Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
MC68340
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
CPU32
Preface
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Section Bus Operation
15.4
Section System Integration Module
Section U 3
Pipeline Synchronization with the NOP Instruction
3.1 Types of Faults 3.1.1 Type I-Released Write Faults 3.1.2
2.4 Command Execution 2.5
Section DMA Controller Module
Section Serial Module
OP1
Rtsa
OP0
Rtsb
1.4 Clock Selection Logic
Section Timer Modules
Section Applications
Section Ieee 1149.1 Test Access Port
Table of Contents Concluded
List of Illustrations
List of Illustrations
External and Internal Interface Signals
10-1 Minimum System Configuration Block Diagram 10-2
Xxi
List of Illustrations Concluded
B l e
List of Tables
List of Tables
Section Device Overview
M68300 Family
Central Processor Unit
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Organization
Advantages
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 1 CPU32
Background Debug Mode
System Integration Module
ON-CHIP Peripherals
6MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Serial Module
Direct Memory Access Module
Power Consumption Management
Timer Modules
Compact DISC-INTERACTIVE
Physical
Document Number Document Name
More Information
Section Signal Descriptions
Input
Signal Index
Signal Index
Signal Name Mnemonic Function Output
CTSA, Ctsb
Data BUS D15-D0
Address BUS
Address Bus A23-A0
Address Bus A31-A24
Function Code Bits Address Spaces
Function Codes FC3-FC0
Chip Selects CS3-CS0
Address Space Encoding
Address Strobe AS
BUS Control Signals
Interrupt Request Level IRQ7, IRQ6, IRQ5, IRQ3
Data and Size Acknowledge DSACK1, DSACK0
BUS Arbitration Signals
Clock Signals
Exception Control Signals
Instrumentation and Emulation Signals
DMA Module Signals
Serial Module Signals
Timer Output TOUT2, TOUT1
Timer Signals
Timer Gate TGATE2, TGATE1
Timer Input TIN2, TIN1
Signal Summary
Test Signals
Synthesizer Power Vccsyn
System Power and Ground VCC and GND
Signal Name Mnemonic Input/Output Active State
Signal Summary
DACK2, DACK1
Section BUS Operation
BUS Transfer Signals
Input Sample Window
Bus Control Signals
Function Code Signals
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Address Bus A31-A0
Bus Cycle Termination Signals
Dynamic Bus Sizing
Data Transfer Mechanism
6MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Operand Transfer Cases
Misaligned Operands
OP0 Data BUS
OP0 OP1 Data BUS
Semiconductor
Long-Word Operand Read Timing from 8-Bit Port
Long-Word Operand Write Timing to 8-Bit Port
Long-Word and Word Read and Write Timing-16-Bit Port
Synchronous Operation with DSACK≈
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Bus Operation
Fast Termination Timing
Fast Termination Cycles
Read Cycle
Data Transfer Cycles
MOTOROLAMC68340 USER’S MANUAL3
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Write Cycle
Word Write Cycle Flowchart
Read-Modify-Write Cycle Timing
Read-Modify-Write Cycle
20MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
10. CPU Space Address Encoding
CPU Space Cycles
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Breakpoint Acknowledge Cycle
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Lpstop Broadcast Cycle
11. Breakpoint Operation Flowchart
12. Breakpoint Acknowledge Cycle Timing Opcode Returned
13. Breakpoint Acknowledge Cycle Timing Exception Signaled
Interrupt Acknowledge Bus Cycles
14. Interrupt Acknowledge Cycle Flowchart
FC3-FC0 CPU Space SIZ0 Byte SIZ1
30MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
16. Autovector Operation Timing
BUS Exception Control Cycles
Control
Signal Result
DSACK≈, BERR, and Halt Assertion Results
Asserted on Rising Edge of State
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Bus Errors
17. Bus Error without DSACK≈
Retry Operation
18. Late Bus Error with DSACK≈
19. Retry Sequence
20. Late Retry Sequence
Halt Operation
21. Halt Timing
Double Bus Fault
BUS Arbitration
22. Bus Arbitration Flowchart for Single Request
23. Bus Arbitration Timing Diagram-Idle Bus Case
Bus Grant Acknowledge
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Bus Request
Bus Grant
Show Cycles
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Bus Arbitration Control
25. Bus Arbitration State Diagram
26. Show Cycle Timing Diagram
Reset Operation
Semiconductor
28. Power-Up Reset Timing Diagram
Module Overview
Section System Integration Module
Module Base Address Register Operation
Module Operation
SIM40 Module Register Block
System Configuration and Protection Operation
4MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
System Configuration and Protection Function
6MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Software Watchdog Block Diagram
Periodic interrupt timer period Pitr count value
Operating
Mode Description
Clock Synthesizer Operation
Clock Operating Modes
Clock Block Diagram for Crystal Operation
Clock Block Diagram for External Oscillator Operation
Fvco = Fsystem
= 0 X = = 1 X =
Clock Control Signals
Chip Select Operation
System Frequencies from 32.768-kHz Reference
14MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Port a Pin Assignment Register
Pin Function Signal PPARA1 = PPARA2 =
External Bus Interface Operation
Pparb =
Pin Function Signal Firq =
Freeze
Low-Power Stop
Programming Model
SIM40 Programming Model
Mbar
MCR
System Configuration and Protection Registers
SHEN1 SHEN0 Action
SHENx Control Bits
RSR
See 4.2.2.5 Software Watchdog for more information
Swiv
Sypcr
MHz External
Deriving Software Watchdog Timeout
Software Timeout Period Crystal Period Clock Period
For more information see 4.2.2.2 Internal Bus Monitor
Interrupts by Sources in the SIM40 for the servicing order
BMTx Encoding
Picr
Pirql Encoding
Pitr
Syncr
Clock Synthesizer Control Register Syncr
Chip Select Registers
Base Address $046, $04E, $056, $05E
Address Mask $042, $04A, $052, $05A
Mode
10. DDx Encoding
11. PSx Encoding
Response
External Bus Interface Control
Porta
PORTB, PORTB1
$01F
Startup
2 SIM40 Module Configuration
MC68340 Initialization Sequence
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
MCR EQU
Sspinit EQU
Mbar EQU
Modbase EQU $FFFFF000
MOVES.L D0,MBAR
MOVEQ.L
MOVEC.L D0,DFC
MOVE.L #MODBASE+1,D0
END
CSAM0$ DC.L $0001FFFD
Overview
Section CPU32
Virtual Memory
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Features
CPU32 Block Diagram
Loop Mode Instruction Execution
Exception Handling
Vector Base Register
CAS, CAS2
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Addressing Modes
Instruction Set
BFFFO, BFINS, BFSET, Bftst
Mnemonic Description
Instruction Set
Privilege States
Processing States
Programming Model
Architecture Summary
User Programming Model
Status Register
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Registers
1 M68000 Family Compatibility
Instruction SET
Instruction Word General Format
Instruction Format and Notation
Example d 16 is a 16-bit displacement
DFC
CCR
SSP
USP
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Instruction Summary
Opcode Operation Syntax
Instruction Set Summary
Extb Llegal
Opcode Operation
Source ⇒ Destination Movep Dx,d,Ay Movep d,Ay,Dx
ROXL,ROXR
Instruction Set Summary Concluded
Operations Special Definition
Condition Code Computations
Instruction Syntax
Data Movement Operations
22MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
DIVS/DIVU
Integer Arithmetic Operations
Logic Operations
Bit Manipulation Operations
Shift and Rotate Operations
Unconditional
Binary-Coded Decimal Operations
10. Program Control Operations
Conditional
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Condition Code Register
11. System Control Operations
Privileged
Trap Generating
Mnemonic Condition Encoding
Using the TBL Instructions
12. Condition Tests
Entry Number Value
13. Standard Usage Entries
Table Example 2 Compressed TABLE. In Example 2 see -8,
14. Compressed Table Entries
Subroutine Instruction
Table Example 15 -Bit Independent Variable Entries
Following value has been calculated for independent variable
Summing, the following result is obtained
Processing States
Nested Subroutine Calls
Pipeline Synchronization with the NOP Instruction
Privilege Levels
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc State Transitions
Exception Processing
Assignment
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Exception Vectors
16. Exception Vector Assignments
Vector Number Dec Hex
40MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
10. Exception Stack Frame
17. Exception Priority Groups
Group Exception Priority Relative Priority Reset
Characteristics
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
11. Reset Operation Flowchart
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
46MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Move USP Movec Moves
Reset RTE Stop
Lpstop
Tracing Function
18. Tracing Control
50MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Fault Recovery
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
54MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
SIZ Func
56MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
58MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
12. Format $0-Four-Word Stack Frame
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 4 CPU32 Stack Frames
14. Internal Transfer Count Register
15. Format $C-BERR Stack for Prefetches and Operands
1 CPU32 Integrated Development Support
Development Support
18. In-Circuit Emulator Configuration
20. BDM Block Diagram
19. BDM Source Summary
Source BDM Enabled BDM Disabled
Atemp
20. Polling the BDM Entry Source
Freescale
Encoding Data Message Type
21. CPU Generated Message Encoding
22. Debug Serial I/O Block Diagram
23. Serial Interface Timing Diagram
25. Bkpt Timing for Forcing BDM
24. Bkpt Timing for Single Bus Cycle
Encoding Operand Size
BDM
22. Size Field Encoding
74MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
27. Command-Sequence Diagram
Command
23. BDM Command Summary
WDREG/WAREG
System Register Select Code
24. Register Field for Rsreg and Wsreg
MS Addr
Operand Data
Dump Long
82MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Write Memory Location XXX Not Ready Next CMD CMD Complete
84MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Chkstat MOVE.B SRA,D0
Command Format Command Sequence
28. Functional Model of Instruction Pipeline
Deterministic Opcode Tracking
29. Instruction Pipeline Timing Diagram
Resource Scheduling
Instruction Execution Timing
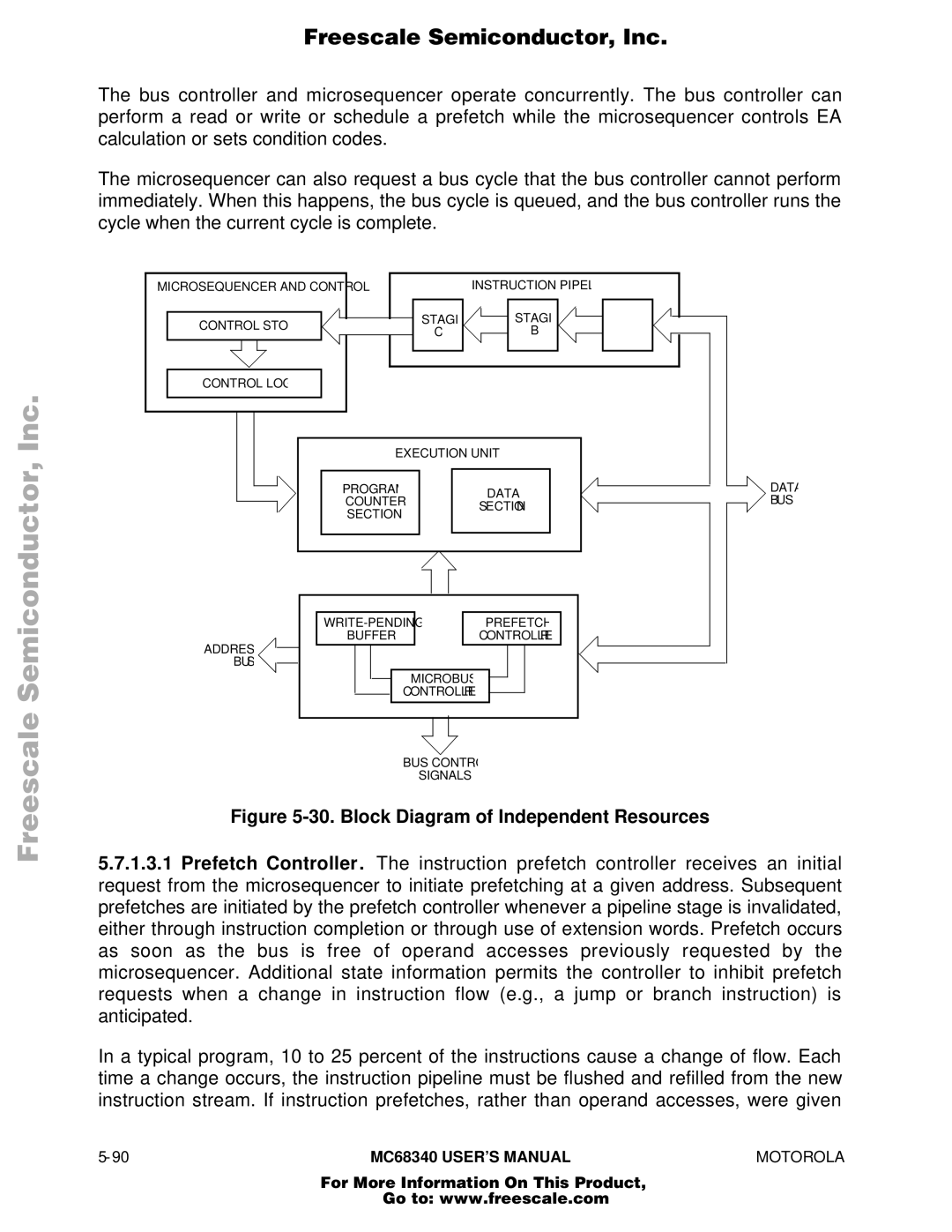
30. Block Diagram of Independent Resources
31. Simultaneous Instruction Execution
32. Attributed Instruction Times
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Instructions
Instruction Stream Timing Examples
33. Example 1-Instruction Stream
BRA.W Faraway MOVE.L
35. Example 2-Branch Not Taken
Instruction Timing Tables
98MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Instruction Head Tail Cycles
100MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Head Tail Cycles
102MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
DIVU.W
104MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
#, Dn 20/1/0
106MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
〈CEA 〉 40/1/x
Clocks Shift Counts
#, Dn 60/2/0
110MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
BSR.B BSR.W BSR.L CHK
112MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Berr on instruction
Section DMA Controller Module
DMA Module Overview
Single-Address Transfers
Transfer Request Generation
DMA Module Signal Definitions
External Request Generation
Data Transfer Modes
Single-Address Mode
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Single-Address Read Timing External Burst
Single-Address Read Timing Cycle Steal
Single-Address Write Timing External Burst
Single-Address Write Timing Cycle Steal
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Dual-Address Mode
Dual-Address Read Timing External Burst-Source Requesting
10. Dual-Address Read Timing Cycle Steal-Source Requesting
MOTOROLAMC68340 USER’S MANUAL6
Inc
CPU Cycle DMA Read
Channel Initialization and Startup
DMA Channel Operation
Data Transfers
Channel Termination
13. Fast Termination Option Cycle Steal
14. Fast Termination Option External Burst-Source Requesting
Register Description
15. DMA Module Programming Model
Module Configuration Register MCR
Action
MCR1, MCR2
FRZx Control Bits
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
INTR1, INTR2
Interrupt Register Intr
Channel Control Register CCR
CCR1, CCR2
Bit Definition
SSIZEx Encoding
REQ Field BB Field Bus Bandwidth Bit Definition
DSIZEx Encoding
REQx Encoding
BBx Encoding and Bus Bandwidth
CSR1, CSR2
Channel Status Register CSR
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
FCR1, FCR2
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Function Code Register FCR
SAR1, SAR2
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Source Address Register SAR
Destination Address Register DAR
BTC1, BTC2
Byte Transfer Counter Register BTC
DAR1, DAR2
16. Packing and Unpacking of Operands
Data Packing
DMA Channel Initialization Sequence
DMA Channel Configuration
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
DMAMCR1 EQU
DMA Channel Example Configuration Code
DMACH1 EQU
DMAFCR1 EQU
DMAINT1 EQU
DMACCR1 EQU
DMACSR1 EQU
LEA
Daradd EQU
MOVE.W #$0E8D,DMACCR1A0 END
MOVE.B #$DD,DMAFCR1A0
MOVE.L DARADD,DMADAR1A0
MOVE.W
Modbase EQU
MOVE.W #$068D,DMACCR1A0 END
$6001 Source address is an ODD address
MOVE.W #$1DB1,DMACCR1A0 END
Section Serial Module
Local Loopback -Remote Loopback
Interrupt Control Logic
Baud Rate Generator Logic
Internal Channel Control Logic
Comparison of Serial Module to MC68681
Serial Module Signal Definitions
Crystal Output
Crystal Input or External Clock
Channel B Transmitter Serial Data Output TxDB
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc External Input Sclk
Channel a Transmitter Serial Data Output TxDA
Channel a Receiver Serial Data Input RxDA
Channel a Receiver Ready R≈RDYA
Channel a Clear-To-Send Ctsa
Channel B Clear-To-Send Ctsb
Channel a Transmitter Ready T≈RDYA
Transmitter and Receiver Operating Modes
Operation
Baud Rate Generator
Transmitter and Receiver Functional Diagram
Transmitter Timing Diagram
MOTOROLAMC68340 USER’S MANUAL7
Receiver Timing Diagram
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Looping Modes
Looping Modes Functional Diagram
Multidrop Mode
Multidrop Mode Timing Diagram
Register Description
Register Description and Programming
18MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Serial Module Programming Model
Freeze
ILR
MR1A, MR1B
IVR
PMx and PT Control Bits
Parity Mode Parity Type
SRA, SRB
B/Cx Control Bits
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Set
CSRA, Csrb
RCSx Control Bits
CRA, CRB
TCSx Control Bits
MISC3 MISC2 MISC1 MISC0
MISCx Control Bits
TCx Control Bits
RBA, RBB
RCx Control Bits
Ipcr
TBA, TBB
ISR
ACR
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
IER
$71D
Opcr
Bit Set
Bit Reset
CMx Control Bits
MR2A, MR2B
Length 6-8 Bits Length 5 Bits
10. SBx Control Bits
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Programming
10. Serial Module Programming Flowchart 1
10. Serial Module Programming Flowchart 2
10. Serial Module Programming Flowchart 3
10. Serial Module Programming Flowchart 4
10. Serial Module Programming Flowchart 5
Serial Module Initialization Sequence
Serial Module Configuration
Mcrl EQU
Serial Module Example Configuration Code
Serial EQU
Mcrh EQU
Mode Register MOVE.B
Wait for Transmitter Empty or Timeout MOVE.W
Negate Rtsa Signal Output MOVE.B
Reset RECEIVER/TRANSMITTER MOVE.B
MOVE.B #$BB,CSRAA0
Mode Register
SET UP Baud Rate for Port in Clock Select Register
Enable Port
Section Timer Modules
Timer and Counter Functions
Internal Control Logic
Timer Functional Diagram
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Interrupt Control Logic
Timer Modules Signal Definitions
Timer Input TIN1, TIN2
Input Capture/Output Compare
Timer Gate TGATE1, TGATE2
Timer Output TOUT1, TOUT2
Operating Modes
TGATE≈
Square-Wave Generator
Square-Wave Generator Mode
Variable Duty-Cycle Square-Wave Generator
Variable-Width Single-Shot Pulse Generator
Variable Duty-Cycle Square-Wave Generator Mode
Variable-Width Single-Shot Pulse Generator Mode
Pulse-Width Measurement
Pulse-Width Measurement Mode
Period Measurement
Event Count
Period Measurement Mode
10. Event Count Mode
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Timer Bypass
OC1 OC0 TOUTx
OCx Encoding
11. Timer Module Programming Model
FRZ1 FRZ0 Action
Control Register CR
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc Interrupt Register IR
IEx Encoding
Enabled Interrupts
Division
TOUTx Mode
POT Encoding
MODEx Encoding
Status Register SR
24MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Cntr
Counter Register Cntr
Preload 1 Register PREL1
PREL2
Preload 2 Register PREL2
Compare Register COM
PREL1
Timer Module Configuration
Timer Module Initialization Sequence
Timer Module Example Configuration Code
CLR.W COM1A0
BEQ.B LOOP2
BNE.B LOOP1
MOVE.W CNTR1A0,D0 NOT.W D0 ADDQ.W #$1,DO
BEQ.B LOOP3
Non-IEEE 1149.1 Operation for details
Section Ieee 1149.1 Test Access Port
TAP Controller
Test Access Port Block Diagram
TAP Controller State Machine
Boundary Scan Register
Name Bit Number
Boundary Scan Control Bits
Type CTL Cell Num Cell Type
Boundary Scan Bit Definitions
Pin/Cell Output
Pin/Cell Output Num Cell Type
Ipipe
Pin/Cell Output Bit Num Cell Type
Freescale Semiconductor
Active-High Output Control Cell IO.Ctl1
Bidirectional Data Cell IO.Cell
Instruction Register
Code Instruction
Extest
SAMPLE/PRELOAD
MC68340 Restrictions
Bypass X1X
HI-Z
NON-IEEE 1149.1 Operation
Processor Clock Circuitry
Minimum System Configuration
Sample Crystal Circuit
Sram Interface
Reset Circuitry
Serial Interface
ROM Interface
Memory Interface Information
Using an 8-Bit Boot ROM
Bit Boot ROM Timing
Access Time Calculations
Access Time
Calculating Frequency-Adjusted Output
Memory Access Times at 16.78 MHz
12. Signal Width Specifications
13. Skew between Two Outputs
CD-I, CD-ROM
Power Consumption Considerations
15. MC68340 Current vs. Activity at 5
16. MC68340 Current vs. Voltage/Temperature
Advantage Benefit
Typical Electrical Characteristics
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 10.3.2 MC68340V 3.3
Parameter
Maximum Ratings
Thermal Characteristics
Rating Symbol Value Unit
Characteristic Symbol Value Unit
PI/O
Power Considerations
AC Electrical Specification Definitions
Pint + PI/O
MOTOROLAMC68340 USER’S MANUAL11-3
Drive Levels and Test Points for AC Specifications
CLKOUT, FREEZE, IPIPE, Ifetch
Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit
11-6MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
MOTOROLAMC68340 USER’S MANUAL11-7
39 MHz 16.78 MHz 25.16 MHz Symbol Min Max Unit
Num.Characteristic
25.16 MHz Num Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc AC Timing Specifications
39 MHz 16.78 MHz
Num Characteristic Symbol Min Max
Read Cycle Timing Diagram
Write Cycle Timing Diagram
Fast Termination Read Cycle Timing Diagram
Fast Termination Write Cycle Timing Diagram
Bus Arbitation Timing-Active Bus Case
Bus Arbitration Timing-Idle Bus Case
Iack Cycle Timing Diagram
10. Background Debug Mode Serial Port Timing
Or 5.0 39 MHz
25.16 MHz Num Characteristic Min Max
Min Max Unit
13. Timer Module Clock Signal Timing Diagram
Freescale
15. Serial Module General Timing Diagram
16. Serial Module Asynchronous Mode Timing
19. Test Clock Input Timing Diagram
20. Boundary Scan Timing Diagram
Standard MC68340 Ordering Information
Section Ordering Information and Mechanical Data
12-2MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
VCC GND
Pin Group FE Suffix
12-4MC68340 USER’S Manualmotorola
Pin Group RP Suffix
12-6
DIM MIN MAX
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc RP Suffix
D E
CTS
Dsack
Index-4
USER’S Manual
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Motorola MC68340 USER’S Manual
Index-8
Index-9