Administrator’s Handbook
•IGMP Forwarding: The default setting is Disabled. If you check this option, it will enable Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) multicast forwarding. IGMP allows a router to determine which host groups have members on a given network segment. See “IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)” on page 100 for more information.
•RIP Send Mode: Specifies whether the gateway should use Routing Information Protocol (RIP) broad- casts to advertise its routing tables to other routers on your network. You may choose from the following protocols:
•
•
•
•
•RIP MD5 Key: Secret password when using
•RIP Receive Mode: Specifies whether the Gateway should use Routing Information Protocol (RIP) broadcasts to update its routing tables with information received from other routers on your network. The protocol choices are the same as for the RIP send mode.
•Proxy ARP: Specifies whether you want the Gateway to respond when it receives an address resolution protocol for devices behind it. This is a way to make a computer that is physically located on one net- work appear to be part of a different physical network connected to the same Gateway. It allows you to hide a computer with a public IP address on a private network behind your Gateway, and still have the computer appear to be on the public network “in front of” the Gateway.
•Static Client Address Translation: If you check this checkbox, this feature allows a statically addressed computer whose IP address falls outside of the LAN subnet(s) to simply plug in and get online without any manual configuration on either the host or the Motorola Netopia® Gateway. If enabled, statically addressed LAN hosts that have an address outside of LAN subnets will be able to communicate via the Router’s WAN interface to the Internet. Supported static IP address values must fall outside of the Router's LAN subnet(s).
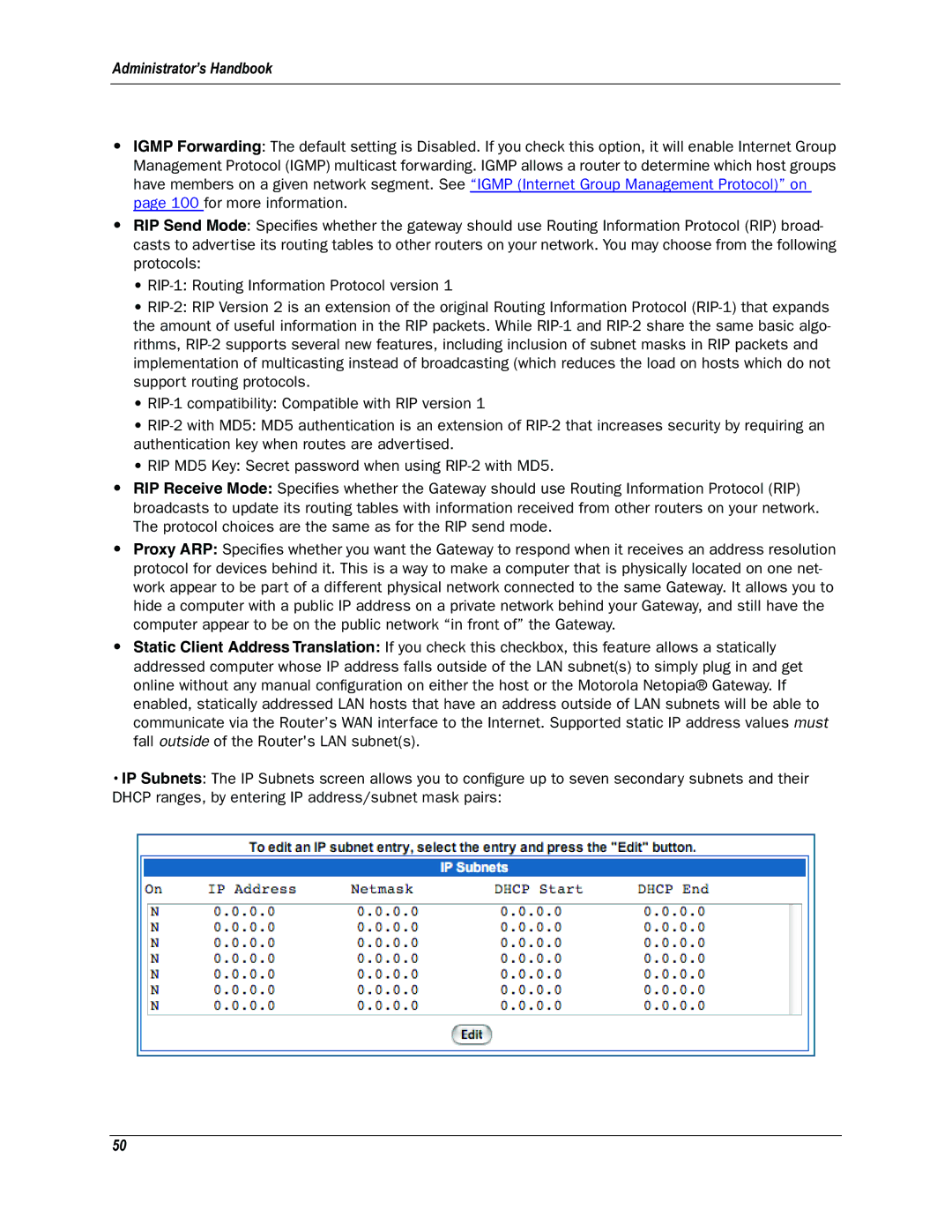
•IP Subnets: The IP Subnets screen allows you to configure up to seven secondary subnets and their DHCP ranges, by entering IP address/subnet mask pairs:
50