This soft copy for use by IBM employees only.
To avoid having to configure the LES′s address at each endstation, LANE provides for a Lan Emulation Configuration Server (LECS), which LECs can query for their proper LES address. This enables backup LESs to be configured, since should the primary LES fail, the LECS merely has to direct connections to a backup LES without having to change any configuration in the workstation. Although the 8285 ATM Control Point does not contain an LECS, either or both of the internal LECs can be configured to use an external LECS, such as that provided by the IBM Multiprotocol Switched Services Server.
This section was intended only as an overview of LANE. For a more detailed description of these functions, please see IBM 8260 As a Campus ATM Switch,
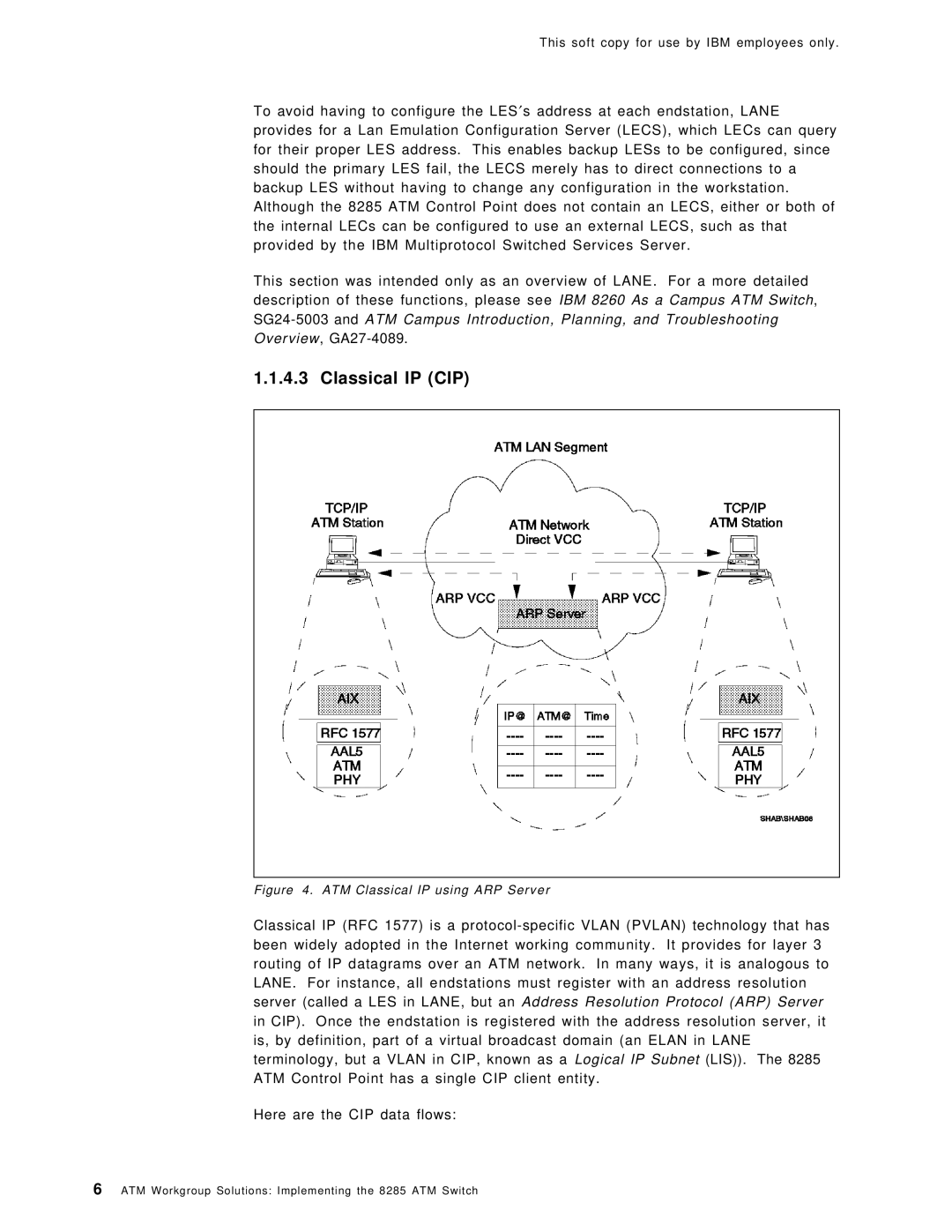
1.1.4.3 Classical IP (CIP)
Figure 4. ATM Classical IP using ARP Server
Classical IP (RFC 1577) is a
Here are the CIP data flows: