Page
„ Who should use this manual
Using This Manual „ Contents of this manual
„ Important precautions
Please Read Prior to Installation for Safety
Wiring
Installation
Maintenance and Inspection
Main Circuit Wiring
Main Circuit Terminal Wiring
Table of Contents
Display and Operation
Trial Run and Tuning Procedure
Control Modes of Operation
Maintenance and Inspection
Specifications 11-1
About this Manual… User Information
Technical Support and Service
This page intentionally left blank
„ Ensure that the product is what you have ordered
Unpacking Check
„ Ensure that the servo motor shaft rotates freely
„ Check for damage
Delta AC Servo Drive and Motor
Ecma Series Servo Motor
Model Explanation Nameplate Information
ASDA-B Series Servo Drive
Model Name Explanation
Unpacking Check and Model ExplanationASDA-B Series
Servo Drive and Servo Motor Combinations
Servo Drive Features
Control Modes of Servo Drive
Storage Conditions
Installation Notes
Operating Temperature
Installation Conditions
Installation Procedure
Installation Procedure and Minimum Clearances
Drive Mounting
Motor Mounting
„ Minimum Clearances
„ Side by Side Installation
Connections Connecting to Peripheral Devices
Connections and Wiring
CN1
Servo Drive Connectors and Terminals
CN2
CN3
Wiring Notes
Single-Phase Power Supply Connection
Wiring Methods
Housing Jowle C4201H00-2*3PA
Motor Power Cable Connector Specifications
Housing Jowle C4201H00-2*2PA
Case Ground BRAKE1 BRAKE2
Motor Model Name Encoder Connector Terminal Identification
Encoder Connector Specifications
GND Braid
Sheld
Cable Specifications for Servo Drive and Servo Motor
Basic Wiring Schematic of 400W and below models
Basic Wiring
Basic Wiring Schematic of 750W models
Basic Wiring Schematic of 1kW and above models
1 CN1 Terminal Identification
Input / Output Interface Connector -CN1
General Signals Pin No Details Wiring Diagram Refer to
Signals Explanation of Connector CN1
Vref
Tref
SON ALL
Srdy ALL
Zspd ALL
Tspd ALL
Warn ALL
Source of Torque Command
Source of Speed Command
Default DI Signals and do Signals
User-defined DI and do signals
User-defined DI and do signals
Connections and WiringASDA-B Series
Wiring Diagrams of I/O Signals CN1
VDD
Connections and WiringASDA-B Series
Connections and WiringASDA-B Series
Encoder Connector CN2
Selection Do not connect this terminal
CN3 Terminal Signal Identification
„ Connection between Keypad and CN3
Connection between PC/Keypad and Connector CN3
„ Connection between PC and CN3
Standard Connection Example Position Control Mode
Speed Control Mode
Torque Control Mode
This page intentionally left blank
ASD-PU-01A Description of Digital Keypad ASD-PU-01A
Display and Operation
Name Function
Monitor Mode
YES
Press Mode key to return to previous display
YES
Fast Edit Mode Fast Editing, Static & Dynamic Auto-tuning
Fast Editing
Abort Setting Display
Status Display Save Setting Display
Fault Message Display
Polarity Setting Display
Monitor Setting Display
Following table lists the display examples of monitor value
Status Display S H
Fault Code Display Operation
S H
JOG Operation
CCW
0 6 F O T
Do Force Output Diagnosis Operation
0 9 M O T
DI Diagnosis Operation
Do Diagnosis Operation
Parameters Read and Write
Display and OperationASDA-B Series
ASD-PU-01B Description of Digital Keypad ASD-PU-01B
Display and OperationASDA-B Series
Display and OperationASDA-B Series
Display and OperationASDA-B Series
Display and OperationASDA-B Series
Display and OperationASDA-B Series
Display and OperationASDA-B Series
Fast Edit Mode Fast Editing Function
Dynamic Auto-tuning Mode Dynamic Auto-tuning Function
Static Auto-tuning Mode Static Auto-tuning Function
Status Display Save Setting Display
Monitor Setting Display
Display and OperationASDA-B Series
Fault Code Display Operation
Display and OperationASDA-B Series
Do Force Output Diagnosis Operation
DI Diagnosis Operation
Do Diagnosis Operation
Parameters Read and Write
Display and OperationASDA-B Series
This page intentionally left blank
Inspection without Load
Trial Run and Tuning Procedure
Trial Run and Tuning ProcedureASDA-B Series
Over voltage
Applying Power to the Drive
Emergency stop activated
Encoder error
Reverse limit switch error
Undervoltage
Forward limit switch error
Overcurrent
Input power phase loss
Magnetic field error
JOG Trial Run without Load
ASD-PU-01A Tuning Flowchart
ASD-PU-01B Tuning Flowchart
Step
Speed Trial Run without Load
P1-11 is set to
„ ASD-PU-01A
Tuning Procedure
„ ASD-PU-01B
Tuning Procedure
Tuning Procedure Display Message
Tuning Flowchart
Load Inertia Estimation Flowchart
AutoMode PI Tuning Flowchart
Trial Run and Tuning ProcedureASDA-B Series
Trial Run and Tuning ProcedureASDA-B Series
Limit of Load Inertia Estimation
Relationship between Tuning Modes and Parameters
KVP
Gain Adjustment in Manual Mode
Trial Run and Tuning ProcedureASDA-B Series
This page intentionally left blank
Control Modes of Operation
Control Modes of Operation
PTT
Command Source of Position Control Mode
External Pulse Input Type Communication Addr H
ASD-PU-01A ASD-PU-01B
Inhibit
Structure of Position Control Mode
Electronic Gear Ratio
Pulse Inhibit Input Function Inhp
Inhp OFF
GR4
Electronic Gear Ratio Denominator Communication Addr DH
GR2
Low-pass Filter
Position Loop Gain Adjustment
Pflt
PF LT
PFG
KPP
PPR
PFF
KPF
REF-GND
Command Source of Speed Control Mode
Basic Structure
Structure of Speed Control Mode
Curve Filter
Smoothing Strategy of Speed Control Mode
Tacc
Acceleration Time Communication Addr H
Deceleration Time Communication Addr H
Tdec
TSL
Accel /Decel S-curve Communication Addr H
Sflt
Analog Speed Command S-curve Filter
Analog Speed Command Low-pass Filter
VCM
Max. Analog Speed Command or Limit Communication Addr H
Analog Speed Input Scaling
Speed Loop Gain Adjustment
Timing Chart of Speed Control Mode
SPD0 OFF
SPD1 OFF SON
PI Structure P2-32
„ Manual Mode
„ Auto Mode
AUT2
Tuning Mode Selection Communication Addr H
Manual Mode
KVP
GDR
Proportional Speed Loop Gain Communication Addr H
KVI
Speed Feed Forward Gain Communication Addr H
SFG
Frequency Domain
KVI
KVI
Time Domain
SFG
Auto Mode Continuous adjustment
NCF
Resonance Suppression
Notch Filter Resonance Suppression Communication Addr H
DPH
Use Low-pass Filter to suppress resonance
NLP
Use Notch Filter to suppress resonance
Command Source of Torque Control Mode
Structure of Torque Control Mode
Tflt
Smoothing Strategy of Torque Control Mode
Analog Torque Input Scaling
TCM
Max. Analog Torque Command or Limit Communication Addr H
TCM0 OFF
TCM1 OFF SON
Control Modes Selection
Speed / Position Control Mode Selection
Mode
OFF Not Care
Torque / Position Control Mode Selection
Speed / Torque Control Mode Selection
Torque Limit
Others Speed Limit
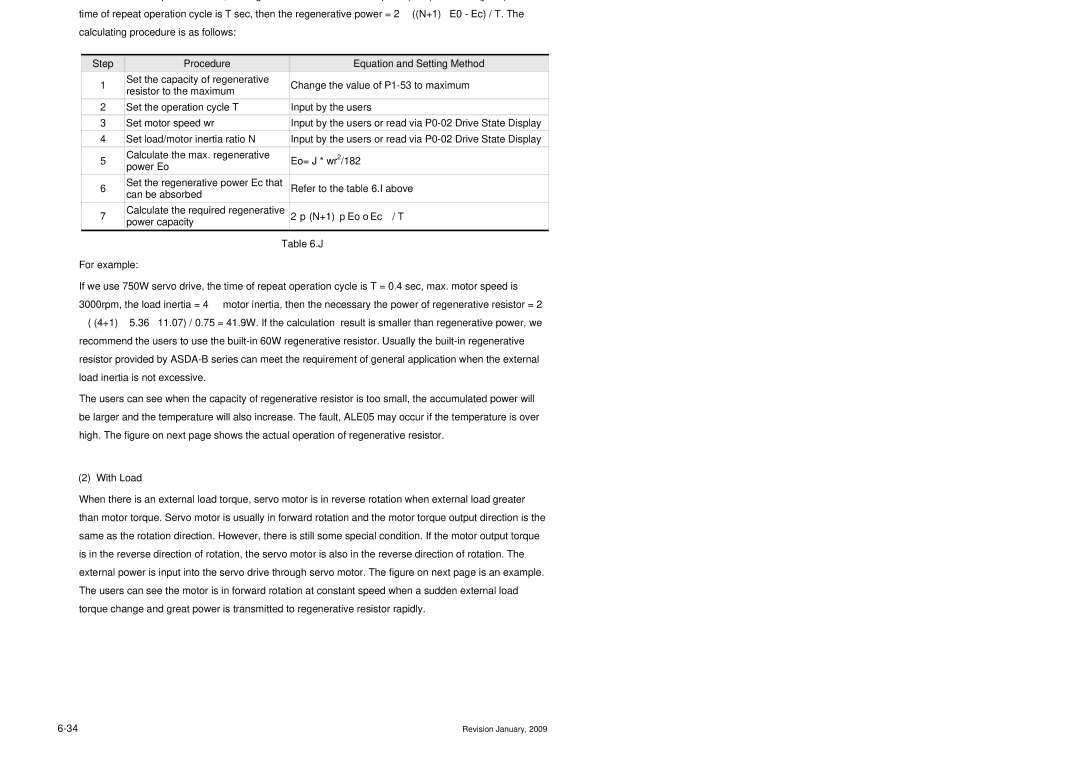
„ Built-in Regenerative Resistor
Regenerative Resistor
„ External Regenerative Resistor
„ Regenerative Power Calculation Method Without Load
With Load
„ Simple Calculation Method
Electromagnetic Brake
Brkr OFF
OFF MBT1 MBT2
SON OFF
Control Modes of OperationASDA-B Series
Abbreviation of control modes
Explanation of symbols marked after parameter
Definition
Parameters Summary Parameters List by Group
Parameter Name Function Default Unit
Group 0 P0-xx
Control
Group 1 P1-xx
Control Parameter Name Function Default Unit Mode
Parameter Name Function Default Unit Mode
Group 2 P2-xx
Control Parameter Name Function Default Unit
AUT2
AUT1
Sdev
Pdev
Group 3 P3-xx
Group 4 P4-xx
Group 8 P8-xx
Monitor and General Use
Parameters List by Function
Gain and Switch
Position Control
External pulse control command P mode
Speed Control
Digital I/O
Communication
Input Status or Force Input Control P4-09
Others
Keypad Communication and Reset Setting P8-05
Detailed Parameter Listings
Drive Fault Code Communication Addr H
Group 0 P0-xx Monitor Parameters
VER
Servo ParametersASDA-B Series
Drive Status Communication Addr H
STS
Reserved Communication Addr H
CM1
CM3
CM2
Svsts
Servo Output Status Display Communication Addr H
Servo ParametersASDA-B Series
Group 1 P1-xx Basic Parameters
CTL
Control Mode and Output Direction Communication Addr H
Pstl
Speed and Torque Limit Communication Addr H
TCM1, TCM0
SPD1, SPD0
Aout
SPD3
SPD1
SPD2
TQ2
TQ1
GR4
Lstp
Tacc
Zspd
Zero Speed Range Setting Communication Addr H
Sspd
Target Rotation Speed Communication Addr H
MBT1
On Delay Time of Electromagnetic Brake Communication Addr AH
MBT2
GR1
Regenerative Resistor Capacity Communication Addr H
RES1
RES2
Positioning Completed Width Communication Addr H
PER
Mspd
Maximum Speed Limit Communication Addr H
KPP
SPR
Speed Loop Gain Switching Rate Communication Addr H
Pctlc
Bounce Filter Communication Addr H
DRT
DI1
Digital Input Terminal 1 DI1 Communication Addr AH
DI5
DI3
DI4
Digital Input Terminal 6 DI6 Communication Addr EH
DI6
DO1
Digital Output Terminal 1 DO1 Communication Addr H
Digital Output Terminal 3 DO3 Communication Addr H
DO3
External Anti-Interference Gain Communication Addr AH
DST
Gain Switching Time Constant Communication Addr CH
Gain Switching Control Selection Communication Addr BH
GCC
GUT
GPE
Gain Switching Condition Communication Addr DH
INH
AUT1
AUT2 Tuning Mode Selection
Sdev
Excessive Error Warning Condition Communication Addr H
Overspeed Warning Condition Communication Addr H
Pdev
Overload Protection Level Communication Addr H
OVL
OVW
Output Overload Warning Level Communication Addr H
Special Function Communication Addr H
Gbit
Afrq
Atur
Atme
Astr
Cclr
Pulse Deviation Clear Mode Communication Addr H
Sjit
Group 3 P3-xxCommunication Parameters
Communication Address Setting Communication Addr H
ADR
BRT
FLT
Transmission Fault Treatment Communication Addr H
CWD
Communication Time Out Detection Communication Addr H
CDT
SDI
Digital Input Communication Function Communication Addr H
ASH3
ASH2
ASH4
ASH5
JOG Operation Communication Addr H
JOG
FOT
Force Output Control Communication Addr H
MOT
Itst
Input Status or Force Input Control Communication Addr H
CEN
Adjustment Function Communication Addr AH
TOF1
SOF1
SOF2
COF2
COF1
COF4
COF3
Tigb
Igbt NTC Calibration Communication Addr H
Analog Speed Input Offset Communication Addr H
SAO
TAO
Analog Torque Input Offset Communication Addr H
CN1
Group 8 P8-xx Keypad Parameters
Keypad Communication and Reset Setting Communication Addr H
Kver
Keypad Firmware Version Communication Addr H
Transmission Speed Keypad Communication Addr H
Kadr
Kbrt
Kcmm
Kptl
Communication Selection Keypad Communication Addr H
Ktst
Memory Block Clear Communication Addr BH
Kblt
Kclr
Memory Block Position Number ROMx Communication Addr CH
Krno
KBL0
Status of Memory Block ROMx Communication Addr DH
Firmware Version of Memory Block ROMx Communication Addr EH
KBL1
Input Function Definition
Setting value of P2-10 ~ P2-15
Inhp is activated, the external pulse input command is not
SPD0 SPD1
Setting value of P2-10 ~ P2-15 14 ~
TCM0 TCM1
Setting value of P2-10 ~ P2-15 16 ~
Emgs
Tllm
Output Function Definition
Setting value of P2-18 ~ P2-20
OFF
Warn
Communication Hardware Interface
RS-232 „ Configuration „ Cable Connection
Modbus CommunicationsASDA-B Series
RS-485, RS-422 „ Configuration „ Cable Connection
Modbus CommunicationsASDA-B Series
Communication Parameter Settings
Modbus CommunicationsASDA-B Series
DI6 DI5 DI4 DI3 DI2 DI1
0307H Communication Response Delay Time
RTU Mode
„ Code Description Ascii Mode
Modbus Communication Protocol
„ Data Format
STX
„ Communication Protocol Ascii Mode
CMD
DATA0 LRC
Ascii Mode Command message Response message
CMD Command Codes and Data Data Characters
STX Communication Start
ADR Communication Address
ADR CMD
RTU Mode Command message Response message
Ascii Mode Command message
LRC Ascii Mode
End1, End0 Communication End Ascii Mode
CRC RTU Mode
Error Code RTU Mode
„ Communication Related Error Code
Modbus CommunicationsASDA-B Series
Modbus CommunicationsASDA-B Series
Basic Inspection
Maintenance and Inspection
Life of Replacement Components
Maintenance
„ Smooth capacitor
„ Relay
„ Cooling fan
This page intentionally left blank
Fault Messages Table
Display Fault Name Fault Description
Fault Messages
Keypad Fault Messages Display Fault Name Fault Description
ALE 20/ALE
ALE 2 / ALE Overvoltage
Servo Drive Fault Messages ALE 1 / ALE Overcurrent
Potential Cause and Corrective Actions
ALE 3 / ALE
Regeneration error
ALE 4 / ALE
Pulse shift
Overspeed
ALE 6 / ALE Overload
ALE 7 / ALE
ALE 10 / ALE Serial communication error
Abnormal pulse control command
ALE 8 / ALE
ALE 9 / ALE
ALE 12 / ALE Adjustment error
ALE 11 / ALE Encoder error Position detector fault
ALE 14 / ALE Reverse CWL limit switch error
ALE 15 / ALE Forward Ccwl limit switch error
ALE 17 / ALE Memory error
ALE 16 / ALE Igbt temperature error
ALE 19 / ALE Motor type error
ALE 20 / ALE Input power phase loss
ALE 31 LED hardware error
Keypad Fault Messages ALE 30 LCM hardware error
ALE 32 KEY hardware error
ALE 33 RAM hardware error
ALE 40 Initial setup error
ALE 35 Comm hardware error
ALE 42 Communication receive error
ALE 41 Communication receive time out
ALE 44 Error communication response command
ALE 43 Error communication response address
ALE 45 Communication parameter address error
ALE 46 Communication parameter content error
Display Fault Name Clearing Method
Clearing Servo Drive Faults
Specifications of Servo Drive ASDA-B Series
Specifications
SpecificationsASDA-B Series
11-3
Low Inertia Servo Motor
Specifications of Servo Motor Ecma Series
Medium / High Inertia Servo Motor
Revision January
Weight
Dimensions of Servo Drive
Order P/N ASD-B0721-A 750W
Order P/N ASD-B1021-A, ASD-B1521-A, ASD-B2023-A 1kW to 2kW
Servo Motor Speed-Torque Curves T-N Curve
„ Chart of load and operating time ECMAC30401…S
Overload Characteristics
„ Overload Protection Function
„ Occasion of Overload
„ Chart of load and operating time ECMAC30604…S
„ Chart of load and operating time ECMAC30602…S
„ Chart of load and operating time ECMAC30807…S
„ Chart of load and operating time ECMAC30804…7
„ Chart of load and operating time ECMAC31020…S
„ Chart of load and operating time ECMAC31010…S
„ Chart of load and operating time ECMAC31305…S
„ Chart of load and operating time ECMAC31303…S
„ Chart of load and operating time ECMAC31309…S
„ Chart of load and operating time ECMAC31306…S
„ Chart of load and operating time ECMAC31315…S
„ Chart of load and operating time ECMAC31310…S
„ Chart of load and operating time ECMAC31820…S
„ Chart of load and operating time ECMAC31320…S
Motor Frame Size 80mm Models
Dimensions of Servo Motor
Motor Frame Size 100mm Models
11-21
11.7 EMI Filters Selection
Application Example Dual Mode S-P Mode Purpose
Connecting to DVP-EH PLC and DOP-A HMI
Explanation Programmable Logic Controller hereinafter PLC
Y1 Sign
PLC Program
Application Examples ASDA-B Series
12-4
12-5
DVP-EH ASDA-B CN1
DVP-EH
Program Screen Homing Operation
HMI DOP-A HMI
Position Control
12-9
JOG Operation
Speed Control Operation
Delta TP04 Series
Connecting to DVP-EH PLC and Delta TP04 Series
Application Example Homing Operation Purpose
12-13
Communication Settings
ASDA-B series Servo Drive Parameter Settings
External Controller Connection Examples
„ Connecting to Delta DVP-EH PLC
„ Connecting to Delta DVP-01PU
„ Connecting to Mitsubishi FX1PG
„ Connecting to Mitsubishi FX2N1PG
„ Connecting to Mitsubishi AD75
This page intentionally left blank 12-20
Delta Part Number ASDBCAPW0100
„ Power Connectors Delta Part Number ASDBCAPW0000
Jowle
Delta Part Number ASDBCAPW0303/0305
„ Power Cables Delta Part Number ASDBCAPW0203/0205
Delta Part Number ASD-CAPW2303/2305
„ Power Cables, Delta Part Number ASD-CAPW1203/1205
Delta Part Number ASD-CAPW2203/2205
„ Encoder Connectors Delta Part Number ASDBCAEN0000
ASDBCAEN1003
„ Encoder Cables, Delta Part Number ASDBCAEN1003/1005
ASDBCAEN1005
Jaws
Appendix a AccessoriesASDA-B Series
Delta Part Number ASD-PU-01B including communication cable
ASDBCAEN0003 ASDBCAEN0005
ASDBCAPW0203 ASDBCAPW0205
200W Servo Drive and 200W Low Inertia Servo Motor
ASDBCAPW0203 ASDBCAPW0205 ASDBCAPW0303 ASDBCAPW0305
ASD-CAPW1203 ASD-CAPW1205 ASD-CAPW1303 ASD-CAPW1305
400W Servo Drive and 500W Medium Inertia Servo Motor
ASDBCAEN1003 ASDBCAEN1005
400W Servo Drive and 300W High Inertia Servo Motor
1kW Servo Drive and 1kW Medium Inertia Servo Motor
750W Servo Drive and 600W High Inertia Servo Motor
1kW Servo Drive and 1kW Low Inertia Servo Motor
2kW Servo Drive and 2kW Low Inertia Servo Motor
1kW Servo Drive and 900W High Inertia Servo Motor
5kW Servo Drive and 1.5kW Medium Inertia Servo Motor
2kW Servo Drive and 2kW Medium Inertia Servo Motor