8284A
Clock Generator
The clock generator consists of a synchronous divide-
Master system Is not being used the AEIii pin should be tied lOW.
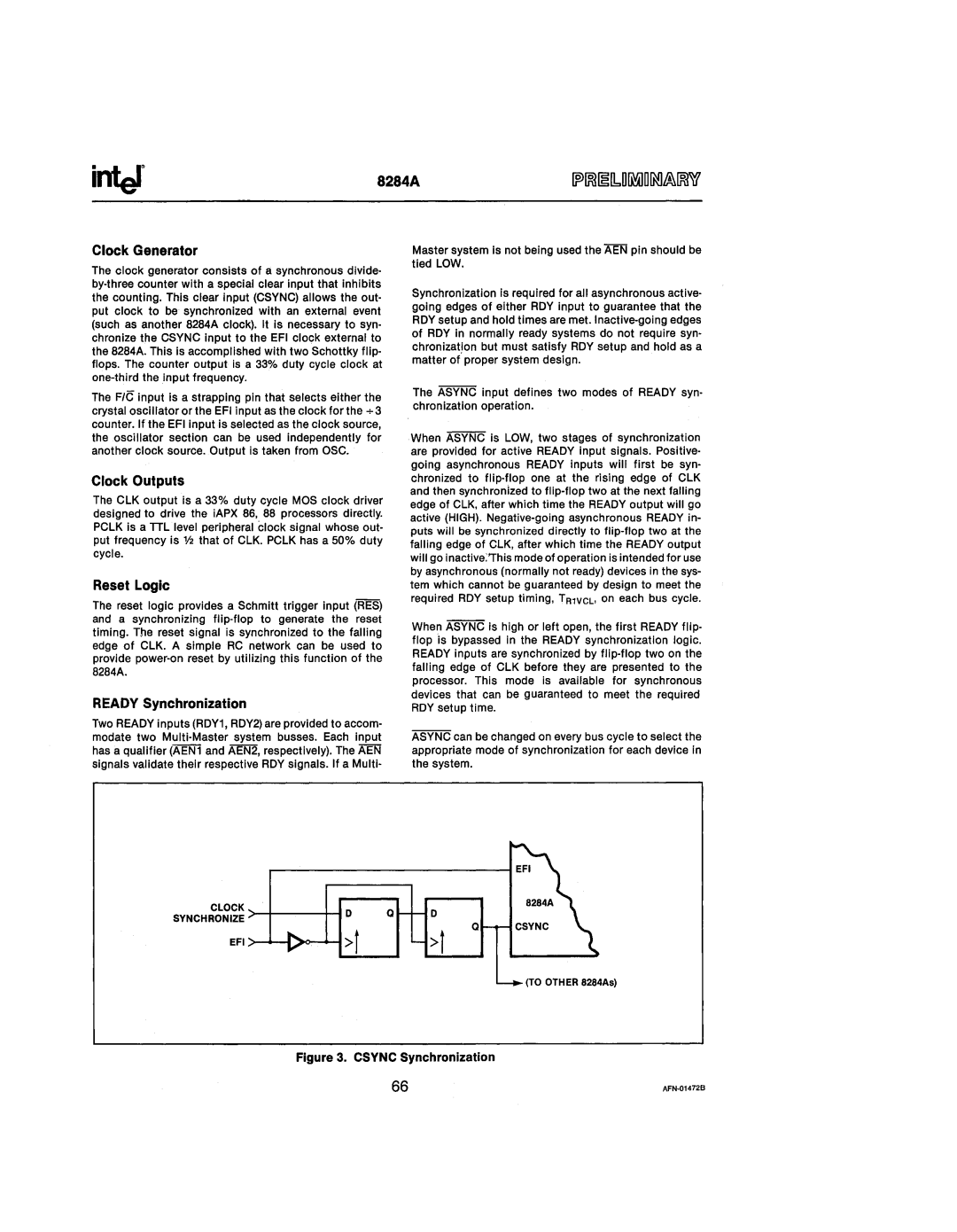
Synchronization is required for all asynchronous active- going edges of either RDY input to guarantee that the RDY setup and hold times are met.
The FIG input is a strapping pin that selects either the crystal oscillator or the EFI input as the clock for the + 3 counter. If the EFI input is selected as the clock source, the .oscillator section can be used independently for another clock source. Output is taken from OSC.
Clock Outputs
The ClK output is a 33% duty cycle MaS clock driver designed to drive the iAPX 86, 88 processors directly. PClK is a TTL level peripheral clock signal whose out- put frequency is V2 that of ClK. PClK has a 50% duty cycle.
Reset Logic
The reset logic provides a Schmitt trigger input (RES) and a synchronizing
READY Synchronization
Two READY inputs (RDY1, RDY2) are provided to accom- modate two
The ASYNC input defines two modes of READY syn- chronization operation.
When ASYNC is lOW, two stages of synchronization are provided for active READY input signals. Positive- going asynchronous READY inputs will first be syn- chronized to
When ASYNC is high or left open, the first READY flip- flop is bypassed in the READY synchronization logic. READY inputs are synchronized by
ASYNC can be changed on every bus cycle to select the appropriate mode of synchronization for each device in the system.
CLOCK |
| Q | D |
SYNCHRONIZE | |||
|
|
| Q |
EFI |
|
|
|
(TO OTHER 8284As)
Figure 3_ CSYNC Synchronization
66 |