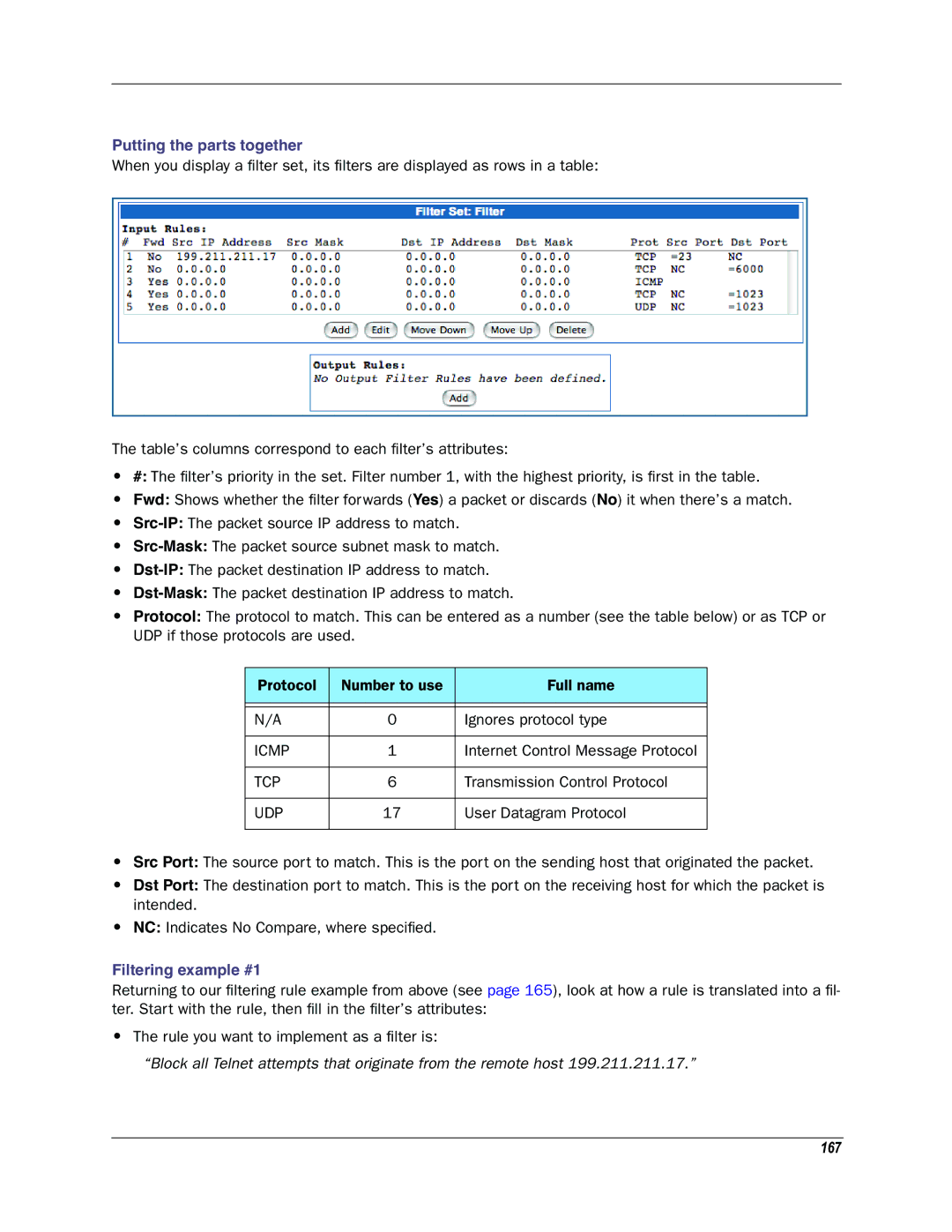
Putting the parts together
When you display a filter set, its filters are displayed as rows in a table:
The table’s columns correspond to each filter’s attributes:
•#: The filter’s priority in the set. Filter number 1, with the highest priority, is first in the table.
•Fwd: Shows whether the filter forwards (Yes) a packet or discards (No) it when there’s a match.
•
•
•
•
•Protocol: The protocol to match. This can be entered as a number (see the table below) or as TCP or UDP if those protocols are used.
Protocol | Number to use | Full name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
N/A | 0 | Ignores protocol type |
|
|
|
ICMP | 1 | Internet Control Message Protocol |
|
|
|
TCP | 6 | Transmission Control Protocol |
|
|
|
UDP | 17 | User Datagram Protocol |
|
|
|
•Src Port: The source port to match. This is the port on the sending host that originated the packet.
•Dst Port: The destination port to match. This is the port on the receiving host for which the packet is intended.
•NC: Indicates No Compare, where specified.
Filtering example #1
Returning to our filtering rule example from above (see page 165), look at how a rule is translated into a fil- ter. Start with the rule, then fill in the filter’s attributes:
•The rule you want to implement as a filter is:
“Block all Telnet attempts that originate from the remote host 199.211.211.17.”