Process control
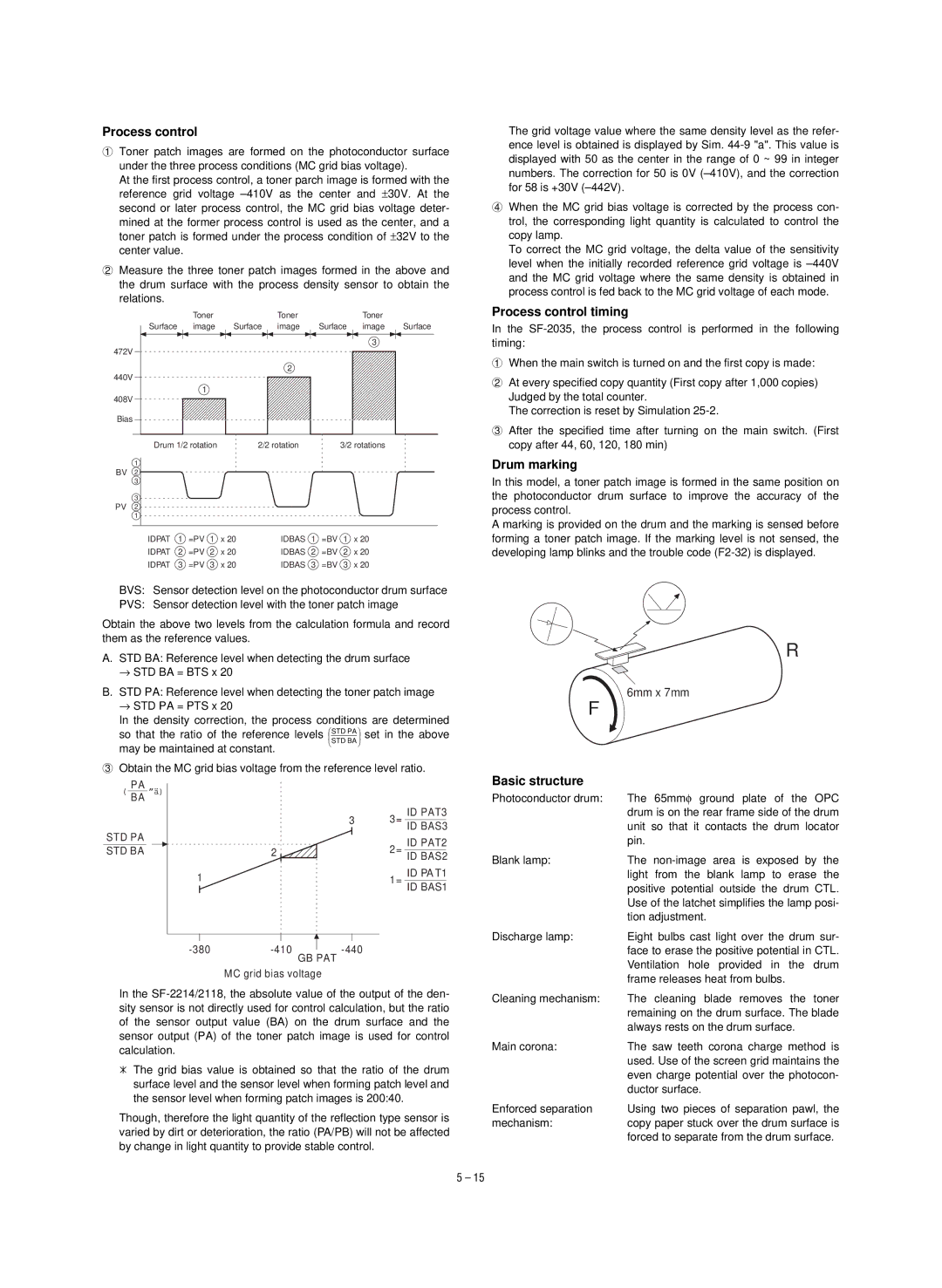
1Toner patch images are formed on the photoconductor surface under the three process conditions (MC grid bias voltage).
At the first process control, a toner parch image is formed with the reference grid voltage
second or later process control, the MC grid bias voltage deter-
mined at the former process control is used as the center, and a toner patch is formed under the process condition of ±32V to the center value.
2Measure the three toner patch images formed in the above and the drum surface with the process density sensor to obtain the relations.
|
|
| Toner |
| Toner |
|
|
| Toner |
| |
| Surface |
| image | Surface | image |
| Surface | image | Surface | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
|
472V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
440V |
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
408V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bias |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Drum 1/2 rotation | 2/2 rotation |
|
| 3/2 rotations |
| |||||
| 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BV | 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PV | 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| IDPAT | 1 | =PV | 1 | x 20 | IDBAS | 1 | =BV | 1 | x 20 |
|
| IDPAT | 2 | =PV | 2 | x 20 | IDBAS | 2 | =BV | 2 | x 20 |
|
| IDPAT | 3 | =PV | 3 | x 20 | IDBAS | 3 | =BV | 3 | x 20 |
|
BVS: Sensor detection level on the photoconductor drum surface
PVS: Sensor detection level with the toner patch image
Obtain the above two levels from the calculation formula and record them as the reference values.
A.STD BA: Reference level when detecting the drum surface
→STD BA = BTS x 20
B.STD PA: Reference level when detecting the toner patch image
→STD PA = PTS x 20
In the density correction, the process conditions are determined
so that the ratio of the reference levels ⎛⎜STD PA⎞⎟ set in the above
⎝STD BA⎠
may be maintained at constant.
3Obtain the MC grid bias voltage from the reference level ratio.
PA |
|
|
|
|
|
( BA | ӊ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3 | 3= | ID PAT3 |
STD PA |
|
| ID BAS3 | ||
|
|
| 2= | ID PAT2 | |
STD BA |
| 2 |
| ||
|
|
|
|
| ID BAS2 |
| 1 |
|
|
| ID PA T1 |
|
|
| 1= ID BAS1 | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
| |||
|
| GB PAT |
|
|
|
|
| MC grid bias voltage |
|
|
|
In the
*The grid bias value is obtained so that the ratio of the drum surface level and the sensor level when forming patch level and the sensor level when forming patch images is 200:40.
Though, therefore the light quantity of the reflection type sensor is varied by dirt or deterioration, the ratio (PA/PB) will not be affected by change in light quantity to provide stable control.
The grid voltage value where the same density level as the refer- ence level is obtained is displayed by Sim.
4When the MC grid bias voltage is corrected by the process con- trol, the corresponding light quantity is calculated to control the copy lamp.
To correct the MC grid voltage, the delta value of the sensitivity level when the initially recorded reference grid voltage is
Process control timing
In the
1When the main switch is turned on and the first copy is made:
2At every specified copy quantity (First copy after 1,000 copies) Judged by the total counter.
The correction is reset by Simulation
3After the specified time after turning on the main switch. (First copy after 44, 60, 120, 180 min)
Drum marking
In this model, a toner patch image is formed in the same position on the photoconductor drum surface to improve the accuracy of the process control.
A marking is provided on the drum and the marking is sensed before forming a toner patch image. If the marking level is not sensed, the developing lamp blinks and the trouble code
R
6mm x 7mm
F
Basic structure
Photoconductor drum: | The 65mmφ ground plate of the OPC |
| drum is on the rear frame side of the drum |
| unit so that it contacts the drum locator |
| pin. |
Blank lamp: | The |
| light from the blank lamp to erase the |
| positive potential outside the drum CTL. |
| Use of the latchet simplifies the lamp posi- |
| tion adjustment. |
Discharge lamp: | Eight bulbs cast light over the drum sur- |
| face to erase the positive potential in CTL. |
| Ventilation hole provided in the drum |
| frame releases heat from bulbs. |
Cleaning mechanism: | The cleaning blade removes the toner |
| remaining on the drum surface. The blade |
| always rests on the drum surface. |
Main corona: | The saw teeth corona charge method is |
| used. Use of the screen grid maintains the |
| even charge potential over the photocon- |
| ductor surface. |
Enforced separation | Using two pieces of separation pawl, the |
mechanism: | copy paper stuck over the drum surface is |
| forced to separate from the drum surface. |
5 – 15