Part Temp Range PIN-PACKAGE
DS33R11
Table of Contents
Integrated T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
Device Registers
Operating Parameters
List of Figures
308
List of Tables
Description
Page
Hdlc Ethernet Mapping
X.86 Link Access Protocol for SONET/SDH Ethernet Mapping
General
Microprocessor Interface
Sdram Interface
Committed Information Rate CIR Controller
MAC Interface
Clock Synthesizer
T1/E1/J1 Line Interface
Jitter Attenuator
TDM Bus
12 T1/E1/J1 Framer
Test and Diagnostics
T1-Related Telecommunications Specifications
Specifications Compliance
Ethernet-to-WAN Extension With or Without Framing
ESF
B8ZS
BOC
CRC
Major Operating Modes
JTAG2 Transmit Serial Port Packet HDLC/X.86 CIR Controller
Clad Ttip Transmit Framer MUX Tring
Bert
Rtip Rring MUX
Jtag Host Interface
Clock
Receive and Transmit T1/E1/J1 LIU
Loopback Sync Framer
Data
Rlclk
Sync Rsync Rmsync Rfsync Internal Rdata Signals Rchclk From
Sync Signaling Tseri Tsig
Rlink
Name PIN Type Function Microprocessor Port
Pin Functional Description Detailed Pin Descriptions
IOZ
Name PIN Type Function
Read Data Strobe Intel Mode The DS33R11 drives the data bus
Chip Select for Protocol Conversion Device This pin must be
Receive Data 0 through 3 MII Four bits of received data
Name PIN Type Function MII/RMII PHY Port
Receive Data 0 through 1 Rmii Two bits of received data
Reference Clock Output Rmii and MII a derived clock output
Reference Clock Rmii and MII When in Rmii mode, all signals
Transmit Data 0 through 3MII TXD 30 is presented
Transmit Data 0 through 1RMII Two bits of data TXD
Sdram Interface
Name PIN Type Function PHY Management BUS
Sdcs
Sdram Data Bus Bits 0 to 31 The 32 pins of the Sdram data
T1/E1/J1 Transmit Framer Interface
Name PIN Type Function T1/E1/J1 Analog Line Interface
T1/E1/J1 Receive Framer Interface
Ethernet Mapper Transmit Serial Interface
Receive Frame Sync Pre Receive Elastic Store for T1/E1/J1
Receive System Clock for the Transceiver 1.544MHz
Receive Multiframe Sync for the T1/E1/J1 Transceiver An
T1/E1/J1 FRAMER/LIU Interim Signals
Transmit Clock Output from the T1/E1/J1 Framer Buffered
Transmit Negative-Data Output Updated on the rising edge
Transmit Positive-Data Output Updated on the rising edge
Transmit Elastic Store Output Updated on the rising edge
Queue Overflow for Ethernet Mapper This pin goes high when
Name PIN Type Function Hardware and Status Pins
Mode Control for Processor Interface
T1/E1/J1 Receive Signaling-Freeze Output Set high when
Name PIN Type Function System Clocks
Name PIN Type Function Jtag Interface
Transmit Analog Signal Ground Connect to the common supply
Name PIN Type Function Power Supplies
Receive Analog Positive Supply Connect to 3.3V power supply
Receive Analog Signal Ground Connect to the common supply
Ball BGA Pinout
Functional Description
Interrupt and Pin Modes
Processor Interface
Read-Write/Data Strobe Modes
Clear on Read
Txclk
Ethernet Mapper Clocks
Clocking Options for the Ethernet Interface
Rmiimiis Speed DCE/ DTE Refclko Rxclk PIN Output Input
Ethernet MAC
T1/E1/J1
Bert Refclk Arbiter
Serial Interface Clock Modes
Ethernet Interface Clock Modes
Reset Functions
Resets and Low Power Modes
Reset Function Location Comments
Example Device Initialization Sequence
Initialization and Configuration
Global Resources
Per-Port Resources
Device Interrupts
Pin
Drawing Legend
Serial Interface
Interrupt Information Registers
Status Registers
Information Registers
Connections and Queues
Arbiter
Registers Related to Connections and Queues
Register Function
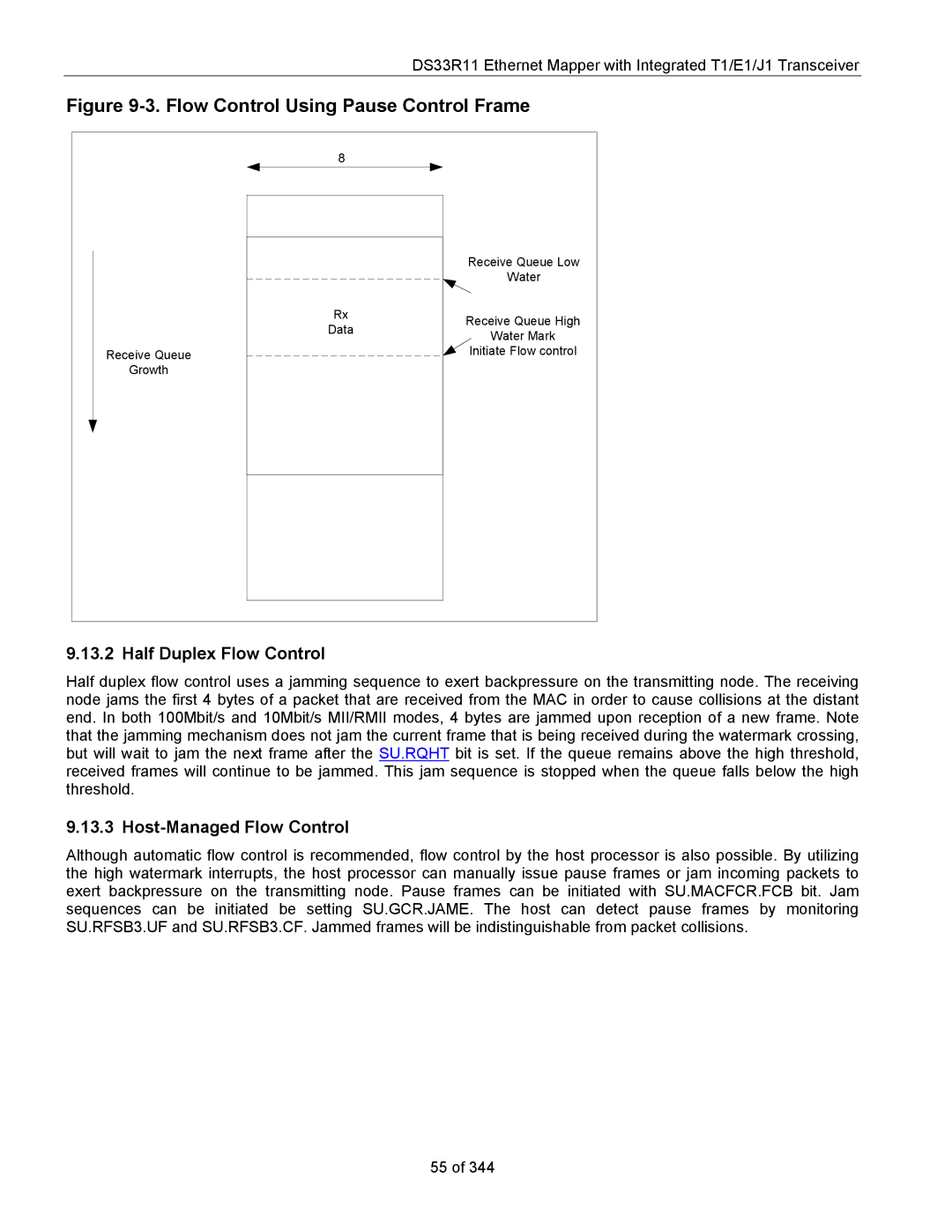
Flow Control
Type Mode
Options for Flow Control
Full Duplex Flow Control
Host-Managed Flow Control
Half Duplex Flow Control
Ieee 802.3 Ethernet Frame
Ethernet Interface Port
Register Name Function
Registers Related to Setting the Ethernet Port
DTE and DCE Mode
Configured as DTE Connected to an Ethernet PHY in MII Mode
Ethernet MAC
DS33R11 Configured as a DCE in MII Mode
MAC Status Registers
MAC Control Registers
Address Register Description
Rmii Mode
MII Mode Options
Bert in the Ethernet Mapper
Bert Features
PHY MII Management Block and Mdio Interface
Receive Pattern Detection
Receive Data Interface
Prbs Synchronization
Pattern Monitoring
Repetitive Pattern Synchronization
Pattern Generation
Performance Monitoring Update
Error Insertion
Transmit Packet Processor
Receive Packet Processor
11. Hdlc Encapsulation of MAC Frame
12. Laps Encoding of MAC Frames Concept
19 X.86 Encoding and Decoding
13. X.86 Encapsulation of the MAC frame
Page
Committed Information Rate Controller
T1/E1/J1 Clock Map
10.1 T1/E1/J1 Clocks
TCSS1 TCSS0 Transmit Clock Source
T1/E1/J1 Transmit Clock Source
Per-Channel Operation
10.3 T1/E1/J1 Transceiver Interrupts
10.4.1 T1 Transmit Transparency
10.4 T1 Framer/Formatter Control and Status
AIS-CI and RAI-CI Generation and Detection
Alarm SET Criteria Clear Criteria
T1 Alarm Criteria
10.4.3 T1 Receive-Side Digital-Milliwatt Code Generation
ITU Spec
10.5 E1 Framer/Formatter Control and Status
E1 Sync/Resync Criteria
Frame or Sync Criteria Resync Criteria Multiframe Level
Per-Channel Loopback
E1 Alarm Criteria
Automatic Alarm Generation
Alarm SET Criteria Clear Criteria ITU Specification
Line-Code Violation Counter TR.LCVCR
Error Counters
T1 Line Code Violation Counting Options
E1 Line-Code Violation Counting Options
Counted
Framing Mode
T1 Path Code Violation Counting Arrangements
Path Code Violation Count Register TR.PCVCR
Frames Out-of-Sync Count Register TR.FOSCR
T1 Frames Out-of-Sync Counting Arrangements
Bit Counter TR.EBCR
10.8 DS0 Monitoring Function
Processor-Based Receive Signaling
Signaling Operation
Change-of-State
Receive Signaling Freeze
Hardware-Based Receive Signaling
Receive Signaling Reinsertion at Rsero
Force Receive Signaling All Ones
10.9.3.1 T1 Mode
Processor-Based Transmit Signaling
Channel Phone
Hardware-Based Transmit Signaling
10.9.3.2 E1 Mode
Time Slot Numbering Schemes
Maps to Channel
Per-Channel Idle Code Generation
10. Idle-Code Array Address Mapping
Bits 0 to 5 of Iaar
Example
Idle-Code Programming Examples
Elastic Stores Operation
10.12.1.1 T1 Mode
10.12.1.2 E1 Mode
Channel Blocking Registers
Transmit Elastic Store
11. Elastic Store Delay After Initialization
Minimum Delay Mode
Initialization Register BIT Delay
CRC-4 Recalculate Method
10.13 G.706 Intermediate CRC-4 Updating E1 Mode Only
Transmit a BOC
10.14 T1 Bit-Oriented Code BOC Controller
Transmit BOC
Receive BOC
Method 1 Internal Register Scheme Based on Double-Frame
Additional Sa and International Si Bit Operation E1 Only
Method 2 Internal Register Scheme Based on CRC4 Multiframe
Additional Hdlc Controllers in T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
Hdlc Configuration
12. Hdlc Controller Registers
Hdlc Mapping
Fifo Control
Register Channels
Receive Packet-Bytes Available
Fifo Information
Receive Hdlc Code Example
Overview
Legacy FDL Support T1 Mode
Receive Section
Transmit Section
10.18 D4/SLC-96 Operation
Programmable In-Band Loop Code Generation and Detection
LIU Operation
Line Interface Unit LIU
Receiver
T1/E1
Receive Level Indicator and Threshold Interrupt
Receive G.703 Synchronization Signal E1 Mode
Monitor Mode
Transmit Short-Circuit Detector/Limiter
Transmit BPV Error Insertion
Transmit G.703 Synchronization Signal E1 Mode
Transmitter
CMI Code Mark Inversion Option
Mclk Prescaler
Clock Data CMI
DS33R11
13. Transformer Specifications
Specification Recommended Value
Recommended Circuits -7. Basic Interface
E1 Transmit Pulse Template
10. Jitter Tolerance
E1 Mode
T1 Mode
Bert Mapping
Bert Status
Xtald Mclk
15. Simplified Diagram of Bert in Network Direction
Bert Alternating Word-Count Rate
Bert Error Counter
Bert Repetitive Pattern Set
Bert Bit Counter
Number-of-Errors Registers
Payload Error-Insertion Function T1 Mode Only
14. Transmit Error-Insertion Setup Sequence
15. Error Insertion Examples
Fractional T1/E1 Support
Programmable Backplane Clock Synthesizer
T1 Transmit
114
E1 Transmit
116
E1 Transmit Flow Diagram
Port Select Registers Interface Transceiver
Register Address Map
Mapper Chip Global Arbiter Bert Serial Ethernet
Interfac
Name
Register Bit Maps
Global Ethernet Mapper Register Bit Map
Global Ethernet Mapper Register Bit Map
Bert Register Bit Map
Arbiter Register Bit Map
Bert Register Bit Map
Arbiter Register Bit Map
Serial Interface Register Bit Map
Serial Interface Register Bit Map
114h
Ethernet Interface Register Bit Map
Ethernet Interface Register Bit Map
MAC Register Bit Map
MAC Indirect Register Bit Map
200h
019
T1/E1/J1 Transceiver Register Bit Map Active when CST =
01A
035
050
06A
085
0AD
0AA
0AB
0AC
0CD
0CA
0CB
0CC
0DF
0DC
0DD
0DE
GL.IDRL
Global Register Definitions for Ethernet Mapper
GL.IDRH
GL.BLR
GL.CR1
GL.SRCALS
GL.RTCAL
GL.LIE
GL.SIE
GL.LIS
GL.SIS
GL.TRQIS
GL.TRQIE
GL.BIE
GL.CON1
GL.BIS
GL.BISTEN
GL.C1QPR
GL.SDMODE1
GL.BISTPF
GL.SDMODEWS
GL.SDMODE2
GL.SDRFTC
AR.TQSC1
Arbiter Registers
Arbiter Register Bit Descriptions
AR.RQSC1
80h
Bert Registers
BCR
Bert Control Register
Bpchr
Bpclr
BSPB3R
BSPB0R
BSPB1R
BSPB2R
BSR
Teicr
Bsrie
Bsrl
RBCB0
RBECB0R
RBECB1R
RBECR2
RBCB2
RBCB1
RBCB3
LI.RSTPD
Serial Interface Registers
Serial Interface Transmit and Common Registers
LI.TSLCR
LI.TPPCL
LI.LPBK
LI.TEPLC
LI.TIFGC
0C7h
Transmit Errored Packet High Control Register
Cleanup routine
LI.TEPHC
LI.TPPSRL
LI.TPPSR
LI.TPPSRIE
LI.TPCR1
LI.TPCR0
LI.TPCR2
LI.TBCR3
LI.TBCR0
LI.TBCR1
LI.TBCR2
LI.THPMUS
LI.THPMUU
LI.TRX8C
11.5.2 X.86 Registers
LI.TX86EDE
LI.TRX86A
LI.CIR
LI.TRX86SAPIL
LI.RSLCR
Receive Serial Interface
LI.RPPCL
LI.RMPSCH
LI.RMPSCL
LI.RPPSR
Repl Rapl Ripdl Rspdl Rlpdl Repcl Rapcl Rspcl
LI.RPPSRL
Receive Packet Processor Status Register Latched
105h
Repie Rapie Ripdie Rspdie Rlpdie Repcie Rapcie Rspcie
Receive Packet Processor Status Register Interrupt Enable
LI.RPPSRIE
106h
LI.RPCB1
LI.RPCB0
LI.RPCB2
LI.RFPCB1
LI.RFPCB0
LI.RFPCB2
LI.RAPCB1
LI.RAPCB0
LI.RAPCB2
LI.RSPCB1
LI.RSPCB0
LI.RSPCB2
LI.RBC3
LI.RBC0
LI.RBC1
LI.RBC2
LI.RAC3
LI.RAC0
LI.RAC1
LI.RAC2
LI.RHPMUS
LI.RHPMUU
LI.RX86S
LI.TQLT
LI.RX86LSIE
LI.TQHT
127h
LI.TQTIE
126h
LI.TQCTLS
SU.MACRADH
Ethernet Interface Registers
Ethernet Interface Register Bit Descriptions
SU.MACRADL
SU.MACWD0
SU.MACRD1
SU.MACRD2
SU.MACRD3
SU.MACAWL
SU.MACWD1
SU.MACWD2
SU.MACWD3
SU.MACRWC
SU.MACAWH
SU.GCR
SU.LPBK
Ncfq Tprhbc Tprcb
SU.TFRC
Transmit Frame Resend Control
151h
SU.TFSH
SU.TFSL
SU.RFSB1
SU.RFSB0
SU.RFSB2
157h
SU.RFSB3
MCF
SU.RQHT
SU.RMFSRL
SU.RMFSRH
SU.RQLT
SU.QCRLS
SU.QRIE
Ucfr Cfrr Lerr Crcerr DBR Miier BFR
SU.RFRC
Receive Frame Rejection Control
15Eh
SU.MACCR
MAC Registers
Bit Random Number Generator Bits Used
SU.MACMIIA
SU.MACMIID
SU.MACFCR
SU.MMCCTRL
010Dh
Reserved
MAC Reserved Control Register
010Ch indirect
0113h
0110h indirect
0111h
0112h
0201h
SU.RxFrmCtr
MAC All Frames Received Counter
0200h indirect
0205h
SU.RxFrmOkCtr
MAC Frames Received OK Counter
0204h indirect
0301h
SU.TxFrmCtr
MAC All Frames Transmitted Counter
0300h indirect
0309h
SU.TxBytesCtr
MAC All Bytes Transmitted Counter
0308h indirect
030Dh
SU.TxBytesOkCtr
MAC Bytes Transmitted OK Counter
030Ch indirect
0335h
SU.TxFrmUndr
MAC Transmit Frame Under Run Counter
0334h indirect
0339h
SU.TxBdFrmCtr
MAC All Frames Aborted Counter
0338h indirect
TR.MSTRREG
Master Mode Register
Effect On Output Pins
11.7 T1/E1/J1 Transceiver Registers
Bit 1 Tsync I/O Select Tsio 0 = Tsync is an input
Configuration Register
Bit 6 Rsync Mode Select 2 RSMS2
TR.IOCR1
TR.IOCR2
OOF2 OOF1
TR.T1RCR1
TR.T1RCR2
Bit 6 Receive Frame Mode Select RFM 0 = D4 framing mode
Bit 5 Receive B8ZS Enable RB8ZS
Bit 1 Receive Japanese CRC6 Enable RJC
TR.T1TCR1
TR.T1TCR2
Bit 7 Transmit B8ZS Enable TB8ZS
TB8ZS TSLC96 Tzse FBCT2 FBCT1 TD4YM TB7ZS
T1 Common Control Register
Bit 2 Transmit Frame Mode Select TFM 0 = D4 framing mode
TR.SSIE1 T1 Mode
TR.T1CCR1
Software Signaling Insertion Enable
TR.SSIE1 E1 Mode
TR.SSIE2 E1 Mode
Lcaw
TR.SSIE3 E1 Mode
TR.SSIE4
TR.T1RDMR2
TR.T1RDMR1
TR.T1RDMR3
TR.INFO1
TR.IDR
RL3 RL2 RL1 RL0
TR.INFO2
11h
Bits 0 3 Receive Level Bits RL0 to RL3. Real-time bits
TR.IIR1
TR.INFO3
TR.IIR2
16h
Ilut Timer Rscos Jalt Lrcl Tcle Tocd Lolitc
TR.SR1
Status Register
Bit 7 Input Level Under Threshold Ilut 0 = interrupt masked
TR.IMR1
Interrupt Mask Register
17h
18h
TR.SR2
Ryelc RUA1C Frclc Rlosc
19h
TR.IMR2
Bit 0 Receive Loss-of-Sync Condition Rlos
1Ah
TR.SR3
Lspare LDN LUP Lotc Lorc V52LNK Rdma RRA
TR.IMR3
Bit 2 Receive Multiframe Event RMF
TR.SR4
1Ch
RAIS-CI Rsao Rsaz TMF TAF RMF Rcmf RAF
Bit 3 Transmit Align Frame Event TAF 0 = interrupt masked
TR.IMR4
1Dh
Bit 7 Receive AIS-CI Event RAIS-CI
1Eh
TR.SR5
Tesf Tesem Tslip Resf Resem Rslip
1Fh
TR.IMR5
20h, 22h
TR.SR6, TR.SR7
Hdlc #1 Status Register
Hdlc #2 Status Register
TR.IMR6, TR.IMR7
PS2 PS1 PS0
TR.INFO5, TR.INFO6
TR.INFO4
TR.IMR8
TR.SR8
26h
TR.SR9
Bbed Bbco BEC0 BRA1 BRA0 Brlos Bsync
TR.IMR9
Rsaoics Rsrcs Rfcs Brcs Thscs Peics Tfcs Btcs
TR.PCPR
Per-Channel Pointer Register
28h
TR.PCDR4
TR.PCDR1
TR.PCDR2
TR.PCDR3
Hdlc #2 Receive Control 31h, 32h
TR.INFO7
TR.H1RC, TR.H2RC
Hdlc #1 Receive Control
TR.E1RCR2
TR.E1RCR1
TR.E1TCR1
TR.BOCC
TR.E1TCR2
RBF1 RBF0
MSB LSB
TR.RSINFO1, TR.RSINFO2, TR.RSINFO3, TR.RSINFO4
TR.RSCSE1, TR.RSCSE2, TR.RSCSE3, TR.RSCSE4
TR.SIGCR
Signaling Control Register
Grsre RFE RFF Rccs Tccs Frsao
Bit 2 Pcvcr Fs-Bit Error-Report Enable Fsbe
Error-Counter Configuration Register
Bit 5 Error-Counter Update Select Ecus
Bit 4 Error-Accumulation Mode Select Eams
TR.PCVCR2
TR.LCVCR1
TR.LCVCR2
TR.PCVCR1
TR.EBCR2
TR.FOSCR1
TR.FOSCR2
TR.EBCR1
Liuc LLB RLB PLB FLB
TR.LBCR
Loopback Control Register
4Ah
TR.PCLR4
TR.PCLR1
TR.PCLR2
TR.PCLR3
Tesalgn Tesr Tesmdm Tese Resalgn Resr Resmdm Rese
TR.ESCR
Elastic Store Control Register
4Fh
TR.TS1 to TR.TS16
Transmit Signaling Registers E1 Mode, CAS Format
50h to 5Fh
Transmit Signaling Registers E1 Mode, CCS Format
TR.TS1 to TR.TS12
Transmit Signaling Registers T1 Mode, ESF Format
50h to 5Bh
CH4-A CH4-B
Transmit Signaling Registers T1 Mode, D4 Format
CH2-A CH2-B
CH1-A CH1-B
60h to 6Bh
Receive Signaling Registers T1 Mode, ESF Format
Receive Signaling Registers T1 Mode, D4 Format
TR.RS1 to TR.RS12
60h to 6Fh
Receive Signaling Registers E1 Mode, CAS Format
Receive Signaling Registers E1 Mode, CCS Format
TR.RS1 to TR.RS16
TCSS1 TCSS0
TR.CCR1
BPCS1 BPCS0
TR.CCR2
TR.CCR3
RLT3 RLT2 RLT1 RLT0
TR.CCR4
TR.TDS0SEL
TR.RDS0SEL
TR.TDS0M
TR.RDS0M
TR.LIC1
T1, Impedance Match Off
Bit 6 Automatic Gain Control Enable Agce
Network Mode GC5 GC4 GC3 GC2 GC1 GC0
TR.TLBC
Bit 7 E1/T1 Select ETS
TR.LIC2
79h
ETS Lirst Ibpv TUA1 Jamux Scld Clds
MM1 MM0
TR.LIC3
TT1 TT0
TR.LIC4
MPS1 MPS0 Jamux
Mclk MPS1 MPS0 Jamux
TR.TCICE1
TR.IAAR
Gric Gtic Function
TR.PCICR
TR.RCICE1
TR.TCICE2
TR.TCICE3
TR.TCICE4
TR.RCBR1
TR.RCICE2
TR.RCICE3
TR.RCICE4
TR.RCBR3
TR.RCBR2
TR.RCBR4
TR.TCBR4
TR.TCBR1
TR.TCBR2
TR.TCBR3
90h, A0h
TR.H1TC, TR.H2TC
Hdlc #1 Transmit Control
Hdlc #2 Transmit Control
TFLWM2 TFLWM1 TFLWM0
TR.H1FC, TR.H2FC
RFHWM2 RFHWM1 RFHWM0
Bit 2 Receive Hdlc Channel Select Bit
Register Name TR.H1RCS1, TR.H1RCS2, TR.H1RCS3, TR.H1RCS4
A2h, A3h, A4h, A5h
Bit 3 Receive Hdlc Channel Select Bit
RCB8SE RCB7SE RCB6SE RCB5SE RCB4SE RCB3SE RCB2SE RCB1SE
TR.H1RTSBS, TR.H2RTSBS
Hdlc # 1 Receive Time Slot Bits/Sa Bits Select
Hdlc # 2 Receive Time Slot Bits/Sa Bits Select 96h, A6h
Bit 2 Transmit Hdlc Channel Select Bit
Register Name TR.H1TCS1, TR.H1TCS2, TR.H1TCS3, TR.H1TCS4
A7h, A8h, A9h, AAh
Bit 3 Transmit Hdlc Channel Select Bit
TR.H1RPBA, TR.H2RPBA
TR.H1TTSBS, TR.H2TTSBS
TR.H1RF, TR.H2RF
TR.H1TF, TR.H2TF
RUP2 RUP1 RUP0
TR.H1TFBA, TR.H2TFBA
TR.IBCC
TC1 TC0
B8h
TR.TCD1
TR.TCD2
Transmit Code Definition Register
Receive Up-Code Definition Register
TR.RUPCD2
BAh
TR.RDNCD2
TR.RDNCD1
Receive Down-Code Definition Register
BBh
RSC2 RSC1 RSC0
TR.RSCC
In-Band Receive Spare Control Register
BDh
TR.RSCD2
TR.RSCD1
RBOC5 RBOC4 RBOC3 RBOC2 RBOC1 RBOC0
TR.RFDL TR.BOCC.4 =
Receive FDL Register
C0h
TR.RFDLM1, TR.RFDLM2
TR.TFDL
TR.RNAF
TR.RAF
Receive Align Frame Register
C6h
TR.RSiNAF
TR.RSiAF
Received Si Bits of the Align Frame
C8h
TR.RRA
TR.RSa6
TR.RSa5
Received Sa5 Bits
CCh
TR.RSa8
TR.RSa7
Received Sa7 Bits
CEh
TR.TNAF
TR.TAF
TR.TSiNAF
TR.TSiAF
Transmit Si Bits of the Align Frame
D2h
TR.TRA
TR.TSa6
TR.TSa5
Transmitted Sa5 Bits
D6h
TR.TSa8
TR.TSa7
Transmit Sa7 Bits
D8h
TR.BAWC
TR.TSACR
TR.BRP4
TR.BRP1
TR.BRP2
TR.BRP3
PS1 PS0
TR.BC1
EIB2 EIB1 EIB0
TR.BC2
RPL3 RPL2 RPL1 RPL0
TR.BBC4
TR.BBC1
TR.BBC2
TR.BBC3
EC9 EC8
TR.BEC1
EC7 EC6 EC5 EC4 EC3 EC2 EC1 EC0
TR.BEC2
TR.BIC
ER3 ER2 ER1 ER0
TR.ERC
TR.NOE2
Number-of-Errors
TR.NOE1
ECh
TR.NOEL2
TR.NOEL1
Tx Serial Interface Functional Timing
Functional Serial I/O Timing
MII and Rmii Interfaces
Transmit Byte Sync Functional Timing
MII Transmit Half Duplex with a Collision Functional Timing
FRAME# RSYNC1 Rfsync RSYNC2 Rsync
FRAME# Rfsync RSYNC1 Rsync 2 RSYNC3
Rchclk RCHBLK1
Rsync Rfsync
Rchclk Rchblk
Rchclk RCHBLK4
Rsysclk Rser O
Tchclk Tchblk
FRAME# TSYNC1 Tssync Tsync TSYNC3
Tchclk Tchblk 2,3
FRAME# Rfsync Rsync
12.4 E1 Mode
Rchclk RCHBLK3
Rsysclk Rsero
RSYNC2 Rmsync RSYNC3 Rchclk Rchblk
Rmsync Rsync
FRAME# TSYNC1 Tssync
Rsync Tsync Rchclk Tchclk Rchblk Tchblk
TSYNC2
Tssync Tchclk Tchblk
26. Transmit-Side Boundary Timing Elastic Store Disabled
312
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN TYP MAX Units
DC Electrical Characteristics
Recommended DC Operating Conditions
AIR Flow THETA-JA
Thermal Characteristics -3. Thermal Characteristics
Theta-JA vs. Airflow
Parameter MIN TYP MAX
MIN TYP MAX
Parameter Symbol
MII Interface Transmit MII Interface
10Mbps 100Mbps
Receive MII Interface Timing
Receive MII Interface
Transmit Rmii Interface Timing
Rmii Interface Transmit Rmii Interface
Receive Rmii Interface Timing
Receive Rmii Interface
Mdio Interface
Parameter Symbol MIN TYP MAX Units
MDC Mdio
Tclke Tsero Tden Tbsync
Transmit WAN Interface 10. Transmit WAN Interface
Rclki Rseri Rden Rbsync
Receive WAN Interface 11. Receive WAN Interface
100 MHz
Sdram Timing 12. Sdram Interface Timing
SDA, SBA
Sdata
RAS, Scas
SWE, Sdcs
Parameter Symbol MIN TYP MAX Units
Intel Bus Read Timing Modec =
11. Motorola Bus Read Timing Modec =
RMSYNC, Rsync
RCHBLK, Rfsync
Rfsync / Rmsync
Rsero / Rdata / Rsig
See Note
Rsero / Rsig
Rchblk Rmsync Rsync
15. Receive Line Interface Timing
Delay Rclko to Bpclk
16. Receive Timing Delay Rclko to Bpclk
TSERI, TSIG, TDATA, TPOSI, Tnegi
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN TYP E1 MAX Units
17. Transmit-Side Timing
18. Transmit-Side Timing, Elastic Store Enabled
Jtag Interface Timing 17. Jtag Interface Timing
20. Jtag Interface Timing Diagram
Jtag Information
Jtag TAP Controller State Machine Description
Capture-IR
Update-DR
Update-IR
Select-IR-Scan
Instruction Register
TAP Controller State Diagram
Instruction Selected Register Instruction Codes
Instruction Codes for Ieee 1149.1 Architecture
Bypass Register
Jtag ID Codes ID Code Structure
Test Registers
Boundary Scan Register
Bypass Idcode State
Jtag Functional Timing
15.1 256-Ball BGA 27mm x 27mm 56-G6004-001
Package Information
Revision Description
Document Revision History