Professional Access Point
Administrator Guide
Interference can occur when multiple access points within range of each other are broadcasting on the same or overlapping channels. The impact of this interference on network performance can intensify during busy times when large amounts of data and media traffic compete for bandwidth.
Channel management uses a predetermined set of channels that minimizes interference. For the b/g radio band, the classic set of
Example: A Network before and after Channel Management
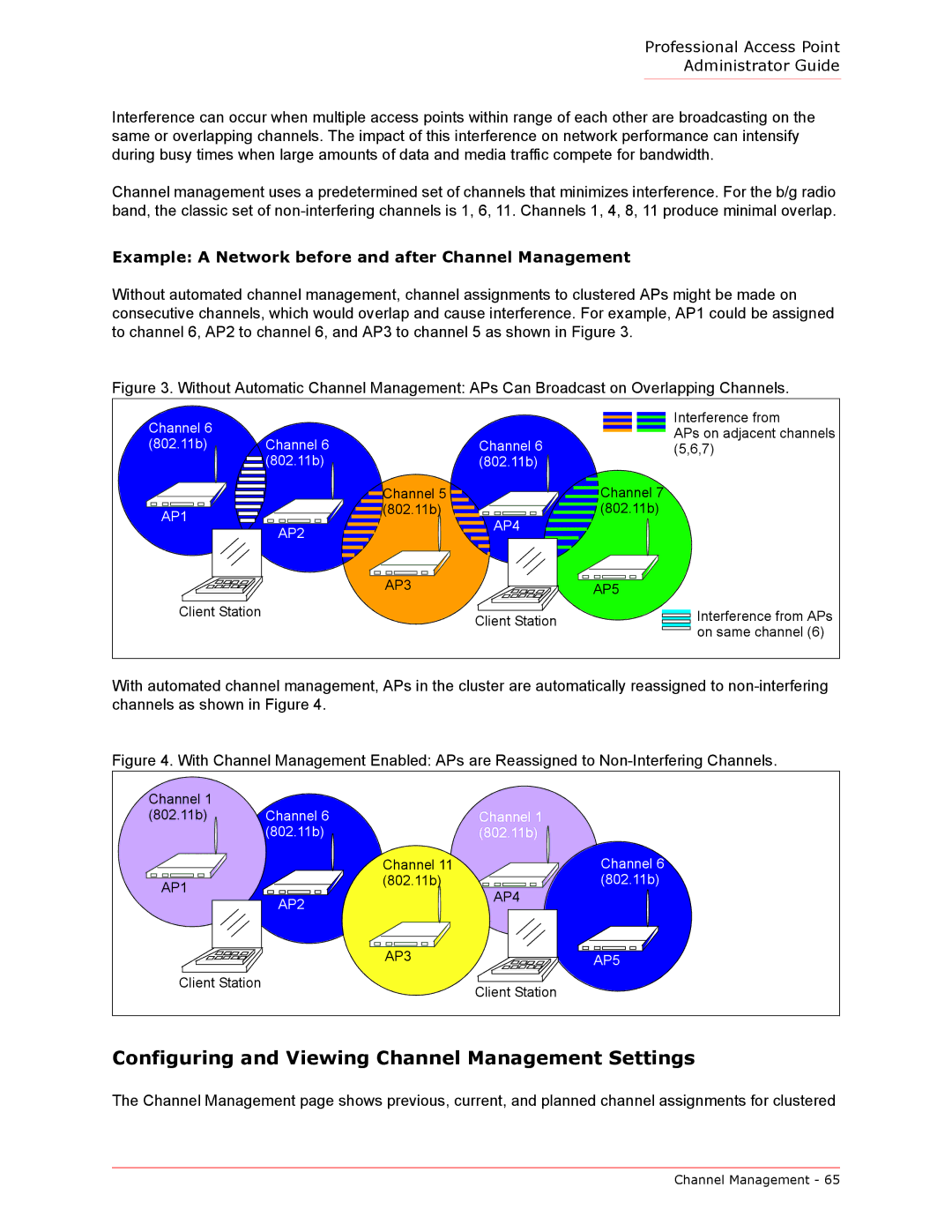
Without automated channel management, channel assignments to clustered APs might be made on consecutive channels, which would overlap and cause interference. For example, AP1 could be assigned to channel 6, AP2 to channel 6, and AP3 to channel 5 as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Without Automatic Channel Management: APs Can Broadcast on Overlapping Channels.
Channel 6
(802.11b) Channel 6
![]() (802.11b)
(802.11b)
AP1 |
AP2 |
Channel 6 (802.11b)
Channel 5 |
(802.11b) |
AP4 |
![]()
![]() Channel 7
Channel 7 ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() (802.11b)
(802.11b)
Interference from
APs on adjacent channels (5,6,7)
Client Station
AP3 | AP5 |
Client Station | Interference from APs | |
on same channel (6) | ||
|
With automated channel management, APs in the cluster are automatically reassigned to
Figure 4. With Channel Management Enabled: APs are Reassigned to Non-Interfering Channels.
Channel 1
(802.11b) Channel 6
(802.11b)
AP1 |
AP2 |
Client Station
Channel 11 ![]() (802.11b)
(802.11b)
AP3 |
Channel 1 (802.11b) ![]()
AP4 |
Client Station
Channel 6 (802.11b)
AP5 |
Configuring and Viewing Channel Management Settings
The Channel Management page shows previous, current, and planned channel assignments for clustered
Channel Management - 65