Communication monitoring
Enabling of communication channels
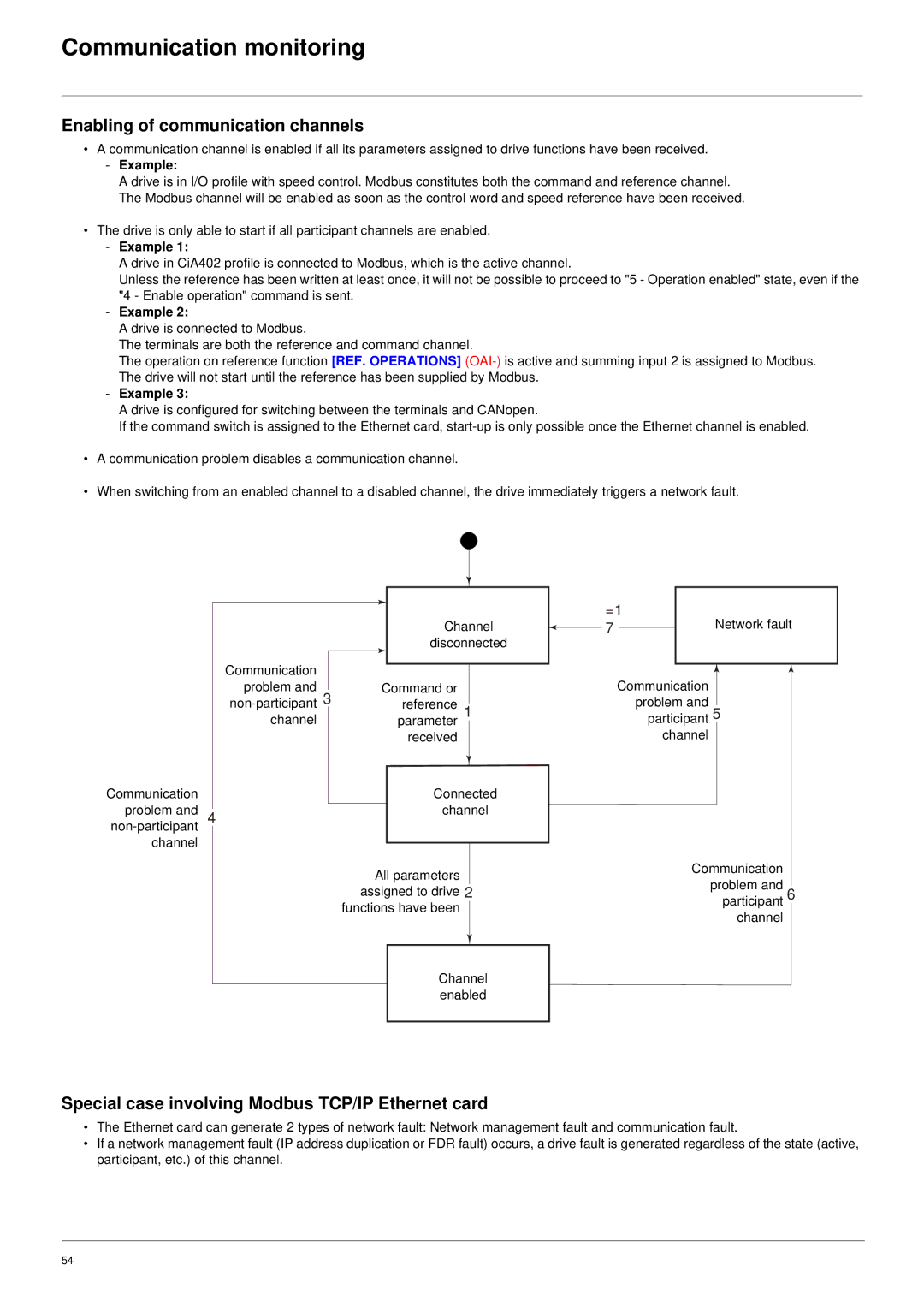
•A communication channel is enabled if all its parameters assigned to drive functions have been received.
-Example:
A drive is in I/O profile with speed control. Modbus constitutes both the command and reference channel. The Modbus channel will be enabled as soon as the control word and speed reference have been received.
•The drive is only able to start if all participant channels are enabled.
-Example 1:
A drive in CiA402 profile is connected to Modbus, which is the active channel.
Unless the reference has been written at least once, it will not be possible to proceed to "5 - Operation enabled" state, even if the "4 - Enable operation" command is sent.
-Example 2:
A drive is connected to Modbus.
The terminals are both the reference and command channel.
The operation on reference function [REF. OPERATIONS]
-Example 3:
A drive is configured for switching between the terminals and CANopen.
If the command switch is assigned to the Ethernet card,
•A communication problem disables a communication channel.
•When switching from an enabled channel to a disabled channel, the drive immediately triggers a network fault.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| =1 |
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Channel |
| Network fault | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
|
| |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| disconnected |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
| Communication |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Communication |
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
| problem and |
|
|
| Command or |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
| 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
|
|
|
|
| reference |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| problem and |
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
| 1 |
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||
|
|
| channel |
|
|
|
| parameter |
|
|
|
|
| participant | 5 |
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| received |
|
|
|
| channel |
|
|
|
| ||||||
Communication |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Connected |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
problem and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| channel |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
channel |
|
|
|
|
| All parameters |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Communication |
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| problem and |
|
| ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| assigned to drive | 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 6 |
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| participant |
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| functions have been |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| channel |
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Channel |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| enabled |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Special case involving Modbus TCP/IP Ethernet card
•The Ethernet card can generate 2 types of network fault: Network management fault and communication fault.
•If a network management fault (IP address duplication or FDR fault) occurs, a drive fault is generated regardless of the state (active, participant, etc.) of this channel.
54