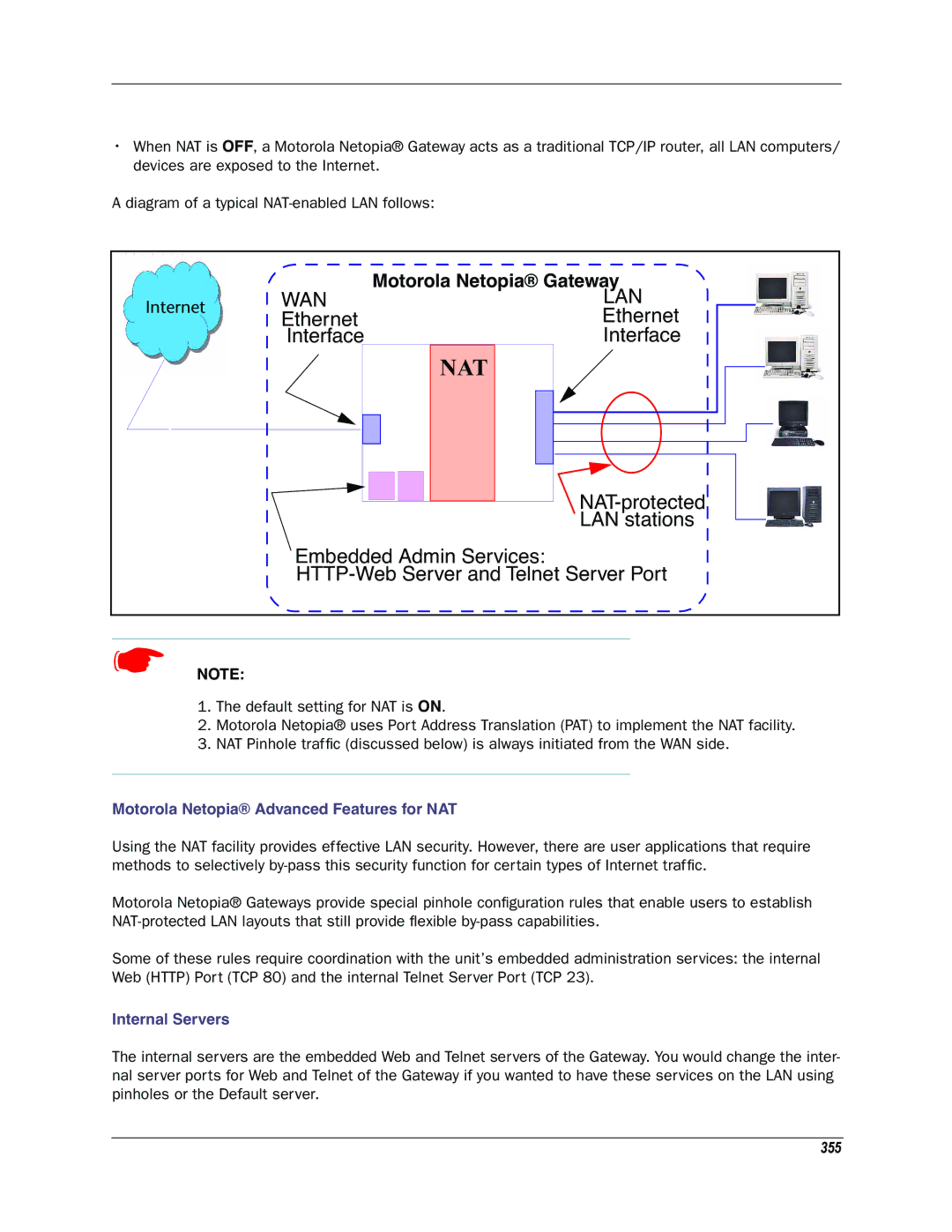
•When NAT is OFF, a Motorola Netopia® Gateway acts as a traditional TCP/IP router, all LAN computers/ devices are exposed to the Internet.
A diagram of a typical
|
| Motorola Netopia® Gateway | |
Internet | WAN | LAN | |
Ethernet | Ethernet | ||
| |||
| Interface | Interface | |
|
| NAT | |
|
| ||
|
| LAN stations | |
| Embedded Admin Services: | ||
|
| ||
☛ NOTE: |
|
| |
1.The default setting for NAT is ON.
2.Motorola Netopia® uses Port Address Translation (PAT) to implement the NAT facility.
3.NAT Pinhole traffic (discussed below) is always initiated from the WAN side.
Motorola Netopia® Advanced Features for NAT
Using the NAT facility provides effective LAN security. However, there are user applications that require methods to selectively
Motorola Netopia® Gateways provide special pinhole configuration rules that enable users to establish
Some of these rules require coordination with the unit’s embedded administration services: the internal Web (HTTP) Port (TCP 80) and the internal Telnet Server Port (TCP 23).
Internal Servers
The internal servers are the embedded Web and Telnet servers of the Gateway. You would change the inter- nal server ports for Web and Telnet of the Gateway if you wanted to have these services on the LAN using pinholes or the Default server.