Using the BayStack 450 10/100/1000 Series Switch
Spanning Tree Considerations for MultiLink Trunks
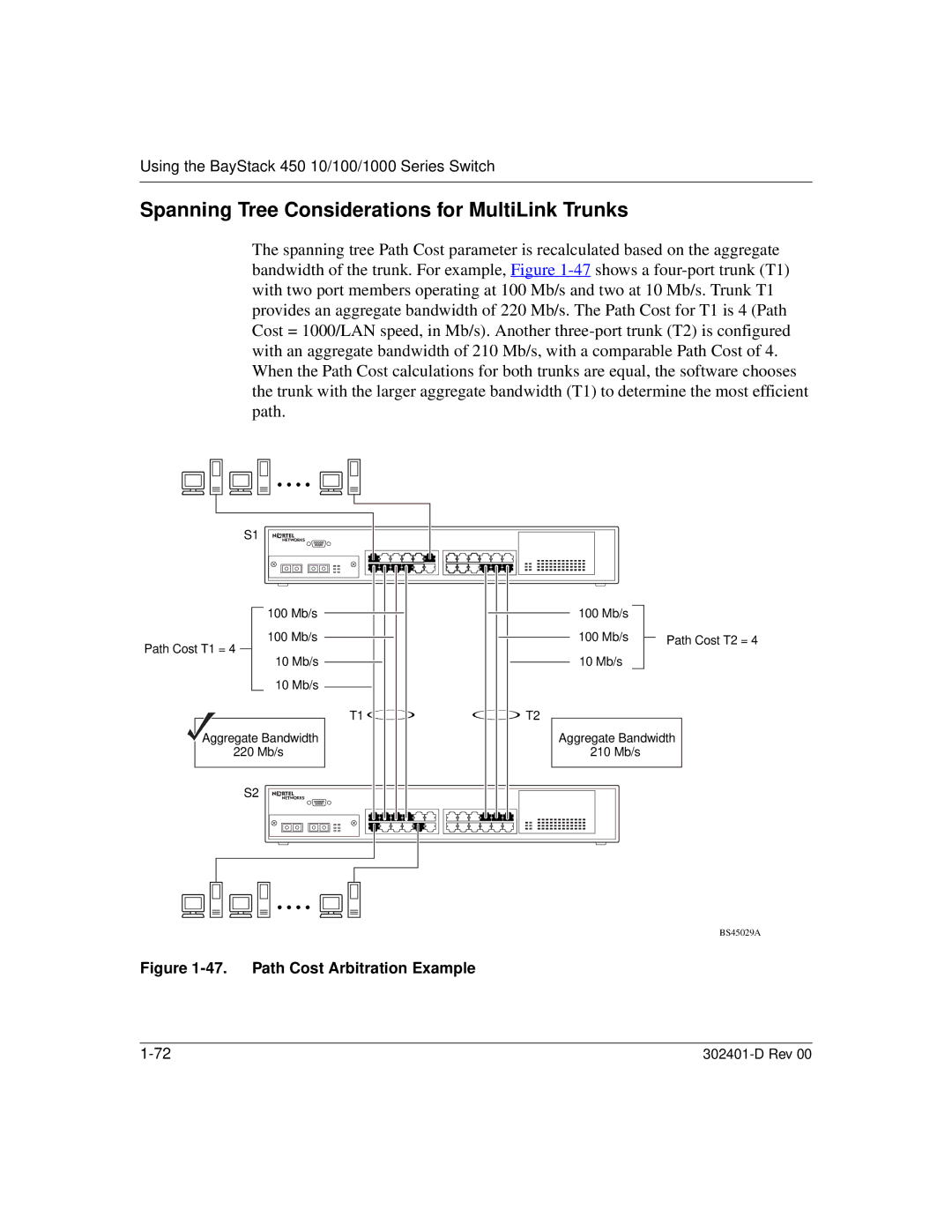
The spanning tree Path Cost parameter is recalculated based on the aggregate bandwidth of the trunk. For example, Figure
S1 |
|
|
100 Mb/s | 100 Mb/s |
|
100 Mb/s | 100 Mb/s | Path Cost T2 = 4 |
Path Cost T1 = 4 |
| |
|
| |
10 Mb/s | 10 Mb/s |
|
10 Mb/s |
|
|
T1 | T2 |
|
Aggregate Bandwidth | Aggregate Bandwidth | |
220 Mb/s | 210 Mb/s |
|
S2 |
|
|
|
| BS45029A |