Configuring routing | Network configuration |
|
|
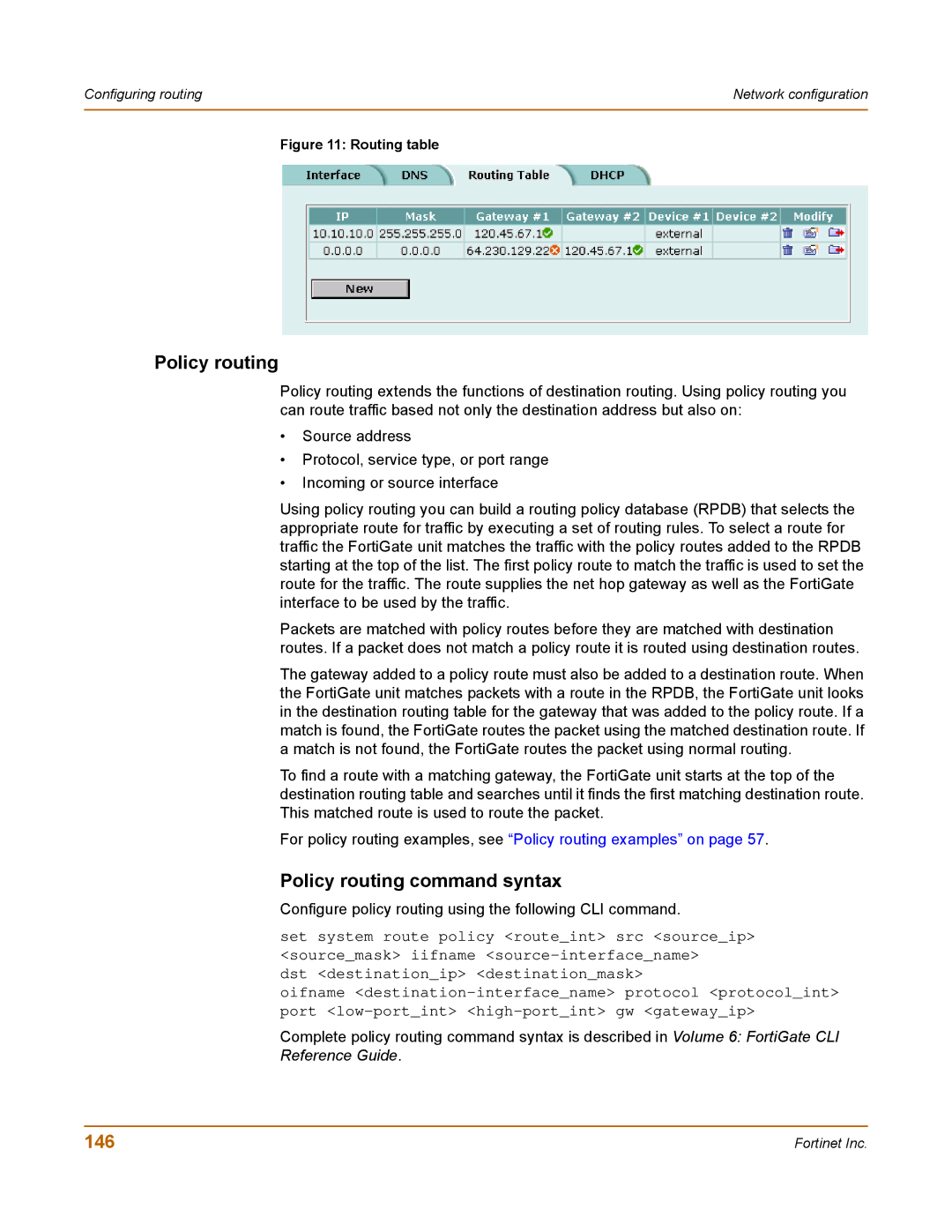
Figure 11: Routing table
Policy routing
Policy routing extends the functions of destination routing. Using policy routing you can route traffic based not only the destination address but also on:
•Source address
•Protocol, service type, or port range
•Incoming or source interface
Using policy routing you can build a routing policy database (RPDB) that selects the appropriate route for traffic by executing a set of routing rules. To select a route for traffic the FortiGate unit matches the traffic with the policy routes added to the RPDB starting at the top of the list. The first policy route to match the traffic is used to set the route for the traffic. The route supplies the net hop gateway as well as the FortiGate interface to be used by the traffic.
Packets are matched with policy routes before they are matched with destination routes. If a packet does not match a policy route it is routed using destination routes.
The gateway added to a policy route must also be added to a destination route. When the FortiGate unit matches packets with a route in the RPDB, the FortiGate unit looks in the destination routing table for the gateway that was added to the policy route. If a match is found, the FortiGate routes the packet using the matched destination route. If a match is not found, the FortiGate routes the packet using normal routing.
To find a route with a matching gateway, the FortiGate unit starts at the top of the destination routing table and searches until it finds the first matching destination route. This matched route is used to route the packet.
For policy routing examples, see “Policy routing examples” on page 57.
Policy routing command syntax
Configure policy routing using the following CLI command.
set system route policy <route_int> src <source_ip> <source_mask> iifname
dst <destination_ip> <destination_mask>
oifname
Complete policy routing command syntax is described in Volume 6: FortiGate CLI
Reference Guide.
146 | Fortinet Inc. |