G |
Subnets
Subnet addressing is an extension of the IP address scheme that allows a site to use a single netid for multiple physical networks. Routing outside of the site continues as usual by dividing the IP address into a netid and a hostid via the class. Inside a site the subnet mask is used to
Consider taking Network 2 (a Class B network) in the previous example and adding another physical network. Selecting the following subnet mask would add two additional netid bits allowing for four physical networks:
11111111 11111111 11000000 00000000 = 255.255.192.0
In effect, two bits of the Class B hostid have been used to extend the netid.
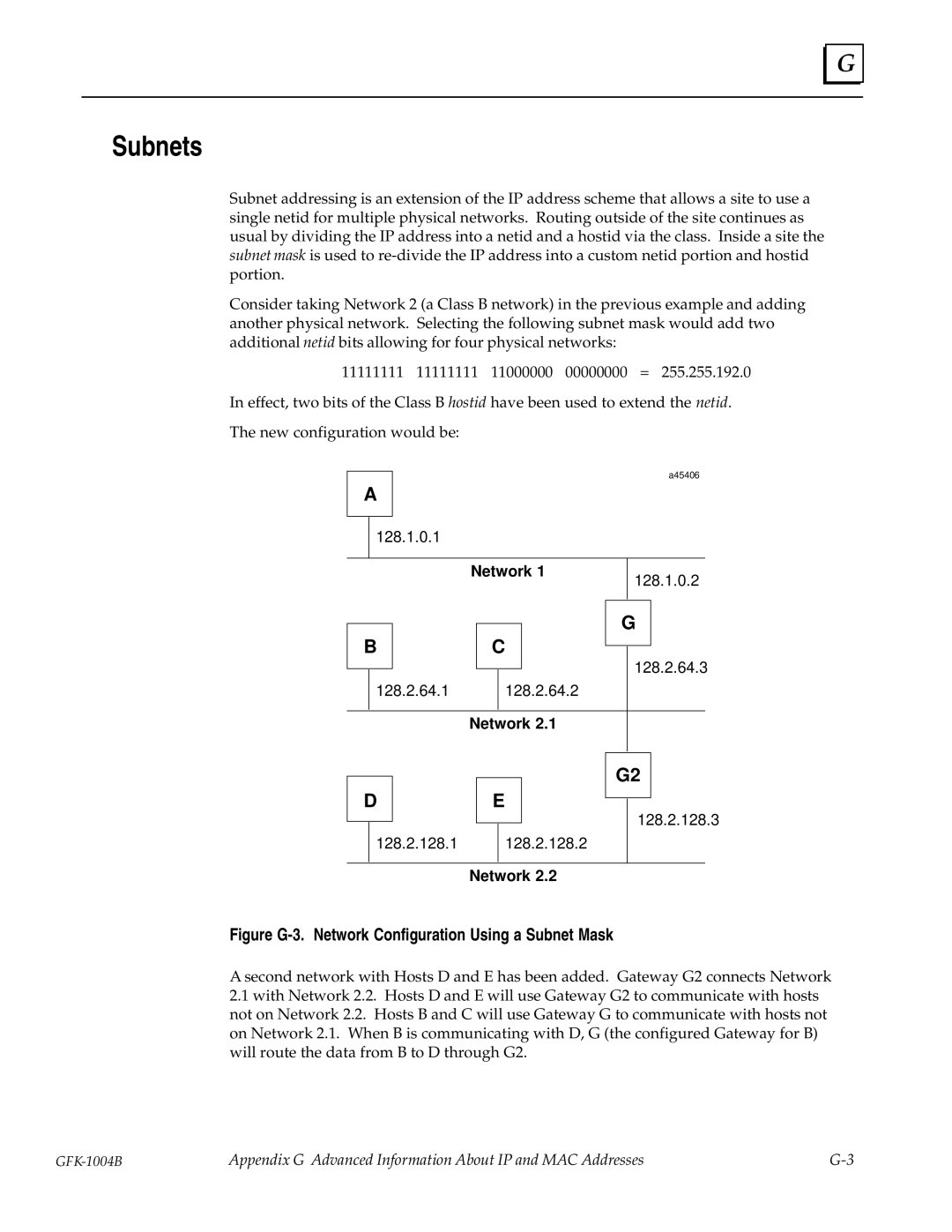
The new configuration would be:
A
128.1.0.1
Network 1
a45406
128.1.0.2
G
B | C |
128.2.64.3
128.2.64.1128.2.64.2
|
|
| Network 2.1 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| G2 |
| ||
D |
|
| E | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
| 128.2.128.3 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| 128.2.128.1 |
|
| 128.2.128.2 |
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Network 2.2 | |||||||
Figure G-3. Network Configuration Using a Subnet Mask
A second network with Hosts D and E has been added. Gateway G2 connects Network
2.1with Network 2.2. Hosts D and E will use Gateway G2 to communicate with hosts not on Network 2.2. Hosts B and C will use Gateway G to communicate with hosts not on Network 2.1. When B is communicating with D, G (the configured Gateway for B) will route the data from B to D through G2.
Appendix G Advanced Information About IP and MAC Addresses |