System Manual
6ES5998-0SH21 12/98 C79000-G8576-C199 Release
Appendices
Siemens Aktiengesellschaft
Contents
Central Controllers and Expansion Units Power Supply Units
CPUs, Memory Cards, Memory Submodules, Interface Submodules
System Manual C79000-G8576-C199-06
Multiprocessor Operation/Coordinators
Vii
10-1
11-1
Index Index-1
System Manual C79000-G8576-C199-06
Slot Requirement
Slots
Controller
Slots
System Manual
System Manual C79000-G8576-C199-06
EMC 89/336/EEC
Installation
Installing
Fields
Order Number Module
Shielded signal cable is required for the following modules
Individual Modules
Order Number
89/392/EEC on
Introduction
EC Directive
Machines
Safety Notes
System Manual C79000-G8576-C199-06
Section Contents
Chapter Overview
Application
Centralized and Distributed Configuration
Then
Interface Module
Installing a PLC with Centralized Configuration
Connecting Cable Max. Distance
Expansion Unit
Interface Module
Installing a PLC with Distributed Configuration
Connecting Cable Max. Permiss. Line Length
Expansion Unit
Centralized Configuration of an S5-135U/155U with ER 701s
Examples
6ES5 EU185U EUs max EU 185U
System Manual C79000-G8576-C199-06
Installation Guidelines
Section Description
Principles of Installation of Systems for EMC
Overview of Possible Types of Interference
Installation Guidelines
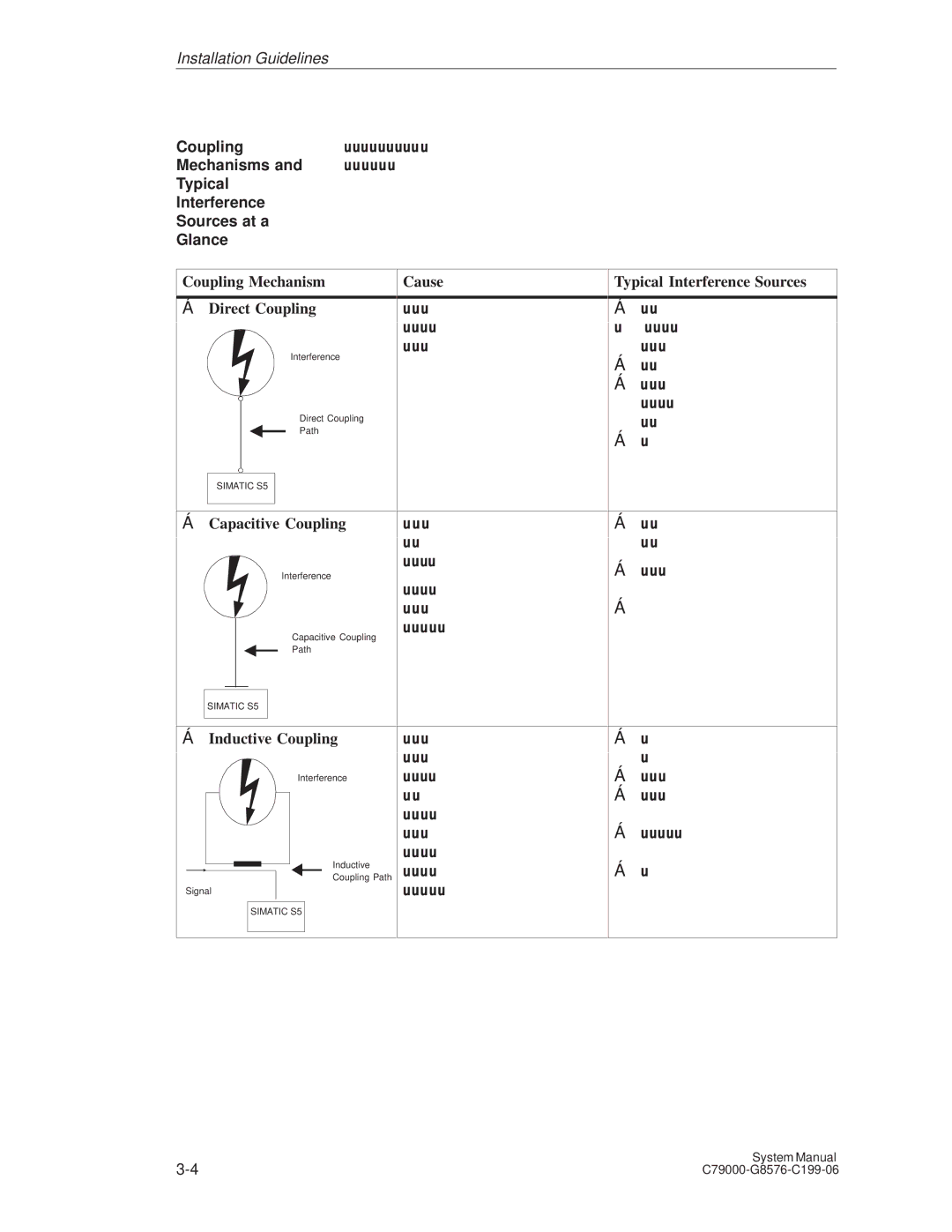
Coupling
Mechanisms
Typical Interference Sources at a Glance
Coupling Mechanism Radiated Interference
Cause Typical Interference Sources
Most Important Basic Rules for Ensuring EMC
Ensure that cable shields are properly secured see Section
Installation Guidelines
Installation of Programmable Controllers for EMC
Example of Cabinet Assembly for EMC
Example of Cabinet Assembly for EMC
Cabinet members
Signal lines
Grounding strips
Mounting bracket for subrack
Example of Rack and Wall Mounting for EMC
Wall Mounting of an S5-135/155U PLC
Wiring of Programmable Controllers for EMC
Routing of Cables
Installation Guidelines
Routing of Equipotential Bonding Conductor and Signal Line
Equipotential Bonding
Shielding of Cables and Lines
Example of Securing Shielded Lines with Cable Clamps
Elements to
Special Measures for Interference-Free Operation
Fitting Quenching
Inductances
Programmers
AC Power
Connection for
Cabinet Lighting
Equipotential bonding Section
EMC Measures Connection of inactive parts Section
Routing of cables Section
Shielding of cables Section
Power Supplies for Programmable Controllers and I/Os
Power Supplies for Control Systems with Simatic S5
Connecting the Programmable Controller and Load Power
Main Switch
Load Power
Grounding
Interference
Operating a
Programmable
Controller with Process I/Os from Grounded Supply
Higher-Level Supply
Controller with
An Ungrounded
Supply
Connecting Non-Floating or Floating Modules
CPU
Installation with
Floating Modules
Isolated
Installation Guidelines
13 Shielding and Grounding the Connecting Cable
Interference-Free Connection of Monitors
Shielding and Grounding
Installation Guidelines
Selection and Installation of Cabinets with Simatic S5
Open Cabinets
Types of Cabinet
Clearances in Cabinets
Closed Cabinets
15 Clearances in the Cabinet
Min. Clearances
Upper Subrack
S5-90U/95U/ 100U Lower Subrack
Max. Clearances
Removal of Power Dissipation from Cabinets
Example
Max. Permissible Ambient Temperature
Examples for Determining the Type of Cabinet
Cabinet Design
Determining the Power Dissipation of Modules
Examples
System Manual C79000-G8576-C199-06
Central Controllers and Expansion Units Power Supply Units
Assembly of a Central Controller
S5-135U/155U Central Controller
Technical Description
Housing
Incoming and outgoing cables at the front of the housing
Assignments S5-135U/155U
Central Controllers and Expansion Units Power Supply Units
CPU
Installation
Central Controller
Filter Subdrawer
Slots Occupied SPS Front Plate Width in mm
Fitting
Double-height Eurocard format h x d = 233.4 x 160 mm
Example
Proceed as follows to fit the modules
IMs
Step Action
Startup
Startup
Validity Check
Repair Guidelines
Important for the USA and Canada
Technical Specifications
Unit safety
Mechanical ambient conditions tested to DIN IEC
Noise immunity, electromagnetic compatibility EMC
Mechanical data
Order No. of Expansion Unit
Power Supply or Fan Subassembly
Expansion Units
EU Type Version
Technical Description of the Expansion Units
Modules and Slot Assignments Expansion Units
Slot No Module type
Installing the Expansion Units
Technical Specifications of the Expansion Units
Product Overview
Power Supply Units
Power Supply
Types
Monitoring
Signaling
Basic Functions
Functions
Plate of the power supply units
Inputs
Outputs
Switch Red LED Yellow LED Pushbutton Green LED
Setting and Connecting the Power Supply Unit
For Startup
PSU in operation without changing the jumper setting
Brief Instructions
Stage Description
Following table
Jumper Settings
Establishing
Subsequent implementation
Jumper Setting Application/Note
Open irrelevant
Relay
Terminals
Cabling
Max. Permissible Conductor Cross-Sections
Switch the Power switch off Standby On/Off
Step
Proceed as follows to change the jumper settings
Setting Jumpers Locations
Setting
Jumper locations are given in the following figure
ªEstablishing the settings and cabling.º
Fitting the Power Supply Unit How to Fit the PSU
Wiring the Power Supply Unit How to Wire
PSU
How to Fit the Lithium Battery
Battery Compartment B Cover a
Lock
Result
Setting the Voltage Selector Switch How to Set
Where to Fit
How to Fit
Switch
Switch the system voltage on
Fault Indications/Fault Diagnostics
Other Faults
LEDs Possible Cause Action
Fans and Fan
Enable EN present, jumper F R closed
Enable EN present, jumper F R open
Following table contains several examples
Battery
Battery Battery Monitoring
Battery Supply Jumpers
Following table contains several examples
Supply in the event of fan failure is described in Section
Maintenance and Repairs
Fans
Follows
Replacement
Lithium Battery
How to Replace
Replacing
Fan
Step Action Result
Ensure correct polarity
Lock
Central Controllers and Expansion Units Power Supply Units
Replacing Rechargeable Battery in the Fan Subassembly
Correct the fault in the following steps
Replacing Filter Mat Inadequate Air
Flow
Standard spare part
Replacing a Power
Lithium battery in the rack is in full working order
Reaction
No backup
Backup
Description of Internal Sequences in the Power Supply Unit
Behavior Upon Failure System Supply When the System
Supply Fails
If a Fan Fails
Resetting the Fault Message
Behavior Upon Failure of Fans
If Another Fan
Technical Specifications of the Power Supply Units
6ES5 955-3LC42 6ES5 955-3LF42 Safety Specifications
Input
6ES5 955-3LC42 6ES5 955-3LF42 Output
Protection and monitoring
Service life of fans Weight Noise emission
Backup battery
Rechargeable battery
Environmental data
Safety Specifications 6ES5 955-3NC42 6ES5 955-3NF42
6ES5 955-3NC42 6ES5 955-3NF42 Protection and monitoring
6ES5 955-3NC42 Backup battery 6ES5 955-3NF42
6ES5 955-3NA12 Power Supply Unit
Type of PSU Designation
Input Voltage Output Voltage
Label Element Purpose
Auxiliary Submodule
Terminals
Function
Setting the Power Supply Unit
Delivered
Jumpers NN-MM closed
Setting the Fan Monitor
Central Controllers and Expansion Units Power Supply Units
Installing the 15 Auxiliary Submodule
General Notes on the Power Supply Unit
Operation
Power Supply
Diagnostics
LEDs indicate the following faults
Relay Contacts
Maintenance
Replacing the Lithium Battery
Battery Submodule
Replacing the Fans
Signaling section Signals for Simatic S5
Output 2 front
Weight Environmental data
Output 2 bus
Output 3 with 15 V auxiliary submodule
LEDs
Fan Submodules Technical Description
Connections
Plate of the -3LA11is shown as an example
Position Voltage Selector Switch Fuse
Setting and Connecting the Fan Submodule
Max. Permissible Cable Cross-Sections
Case of a fault, the red LED ªFan Faultº lights up
Terminals Cabling
Fan Submodule Relay Contact Relay contact
6ES5 988-3LA11 6ES5 988-3NA11 Safety Specifications
Service life Weight Environmental data
Chapter Contents
CPUs, Memory Cards, Memory Submodules, Interface Submodules
CPU 948B -3UA13 or CPU 948B -3UA23
Design
Installation and Startup
Inte Intf Intg
Removing Inserting Module Insertion
Step Action
Removal
Proceed as follows to remove the CPU
Indicators
Controls
Module
Momentary
Mode Switch
Contact Mode
Restart
Off
Off Rapid Flashing Slow
Status
LEDs for Fault Indication and Signaling
Possible causes
Fault LEDs SI1
SI2
SI2
Reset
Overall Reset
Step Action Result Set the mode switch to Stop
Continue as follows
Set the mode switch from Stop to RUN
Restart is permissible
Interfaces of the CPU
PG interface SI1
Second Interface
Communication
Via Backplane Bus
With Sinec H1
Technical Specifications
CPUs, Memory Cards, Memory Submodules, Interface Submodules
CPU
View of underside of module
Removing Inserting Module Insertion
Controls and Indicators of the CPU
STOP. The red Stop LED will then light up
Into the internal RAM
Retained during stoppage of the CPU
RUN Stop LED
Initialization after power on and during operation
Event of system faults
This LED is continuously lit for a short time during
Fault LEDs SI1
Set the mode switch to Stop Switch the system voltage on
Resultat
Restart
Interface SI2
Interface Submodules
Technical Specifications
CPUs, Memory Cards, Memory Submodules, Interface Submodules
CPU 928B -3UB21
User Memory
Memory Card
Second Interface SI2
Jumper Settings Removing Inserting Module Insertion
Removal
Front Plate of the CPU 928B-3UB21
RUN setting, the CPU 928B processes the user program when
Green RUN LED is lit
Status Indicators
Stop LED
Maximum cycle monitoring time has been exceeded
Manual restart is permissible
DB RAM
CPUs, Memory Cards, Memory Submodules, Interface Submodules
Electronic circuitry of the CPU 928B is on two PCBs basic
Delayed from Version 6ES5 928-3UB12
CPU 928B
Front plate width is 2 2/3 standard plug-in stations
Bytes
Order numbers are given in the ordering information
CPU 928B Programming Guide
Second Interface SI2
Installation and Startup
Removal
CPU 928B
SI1 Siemens
RUN
Status Indicators
Internal error
No communication possible at both interfaces
Startup
Technical Specifications
CPUs, Memory Cards, Memory Submodules, Interface Submodules
CPU 928 -3UA21
Closed-loop tasks
Cyclical
User Memory
Removing Inserting Module Insertion Removal
Front Plate of the CPU 928 -3UA21
STOP. The red Stop LED then lights up
LEDs for Fault Indication Signaling
Startup
Technical Specifications
CPU 928 comprises two PCBs PCB 1 and PCB 2 in the double
Process Interrupt
Processing
Installation and Startup
Front Plate of the CPU
RUN
Off Slow flashing Rapid flashing
LEDs for Fault Indication Signaling
Startup
Technical Specifications
S5-135U/155U CC see . Up to four CPUs can be used
Time-controlled 1 timebase
22 x 210 bytes
Is full or an Eprom submodule is inserted
Installation and Startup
6ES5922-3UA11
RUN
Status Indicators
Upon reset of the CPU 922 in the area of the process
Startup
Technical Specifications
374 Flash Eprom Cards
Technical Specifications
Memory
376 Memory Submodules
Programming
Submodules
Technical Specifications
10 377 Memory Submodules
Without Battery Backup
With Battery Backup
Loading RAM
RAM Submodules with Battery Backup
Operational States
Normal Operation
Standby Operation
Standby
Inserting or Replacing the Backup Battery
Battery Screw Fault LED
Using the RAM Submodule with Battery Backup
Proceed as follows to replace the submodule battery
Inserting Unprogrammed Memory Submodules
Whose contents are not to be erased
Programmed
Initial situation
Submodules without Battery Backup
Access time tACC 150 ns 16/64 Kbytes 200 ns 32 Kbytes
All 377 Memory Submodules
Submodules with Battery Backup
Current consumption at 5 Backup current Backup voltage
To use the second interface as
Using the Interface Submodules
Interface Submodules
You require
Installing and Removing the Interface Submodules
Check the jumper settings of your interface submodule
Remove your interface submodule in the following steps
Circuitry
PG Submodule
Interface Submodule For Use With
Rate
Pin Assignments
Pin Designation Current Remarks Direction
Jumper Settings on the PG Submodule
Operation in CPU 928B/CPU
Operation in CPU
Standard Connecting Cable for the PB Submodule
Connecting cable CPU PG
Submodule CPU 928B CPU
11.3 V.24 Submodule
V.24 submodule can be inserted in the following CPU
Receive lines
Des. to Int. Abbre Input
Data Transmission Rate Pin Assignments Submodule
Pin Des. to DIN
Viation Output
15 V.24 Submodule Jumper Settings when Delivered
Immediately
Connecting cable for CPU, CP 524, CP 525, CP
Standard Connect- ing Cables of the V.24 Submodule
CPU, CP524/525, CP544 Receiver Transmitter
Connecting cable CPU N10 modem
Modem N10
Connecting cable CPU DR 210/211, DR 230/231
DR 210/211, DR 230/231
Receiver Transmitter
Wiring of a connecting cable for RTS/CTS flow control
Transmitter Receiver
TTY submodule can be inserted in the following CPU
Current loop signals
TTY Submodule
TTY submodule CPU 928B CPU
Data Transmission Rate Pin Assignments TTY Submodule
Pin Designa Tion Shield
Current direction Remarks
Jumper Settings on the TTY Submodule
21 TTY Submodule Jumper Settings when Delivered
Standard Connect- ing Cables for the TTY Submodule
Connecting Cable CPU IM
CPU
+RxD +20mA +24V
RS422 A/485 submodule CPU 928B CPU
11.5 RS422 A/485 Submodule
RS422 A/485 submodule can be inserted in the following CPU
Ccitt Recommendation
Submodulesubmodule
RS422 A/485 submodule when used in a CPU
Data Transmission
Pin Des. to Ccitt Input Remarks Output
Jumper Settings on RS422 A/485 Submodule
Front Connector
115
116
1200 m
Connecting cable for CPU, CP 524, CP
For
RS422-A/485
Sinec L1 Submodule
Sinec L1 submodule can be inserted in the following CPU
9600 bps
Submodulessubmodule
Pin Designation
On the Sinec L1
Submodule immediately
BT 777 Bus Terminal
Connecting Cable for Point-to-Point Communication
Connecting cable CPU partner point-to-point communication
CPU 928B CPU 102, 103, AG 90U/95U
Technical Specifications of the Interface Submodules
Multiprocessor Operation/Coordinators
Introduction
Coordinator
Overview
Procedure
Starting the Multiprocessor Operation
Voltage
RUN,STOP,TEST
EP 62 JY 916
923A Coordinator
Setting the communication flag areas
Step
923C Coordinator
Jumper Comm. Flag Byte Address
Examples
Precondition The central controller is not yet switched off
Inserting CPUs and coordinator in the central controller
Substep Action Reaction
Executing an Overall Reset on all CPUs
Possible Faults
Symptom
Remedy
Loading user programs in all CPUs
Prerequisites
Executing a Reset at all CPUs
Multiprocessor
Setting the coordinator mode switch to RUN or Test
Then Reaction
Start
Stop State
Event of Faults
Coordinator Modes
Stop
Test mode
Test Mode Enabling the Test Mode with the 923A
Enabling the Test Mode with the 923C
923A Coordinator
923A Coordinator Module Technical Description
Bus arbitration
Communication memory
Principle
CPU utilize the common S5 bus
Settings on the Coordinator
Settings RUN, Stop and Test
User Control
923C Coordinator Module Technical Description
Central programmer connection PG MUX
Following order according to the preset number of CPUs
Faults are indicated by five small red LEDs
Signal is removed by the power supply, and enables the CPUs
Operator functions
Timing Sequences of the Bus Control Signals
Monitoring for continuous bus assignment
Addressing method for the page memory vector register
PG Multiplexer
For the Serial
Switch
Selection Method
Interfaces
COR 923C
Front plate of the COR 923C
Coordination
Setting the DIL Switches
Setting Off Meaning
Section Number
Activating
Addesses
Slot No. in the S5-135U/155U
Example
Address Activation
Slot No. Operable Slots S5-135U/155U End Address
Fault Register
Switch off
Signals
Jumpers to
Technical Specifications of the Coordinators
923A Coordinator 923C Coordinator
Interface Modules
300 and 312 Interface Modules
EU 183U, EU 185U
EU 184U
EU 187U
Addressing
Indicators and Controls
IM 300-5 -5CA11
IM300-3 IM300-5 IM312
Purpose
Modes/Jumper Assignments of the IM
Jumper Assignments
Extended I/O area O area
LED1 LED2
Jumper
IM 300-5 -LB11
As possible to the CC
EU 183U EU 185U only I/O modules
301 and 310 Interface Modules
EU Interface Module EU Type
EU 184U, EU 187U EU 183U
Centralized Connection Fault
LED1 LED2
Centralized EU 183U EU183U IIM312±3 EU 184U
A centralized arrangement to the distributed EUs
304 and 314 Interface Modules
Line Length
EU 183U EU 185U ER 701-2 ER
Interface Fault Signal Interface X3 Faulty
12 Location of Jumpers on the IM 304 when Delivered
You must match the IM 304 to the cable length with jumper
Purpose Jumpers
Function
X11 Jumper
Set the jumpers according to the expansion unit in use
13 Location of Jumpers on the IM
Setting Addresses
Switch Setting
Area Address
IM304
1 6ES5 721 Connecting Cable
General Specifications
Specifications for Specific IMs
Red Green Yellow No.18 Brown No.19 Black No.20 Blue No.21
2 6ES5 7602 Terminator
16 Pin Assignments of the 760 Terminator
Digital Input/Output Modules
Digital output modules
Description below applies to the following modules
S5-115U PLC
Digital input/output modules
Digital Output
Signal Output
Digital Input
Short-Circuit
LED Indicators Addressing Switch
Design
Function of the Enable Inputs
Enable Input
With an Active
Switching on
Switching off
Supply for CC/EU and I/Os
Common
AC supply for CC/EU and load power supply
Separate or
Shutdown
Special Features of the 432 Digital Input Module
Open jumpers X3 Set switch rows S1 and S2 to Off
Setting for switch row S3 is arbitrary in this mode
Process Inputs
Settings on
Scanning
Via interrupt
PW128 Load I/O word
Switch S2
Via IB
PW130 Etc
Via IB
OFF IR-G INT
Process Alarm
Special Features of the DI/DQ
Using Two or More
Modules with
Slide Switch S2
Setting the Module Address
Labeling Field
Program is independent of the slot
Start Address
Bytes of the same module are decoded on the module
IB 80 or QB
Input/output modules
Significance Byte Address 128 64 32
Removing and Inserting Modules
Wiring
Remove a digital input/output module as follows
Protective measures can be found in Chapter
Marking of Modules
Connecting the Signal Lines
Type
Digital Output Modules for DC Voltage
Modules for AC
Must not be exceeded
Load can also be switched via a contact
Connection Input/Output Modules to Two Power Supply Units
Short-Circuit Protection and Fusing
Arc-Quenching for Inductive Loads
Result in a fault in the long term
Disconnecting
Switched-Through
Following applies to digital outputs for DC voltage
DC Voltage AC Voltage
Mechanical ambient conditions
Common Technical Specifications
Climatic ambient conditions
Operand identifiers
Safety tests
Specification Sheets for the Modules
Common technical specifications are given in Section
1 6ES5 420-4UA13/4UA14 Digital Input Module
Data Memory
2 6ES5 430-4UA13/4UA14 Digital Input Module
±4UA13 ±4UA14
Example of connection designation for an input
Data Memory and S5 Bus Control
3 6ES5 431-4UA12 Digital Input Module
Process Signal
4 6ES5 432-4UA12 Digital Input Module
Example of connection designation for an input
Mark the switch settings in the free fields
Labeling for module cover
5 6ES5 434-4UA12 Digital Input Module
Namur
Namur Cmos TTL
Input 5 5th bit
6 6ES5 435-4UA12 Digital Input Module
Example of connection designation for an input X20 2 I
2nd group not specified in the address
7 6ES5 436-4UA12 Digital Input Module
Data Memory and S5 Bus Control
8 6ES5 436-4UB12 Digital Input Module
X20 6 I
9 6ES5 441-4UA13/4UA14 Digital Output Module
Short-circuit monitoring
Ext
10 6ES5 451-4UA13/4UA14 Digital Output Module
To 255 possible = Output
11 6ES5 453-4UA12 Digital Output Module
Example of connection designation for an output
Mechanical specifications
12 6ES5 454-4UA13/4UA14 Digital Output Module
X20 Data Memory and S5 Bus Control
13 6ES5 455-4UA12 Digital Output Module
X20 2 Q
14 6ES5 456-4UA12 Digital Output Module
Example of connection designation
15 6ES5 456-4UB12 Digital Output Module
1Q0.0 2Q0.1 3Q0.2 4Q0.3
16 6ES5 457-4UA12 Digital Output Module
Block Diagram Module Inputs
17 6ES5 458-4UA12 Digital Output Module
S5 Bus Control
External Suppressor Circuitry for Inductive Load
18 6ES5 458-4UC11 Digital Output Module
Process Signal Module Inputs Lines
19 6ES5 482-4UA11 Digital Input/Output Module
Inputs
Outputs
Synout
Analog Input/Output Modules
Analog Input Modules
Programmable logic controller
Analog Input Modules and Cards
Analog Output Modules
Address range
128 to 255 0 to
460 Analog Input Module Design
Function of the Enable Input
Switch, Mode
Modules are protected by covers on both sides
Enable Input and Enable Jumper
Acknowledge
Configuring
Power Supply
Special Features of the 460 Analog Input Module
Basp Output
Time-Controlled
Program
Inhibit
Subaddress
On Setting Switch Pressed
Addressing for
Cyclic/Selective
Sampling
Removing and Inserting Modules
Module with Front Connector
Remove an analog input/output module as follows
Marking of Modules and Front Connectors
Marking and Labeling of Modules
Without fan
To 60 V DC 20 mm
Current or Voltage
Connection of Sensors
Connection
Sensors
MUX
Connecting a Compensating Box for Thermal E.M.F. Measurement
CH0
24V
Standard Pt Range
Broken Wire Signal
Broken Wire at Module Reaction, Encoded Value Error Bit E
Extended Pt
Connecting Transducers
Four-wire transducer with separate supply voltage
Four-wire transducer with a two-wire transducer card
Rated input range $ 50 mV
Measured-Value Representation
Digital
Measured-Value Representation as Twos Complement
Measured-Value Representation as Value and Sign
Bit 212 is interpreted as the sign
Ohm 10 units
Measured-Value
Representation for
Resistance Thermometers Standard Pt Range
Units Pt 100/ohms
Current Measuring Ranges from 4 to
20 mA
Current Limiting
6ES5 460-4UA13 Analog Input Module
Analog Input/Output Modules
Mode
Labeling of switches on the module cover
Range
Analog Input/Output Modules
Assignmentstransducer
ADU
463 Analog Input Module Design
12 Analog Input Module
Timeout QVZ occurs in the CC
Switching off the Enable Input
Power Supply Load Power Supply
10000 ∝F/40V
Special Features of the 463 Analog Input Module
Switches should be switched off
Module with 4 inputs therefore reserves 8 byte addresses
Channel number
Module, is given by
On Setting Switch Pressed 128
Removing and Inserting Modules
Module
16 Marking and Labeling of Modules
Connecting the Signal Lines
Representation as Value and Sign
Shunt Resistor
Load Voltage
6ES5 463-4UA12 and 6ES5 463-4UB12 Analog Input Modules
Setting the Data Format for the 4 to 20 mA Range
Connecting Transducers
Front Connector Assignments
465 Analog Input Module Design
18 Analog Input Module
Enable Jumper
Configuring
10000 ∝F/40V
Special Features of the 465 Analog Input Module
Is set
Selective Sampling
To AUX Flag
20 Labeling of the Addressing Switch
Inputs or outputs reserves 32 byte addresses
Example
Addressing for
Removing and Inserting Modules
21 Module with Front Connector
22 Marking and Labeling of Modules
Rated Voltage Ule To 60 V DC Mm Operation With fan 40 mm
23 Connecting a Compensating Box
Analog Input/Output Modules
Connecting a Pt
Module Reaction, Encoded Value Error Bit E
Broken Wire Signal for Resistance Thermometers
Broken Wire at
Channel and the value 0 would be encoded
Connecting Transducers
Measured-Value Representation
Measured-Value Representation as Value and Sign
Ohm 10 units
Pt 100 Resistance Thermometers
Short-circuit with two
6ES5 465-4UA12 Analog Input Module
Analog Input/Output Modules
Mode
Mode 50 mV 50 mV 100 mV 1 V 2 mA 500 mV ±
25 Front Connector Assignments
Special Features of the 466 Analog Input Module
Switches on the board
466 Analog Input Module Design
Individual Channel
Current/Voltage
Measurement for
Groups
Channel Group III Channels 8 to
Switch S5
Switch S7
Channel Group IV Channels 12 to
Range
20 mA $ 20 mA $ 1.25 $ 2.5 $ 5 $ 10
Data Format
Setting the Data Format
S9 Switch Setting
Twos complement Value and sign Binary
Setting the Module Start Address
466-3LA11 Module
Module Address
Removing and Inserting Modules
28 Module with Front Connector
29 Marking and Labeling of Modules
Connecting the Signal Lines
Connecting Sensors to the 466 Analog Input Module
Compensates for the interference acting on both lines
Differential
Measurement
Jumper between M+ and M
UCM2
Range exceeded Broken wire Not used
OV Overflow bit Error bit Active bit
Signal Status Meaning
Measured-Value Representation with Various Ranges
Measuring Range 20 mA, 0-5 V Unipolar
Twos Complement Measuring Range 20 mA Bipolar
Binary measuring range $ 5 V, $ 20 mA and $ 10 V bipolar
Measuring range 0-1.25 V and 0-2.5 V unipolar
Value and sign measuring range $ 1.25 V and $ 2.5 V bipolar
Binary measuring range $ 1.25 V and $ 2.5 V bipolar
6ES5 466-3LA11 Analog Input Modules
Analog Input/Output Modules
Voltage-to-ground measurement Differential measurement
Front Strip Pin
470 Analog Output Module Design
Module address
35 Enable Input and Enable Jumper
Configuring
Load Power Supply System Manual
Function Block
Special Features of the 470 Analog Output Module
Output, a value is retained
Function block from the ªbasic functionsº package
Start Address
Addressing for
Removing and Inserting Modules
37 Module with Front Connector
Remove an analog output module as follows
4 1 5
Connecting the Signal Lines
Connecting Loads to the 470 Analog Output Module
Voltage Outputs
41 Connecting Loads
Digital Measured-Value Representation as Twos Complement
Technical Specifications
42 Front Connector Assignments
470-4UB 470-4UA 470-4UC
System Manual C79000-G8576-C199-06
Monitoring Module
Monitoring Module
Mode of Operation Block Diagram Address bus
Data bus
Faults
Fault Detection
Data Bus Faults
Address Bus
Resetting
Control Line
Messages
Installation Possible Configurations
Removing and Inserting
Connecting the Reset Input
Switch Positions of the Relay Contact
Installation Guidelines
Write
Acknowl- edged by module with RDY
10-9
Addressing
1st MM 2nd MM 3rd MM Last EU
Without S5-DOS With S5-DOS
S5-115U 128 80H 129 81H 213 D5H 170
213 D5H 170
128 129 213 170
Setting the Address Switches S1, S2, S3, S4
Setting the Switch S5
Sensor supply for Reset input
Power supply
Reset input
Safety test
Ambient conditions
Address Table
Connector Assignments
Back- plane conn
M24 V P24 P15
11-3
Pin designation of the interrupt signals on the backplane
11-5
Connector assignments of the backplane for the EU 185U
Backplane conn
11-7
11-8
5V/18A power supply units
Connector assignments of the power supply units
Connector
5V/40A power supply units
Terminals of the supply lines between the power supply unit
Plug connector, 37-way, Series D to MIL-C24308
Contacts, Series D to MIL-C24308
Assignments of the backplane connector CPU
Assignments of the backplane connector CPU 928B
Pin Pin Row + 5
Steu Stoppa M 5 V R x D Pero M 24 V M 5
Assignments of the backplane connectorCPU
11-14
11-15
Assignments of the backplane connector 923A coordinator
Memw RDY DB 0 DB 1 DB 2 DB 3 DB 4 DB 5 DB 6 DB
Assignments of the backplane connector 923C coordinator
RxD TxD
11-18
Assignments of the backplane connectors of the IMs
+5V DB12
+5V Shield
+5V
DB13
11-21
Assignments of the front blade connectors
+ PEU ± PEU
11-23
System Manual C79000-G8576-C199-06
Appendix
For Chapter
Central Controllers
Expansion Units
Power Supply Units
WKF RZF
Bbytes 6ES5 376-0AA11 6ES5 376-0AA21 6ES5 376-0AA31
CPUs
Memory Cards
Interface Submodules
Coordinators
Interface Modules
Front Connectors
Digital Input/Output Modules Adhesive Label
Analog Input/Output Modules
6ES5 460-4UA13 6ES5 465-4UA12
Features
Range Cards Modules
Range Card
Programmable Controllers
Catalog ST
Programmers
C79000-G8576-C140 6ES5 998-2EA21
Chapter Overview
What is ESD?
Definition
To overvoltages and thus to any electrostatic discharge
Its surroundings can be charged electrostatically
Electrostatic Charging of Persons
Charging
IEC
Ensure Sufficient
Avoid Direct
Contact
Index
Index
Index-3
Index-4
Index-5
Index-6
Index-7
System Manual C79000-G8576-C199-06
System Manual 6ES5998-0SH21-06
System Manual