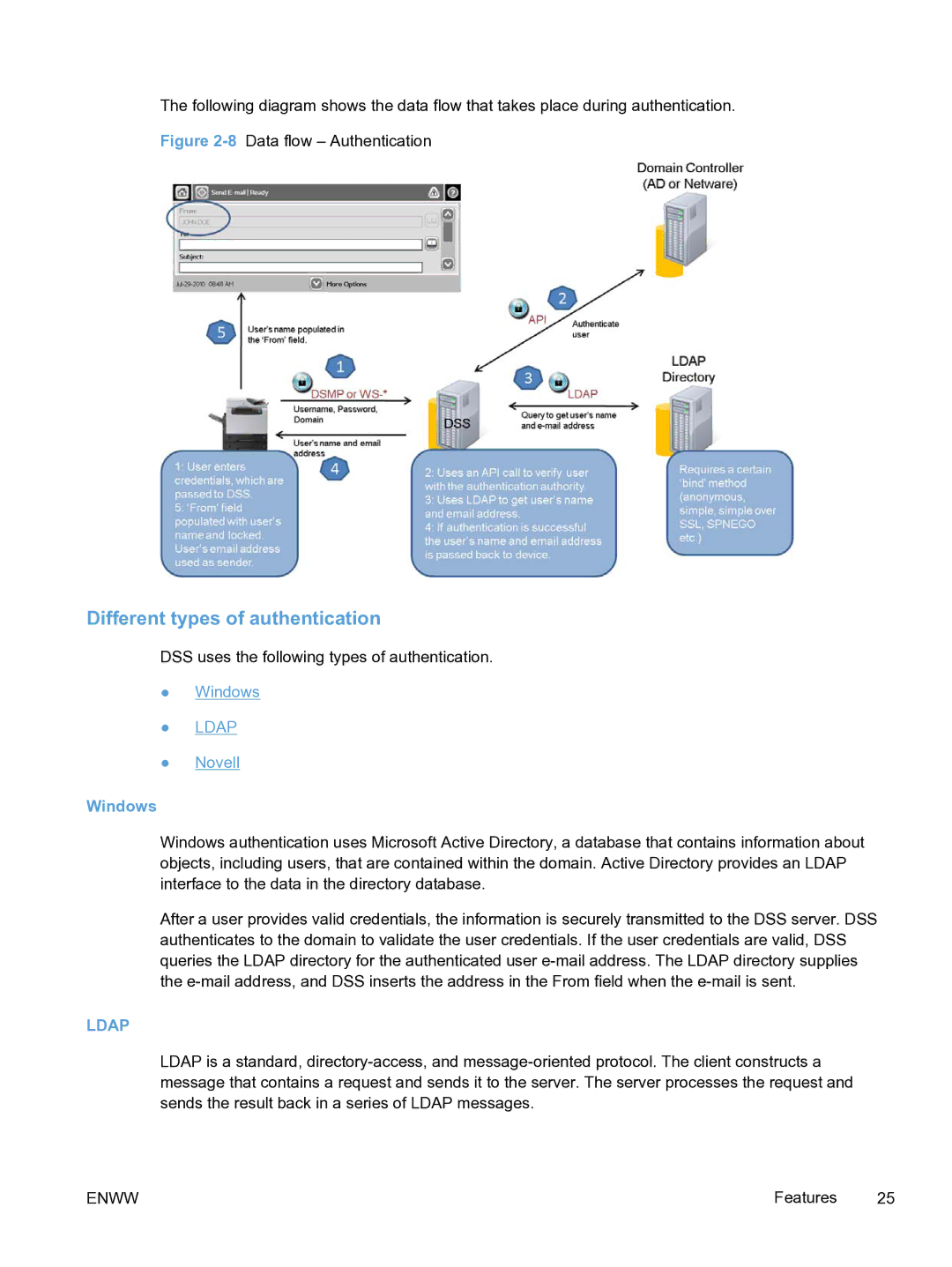
The following diagram shows the data flow that takes place during authentication.
Figure 2-8 Data flow – Authentication
Different types of authentication
DSS uses the following types of authentication.
●Windows
●LDAP
●Novell
Windows
Windows authentication uses Microsoft Active Directory, a database that contains information about objects, including users, that are contained within the domain. Active Directory provides an LDAP interface to the data in the directory database.
After a user provides valid credentials, the information is securely transmitted to the DSS server. DSS authenticates to the domain to validate the user credentials. If the user credentials are valid, DSS queries the LDAP directory for the authenticated user
LDAP
LDAP is a standard,
ENWW | Features | 25 |