Qvwuxphqw
Trademarks
III
About this Manual What this Manual Contains
Initializing the CombiScope Instrument
Measuring Signal Characteristics
15.4.2 Error-reporting using the SRQ mechanism
Readout of measurement data
15.1.1
15.1.2
Command Reference
Application Program Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
VII
What this Manual Contains
About this Manual
About this Manual
System setup
Preparations for Scpi Programming
Getting Started with Scpi Programming
Programming environment
Command
Commands
Addresslist
Constant -1 Ffff hex
Program Example
Programming Note
How to reset the CombiScope instrument
How to identify the CombiScope instrument
How to switch between digital and analog mode
Initializing the CombiScope Instrument
Error Reporting
’Requests for error
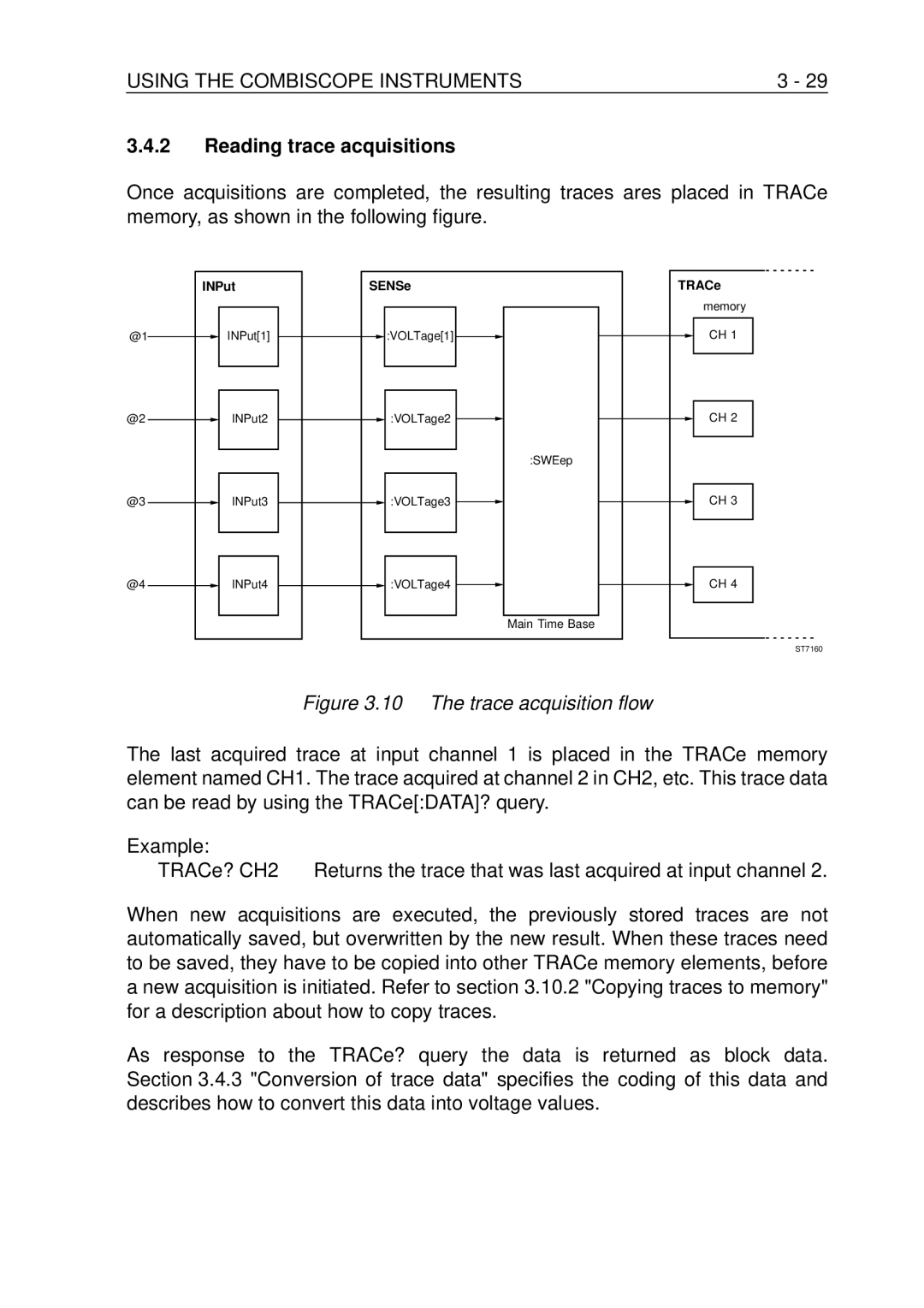
Acquiring Traces
Channels and memory registers Example Send -- FORMat INT,16
Format of the trace response data is as follows
Example
How to acquire a single shot trace
Preparations
This string data
How to acquire repetitive traces
Connect a probe from the Probe Adjust signal to channel
Measuring Signal Characteristics
CONFigure + READ?
MEASure?
INITiate + FETCh?
How to make a single shot measurement
How to make repeated measurements
Using the Combiscope Instruments
Introduction
Using the Combiscope Instruments
Fundamental Programming Concepts
TRACe? CH1
SAV
RCL
DISPlayMENU TRIGger
SYSTemKEY
Measurement instructions
Single function programming using the instrument model
Explanation of the Instrument Model
Instrument setup
Read ← blockdata Instrument setup
Front panel simulation
MEASure? query
MEASureAC?
Benefits of using parameters
Voltageparameters = expectedvoltage,resolution
Generic form of a measurement instruction is as follows
Examples
MEASureAMPLitude?
MEASureVOLTageAMPLitude? 10, @2
MEASureVOLTageFREQuency? 10E6, @3
Pulse characteristics
Waveform measurements
MEASureFALLTIME? @3
MEASureRISETIME? 20,80
Measurefunctionmeasureparameters
FTIMe = alias for Falltime RTIMe = alias for Risetime
Customizing settings
CONFigureAC
SENSeAVERage on
SENSeAVERageCOUNT
CONFigureRISETIME
READRISEOVERshoot?
Multiple measurements
Multiple characteristics from a single acquisition
READFREQuency?
Starts Acquisition Returns
Starts a Next acquisition Returns New Frequency result
Trigger control via Gpib
TRIGgerSOURce BUS
INITiate
FETChAC?
Fetching characteristics from memory traces
M12,CH2
Acquisition
Acquisition control
Using the Combiscope Instruments
Triggering
Trigger Type
Trigger Source
Trigger Level
Trigger Slope
Trigger Coupling
DC Coupling 0 Hz cutoff frequency
DC Coupling
AC Coupling 10 Hz cutoff frequency
LF-REJECT 30 KHz cutoff frequency
HF-REJECT 30 KHz cutoff frequency
Video triggering
Ntsc
Lines per frame
PAL
Secam
Trigger modes
OFF
Line
BUS
Commands
State Description
Pre- and post-triggering
Trace
External triggering
Reading trace acquisitions
10 The trace acquisition flow
Single-shot acquisition
Repetitive acquisitions
Conversion of trace data
11 Relation between screen position and trace value
’Array of 512 integers
Byte1 = ASCMID$response$, J
Ps = Ts
For 8-bit sample traces
Ps = Ts / 25600 * 100 = Ts
Using the Combiscope Instruments Program Example
’1-byte samples
Averaging Acquisition Data
AVGn = ∑X1 + .. + Xn ⁄ n
13 The Trigger Model during acquisition averaging
Channel Selection
Programming tip
Signal Conditioning
1 AC/DC/ground coupling
Input filtering
Input impedance
Input polarity
Vertical range and offset
Vs = Ts / 200 * PTPeak OFFSet
Autoranging attenuators
Limitation
Time Base Control
Number of samples
Time base speed
MTB = 50 * SENSeSWEepTIME / TRACePOINts
Ts = sampleindex * SENSeSWEepTIME / TRACePOINts
Real time acquisition
16 Definition of a signal period
Autoranging time base
How to do post processing
Post Processing
Select the source for the post processing function
Send → CALCulateFEED M21 ’M21 = source for CALC1
Standard Available
Mathematical calculations
Math
Optional
Check the result of the post processing function
Example Send → TRACe? M21
Read ← tracebuffer ’Reads M21 trace
Mathematical calculations
Differentiating and integrating traces
Frequency domain transformations
Relative FFT
Absolute FFT
Trace Point Values
For 16-bit samples Ps = Ts 25600
Trace data
This can be calculated as a signal level
Example for attenuator setting 0.5 V/div
Vrms offset calculation
DBm 50Ω offset calculation
DBm 600Ω offset calculation
DBμV offset calculation
DBμV = 1 μV 1.0E-6 V at 50Ω impedance
Setting
Trace Point Frequencies
Fs = sampleindex * 1250 / TRACePOINts * MTB
Program Example
Histogram functions
Amplitude belt = peak-to-peak range
Frequency filtering
Trace Memory
20 Trace memory control
Channels Memory Registers Standard
PM33x0B 512 +EXT
Extended
Trace formatting
Copying traces to memory
Writing data to trace memory
Send → TRACe? CH3
’Queries for CH3 trace
Read ← trace block
Reading data from trace memory
Screen/Display Functions
Brightness control
Display functions
Menu
Measurement Value
MEAS1/MEAS2 Data
Meastype,measvalue,suffixunit
Description
Cursors Data
Type Unit Description
Math FFT Data
Call Send0, 8, DISPlayMENU MEASure
Display of user-defined text
Program Example 2 text as block data
Selection of softkey menus
Print/Plot Functions
Device Type
Hpgl
Hplaser
22 Hardcopy of screen on printer/plotter
Real-Time Clock
Auto Calibration
= okay
Status Reporting
Status data for the CombiScope instruments
Digital mode
Operation status data
CALibrating
RANGing
TEMPerature
Questionable status data
VOLTage
CALibration
How to reset the status data
Status Register Data Structure Preset Value
How to enable status reporting
Program example using the status byte STB
’Defines SRQ-routine
How to report errors
Error-reporting routine
’Sends error query
Saving/Restoring Instrument Setups
How to restore initial settings
How to save/restore a setup via instrument memory
How to save/restore a setup via the Gpib controller
How to simulate the pressing of a front panel key
Front Panel Simulation
Row 201
Row 801
How to simulate the operation of a softkey menu
Autoset Simulation
Functions not Directly Programmable
Envelope
DISPlayMENU ACQuireSYSTemKEY 3 toggles on/off
MULTiple-shot
Syntax specification notations
Meta symbols
Non-terminal symbols
Terminal symbols
Default
Not contain the message element
Between the square brackets, without
MEASureVOLTageDC? is the same
Data types
An explicit decimal point and may or may not be
Preceded by a sign, e.g
Bit codes
Double quotes
Examples This is a string
’This also’
Command Summary
Feed
Gate
Command Reference Parameters
Menu Name
State
DATA?
Read
TYPE?
Auto
DTR
RTS
Baud
Bits
ALL
Type PAL Secam Ntsc Hdtv
Expectedvoltage ,resolution
Timeresolution
Measurefunction Measureparameters
Referencelow ,referencehigh,expectedtime
Command Descriptions
Errors
Front panel compliance
Specifies the compliance with front panel operations
CAL? CALibration
Syntax *CAL? Response 0
Calibration okay Calibration not okay
Limitation
16COMMAND Reference
Clear Status
Event Status Enable
Byte Register. Alternative commands *ESE #B10001
Ation Complete bits to be summarized in the Status
*ESE #H11
18COMMAND Reference
Event Status Register
Response Integer Description
PON URQ CME EXE DDE QYE RQC OPC ESR
IDN? Identification
Syntax *IDN?
20COMMAND Reference
Operation Complete
Query form *OPC? Response Description
Restrictions
OPT? Option identification
Ieee EXT EM MP
Recall instrument setup
22COMMAND Reference
Syntax RCL numericdata Description
RST Reset
Function Default Settings
Syntax *RST Description
Beeper Hardcopy Print & Plot Plotter Hpgl Pass/Fail testing
Measure 1
Math 1
Cursors
Save instrument setup
Syntax SAV numericdata Description
Service Request Enable
26COMMAND Reference
Request Enable Register
STB? Status Byte
Syntax STB? Response Integer Description
TRG Trigger
Syntax *TRG Description
TST? Self-test
Syntax *TST? Response 0
Self-test okay Self-test not okay
Command Reference
Configures for AC-RMS value
ABORt
Syntax ABORt Description
Aborts the current acquisition
Switches the differentiate
CALCulatenDERivativePOINts CALCulatenDERivativeSTATe
Function on
CALCulatenFEED
Filter function turned off Filter function turned on
CALCulatenINTegralSTATe
Integrate function turned off Integrate function turned on
Switches MATH2 function on
CALCulatenMATHEXPRession
Switches MATH1 function on
CALCulatenMATHSTATe
Query form CALCulatenTRANsformFREQuencyTYPE?
Response ABS REL
Switches MATH2-FFT on
Selects relative MATH2-FFT calculation
Selects MATH2-FFT-HANNing window
Switches
CALCulatenTRANsformHISTogramSTATe
Histogram function turned off Histogram function turned on
CALibrationALL
Syntax CALibrationALL Query form CALibrationALL?
Response 0 Description
Starts auto calibration
Reads condition register
Conditions
CONFigure
Syntax CONFigureVOLTagemeasurefunction
Syntax elements are specified with the MEASure? query
Signal on channel
Expected voltage 600 mV
Channel 2 AC coupled
Initiates + fetches AC-RMS
DISPlayBRIGhtness
Query form DISPlayBRIGhtness? MINimum MAXimum
Response NR3
NR30.00E00 .. .00E00
DISPlayMENUNAME
Switches TB Mode menu display on
DISPlayMENUSTATe
Display turned off Display turned on
Type Analog Mode Digital Mode
DISPlayWINDow1TEXTnDATA?
Syntax DISPlayWINDow1TEXTnDATA?
Response is peak-peak value of 608.4 mV MEAS1
Display on
DISPlayWINDow2TEXT1CLEar
Clears all user text
DISPlayWINDow2TEXT1DATA
As text
Sends 25 decimal
Character byte
Command Reference
DISPlayWINDow2TEXT1STATe
54COMMAND Reference
FETCh?
FETChVOLTagemeasurefunction?
Voltageparameters, measureparameters
Restrictions
Acquisition
FORMatDATA
INT,8
HCOPyDATA?
HCOPyDEVice
INITiateCONTinuous
Response 1
INITiateIMMediate
Syntax INITiateIMMediate
Trigger level becomes
Single shot acquisition
INPutnCOUPling
INPutnFILTerLPASsSTATe INPutnFILTerLPASsFREQuency?
Response 2.00E+07
Query form INPutnFILTerLPASsSTATe?
Common low pass filter off Common low pass filter on
After a *RST command, the impedance is 1 MΩ
INPutnIMPedance
Syntax INPutnIMPedance NRf MINimum MAXimum 1E6
INPutnPOLarity
Response Norm INV Description
INSTrumentNSELect INSTrumentSELect
Response DIG Anal
DIG
Anal
MEASure?
Channellist =
Measurefunction measureparameters
Falltime
High
Signal. The peak to peak value is the difference between
First falling edge equals the REFerence MIDDle until
PDUTycycle Referencemiddle
Ratio percentage of the positive width PWIDth
Risetime
Measureparameters
Executed. The unit of timeresolution is second
Frequencyresolution = NRf DEFault
Referencemiddle is volt Expectedperiod = NRf DEFault
Periodresolution = NRf DEFault
Limitations
Description
74COMMAND Reference
Syntax READVOLTagemeasurefunction?
Example
SENSeAVERageSTATe
SENSeAVERageCOUNt SENSeAVERageTYPE?
Syntax SENSeAVERageCOUNt NRf 8 16 SENSeAVERageTYPE?
Response Scal
Initiates trace averaging
SENSeFUNCtionOFF SENSeFUNCtionON SENSeFUNCtionSTATe?
Addition of channel i+j is off Addition of channel i+j is on
Limitations
SENSeSWEepOFFSetTIME
SENSeSWEepPDETectionSTATe
Real-time mode switched off Real-time mode switched on
SENSeSWEepREALtimeSTATe
Slope = either pos. or neg
Reads AC-RMS
MTB values in the digital mode
SENSeSWEepTIME
Query form SENSeSWEepTIME? MINimum MAXimum
Base range is limited to 10 μs non-alternating time base
Coupled values
Requests sweep time
Reads sweep time
Requests nr of trace points
Autoranging MTB switched off Autoranging MTB switched on
SENSeSWEepTIMEAUTO
Sets trigger source CH1
Sets autoranging MTB on
Switches CH1 on
Switches CH2 on
SENSeVOLTagenDCRANGeAUTO
Autoranging CH2
SENSeVOLTagenDCRANGeOFFSet
Channel
SENSeVOLTagenDCRANGePTPeak
Query form SENSeVOLTagenDCRANGePTPeak? MINimum MAXimum
Peak-to-peak =
Sensitivity = 0.8 / 8 =
100 mV/div
Trigger source =
Response NR1 Description
BIT Decimal Meaning Number Value
STATusPRESet
Syntax STATusPRESet
Following table defines the effect of STATusPRESet
Status Register Filter / Enable Preset Value
Response NR1 Description
TEMPerature too high or too low
Returned value 16 equals bit 4 set temperature too high/low
Enables report of TEMPerature too high/low 0
Enables report of TEMPerature within allowed limits 1
No error
Error number is -222 and the meaning is Data out of range
STATusQUEueNEXT?
350,Queue overflow
Beeper disabled Beeper enabled
Reads the error queue
Beeps on error
SYSTemBEEPer SYSTemBEEPerSTATe
Wire control
Response on Stan
Stan
XON
None
Even ODD None
Response 7
Response XON None
No X-on/X-off handshaking
1200
Becomes
SYSTemDATE
Sets the system date to Nov 7
SYSTemERRor?
SYSTemKEY
Response NR1
Front Panel KEY
Enables Utility softkey menu
Returns the last key simulation
SYSTemSET
Nodenr nodelength firstbyte ... lastbyte
SYSTemTIME
*RST command doesn’t change the current Scpi version
SYSTemVERSion?
Syntax SYSTemVERSion?
Response YYYY.V
TRACeCOPY
TRACeDATA
Response definiteblock
Initiates single acquisition
Requests channel 1 trace
Reads channel 1 trace
Queries peak-to-peak
Reads peak-to-peak
TRACePOINts
Number of trace points for all
Requests M23 trace
Reads M23 trace
Pass Boolean
Sets high-pass filter off
Sets high-pass filter on
Low-pass filter active High-pass filter active HF-reject
Automatically switches
Filter Frequency LOW-PASS on HIGH-PASS on
DC coupling HF-reject AC coupling KHz LF-reject
Low-Pass filter off
TRIGgerSEQuence1FILTerLPASsFREQuency NRf
TRIGgerSEQuence1FILTerLPASsSTATe Boolean
TRIGgerSTARtFILTerLPASsFREQuency NRf
TRIGgerSTARtFILTerLPASsSTATe Boolean
Filter
Frequency LOW-PASS on HIGH-PASS on
Sets cutoff frequency = 30 KHz
TRIGgerSEQuence1HOLDoff TRIGgerSTARtHOLDoff
TRIGgerSEQuence1LEVel NRf MINimum MAXimum
TRIGgerSEQuence1LEVelAUTO Boolean
TRIGgerSTARtLEVel NRf MINimum MAXimum
TRIGgerSTARtLEVelAUTO Boolean
Trigger source Becomes
Channel Continuous initiation
Div. sensitivity
Trigger level becomes 0.2
After a *RST command, the trigger slope is POSitive
TRIGgerSEQuence1SLOPe TRIGgerSTARtSLOPe
POS
NEG
Configures AC-RMS CH2
Sets real-time mode on
Triggering is done at positive
Rising and negative falling
TRIGgerSEQuence1SOURce TRIGgerSTARtSOURce
IMM
EXT
Configures AC-RMS CH1
Input channel 1 becomes
Trigger source
Single initiation
TRIGgerSEQuence1TYPE TRIGgerSTARtTYPE
Edge
Selects edge triggering
Selects lines triggering
Numb
Linenr = linenr + 625/2 linenr = linenr 625/2
Selects TV video
Selects video lines
Selects video line
Secam Ntsc Hdtv
Scam Secam
Scam
Selects
Lines/frame Selects
Lines/frame Selects Secam
Lines/frame Selects Hdtv
Positive video signal polarity selected
Response POS NEG
123 Selects Negative Video Signal polarity
PAL or Secam From 1 to
Making a Hardcopy of the Screen Pass/Fail Testing
Error reporting is invoked as follows Call errorcheck
Application Program Examples
Making automatic measurements
Application summary
FETChNWIDth?
Application program
’Termination Receive on EOI
Making programmed measurements
Acquiring Waveform Traces
Reading measurement values
Saving/Recalling Instrument Setups
Save/recall settings to/from internal memory
Application summary
Application program
Making a Hardcopy of the Screen
CombiScope Instrument
Ieee
Pass/Fail Testing
Saving a pass/fail test setup
Application program Restoring a pass/fail test setup
Running a pass/fail test
DISPlayMENU MEASure
Cross Reference Front Panel Keys / Commands
Cross References
Channel 4 is external trigger input for PM33x0B
Page
Cross Reference Softkey Menus / Commands
Acquire menu
Programmable with the *SAV/*RCL and Systset commands
Cursors menu
Display menu
Ext instead of ch4 for PM33x0B
Mathplus Math menu
Other functions with RCL/SAV and Systset
Yes no
Page
Measure menu
DTB DEL’D TB menu
Setups menu
SAVE/RECALL menu
TB Mode menu
Systset RCL/SAV
Analog Mode
Trigger menu
Logic
Wire
Utility menu
Ieee
Vertical menu
Inpfilt Onoff INP1IMP INP2IMP INP3IMP INP4IMP
Cross Reference Functions / Commands
Function + KEYS/MENUS Related Scpi Commands Autoset
Average
BW Limit
Calibration Autocal
Delay
Delay Measurement
Delayed Timebase DEL’D TB
Differentiate Mathplus
FFT ON/OFF
Histogram Mathplus
Hold OFF
CH1
Integrate Mathplus
Logic Trigger
Magnify Horizontal
Main Time Base
Function + KEYS/MENUS Related Scpi Commands Mathematics
Pass Fail Testing Mathplus SAV, *RCL
Power Supply
Measure Menu
Remote Control IEEE-488.2
Remote Setup
Remote Control RS-232
Probe Utilities
Function + KEYS/MENUS Related Scpi Commands
Status Screen
Subtract Mathematics
Text OFF
Trig
Single
Multi
Roll
Trigger Coupling
Trigger DEL’D TB
Trigger Level
Trigger Main TB
User Text
Util Menu
Util Screen & Sound
DISPlayWINDow1TEXT12DATA?
Abbreviations Used
IDY
IDN
IEC
IFC
Manual Conventions RAM
REN
RQC
RQS
Glossary of Symbols Used
List of Tables
4MANUAL Conventions
List of Figures
Documents Referenced
TRIGgerSEQuence1 STARtVIDeoFORMatTYPE type command Purpose
Scpi Conformance Information
Standards Information
Or abbreviation, e.g., type = Hdtv
List of Implemented IEEE-488.2 Syntactical Elements
Command Program Header
Standards Information Program Message Unit Separator
Program Data Separator
Program Header Separator
End node settings
Channel 1/2/3/4 settings
Probe scale settings
Common vertical settings
Delayed timebase settings
Event trigger delay settings
Cursor settings
Cursor autosearch settings
MATH1/2 settings
Display settings
Trace intensity settings
Display trace position settings
Numerics
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index

![]() :VOLTage[1]
:VOLTage[1] ![]()
![]() :VOLTage2
:VOLTage2 ![]()
![]() :VOLTage3
:VOLTage3 ![]()
![]() :VOLTage4
:VOLTage4 ![]()