6.4 Basic Traffic Rule Types
Multihoming
Multihoming is a term used for situations when one network interface connected to the Internet uses multiple public IP addresses. Typically, multiple services are available through individual IP addresses (this implies that the services are mutually independent).
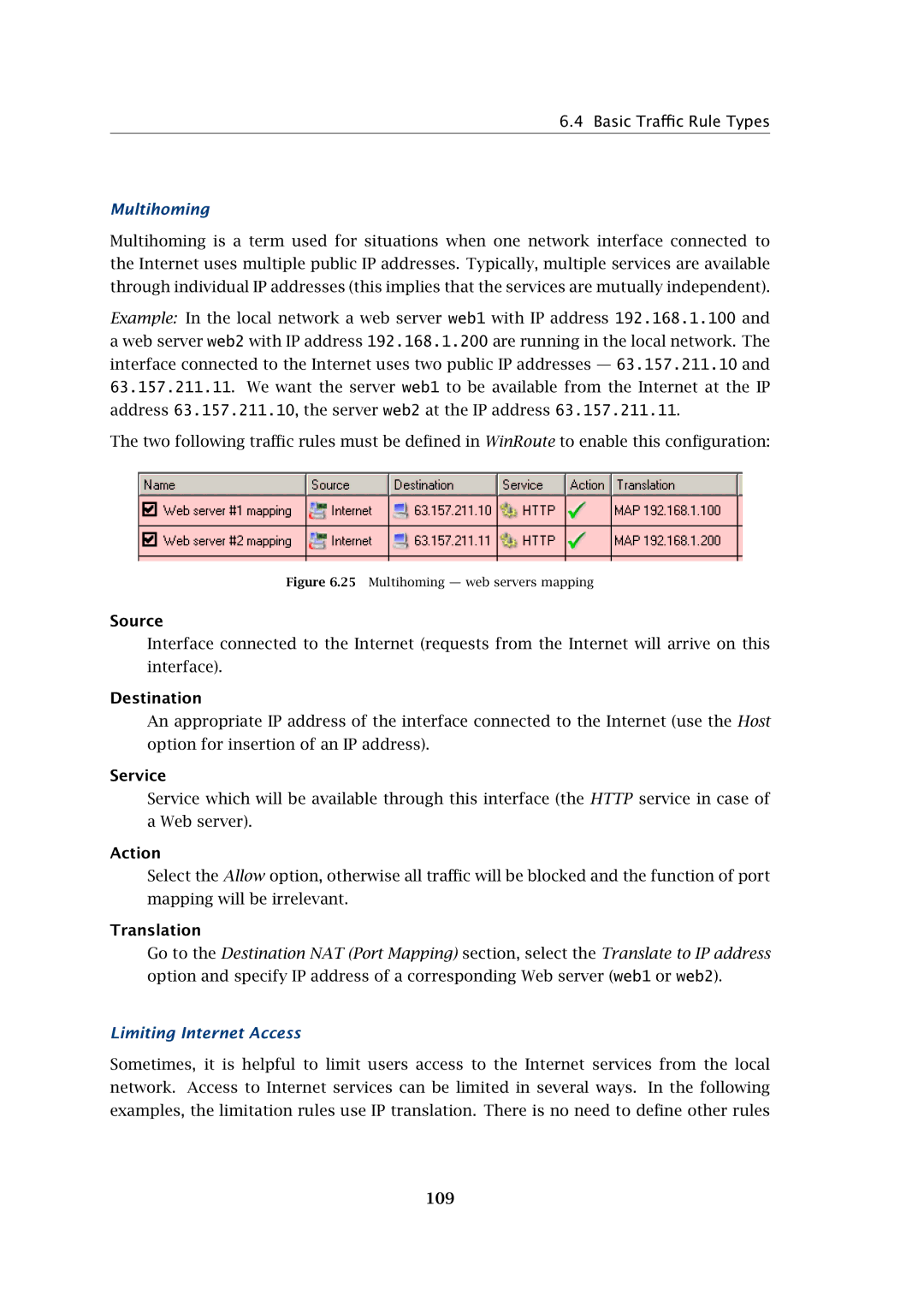
Example: In the local network a web server web1 with IP address 192.168.1.100 and a web server web2 with IP address 192.168.1.200 are running in the local network. The interface connected to the Internet uses two public IP addresses — 63.157.211.10 and 63.157.211.11. We want the server web1 to be available from the Internet at the IP address 63.157.211.10, the server web2 at the IP address 63.157.211.11.
The two following traffic rules must be defined in WinRoute to enable this configuration:
Figure 6.25 Multihoming — web servers mapping
Source
Interface connected to the Internet (requests from the Internet will arrive on this interface).
Destination
An appropriate IP address of the interface connected to the Internet (use the Host option for insertion of an IP address).
Service
Service which will be available through this interface (the HTTP service in case of a Web server).
Action
Select the Allow option, otherwise all traffic will be blocked and the function of port mapping will be irrelevant.
Translation
Go to the Destination NAT (Port Mapping) section, select the Translate to IP address option and specify IP address of a corresponding Web server (web1 or web2).
Limiting Internet Access
Sometimes, it is helpful to limit users access to the Internet services from the local network. Access to Internet services can be limited in several ways. In the following examples, the limitation rules use IP translation. There is no need to define other rules