Chapter 5: System Configuration
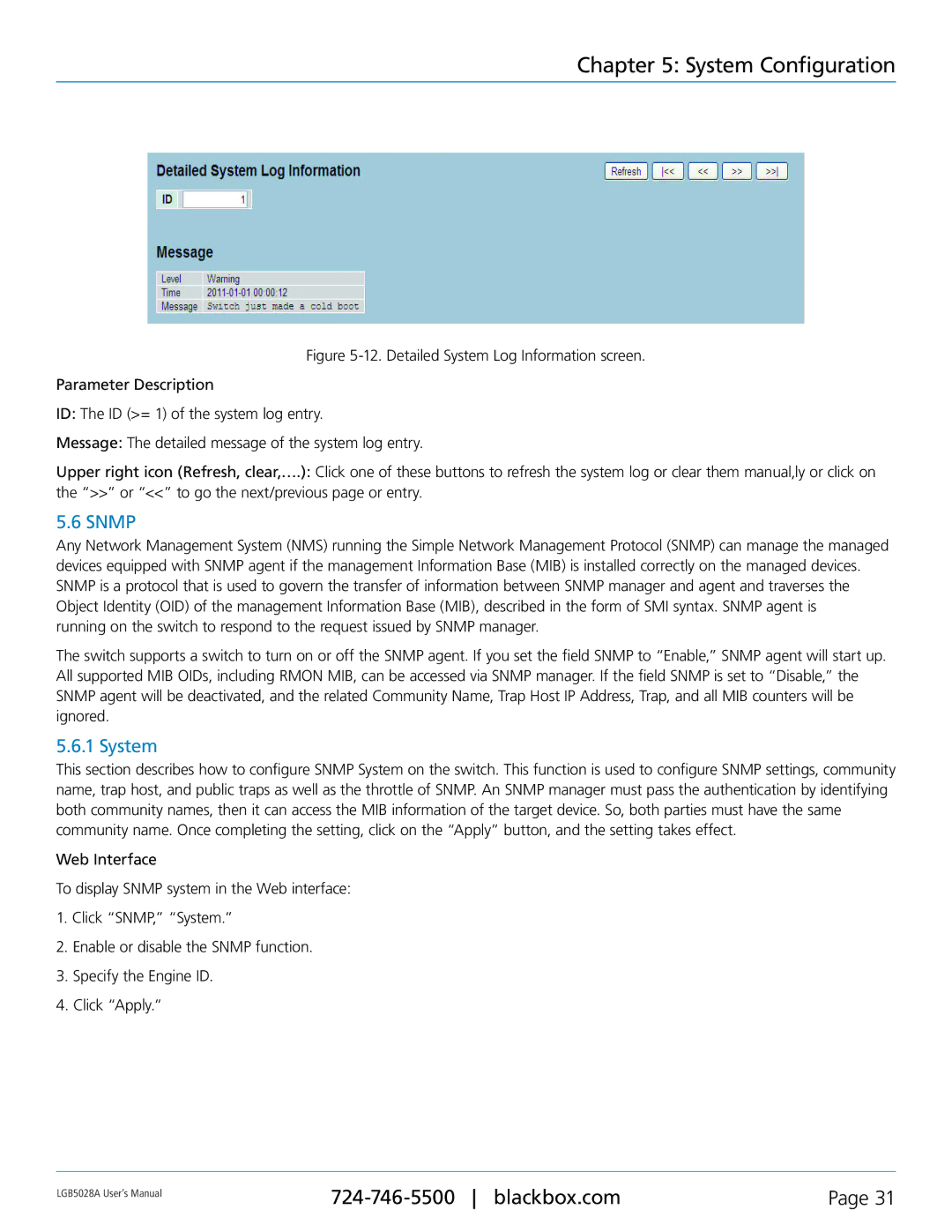
Figure 5-12. Detailed System Log Information screen.
Parameter Description
ID: The ID (>= 1) of the system log entry.
Message: The detailed message of the system log entry.
Upper right icon (Refresh, clear,….): Click one of these buttons to refresh the system log or clear them manual,ly or click on
the “>>” or “<<” to go the next/previous page or entry.
5.6 SNMP
Any Network Management System (NMS) running the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) can manage the managed devices equipped with SNMP agent if the management Information Base (MIB) is installed correctly on the managed devices. SNMP is a protocol that is used to govern the transfer of information between SNMP manager and agent and traverses the Object Identity (OID) of the management Information Base (MIB), described in the form of SMI syntax. SNMP agent is running on the switch to respond to the request issued by SNMP manager.
The switch supports a switch to turn on or off the SNMP agent. If you set the field SNMP to “Enable,” SNMP agent will start up. All supported MIB OIDs, including RMON MIB, can be accessed via SNMP manager. If the field SNMP is set to “Disable,” the SNMP agent will be deactivated, and the related Community Name, Trap Host IP Address, Trap, and all MIB counters will be ignored.
5.6.1 System
This section describes how to configure SNMP System on the switch. This function is used to configure SNMP settings, community name, trap host, and public traps as well as the throttle of SNMP. An SNMP manager must pass the authentication by identifying both community names, then it can access the MIB information of the target device. So, both parties must have the same community name. Once completing the setting, click on the “Apply” button, and the setting takes effect.
Web Interface
To display SNMP system in the Web interface:
1.Click “SNMP,” “System.”
2.Enable or disable the SNMP function.
3.Specify the Engine ID.
4.Click “Apply.”
LGB5028A User‘s Manual | Page 31 | |
|
|