Configuring the RAID Controller
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Devices) options are available for your system, providing added security and high availability.
If you order a system with a RAID controller, the system is
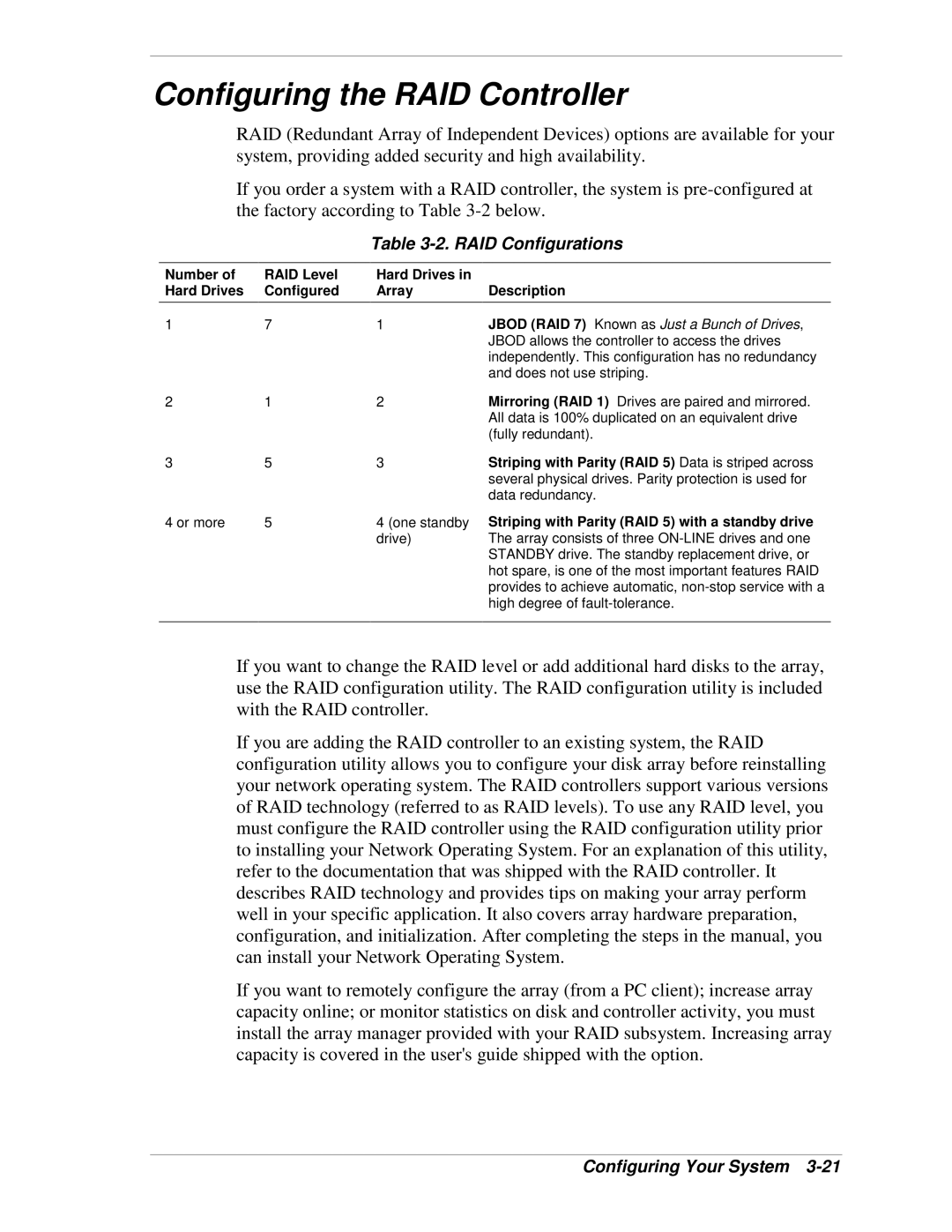
Table 3-2. RAID Configurations
Number of | RAID Level | Hard Drives in |
|
Hard Drives | Configured | Array | Description |
1 | 7 | 1 | JBOD (RAID 7) Known as Just a Bunch of Drives, |
|
|
| JBOD allows the controller to access the drives |
|
|
| independently. This configuration has no redundancy |
|
|
| and does not use striping. |
2 | 1 | 2 | Mirroring (RAID 1) Drives are paired and mirrored. |
|
|
| All data is 100% duplicated on an equivalent drive |
|
|
| (fully redundant). |
3 | 5 | 3 | Striping with Parity (RAID 5) Data is striped across |
|
|
| several physical drives. Parity protection is used for |
|
|
| data redundancy. |
4 or more | 5 | 4 (one standby Striping with Parity (RAID 5) with a standby drive | |
|
| drive) | The array consists of three |
|
|
| STANDBY drive. The standby replacement drive, or |
hot spare, is one of the most important features RAID provides to achieve automatic,
If you want to change the RAID level or add additional hard disks to the array, use the RAID configuration utility. The RAID configuration utility is included with the RAID controller.
If you are adding the RAID controller to an existing system, the RAID configuration utility allows you to configure your disk array before reinstalling your network operating system. The RAID controllers support various versions of RAID technology (referred to as RAID levels). To use any RAID level, you must configure the RAID controller using the RAID configuration utility prior to installing your Network Operating System. For an explanation of this utility, refer to the documentation that was shipped with the RAID controller. It describes RAID technology and provides tips on making your array perform well in your specific application. It also covers array hardware preparation, configuration, and initialization. After completing the steps in the manual, you can install your Network Operating System.
If you want to remotely configure the array (from a PC client); increase array capacity online; or monitor statistics on disk and controller activity, you must install the array manager provided with your RAID subsystem. Increasing array capacity is covered in the user's guide shipped with the option.