for using the Tftp server
Enable the Tftp server program
Tftp server application can run on Windows 95/98/NT
Press Enter and the following prompts will be displayed
Tftpd32 Set interface
Enter Ctrl+B and the system prompts
Network Interface Parameters
Download configuration files from a Tftp server
Operation Command Downloads the 3Com Router main
Press Enter for loading
Get ip-addr file-name system
Prepare for using the FTP server
Set an authentication mode for an FTP server
Upgrade the 3Com Router Main Software with FTP
Enable FTP server
Back up the 3Com Router Main Program Software
Tftp Approach
FTP Approach
Copy ip-addr file-name system
Setup Users Dialog Box
Configure on-line upgrading of the card
Update slot slot-number ftpserver host-name
Port-number user user-name password
Password
Configuration File Management
Download Configuration File
Perform the following command in system view
Content and Format of the Configuration File
Load configuration files
Download Config
Router download config
Set the binary transmission protocol to XModem/CRC
Display current-configurationcommand output backup approach
Back up Configuration Files
Upload configuration files to a Tftp server
File-name config
Please use the following commands in corresponding views
View router configuration
Select and view the storage media of configuration file
Save current configuration
Set the Flag Bit to Enter the Initial Setup Mode
Erase the configuration file in storage media
Configure FTP
Configure authentication and authorization of FTP server
Client via port 20 and transfer data
Files on the router
Enter the following commands in system view
Configure Parameters of FTP Service
Please enter the following commands in system view
Set the authentication mode of FTP server
Set FTP update mode
Set the connection time limit of FTP service
Force to shut down FTP process
Force to shut down FTP process
Display FTP Server Display FTP server
Display ftp-server
Server Display detailed information of the FTP user
Display local-user
System Management
Terminal Service
Features of Terminal
Service at Console Port
Overview
Service
Set the attributes of terminal service
Terminal Message
On one router
Perform the following configuration in all views
Configure Terminal Message Service
Display Terminal Message Service
Enable/disable receiving messages from other terminals
Typical Example Terminal Message Service Configuration
Terminal Service
Dumb Terminal
Configuration Examples Dumb Terminal Service
Configure Dumb Terminal
Configure Auto-execute command
By default, no dumb terminal service is configured
Terminal Service Telnet Connection
Configure the interface to dumb terminal mode
Configure the auto-execute command command
Router-Serial1auto-execute command telnet
Terminal service features of telnet connection
Service Value
Establish Telnet Connection
Setup Reverse Telnet Connection
Enable Reverse Telnet connection
Service-port
Establish Telnet Server or Telnet Client connection
Typical Configuration Example of Telnet Reverse Telnet
Force shut down Telnet Process
Example of Telnet
Force to shut down Telnet process
Rlogin Terminal
Use Rlogin protocol
Example of Reverse Telnet
Router telnet 10.110.164.44
Establish a Rlogin connection
Typical Rlogin Configuration Examples
Rlogin ip-address username
Use local user name abc to log on
Access Service
PAD Remote
Communicate with other terminals through the X.25 network
Configure X.25 PAD remote user
Configure X.25 PAD remote user
Service-type type password
Local-user user-name
Start AAA authentication of X.25 remote users
Enable AAA authentication for X.25 remote PAD users
Establish an X.25 PAD call
Establish a X.25 PAD call
II. Networking Diagram
III. Configuration Procedure
Display and Debug
Set the Response Time to the Invite Clear Message
Fault Diagnosis Troubleshooting
Set its X.121 address as
RouterA-serial0x25 x121-address
RouterB-serial0x25 x121-address
Snmp Overview
Development of Snmp
Configuring Network Management
Snmp architecture
SNMP-supported MIB
By default, the system disables Snmp service
3Com Router-supported MIB
Engineid
Perform the following configurations in system view
Configure Snmp version and related tasks
Configure information of router administrator
Configure the traps to be sent by the router
V1 username
Interface-number
Perform the following commands in all views
Display and debug Snmp
Name
Byte-count
Example 1 Configure Network Management of SNMPv1
Set the community name and access authority
Configure an IP address for the Ethernet interface ethernet
Examples Networking Requirements
Configure an IP address for the Ethernet interface ethernet
Rmon Overview
Network equipment
Schematic diagram of Rmon application
Enable Rmon statistics
Examples Networking Requirement
RouterA-Ethernet0 rmon promiscuous
Commands to display information of the whole system
Ping command
Test Tool of Network Connection
Ping supporting IP protocol
System displays
Ping supporting IPX protocol
Ip-address
Following command can be executed in any command modes
Tracert command
Timeout host
MaxTTL -p port -q nqueries
Configure on the router
Log Function
Set the direction of syslog outputting log information
Set Severity of Log Information
Perform the following task in system view
Sylog-defined severity is as follows
Set Filter of Log Information
Configuration of Log Host
Turn on/turn off syslog
Display and Debug Syslog
Turn on/turn off syslog
Syslog Configuration Example
Turn on debugging switch of PPP module
Routerinfo-center enable
Routerdebug ppp all
Display and Debugging Tools
POS Terminal Access Service
Dial-up POS Access
POS Network Access
Advantages of POS network access are as follows
POS Access Service Configuration
Configure POS access port
Start POS server
Configure a POS application
Interface-type interface-number
App-number
Ip-address port-number
Configure POS multi-application mapping table
Default app-number
Bind the source address of TCP connection
Display and Debug POS Access
Display and debug POS access
Set the parameters of FCM used during Modem negotiation
Set the parameters of FCM used during Modem negotiation
Typical Configuration Example of POS Access Service
Configure the Ethernet interface Ethernet
Configure the POS access interface FCM0
Configure POS access interface FCM1
Configure POS access interface FCM2
Configure POS access interface FCM0
III. Configuration Procedure 1 Start the POS access server
Configure Async 0 to operate in POS application mode
Configure Async 1 to operate in POS application mode
III. Configuration Procedures
Configure Router a Start the POS access server
Configure Router B Configure the Ethernet interface Ethernet
RouterA ip route-static 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 serial
III Interface
106
Configure Interface
Interface
Enter the Interface View
Exit the Interface View
Interface view, input quit to return to the system view
Set time interval for flow control statistics
Interface-description
Please use the following commands in all views
Display and Debug Interface
Display and debug interface
Interface state information
Interface Configuration Overview
Configure Ethernet Interface
Ethernet Interface
Enter view of specified Ethernet interface
Set IP address
Set IPX address
Set frame format of sending message
Select work mode of Ethernet interface
Enable or disable internal loopback and external loopback
Display and Debug
Select working rate of fast Ethernet interface
Typical Ethernet Interface Configuration Example
Troubleshooting
II. Network Diagram
Troubleshooting
Configuring LAN Interface
WAN Interface
Introduction
Asynchronous Serial Interface
Enter view of specified asynchronous interface
Interface async number
Interface serial number
Set the work mode of asynchronous serial interface
Set the baud rate of asynchronous serial interface
Modem in out
Link-protocol slip ppp
Async Mode protocol
Flow-control none software
Hardware inbound outbound
Works in flow mode
Parity even mark none
Odd space
Stopbits 1 1.5
Backup
AUX Interface
Set MTU of asynchronous serial interface
Set the coding format of Modem
Configure AUX interface
Configure AUX interface
Configure Synchronous Serial Interface
Synchronous Serial Interface
Enter view of specified synchronous interface
Set the link layer protocol of synchronous serial interface
Physical-mode sync
Link-protocol fr hdlc
Select work clock
Working modes have different working clocks
Set the baud rate of synchronous serial interface
Synchronous serial interface is 64000 bps
Inversion is disabled by default
Select work clock
Set clock inversion
Internal loopback/external loopback are disabled by default
Detect dcd
Undo detect dcd
Reverse-rts
Isdn BRI Interface
Idle coding of synchronous serial interface is 7E
Technical Background
Graphics and video
Preparations before Configuration
Be clear about the following items before the configuration
Function group includes
Channelized operating mode
CE1/PRI Interface
Network protocols such as IP and IPX
Interface or a PRI interface
Configure CE1/PRI CE1/PRI interface configuration includes
Dial-on-Demand Routing
Interface
Enter the view for a specified interface
Enter the synchronous serial interface view
Bind the interface to be channel sets
Number set-number
Bind the interface to be a pri set
Enter the Isdn interface view
Pri-set timeslot-list range
Undo pri-set
Enable/disable the internal loopback/external loopback
Set the line code format on the CE1/PRI interface
Set the line clock of the CE1/PRI interface
Set the frame format of CE1/PRI interface
Configure CT1/PRI
CT1/PRI Interface
Operation Command Enter the view of CT1/PRI interface
Controller t1 number
Timeslot-list range speed
Interface serial number23
Set the line code format on the CT1/PRI interface
Set the line clock of the CT1/PRI interface
Set the frame format of CT1/PRI interface
Choice for E1 access
E1-F interface does not support PRI operating mode
E1-F Interface
Them into multiple channel sets
Set Operating mode for an E1-F interface
Enter the view of an E1-F interface
Interface serial serial-number
Fe1 unframed
Set interface rate after binding operation
Set line code format for E1-F interfaces
Set line clock for an E1-F interface
Enable/Disable local/remote loopback on an E1-F interface
Set frame format for an E1-F interface
Display and debug E1-F interface
Serial-number
Choice for T1 access
T1-F interface does not support PRI operating mode
T1-F Interface
193 X 8k = 1544kbps
Set line code format for T1-F interface
Enable/Disable local/remote loopback on a T1-F interface
Set line clock for a T1-F interface
Set frame format of T1-F interface
Other related information
CE3 Interface
Display and Debug T1-F
Display and debug T1-F interface
Enter the view of the specified E3 interface
Set the operating mode of CE3 interface
Set the operating mode of E1 channel
Set E1 frame format
Mode non-channelized mode
CT3 Interface
44.736Mbps
Data bandwidth 44736kbps
Set clock mode of the CT3 interface
Set clock mode of the T1 channel
Enter specified CT3 interface view
Set cable length of the CT3 interface
By default, loopback is disabled Set Frame Format
By default, the CT3 interface uses the C-bit frame format
Perform the following configurations in CT3 interface view
Set the operating mode of T1 channel
Set CRC of the serial interface
T1 line-number unframed
Disable and Enable CT3 interface
Display and debug of the CT3 interface
Configuring WAN Interface
Logical Interface
Dialer Interface
Configure Loopback
Null Interface
Sub-Interface
Configure sub-interfaces of Ethernet interface
Create and delete WAN sub-interface
Number.sub-number
Number.sub-number multipoint
Enter the view of WAN interface Serial0 of router a
Select frame relay link layer protocol
Routerinterface serial
Configure the static route from router a to LAN2 and LAN3
Specify DTE as its frame relay terminal type
Set its IP address to 202.38.160.1 and address mask to
Allocate a virtual circuit with Dlci 50 to it
Set work parameters of virtual-template
Create or delete virtual-template
Interface virtual-template
Undo interface
Fault 1 Fail to create virtual interface
Troubleshooting the reasons may be as follows
Display state of the specified virtual-template
Virtual-template-number
Link Layer Protocol
164
PPP Authentication Mode
PPP Overview
Configuring PPP and MP
Configure PPP
MP Overview
For detailed description of PPP, refer to RFC1661
Transmission time of large packets
Configure the link layer protocol of the interface to PPP
Configure the local authenticates the peer in PAP mode
Configure the peer authenticates the local in PAP mode
Name-list
Configure the local authenticates the peer in Chap mode
Configure as the peer authenticates the local in Chap mode
Cipher password
User username
Configure AAA authentication and accounting of PPP
Configure the time interval of PPP negotiation timeout
Configure PPP compression
Perform the following configuration in interface view
Configure PPP link quality monitoring
Ppp lqc forbidden-percentage
Resumptive-percentage
Configure MP Protocol Parameters Create Virtual Template
Configure Operating Parameters of Virtual Template
Create/Delete virtual template
Bind the physical Interface to a Virtual Template
Specify the conditions for MP binding
User-name
Configure virtual Baud rate on interface
Frags
Typical PPP Configuration Example
Configuration Requirement
Example
Typical MP Configuration Example
II. Configuration Procedure
Configure to start Chap authentication at this side
Set local username as Router1
Configure virtual interface template
Configure router-b Add a user for router-a
Configure router-c Add a user for router-a
Fault Diagnosis Troubleshooting
Fault 1 Link always fails to turn to up status
Fault 2 Physical link fails to turn to Up status
Indicates that the interface is shutdown
PPoE Overview
Introduction to PPPoE client
Configure PPPoE
Client
Configure PPPoE session
Reset or delete PPPoE session
Typical PPPoE Configuration Example
Perform the display and debugging command in all views
Access a LAN to the Internet via Adsl
III. Configuration Procedure 1 Configure a dialer interface
Configure a PPPoE session
Configure the LAN interface and the default route
Configure the DDN interface Serial
Use Adsl as Standby Line
Configuring Pppoe Client
Configure Slip
Asynchronous mode
Slip Overview
For further details about SLIP, you can refer to RFC1055
Enable/Disable the information debugging of Slip
Typical Slip
Time
Interconnect two Router routers via Pstn and run IP
Configure Router a Configure Dialer Rule
Configure IP address of synchronous/asynchronous interface
Configure the Dialer String to router B
Configure the default route to Route B
Routerip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
Configure Isdn
Isdn Overview
By default, DSS1 signaling is used on Isdn PRI interfaces
Configure type of signaling on Isdn interface
Configure the length of call reference
Configure the receiving mode
Configure the sending mode
Configure interval for Qsig signaling timer
Timer-name all
Time-interval
Configure Call Processing Method on an Interface
Perform the following configuration in Isdn interface view
Perform the display and debugging commands in all views
Typical Configuration Example
Configure Router a Create an Isdn PRI interface
Configure the Isdn PRI interface
RouterB transmit data after the call is set up
Configure Router a
Configure Router B
Lapb
Protocols Overview
PSN
25 packet and Lapb frame
Configure Lapb
By default, the Lapb modulus is Modulo
By default, k is Configure Lapb N1, N2
Configure
Configure X.25 Interface
Set/Cancel the X.121 address of the interface
Set X.25 working mode
Address
25 channel delimitation parameters
Parameter Meaning
By default, X.25 interface use modulo 8 mode
Set/cancel X.25 virtual circuit range
Set/Cancel X.25 packet numbering modulo
Finally, the following should be noted
Configure X.25 flow control parameter
Configure X.25 Interface Supplementary Parameter
Set the default flow control parameter
Out-packets
25 layer 3 timer
Set X.25 layer 3 timer delay
Specify/Cancel an alias for the interface
Alias match modes and meanings
Alias-string
Match-type alias-string
Set/Cancel the default upper layer protocol borne on
Configure X.25 Datagram Transmission
Create the permanent virtual circuit PVC
Protocol-address x121-address
Address option
Configure Additional Parameters Datagram Transmission
Create/Delete permanent virtual circuit
X25 pvc pvc-number protocol
Undo x25 pvc pvc-number
Interface view, perform the following task
Specify/Cancel packet pre-acknowledgement
Configure X.25 user facility
Configure the sending queue length of virtual circuit
Serial port view, list1 can be quoted
Set broadcast via
Set interface with standby center
Address broadcast
Address logic-channel
Switching Function
Configure X.25 sub-Interface
Configure X.25 Switching
Number.subinterface-number multipoi
Configure X.25 Load Balancing
Add or delete a PVC route
Introduction to X.25 Load Balancing
Configure X.25
List of Configuration Tasks of X.25 Load Balancing
Diagram of X.25 network load balancing
Start /Close X.25 switching function
Create/Delete X.25 hunt group
Add/Delete interfaces or XOT Tunnels in hunt group
Configure X.25 over Other Protocols
Add/delete other X.25 switching routes
Configure X.25 over TCP XOT
Introduction to XOT Protocol
Configure XOT
Start X.25 switching
Configure local switching
Configure SVC XOT switching
For PVC, perform the following tasks in interface view
Configure Annex G Data Interoperation
Configure PVC XOT switching
Configure X.25 over Frame Relay Annex G
Configure Keepalive and xot-source attributes
Configure the X.25 Attributes for a Dlci
Configure the X.25 attributes for an Annex G Dlci
Typical Lapb Configuration Example
By default, X.25 template is not applied on DLCIs
Current status of Lapb
Specify IP address for this interface
Configure Router B Select interface
Configure Router a a Select interface
Specify X.121 address of this interface
Specify address mapping to the peer
Connect the Router to X.25 Public Packet Network
Configure Router a Configure interface IP address
Configure Router B Configure interface IP address
Configure Router C Configure interface IP address
Configure Virtual Circuit I. Networking Requirement
Disabled
Range
Transmit IP Datagram via X.25 PVC
Typical Sub-Interface Configuration Example
Router-Ethernet0ip address 196.25.231.1
Configure Router C
Configure Router D
Create sub-interface serial
SVC Application of XOT I. Networking Requirement
Configure Router C Start X.25 switching
Configure Serial
Routerx25 switch svc 2 interface serial
Routerx25 switch svc 1 xot
Application of X.25 Load Balancing
Enable X.25 switching in system view
Configure X.25 switching route to forward to X.25 terminal
S11
Add Serial 1, Serial 2 and XOT Tunnel to hunt group
Routerx25 switch svc 1111 xot
Routerx25 switch svc 8888 interface serial
Load Balancing Carrying IP Data Transmission
Routerinterface serial Router-Serial0link-protocol x25 dce
Configure RouterA Configure interface Ethernet
Configure interface Serial
Configure static route to RouterC
Configure RouterB Configure interface Ethernet
Configure the static route to RouterA and RouterB
Configure RouterA Create an X.25 template
Configure the local X.25 address
Configure an IP address for the local interface
Configure RouterB Create an X.25 template
Map the Frame Relay address to the destination IP address
Associates an X.25 template with the Dlci
SVC Application of X.25 over Frame Relay
Configure the router Router B Enable X.25 switching
Enable switching on Frame Relay DCE
Configure Serial 0 as the X.25 interface
Configure Serial 1 as the Frame Relay interface
Configure X.25 over Frame Relay switching
Configure the router Router C Enable X.25 switching
Configure the Frame Relay Annex G Dlci
Configure local X.25 switching.Router-fr-dlci-100annexg dte
Configure Router D Configure the basic X.25 parameters
Configure Router B Enable X.25 switching
Configure an X.25 template
Configure S1 as the Frame Relay interface
Configure Serial Configure S1 as the Frame Relay interface
Lapb
Facility options inhibited by network have been carried
Fault Diagnosis and Troubleshooting of X.25
Configuring Lapb
Configuring Frame Relay
By default, the interfaces link layer protocol is PPP
Link-protocol fr ietf
Relay
Nonstandard
Configure Frame Relay interface type
Configure Frame Relay LMI protocol type
Fr lmi n391dte n391-value
Undo fr lmi-n391dte
Fr lmi n392dce n392-value
Undo fr lmi n392dce
Undo fr lmi n393dce
Fr lmi t391dte t391-value
Undo fr lmi t391dte
Fr lmi t392dce t392-value
Configure Frame Relay static address mapping
Configure Frame Relay dynamic address mapping
Configure Frame Relay local virtual circuit number
Create Frame Relay sub-interface
Fr dlci
Undo fr
Configure virtual circuit of Frame Relay sub-interface
Applying dynamic address mapping to the sub-interface
Establish static address mapping
Configure the Frame Relay local virtual circuit number
Configure the route for Frame Relay PVC switching
Configure Frame Relay local switched PVC number
Configure the Frame Relay switched PVC
Configure Multilink Frame Relay FRF.16
Overview
Configure MFR
Configure a MFR bundle interface MFR interface
Configure MFR interface parameter
Subnumber
Frame Relay Compression Configuration
Configure the parameters of the bundle link interface
By default, interfaces use initiative compression
Configure Frame Relay Fragment FRF.12
Configure Frame Relay Fragment Attributes
Configure Frame Relay Compression on multipoint interface
Disable the Frame Relay traffic shaping
Frame Relay Traffic Shaping
Fr traffic-shaping
Undo Fr traffic-shaping
Rate
Frame Relay Queueing Management
Frame Relay Traffic Policing
150 Kbps
100 Kbps CI R ALLOWº£ 64 Kbps
Frame Relay Congestion Management
Frame Relay DE rule list
By default, no Frame Relay class is created
Configure the Frame Relay class parameters
Configure Frame Relay Traffic Shaping
Undo fr-class class-name
Enable/Disable the Frame Relay traffic shaping
Configure the parameters of Frame Relay class
Enable/Disable the Frame Relay traffic policing
Queue-percentage
Dequeue-percentage
Configure Frame Relay DE Rule List
Configure Frame Relay Queueing Management
Configure the Frame Relay PVC queueing
Configure Pipq
Configure Frame Relay over Other Protocols
Configure Frame Relay over IP
Configure a tunnel interface
Configure Frame Relay switching
Frame Relay over Isdn Operation Process and Fundamentals
Networking of a typical Frame Relay over Isdn application
Frame Relay switching connection between DTE devices
Physical Connection Between Frame Relay over Isdn Devices
Back-to-back connection between DTE and DCE devices
Configure Frame Relay over Isdn
Configure the Frame Relay-related commands
Configure the commands related to Frame Relay switching
Configure the link layer protocol of the interface
Dlci
Configure parameters related to dialer profiles
Display and debug Frame Relay
Display and Debug Frame Relay
Isdnsubaddress
Number dlci dlci-number
Number interface serial
Type number dlci
Mfr number
Typical Frame Relay Configuration Example
Configure static address mapping
Interconnect LANs via Frame Relay Network
Router-Serial1fr map ip 202.38.163.251 dlci
Configure local virtual circuit
Relay FRF.16
Interconnect LANs via Private Line
Router-Serial1ip address 202.38.163.253
Create a MFR interface
Bundle Serial 0 and Serial 1 to mfr
Example FRF.9
Them
III. Configuration Procedure 1 Configure Router a
III. Configuration Procedure 1 Configure RouterA
FRF.12
Fragment between them
IP Configuration
Routerfr class 96k
Router-fr-class-96ktraffic-shaping adaptation becn
Typical Frame Relay over
Configure IP interface Ethernet0
Configure tunnel interface
Configure Frame Relay over IP
Router-Serial0fr interface-type dce
Configure the Frame Relay parameters on Bri0
Router-Bri0fr map ip 110.0.0.2 dlci
Router-Dialer0dialer number Router-Dialer0dialer call-in
Router-Dialer0fr interface-type dce
Configure the Frame Relay-related parameters on Bri0
Configure Frame Relay SVCs
Router-Serial1.1ip address 130.0.0.2
Fault Diagnosis Troubleshooting Frame Relay
Fault 1 the physical layer in Down status
Fault 4 Frame Relay data cannot be transmitted across Isdn
Configuring Frame Relay
Configure Hdlc
Configure Hdlc Display and Debug Hdlc
By default, the link layer protocol of the interface is PPP
Configure the link layer protocol of the interface to Hdlc
Enable Hdlc packet debugging
Debugging Hdlc Packet Interface
Configure Bridge’s Routing Function
Typical Bridge Configuration
Bridge Overview
Bridge Overview
Obtain address table
Main Functions of Bridging
Bridge Overview
Forward and Filter
Final bridging address table
Eliminating loop
Filter not forward
Preliminary examination state of bridging loops
Spanning Tree Topology
Bpdu Forwarding Mechanism
Spanning tree topology
Configure Bridge’s Routing Function
By default, disable bridging functions
Enable/Disable bridging functions
Bridge enable
Configure static address table entries
Specify the STP version supported by the bridge-set
Add ports to a bridge-set
Mac-address
Enable/Disable forwarding by using dynamic address table
Configure the aging time of dynamic address table
Disable/Enable STP on ports
Configure the bridge priority
Configure the path cost of bridge port
Configure the bridge port priority
Configure the interval for sending BPDUs
Configure the forward delay for the port status transition
Configure the Max age of Bpdu
Create ACLs based on varied Ethernet encapsulation formats
Acl acl-number
Enable/Disable bridge’s routing
Configure a bridge-template interface
Bridge-set
Define a link-set
Share load by source MAC address
Link-set
Bridgebridge-set link-set link-set
Configuration on the interface
Map the bridge address to Dlci
Define a dialer list
Typical Bridge Configuration
Display and Debug Bridge
Display and debug bridge
Transparent Bridging Multiple LANs
Configure Router a
Configure Router B
Router-Serial0bridge-set 1 stp disable
Transparent Bridging over Frame Relay
Transparent bridge over the Frame Relay
Router-Serial1dialer route bridge broadcast
Asynchronous Dial-in
Standby
Connected are failed
Please refer to Figure
Bridge-Template interface
Networking of bridge-template interface
Bridging on Sub-Interfaces
Networking for bridging on sub-interfaces
Link-Set Configuration I. Networking Requirements
Routerbridge enable Routerbridge 1 stp ieee
Router-Serial1bridge-set 1 link-set
Network Protocol
316
Configuring IP Address
IP address classes and ranges
Network IP network range Description Class
Sub-net classification of IP address
Configure IP Address Configure IP Address for an Interface
By default, the interface has no master IP address
Configure master IP address of an interface
Ip address ip-address mask
Configure slave IP address of an interface
Ip address ip-address mask Mask-length sub
Delete slave IP address of an interface
Undo ip address ip-address
By default, the interface has no negotiating IP address
Configure IP Address Unnumbered for an Interface
Introduction to IP address unnumbered
Set negotiable attribute of IP address for an interface
Configuration Example I. Configuration Requirements
Configure routing to Ethernet segment of Shenzhen router R1
Configure IP address unnumbered
Borrow IP address of Ethernet interface
Configure router R1 of Shenzhen subsidiary
Borrow IP address of Ethernet
Router-Ethernet0ip address 172.16.20.1
Router ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
Page
Configuring IP Address
Define a static ARP mapping
Arp static ip-address
Undo arp static ip-address
Arp dynamic ip-address
Configure Domain
Name Resolution
Name Resolution
Display and Debug ARP
Display and Debug Domain Name Resolution
Display and Debug domain name resolution
Display ip host
Create Ethernet subinterface
Specify the Vlan on which Ethernet subinterface is located
Interface-number.subinterface-number
Vlan-type dot1q vid vlan-id
Configure IP address of Ethernet subinterface
Typical Vlan Configuration Example
Display and Debug Display and Debug Vlan
Display vlan
Configure IP address for the subinterface
Configure Vlan information of LAN Switch
Troubleshooting The steps below can be taken
Router-Ethernet0.1ip address 3.3.3.8
Dhcp Server Configuration
Fault Ping Two PCs, but fails to ping them through
Dhcp vs Bootp
Background of the Dhcp development
Occasions in which Dhcp server is applied
Following figure
Dhcp server Dhcp clients
Dhcp client logs into the network again
Dhcp Server Configuration
Enable/disable the Dhcp service
Dhcp Enable
Undo Dhcp enable
Dhcp server ip-pool pool-name
Configure the statically binding IP address and MAC address
Netmask
Network ip-address
Low-ipaddress high-ipaddress
Low-ipaddress high -ipaddress
By default, the IP address of DNS is not configured
Configure the gateway router address of client
Configure the domain names of Dhcp clients
Configure the DNS addresses in a Dhcp address pool
Set the type of NetBIOS node for Dhcp client
Set the type of NetBIOS node for Dhcp client
Nbns-list ip-address1
Ip-address2 ... ip-address8
Use reset, debugging and display command in All views
Configure Dhcp self-defined options
Display and Debug Dhcp Server
Display and Debug Dhcp servers
III. Configuration Procedures 1 Enable the Dhcp service
Router dhcp enable
Router dhcp server forbidden-ip
At the client, use ipconfig /releaseall
Router-dhcp2nbns-list Router-dhcp2gateway-list
Configure interface relay address
Operation Command Configure interface relay address
Ip relay-address ip-address
Delete interface relay address
Dhcp Relay Configuration Requirement
Dhcp Relay
IP address from Dhcp server through application
Available on Dhcp server
Configure Dhcp relay router
Networking diagram of an Dhcp relay configuration example
Fault 2 fail to forward transparent transmission protocol
Private Network Address and Public Network Address
Under which condition should the address be translated
Characteristic of Network Address Translation NAT
Role the Network Address Translation NAT plays
Mechanism of Network Address Translation NAT
Configure address pool
Performance of Network Address Translation NAT
End-addr pool-name
Pool-name
Nat outbound acl-number
Address-group pool-name
Undo nat outbound acl-number
Undo nat outbound
Configure the Internal Server
Configure the Timeout of address translation
Nat server global global-addr global-port
Www inside inside-addr inside-port any
Typical NAT Configuration Example
Display and Debug NAT Display and debug NAT
Configure address pool and access list
Allow address translation of segment at 10.110.10.0/24
Set internal FTP server
Set internal WWW server
Configure address access control list and dialer-list
Configure dial-up property for the interface
Configure a default route to serial
Correlate the address translation list and the interface
Fault 2 Internal server abnormal
Configuring IP Application
Configure IP
To configure IP performance, carry out the following steps
Configure maximum transmission unit on an interface
Performance
Configure TCP
Tcp window size
Configure Fast
Forwarding
Perform the following configuration in system view
Display and Debug IP
Forwarding
Display and Debug Fast Display and Debug fast forwarding
Troubleshooting IP Performance Configuration
Router info-center enable Router debugging tcp packet
Router info-center enable Router debugging tcp event
Configuring IP Count
IP Count Configuration
Enable/Disable IP Count service
Ip count enable
Undo ip count enable
Configure IP Count on an interface
Configure IP Count list
Specify count maximum of exterior
By default, IP Count entries time out after 720 minutes
Count
Specify count maximum of interior
Display and debug IP Count
IV. Test Procedure
Not been configured on the interface of the router
Information is displayed
Configuring IP Count
Configuring IPX
IPX address
SAP
Configure IPX
Modify length of service information reserve queue
Configure relative parameters of IPX SAP
Its first Ethernet interface as its node address
Enable IPX interface
Configure IPX RIP static route
Enable/Disable a Default Route
Perform the following task in interface view
Configure RIP updating period
Configure RIP aging period
Configure the maximum size of RIP update packet
Configure the maximum number of IPX parallel route
Configure length of route reserve queue
Configure static service information table item
Configure SAP aging period
Configure size of SAP maximum updated message
Configure reply to SAP GNS request
Ipx sap timer update seconds
Configure Using touch-off for an interface
Disable split-horizon
Configure the delay of interface sending IPX packets
Configure management of IPX packet
Modify Encapsulation Format of IPX Frame on Interface
Encapsulation format of IPX frame
Configure Router a a Activate IPX
Display and Debug IPX Display and Debug IPX
Configure an address map to Router B
Configure a static route to network ID
Configure an information about Server2 file service
Configure an information about Server2 directory service
Configure an information about Server1 directory service
DLSw Protocol
Configuration of DLSw
Create DLSw local peer entity
Init-window-size max-frame
Max-frame-size max-window
Configure Bridge set connecting to DLSw
Create DLSw remote end peer entity
Configure to add ethernet port to Bridge set
Configure Sdlc role
Configure Sdlc virtual MAC address
Configure Sdlc address
Sdlc-address
Controller sdlc-address
Configure Sdlc peer entity
Configure XID of Sdlc
Add synchronous Interface to Bridge set
Configure to stop running DLSw
Configure baud rate of synchronous Interface
Baudrate
Configure Idle time encoding mode of synchronous Interface
Configure parameters of DLSw timer
Configure LLC2 local acknowledgement delay time
Mseconds
Configure LLC2 premature acknowledgement window
Configure modulo value of LLC2
Configure retransmission number of LLC2
Configure LLC2 local acknowledgement time
Configure Busy status time of LLC2
Configure P/F wait time of LLC2
Configure REJ status time of LLC2
Configure queue length of sending message of LLC2
Configure Queue Length of Sending Message of Sdlc
Configure Sdlc local acknowledgement window
Configure maximum receivable frame length of Sdlc
Configure retransmission number of Sdlc
Configure poll time interval of Sdlc
Configure SAP address for transforming Sdlc to LLC2
Configure data bi-directional transmission mode of Sdlc
Lsap
Dsap
Typical DLSw Configuration Example
DLSw Configuration Networking Requirement
DLSw
IP across WAN
Router a Configuration
Router B Configuration
DLSw Configuration
Router dlsw local
Networking diagram of DLSw configuration of SDLC-SDLC
Networking Diagram of SDLC-LAN
DLSw Fault
When using command display dlsw remote
Diagnosis
Virtual circuit cant attain Connected state
Diagnosis and Troubleshooting of DLSw Fault
Configuring Dlsw
VI Routing
404
IP Routing Protocol
IP Routing Protocol
Routing Protocol and Routing Priority
Routing Protocol or Type Corresponding Routing Priority
Ospf ASE
Configuring Static Routes
Default Route
Configuring a Static Route
Configuring a Static Route
Configure a Static Route
Transmitting interface or next hop address
Configuring a Default Route
Displaying Debugging Routing Table
Preference
Other parameters
Troubleshooting a
Static Route
Other
RIP Overview
Configure RIP
Features is not subject to whether RIP has been enabled
Enable RIP at the Specified Network
Enabling RIP
By default, the interface runs RIP-1
Define a Neighboring Router
Specify RIP Version
Peer ip-address
RIP Version 1 enables zero field check by default
Configure Check Zero Field of RIP Version
Disable a Host Route
Specify the Status of an Interface
Authentication on
Enabling Route
Summarization for RIP
Version
By default, the default route metric for RIP is
Configure RIP Horizontal Segmentation on the Interface
Configure Route Import for RIP
Specify a Default Route Metric Value for RIP
Configure filtering route information received by RIP
Distribution for RIP
Specify Additional Route Metric Value for RIP
Set Route Preference
Reset RIP
Displaying and Debugging RIP
Filter the Routing Information Being Advertised by RIP
Display and Debug RIP
RIP Unicast
Ospf Configuration Example
Ospf Overview
Ospf Overview
Displaying and Debugging Ospf
Configuring Ospf
Enable Ospf
Specify Router ID
Router id router-id
Undo router id
By default, Ospf is disabled
Area-id
Area area-id
Configure the Network Type of the Ospf Interface
Configure Sending Packet Cost
Ospf network-type broadcast nbma
P2mp P2p
Configuring a Peer for the Nbma Interface
Cost
Operation Command Set the priority of the interface when
Specify the Router Priority
Ospf Dr-priority value
Undo Ospf dr-priority
Specify Hello Intervall
Specify Dead Interval
Configuring a Stubby Area and a Totally
Specify Transmit-delay
Specify Retransmitting Interval
Perform the following configuration under Ospf view
Configure Totally Stubby Area of Ospf
Stub cost cost area area-id
No-summary
Perform the following configuration in Ospf view
Configure an Nssa Area of Ospf
Configure Route Summarization Within Ospf Domain
Abr-summary address mask mask area
Area-id advertise notadvertise
Undo abr-summary address mask mask
Create and Configuring a Virtual Link
Area-id None Router-id None
Configure Authentication
Key-id
Configure Route Import for Ospf
Configure Parameters When Importing External Routes
Configure filtering route information received by Ospf
Displaying
Debugging Ospf
Filter for Ospf
Ospf Configuration Example
Configuring Ospf on the Point-to-Multipoint Network
Router D 201 Router B 301 302 Router C 1.3
Enable Ospf
RouterC ospf enable
RouterA-Serial0ospf network-type p2mp
RouterB-Serial0ospf network-type p2mp
Configure DR on Ospf Preference
1.1 4.4 E0 192.1.1.1/24
E0 192.1.1.4/24
E0 192.1.1.2/24 E0 10.1.2.3/24
2.2 3.3
RouterA display ospf peer
RouterD display ospf peer
To configure an Ospf virtual link Configure Router a
Between Router B and Router C
RouterB-ospfVlink peer-id 3.3.3.3 transit-area
To configure Ospf peer authentication Configure Router a
Troubleshooting an
Ospf Configuration
Normally
Ospf Configuration Example
Configuring Ospf
BGP Configuration Example
BGP Overview
BGP Overview
Displaying and Debugging BGP
Configuring BGP
Resetting BGP Connections Enabling BGP
Perform the following configurations in system view
By default, BGP is disabled
Perform the following configurations in BGP view
Configure the BGP Version of the Peer
Set the Timers for BGP Peer
Configure BGP Route-update Interval
Configure to distribute default route to the peer
Configure to Send Community Attribute to the Peer
Configure the Peer to be the Client of the Route Reflector
Configure to Distribute Default Router to the Peer
Create a Fltering Policy Based on Access List for the Peer
Configure the BGP MED Metric
Create a BGP Route Filtering Based on AS Path for the Peer
Allow Comparing Path MED
Configure the Local Preference
Configure the Keepalive Timer and Holdtime Tmer for BGP
Timers keepalive-interval
Holdtime-interval
By default, there is no BGP peer in a peer group
Add a Peer to the BGP Peer Group
Peer group-name
Group-name
Configure AS Number of BGP Peer Group
Configure Connection Between Peers Indirectly Connected
Set the Timers of BGP Peer Group
Configure BGP Routing Update Sending Interval
Configure to send the default route to the peer group
Configure to Send the Default Route to the Peer Group
Create Routing Policy for Peer Group
By default, software accepts BGP Version
Configure BGP Version of Peer Group
Create an Aggregate Addresses
By default, an aggregate is disabled
Aggregate address mask
As-set
Undo aggregate address
Reflect between-clients
Clients within the reflection group
Undo reflect between-clients
Configure the Cluster ID
Configure BGP Community
Standard-community-list-number
Extended-community-list-number
Configure a Confederation
Configure the Sub-system of E Confederation
As-number …
Schematic diagram of route dampening
Display Route Flap Information
By default, BGP synchronizes with IGP
Is insured When AS is not a transitional AS Configuring
Configure Route Import for BGP
Still exists
Define an access list entry
Entry, an AS Path-list
Define an AS Path-list entry
Define a routing policy
Perform the following configurations in Routing policy view
Define a match rule
Define an apply clause
Filter for BGP
Reset BGP Connections
Debugging BGP
Filter Routing Information Being Advertised by BGP
Display and Debug BGP
BGP Configuration
Procedure for each configuration
As-regular-expression acl
Acl-number network-address
Networking diagram of configuring AS confederation
Configure Router B Configure BGP peers
RouterA-bgppeer 192.1.1.2 as-number
RouterB-Serial1ip address 193.1.1.2
RouterC-ospfinterface serial
Configure Router D Configure BGP peers
Configure peer
Start BGP
Specify BGP transmission network
RouterA-acl-1rule permit source 1.0.0.0
RouterC-acl-1rule permit source 1.0.0.0
RouterC-bgppeer 193.1.1.1 route-policy localpref import
RouterD-ospf network 4.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 RouterD bgp
Configuring BGP
IP Routing Policy
Configuring IP Routing Policy
Configure IP Routing
Operation Command Define a routing policy and enter into
Policy
Define a Routing Policy
Configure a Matching Rules
Define a Setting Clause
Apply community aa nn
No-export addtive none
Apply tag tag-value
Configure Route Import
Route-policy route-policy-name
Tag tag-value type 1
Define an IP Prefix List
Ip ip-prefix prefix-list-name
Ge-value less-equal le-value
Perform the following configurations in all views
Debugging IP Routing Policy
OSPF-ASE external route discovered by Ospf protocol
BGP route discovered by BGP protocol
Configuring IP
With different weighting values
Routing Policy
Protocol
Route Information
Troubleshooting IP
Configure RIP protocol
Normal operation
Routerip ip-prefix p1 permit 192.1.1.0/24
Configuring IP Routing Policy
Configuring IP Policy
IP Policy Routing
Routing
Create a Routing Policy
Define Match Rules
Define Apply Clause
By default, interface policy routing is disabled
Enable/Disable Interface Policy Routing
Displaying Debugging IP Policy Routing
Interface Policy Routing
Suggested procedure for each configuration
Define access list
Router-acl-101rule deny tcp source any destination any
Router-acl-102rule permit tcp source any destination any
Adopt policy aaa in Ethernet interface
Router-Ethernet0ip policy route-policy aaa
RouterA-Ethernet0ip policy route-policy lab1
RouterB-ripnetwork
RouterAdebugging ip policy-routing
Configuring Igmp Configuring PIM-DM Configuring PIM-SM
Chapter
IP Multicast
498
IP Multicast
Range and Meaning of Class D Addresses
List for Reserved Multicast Addresses
Class D address range Meaning
IP Multicast Routing Protocols
IP Multicast
IP Multicast Packet
IP Multicast
Application
IP Multicast
Configuring Igmp
Igmp Configuration Example
Igmp Overview
Igmp Overview
Configuring Igmp
Make the following configuration in interface view
Configure the Igmp Version Number Run at Router Interface
Configure Igmp Maximum Query Response Time
Igmp Configuration
Debugging command in system view to debug Igmp
Displaying and Debugging Igmp
Interfaces are all fast Ethernet FE
Router a Router B
Configuring Igmp
Configuring PIM-DM
Make the following configuration in the system view
By default, the system disables the multicast routing
Enable Multicast Routing
Operation Command Enable multicast routing
Start/Disable PIM-DM Protocol
Displaying and Debugging PIM-DM
Display and Debug PIM-DM
Group-address source-address
PIM-DM Configuration
Enable multicast routing protocol
Enable PIM-DM protocol
Receiver 2 are the two receivers of this multicast group
PIM-SM Overview
PIM-SM Configuration
Enabling Multicast Routing
By default, the interface disables PIM-SM protocol
Enable/Disable PIM-SM Protocol
Configure Candidate BSR
Configure Candidate RP
By default, no interface is configured to be candidate RP
By default, no PIM-SM domain boundary is configured
Configure PIM-SM Domain Boundary
Use the pim command in system view to enter PIM view
Debugging PIM-SM
Configure Router a Enable PIM-SM protocol
Configure Router B Enable PIM-SM protocol
RouterA multicast routing-enable RouterA interface ethernet
RouterA-pimspt-switch-threshold 10 accept-policy
Display pim neighbor command can be used to check whether
Follow these steps
Neighbors have discovered each other
RouterB-acl-5rule permit source 225.0.0.0
Configuring PIM-SM
Viii Security
524
Terminal Access
Configuring Terminal
Access Security
Configuring a User
Configure EXECLogin Authentication
Enable AAA
Configure Radius server and the shared secret
Configure the authentication method list of Exec users
Configuring Terminal Access Security
AAA Overview
Radius Overview
Components of Radius server
Basic message interaction process of Radius
Request Authenticator Adopts 16-byte random code
Type of Packets Decided by Code Field
Code Packet type Explanation of the packet
Attribute Fields
By default, AAA is disabled
AAA Enable/Disable AAA
Configure AAA Login Authentication
Server-template-name method1
Configuring an Authentication Method List for PPP Users
Configure PPP Authentication Method List of AAA
Default methods-list method1
Default methods-list
By default no address pool is defined by the system
Configure AAA Local-First Authentication
Configure AAA Accounting Option
Configure Local IP Address Pool
By default pool-number is
Configure a User and Password
Configure Callback User
Configure Ordinary User and Password
Configure User with Caller Number
Configure FTP User and the Usable Directory
Configure Callback User and the Callback Number
Configure User with Caller Number
Authorize a User with Usable Service Types
Configure FTP User and the Usable Directory
Configure Authorizing a User with Usable Service Types
Directory
Configure Radius Server Shared Secret
By default, no key is configured for the Radius server
Configure Radius Server Shared Secret
Radius server hostname ip-address
Configure the Request Retransmission Times
Configure the Time Interval for the Inquiry Packet
Accessing User
Authentication Case
Displaying Debugging AAA
AAA and Radius
Configure IP address and port of Radius server
Configure local-first authentication
Router aaa authentication-scheme local-first
Routerradius server
Troubleshooting AAA
Radius
Users Radius authentication is always rejected
Connected user cannot be seen in display aaa user
Can
Configuring AAA and Radius Protocol
Firewall Overview
Classification of Firewalls
Packet filtering schematic diagram
Extended access control list
Command format when the protocol is IGMP, IP, GRE or Ospf
Command format when the protocol is TCP or UDP
Operators of the Extended Access Control List
Mnemonic Symbol of the Port Number
Protocol Mnemonic Symbol Meaning and Actual Value
UDP
Configure the match sequence of access control list
Mnemonic Symbol of the Icmp Message Type
Operator and Syntax Meaning
Configure Firewall
Effect Perform the following configurations in system view
Firewalls are disabled by default
Firewall
Configure Standard Access Control List
Configure Extended Access Control List
Enabling and disabling filtering according to timerange
Configuring Special Timerange
Set Default Firewall Filtering Mode
Destination dest-addr dest- wildcard
Enable/Disable Filtering According to Timerange
Set special time range
Set Special Time Range
Settr begin-time end-time
Use debugging, reset and display commands in all views
Displaying and Debugging Firewall
Specify Logging Host
Display and Debug Firewall
Enable firewall
Configure access rules to inhibit passing of all packets
Routerfirewall enable
Routerfirewall default permit
Apply rule 102 on packets coming in from interface Serial0
Router-Ethernet0firewall packet-filter 101 inbound
Router-Serial0firewall packet-filter 102 inbound
IPSec Protocol
IPSec Related Terms
Following terms are important to an understanding of IPSec
IPSec Message Processing
Configuring IPSec
Access Control List
Creating an Encryption
Create Encryption Access Control List
Operator port1 port2
Configure Ndec Cards Enable the crypto cards
By default, all the crypto cards are enabled
Set the output of the crypto card log
By default, no proposal view is configured
Enable/Disable the Host to Backup the Ndec Cards
Set the Mode for Security Protocol to Encapsulate Messages
Define IPSec proposal
Selecting the Encryption Authentication Algorithm
Default mode is tunnel-encapsulation mode
Select Security Protocol
Select Security Protocol
Select Encryption Algorithm and Authentication Algorithm
Creating a Security Policy
By default, no security policy is created
Configure access control list quoted in security policy
Perform the following configurations in IPSec policy view
Set start point and end point of security tunnel
By default, the security policy quotes no IPSec proposal
Configure IPSec Proposal Quoted in Security Policy
Set IPSec proposal quoted in security policy
Set SPI of security policy association and its adopted key
By default, no key is used by any security policy
Configure SPI Parameters of Security Policy Association
Configure Key Used by Security Policy Association
Hex-key
Set access control list quoted by security policy
Set end point of security tunnel
Creating a Security Policy Association with
Specify End Point of Security Tunnel
Set the IPSec proposal quoted in security policy
Set SA lifetime
Proposal proposal-name1
Proposal-name2...proposal-name6
Configure a separate SA lifetime
By default, apply the global SA lifetime
Configure Global SA LIfetime
Configure Separate SA LIfetime
Use debugging, reset and display commands in all views
Debugging IPSec
Apply Security Policy Group on Interface
Ipsec sa dynamic-detect
Reset crypto card
Display and Debug IPSec
Dest-address protocol spi
IPSec Configuration Example
Use the debugging, reset and display command in all views
Displaying and Debugging the crypto card
Creating an SA Manually
Adopt tunnel mode as the message-encapsulating form
Select authentication algorithm and encryption algorithm
Quote access list
Create the IPSec proposal view named tran1
Configure the route
Create a security policy with negotiation mode as manual
Apply security policy group on serial interface
Exit to system view
Create a security policy with negotiation mode as isakmp
Create the IPSec proposal view named trans1
Set remote addresses
Configure ip address of the serial interface
Configure corresponding IKE
Configure serial interface Serial0
Create a security policy with negotiation view as isakmp
Establish a security policy with manual negotiation mode
Adopt tunnel module for packets encapsulation form
Return to system view
RouterB ike pre-shared-key abcde remote
Enter Ethernet interface view and configure IP address
Set local address
Set encryption key
Apply security policy base on serial port
Establish a security policy with manual configuration mode
Troubleshooting IPSec Ndec card cannot be configured
Return to the system view
RouterB ipsec policy map1 10 manual
Do the following
Configuring Ipsec
Configuring IKE
Configuring IKE
IKE features
Policy
Create IKE Policy
Ike proposal policy-number
View Delete IKE policy
Undo ike
Selecting an Authentication Algorithm
Select Authentication Method
Configure Pre-shared Key
Select Encryption Algorithm
By default, 768-bit Diffie-Hellman group is selected
Select Hashing Algorithm
Select DH Group ID
Set Lifetime of IKE Negotiation SA
Configure IKE Keepalive Timer
Reset ike sa connection-ike-sa-id
Displaying and Debugging IKE
Display and Debug IKE
IKE Configuration
Invalid user ID information
Unmatched policy
Unable to establish security channel
Configuring VPN Configuring L2TP Configuring GRE
IX VPN
596
VPN Overview
Basic Networking
Applications of VPN
Classification of IP
Authority given by local ISP
Layer 2 tunneling protocol
Layer 3 tunneling protocol
Comparison of layer 2 and layer 3 tunnel protocols
Configuring VPN
Vpdn and L2TP
Vpdn Operation
Methods of Implementing Vpdn
L2TP channel
Networking diagram of two typical methods of Vpdn
Tunnel and session
IV. Call setup flow of L2TP tunnel
Control message and data message
Features of L2TP
Call setup flow of L2TP channel
Basic Configuration at
Enable L2TP
Enable/Disable L2TP
L2tp enable
Originate L2TP Connection Request and LNS Address
L2tp-group group-number
Ip-address … domain domain-name
By default, L2TP is disabled
Configure AAA and Local Users
Default list-name method1
L2TP Attribute Table
Operation Command Create a L2TP group
Operation Command Create a virtual template
Create/Delete L2TP Group
Create/Delete a Virtual Template
Advanced Configuration at LAC or LNS
By default, receiving dial-in from LAC is disabled
Configure the Name of the Receiving End of the Tunnel
Configure Local VPN Users
Enable Tunnel Authentication Setting Password
By default, the local name is the host name of router
Set Local Name
Tunnel name name
Configure the Interval For Sending Hello Messages
Set Tunnel Authentication and Password
Set the Interval for Sending Hello Message
Configure Domain Delimiter and Searching Order
Force
Set Domain Name Delimiter and Searching Order
This configuration is applicable to LNS only
Operation Command Force to disconnect tunnel
Reset l2tp tunnel remote-name
Force to Disconnect Channel
Configure the Local Address and Address Pool
LCP does not renegotiate by default
LCP to Renegotiate
Enable/Disable Hiding Attribute Value Pairs AV
By default, AV pairs are hidden
Enable/Disable Hiding AV Pairs
Number of L2TP Sessions
L2TP Configuration Examples
By default, the maximum number of L2TP sessions is
Use debugging, display command in all views
Display and Debug L2TP
Implement local AAA authentication on VPN user
Configure the IP address of Serial1 interface of LAC
Enable L2TP service and configure a L2TP group
Configure BDR dialup parameters
Configure the IP address of Serial0 interface of LNS
Configure the Virtual-Template-related information
Internet Connection Wizard
Internet Connection Wizard
Internet Connection Wizard
Internet Connection Wizard
Client-originated VPN Networking
Router-LACip pool 1 192.170.0.3
Configure the IP address of Serial1 interface at LAC side
Configure BDR parameters
Configure the IP address of Serial0 interface at LNS side
Disable tunnel authentication
Network Connection Wizard
Network Connection Wizard
Connect Connection to
Configure an IP address on Serial0 interface
Configure a L2TP group and the related attributes
Configure the domain suffix separator to @
Router1 l2tp domain suffix-separator @
Enable AAA authentication
Configure Virtual-Template
Force to implement local Chap authentication
III. Procedures
Configure a L2TP group and configure the related attributes
Configuration at Router2 LNS side Enable AAA authentication
Configure an address pool 1 in the range of 192.168.0.2 to
Configure an access control list and specify L2TP data
Fault 1 The users fail to log
PPP negotiation fails. The reasons may be
Troubleshooting L2TP
Configuring L2TP
GRE Protocol
Encapsulation
Packet
Encapsulated tunnel message format Refer to RFC
Enlarge network operating range
Configuring GRE
By default, no virtual tunnel interface is created
Creating a Virtual Tunnel Interface
Create Virtual Tunnel Interface
Address of a Tunnel Must be configured Interface
Setting the Network
Perform the configurations in the tunnel interface view
Address of the Tunnel
Number discarded
Set Tunnel Interface to Check with Checksum
Set the Tunnel to Synchronize Datagram Sequence Numbers
Gre key key-number
GRE Configuration Example
Group1 and group2. It can be implemented by using GRE
Debugging GRE
All views
Configure the IP address of Ethernet0 interface
Configure Router B Configure the IP address of Serial0
Configure Router a Activate IPX
Configure the IP address and IPX address of Ethernet0
Configure the static route to Novell Group2
Configure Router B Activate IPX
Networking of troubleshooting GRE
RouterB ipx route 1e 1f.a.a.a tick 30000 hop
Configuring a Standby Center Configuring Vrrp
646
Configuring Standby Center
Standby Center
Enter the Logic Channel View
Address logic-channelnumber
Fr map protocol address dlci dlci
Next-hop-address dialer-number
Channel to check whether it has recovered
Standby timer enable-delay seconds
Undo standby timer enable-delay
Standby timer disable-delay seconds
Please perform the following configuration in all views
Load Sharing view
Interfaces
Enter the view of Serial
Enter the view of logic channel
Channel
Router-logic-channel10standby interface serial
Router-Serial1logic-channel
Vrrp Configuration Examples
Troubleshooting Vrrp
Vrrp Overview
Vrrp Overview
Configuring Vrrp
Adding a Virtual IP
Address
Configure Router Priority in Standby Group
Add Virtual IP Address
Vrrp vrid virtualrouterid
Undo vrrp vrid virtualrouterid
Configuring Authentication Method Authentication Key
Vrrp provides simple character authentication method
Configure Authentication Method and Authentication Key
Virtualrouterid
Configure Standby
Group Timer
Debugging Vrrp
Monitoring
Vrrp Configuration
Procedure for each configuration
Backup with preemption aII. Networking diagram
Vrrp Single Standby
Gateway services instead
Balancing and mutual backup are implemented
Gateway function as the master
Multiple Standby
There is requent switchover of the Vrrp state
Many master routers exist within the same standby group
XI QOS
662
Three Types of QoS Services
QOS Overview
QOS Overview
Benefits of QoS for the Network Service
QOS Overview
Traffic Classification
Traffic Policing
Traffic POLICING, Traffic Shaping and Line Rate
Committed Access
Rate CAR
Defining Rules
Define CAR Rules
Qos carl carl-index precedence
Precedence-value mac mac-address
By default, no CAR rule of ACL list is established
Applying the CAR Policy on the Interface
Apply the CAR Rule on the Interface
CAR Configuration Applying a CAR Policy to all Packets
Configure the Priority Level Based CAR Policy
Displaying and Debugging CAR
Display and Debug CAR
Configure the CAR Policy Based on the MAC Address
Traffic Shaping
Apply a CAR Policy on the Packets that Match ACL
Matches ACL
Packets
Configuring shaping parameters for a specified flow
Schematic diagram of GTS processing
Configuring shaping parameters for all flows
Configure the ACL
Shape the flows matching 110 on Ethernet interface
Configure the Physical Interface LIne Rate
Physical Interface Line
Rate
Shape all the flows on Ethernet interface
Operation Command Display the LR configuration conditions
Displaying Display and Debug LR Debugging LR
Display qos lr interface type
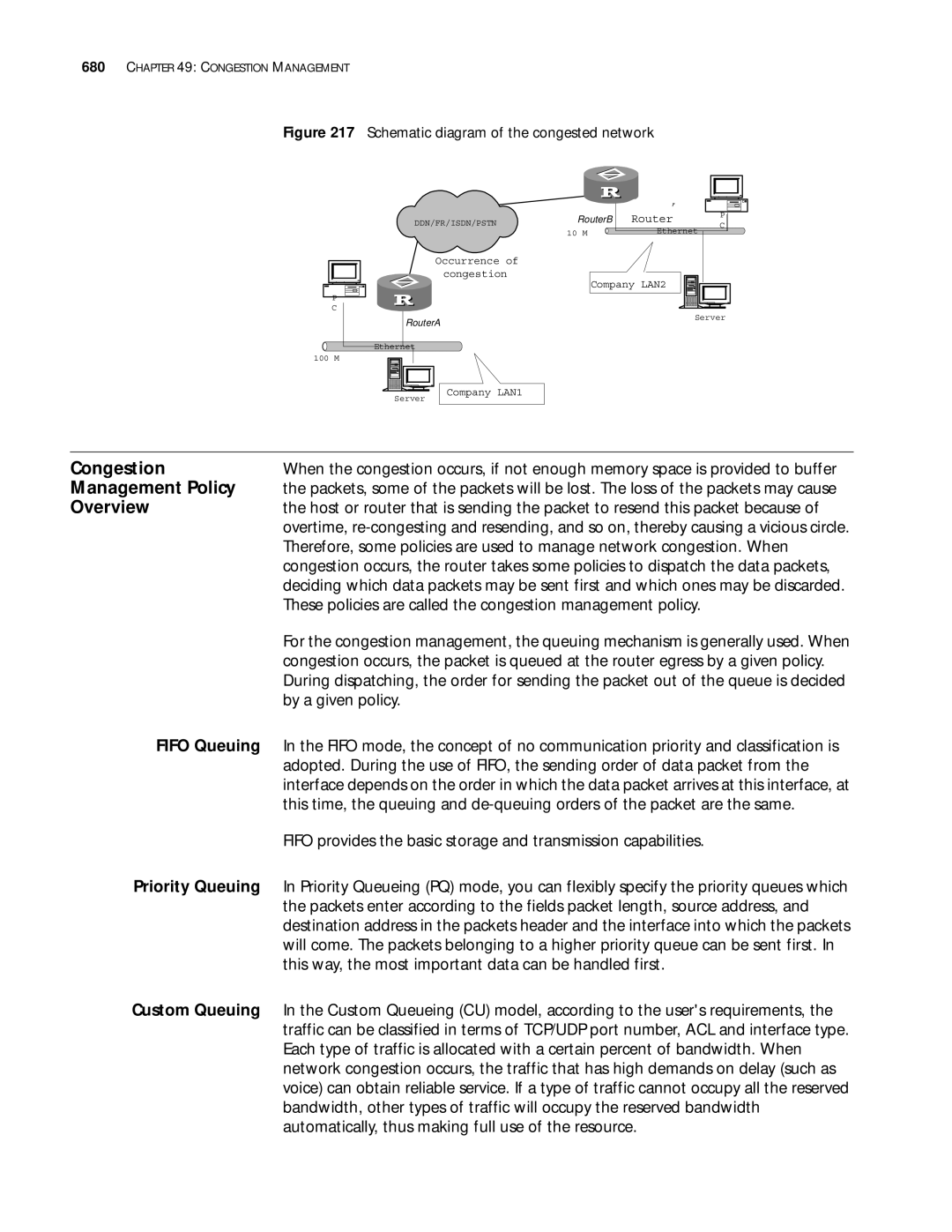
Congestion Management
Congestion
Management Policy
Fifo Queuing
Priority Queuing
Selecting Congestion Management Policies
Comparison of Several Congestion Management Policies
Number Queues Advantage Disadvantage
Schematic diagram of the first in first out queue
Schematic diagram of the custom queuing
Weighted Fair Queuing WFQ
Schematic diagram of weighted fair queuing
Configuring Congestion Management
Configuring Fifo Queuing
Configuring priority queuing
Configure the First In First Out Queuing
By default, no priority queue is established
Values of Queue-Option with Protocol as IP
Protocol-name queue-option queue
Pql-index protocol
By default, the interface utilizes the Fifo queue
Applying the priority-list queuing group to the interface
Specifying the queue length of the priority-list queuing
Configuring custom-list queuing
Configuring Custom Queuing CQ
Default Length Value of the Priority Queue
Displaying and debugging the priority queue
Configure the Custom-Lst Queuing According to the Interface
Configure the Default Custom-List Queuing
Queue-number
Queue queue-number
By default, the interface uses the Fifo queue
Configuring the queue length of the custom-list queuing
Configure the Queue Length of the Custom-List Queuing
Applying the custom-list queuing group to the interface
Configuring Weighted fair queuing
Displaying and debugging the weighted fair queue
Displaying and debugging the custom-list queue
Congestion Management Configuration Examples
PQ Configuration Example
Apply the priority queue 1 to Serial
Apply the priority queue 2 to Serial
Configure the CQ queue
Configure Router B Configure the access control list
RouterA-Tunnel0ip address 10.1.1.1
RouterA-Tunnel1destination
Configure Serial0 master/slave addresses
Configure Tunnel0
Configure Tunnel1
WFQ Configuration Example
Congestion Management
Congestion Avoidance
Congestion Avoidance
Wred Configuration
Enable the Wred
Enable Wred
Function of the Interface
Discard-prob
Ip-precedence
Congestion Avoidance Configuration Example
Configure a WFQ queue
Enable Wred
Displaying Debugging Congestion Avoidance
Congestion Avoidance
Configuring DCC Configuring Modem
XII DIAL-UP
704
Terms in DCC Configuration
DCC Overview
Circular DCC
DCC
Resource-Shared DCC
Basic DCC features
With 3Com Routers
Implementing callback through DCC
Configuring DCC
Preparing to Configure
Prepare the data for DCC configuration
Configure the local parameters of DCC
Configuring the mode of the physical interface
Configure Physical Interface Mode
Linklayer-protocol-type
Ip address ipaddress mask
Associating a DCC dialer ACL with the interface
Configuring an interface to originate calls to a remote end
Configure an interface to receive calls from a remote end
Dialer enable-circular
Dialer number dial-number
Undo dialer number
Dialer
Route protocol
Next-hop-address dial-number
Undo dialer route protocol
Next-hop-address
Undo interface dialer number
Dialer circular-group number
Undo dialer circular-group
Dialer priority priority
Interface dialer number
Undo interface dialer number
Dialer circular-group number
Undo dialer circular-group
Router Dialer0
Configuring dialing authentication for resource-shared DCC
Configuring the dialer interface and dialer number
By default, no dialer interface is created
Enabing Resource-Shared DCC
Configuring dialing authentication for resource-shared DCC
Configuring MP binding in circular DCC
Configure MP Binding in Circular DCC
Threshold traffic-percentage
Configuring MP binding in resource-shared DCC
Configuring PPP callback in the circular DCC implementation
Configure MP Binding in Resource-Shared DCC
Dialer threshold traffic-percentage
Implement PPP Callback Client Configuration in Circular DCC
Implement PPP Callback Server Configuration in Circular DCC
Command
Telephone-number
Next-hop-address user username
Dial-number
Features of Isdn caller identification callback
Primary rule The best match is the number with the fewest
Dialer callback-center dial-number
Operation Command Configure the local end to implement
Identification
Undo dialer call-in remote-number
Callback according to the Isdn caller
Configuring Isdn leased line
Configuring auto-dial
Configuring Special DCC Functions
Configure Isdn leased line for Circular DCC
Configuring dialer number circular standby
Configuring the Link Idle Time
Configure Auto-Dial
Configure Dialer Number Circular Standby
By default, the link idle time is 120 seconds
By default, the link disconnection time is 20 seconds
Configuring the link idle time when interface competion
Configure the Link Idle Time
Configuring the timeout of call setting up
By default, the timeout of call setting up is 60 seconds
Configuring the buffer queue length of the dialer
Debugging DCC
DCC Configuration Examples
Solution
DCC Applications in Common Use
Configure RouterC
Configure RouterB
Router-Serial1dialer circular-group
Router-Serial0dialer route ip 100.1.1.1
Router-Serial0dialer bundle-member
Router-Serial1dialer bundle-member
Configure RouterC
Configure RouterC
Configure RouterA
Router-Dialer0dialer threshold
Router-Bri0dialer bundle-member
Router-Serial015dialer route ip 100.1.1.1
Router-Bri1dialer route ip 100.1.1.1
Router-Serial1dialer enable-circular
Router-Serial0dialer route ip 100.1.1.2
Router dialer-rule 1 ip permit Router interface serial
Router-Bri0dialer route ip 100.1.1.2 user usera
Configure the PC
Callback for DC C
By the NT server
NT Server-to-Router
Router-Async0dialer route ip 100.1.1.254
Dial Number Circular Standby and Internet Access for DCC
Configure subscriber PC
Router-Serial0dialer route ip 100.1.1.254
Router-Serial215ppp authentication-mode chap
Router-Serial215ppp chap password simple passb
Router-Serial1standby logic-channel
Remote end cannot be pinged after the modem is connected
DCC Fault Messages
Message Fault
DCC peeraddr matching error
Modem Function Provided by 3Com Routers
Modem Script
Syntax description of modem script
Modem script format in common use is as follow
Receive-string1 send-string1 receive-string2 send-string2
Which, seconds defaults to 180 and is in the range of 0 to
Configure the Modem Dial-in and Dial-out Authorities
By default, modem dial-in and dial-out are allowed
Configure Modem Through the AT Command
Configure a Modem Script
Configure a Modem Script
Execute a Modem Script Manually
By default, the modem works in non-auto answer mode
Configure the Answer Mode for the Modem
Configure Authentication for a Modem Dial-in User
Specify the Events Triggering the Modem Scripts
Modem Configuration Examples
Executethe debugging command in all views for the debugging
Configure a Modem adaptation baud rate
Displaying and Debugging a Modem
Restore the ex-factory modem settings
Configure the modem initialization parameters
AT&b1&c1&d2&s0=0
Power-on Initialization Through Initialization Script
Authentication for
Directly
Modem Dial-in User
Troubleshooting
Configuring Modem