STUDIO3511/4511
Toshiba TEC Corporation
Service of Machines
General Precautions Regarding the Installation
Main Service Parts for Safety
Contents
Control circuit for the exposure lamp
Control Panel
10-1
10.1
10.2
10-5
12-1
12.1
12.2
12.3
15-1
15.1
15.2
15.3
STUDIO3511/4511 Contents November 2003 Toshiba TEC
Specifications
SPECIFICATIONS/ACCESSORIES/OPTIONS/SUPPLIES
ADU PFP LCF
System copy speed
To 550 sheets 64-80 g/m2 17-22 lb. Bond
Automatic duplexing unit Stackless/switchback type
Sheets 64-80 g/m2 17-22 lb. Bond
M2 17-22 lb. Bond
718
Accessories
Supplies
Options
STAPLE-2000
System List
Radf
STAPLE-600
STUDIO3511/4511 Specifications November 2003 Toshiba TEC
Front side view
Outline of the Machine
Sectional View
Drum cleaning blade
Recovery blade
Drum cleaner brush
Toner recovery auger
Rear side view Drive system
Scan motor
Drum cleaner brush motor
Main motor
Transport motor
Front side
Electric Parts Layout
Unit construction
A4 series
Scanner unit Motor, sensor, lamp
LT series
EXP
DH1
Switch, PC board, heater, thermostat, other part
ASD/AUD/CND/SAD/TWD models Standard NAD/MJD models Option
Control panel unit
Process unit Motor, sensor, switch, clutch, solenoid
Laser unit
Motor, switch
S25 S26 M13 Front side
Transport unit
Paper feeder unit
CLT3
CLT5
Automatic duplexing unit
Bypass unit
SFB CLT6 SOL3
ADU CLT7
Drive unit
Fuser unit
HDD NIC BRK
PC board unit
LGC SYS
Symbols and Functions of Various Components
Sensors and switches
CCL-R-POS-SW
CCL-F-POS-SW
CST-U-TRY-SNR
CST-L-TRY-SNR
Solenoids
Electromagnetic clutches
PC boards
Thermistors and thermostats
Lamps and heaters
Others
Transformer
24GeneralDescription
Function of each board CCD board
Construction of boards Construction diagram of boards
Page
HVT
Receiving tray
Disassembly and Replacement of Covers and PC boards
Covers Front cover / Toner bag
Front lower cover
Tray back cover
Front right cover
Left cover
Left upper cover
Left rear cover
Front upper cover
Right upper cover
Right rear cover
IH terminal cover
Right rear hinge cover
Right lower cover
Right front hinge cover
Rear cover
Upper rear cover
Hard disk HDD
PC boards Logic PC board LGC board A-1 LGC board case
LGC board
System control PC board case SYS board case
NIC board / System control PC board SYS board
Remove 4 screws and take off the SYS board case
Flow
Power supply unit
High-voltage transformer
Fuse board FUS board
Noise filter
Options MR-3015 Reversing Automatic Document Feeder Radf
Driving PC board DRV board
Page
KD-1011 Paper Feed Pedestal PFP
Heater is installed
KD-1012 Large Capacity Feeder LCF
Page
Lift up the equipment and take off the LCF
MJ-1022 Hanging finisher When PFP/LCF is not installed
Remove 2 screws Lift up the finisher and take it off
When PFP/LCF is installed
Page
MJ-1023 Console finisher
MJ-1024 Console finisher
Page
MJ-6004 Hole punch unit
Page
KN-3511 Bridge unit
Remove 2 screws Lift up the punch unit and take it off
November 2003 Toshiba TEC
Expression of Colors and 4-Step Copy Process
Copy Process
Photocon
General Description of Copying Process
Details of Copying Process
CCD board
White background Image is not Developed
Photoconductive
Photoconductive Layer Aluminum Base
Blade cleaning
Recovery blade Drum rotation
List of Copying Process Conditions
Pressure roller Silicon sponge
STUDIO3511/4511 Copy Process November 2003 Toshiba TEC
Overview of Operation
General Operation
Description of Operation
Warming-up
Drawer feed copying Upper drawer paper feeding
Ready ready for copying
Page
Page
Scan motor fwd
Interruption copying
Bypass feed copying
Description of abnormality A-1 Add paper
Detection of Abnormality
Types of abnormality
STUDIO3511/4511 General Operation November 2003 Toshiba TEC
Paper jam E010 → The copying operation is Stopped
Registration clutch turned on ↓ Approx 1.2 sec
Approx 1.2 seconds
Registration clutch turned OFF
Exit sensor detects jamming of the trailing edge Paper
After approx 1.3 seconds
Paper jam E020 → The copying operation is
November 2003 Toshiba TEC STUDIO3511/4511 General Operation
Power on to ready
Flow Chart
Ready
Automatic feed copying
Main charger on
YES
Control Panel and Display Panel
Control Panel
Items Shown on the Display Panel
Display
Tray Full Ready
Saddle Stitch
Change Drawer To Correct Paper Size
Copying
This Size Paper
Check Paper
Large Capacity Feeder Cannot Punch
Counter
Department
To Correct Media Type Press Basic
Radf
Structure
Dot matrix LCD circuit
Load Frame
Data Transmission
Frame
Method of LED display ex Displaying Copy
LED display circuit
Slide the stopper and pull it out
Disassembly and Replacement
Stopper
November 2003 Toshiba TEC STUDIO3511/4511 Control Panel
Remove 16 screws and take off the KEY board
Function
Scanner
Construction
Mirror-2 Mirror-3
Scan motor
PS-ACC-350
Scanning drive circuit
Input/output signals
Onno YES
Initialization at power-ON
OFF YES
On no YES
General description
Control of Exposure Lamp
PWA-CCD CCD PWA-CCDPWA-SLG
CPU
Exposure lamp
Control circuit for the exposure lamp
Shading correction
General Description of CCD Control
Opto-electronic conversion
Process of detection of original size
Automatic Original Size Detection Circuit
Principle of original size detection
APS-1 APS-2
APS-3
ST-R
APS-C APS-R APS-1 APS-2 APS-3
APS-C APS-R APS-2 APS-3
Original LEDPhototransistor
SLG board cooling fan
Original glass
Lens cover
LT series
Automatic original detection sensor APS sensor A4 series
Lens unit
Carriages-1
Carriage-1
Carriage Refer to the Service Handbook for more details
Scanning section control PC board SLG board
Platen sensor
Carriage home position sensor
Followings are the boards used for image processing
Image Processing
General Description
CCD
-201 shows the image processing section of this equipment
Configuration
Asic
Asic ACS
SYS Board PWA-F-SYS-350
Features
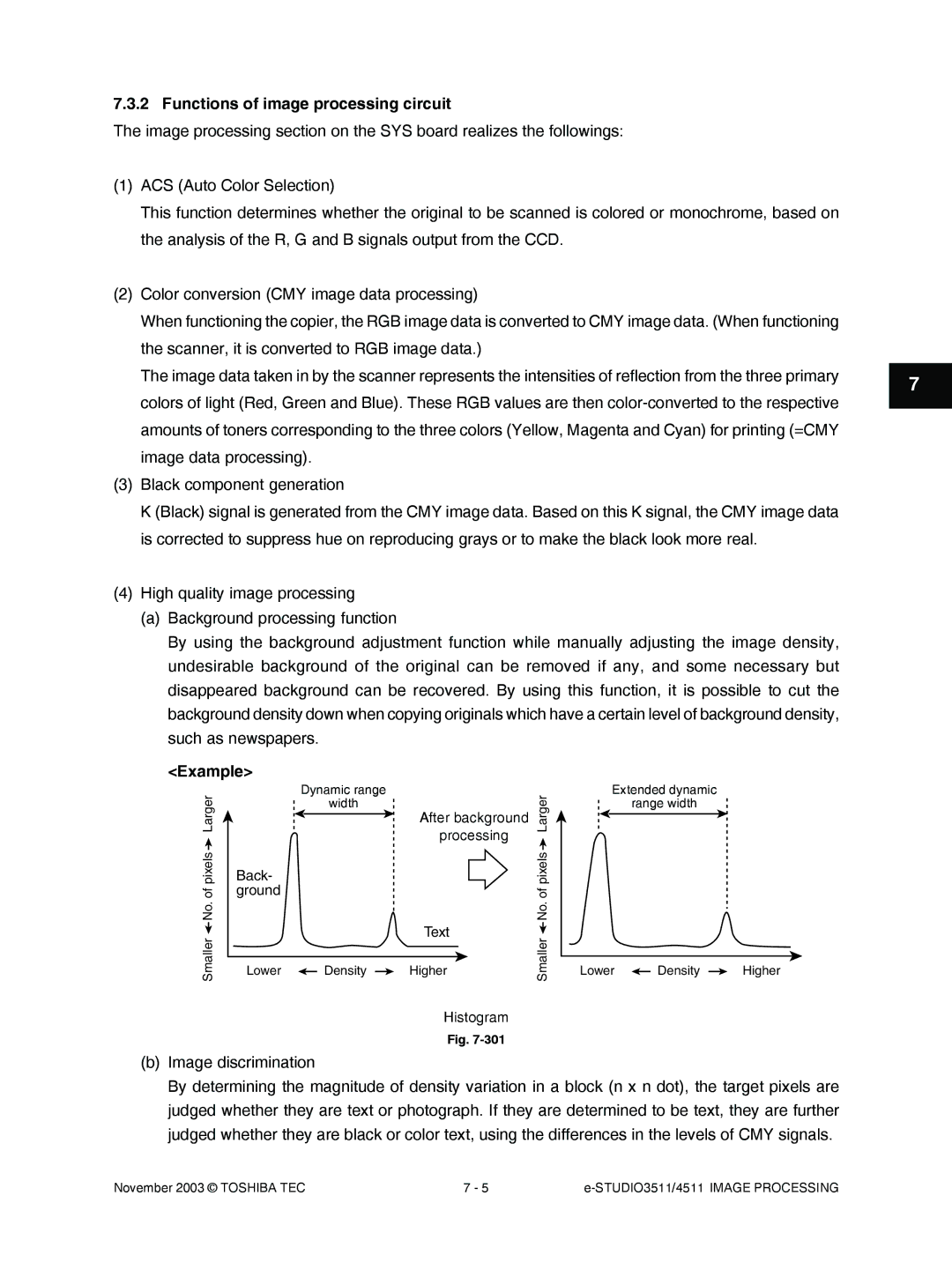
Example
Functions of image processing circuit
’ = + b +
Example Reduction
Example Enlargement
Paper
November 2003 Toshiba TEC STUDIO3511/4511 Image Processing
Laser Driving PC Board LDR Board
LGC Board PWA-F-LGC-350
Laser Optical Unit
Writing Section Overview
Structure
STUDIO3511/4511 Laser Optical Unit November 2003 Toshiba TEC
Deviation
STUDIO3511/4511 Laser Optical Unit November 2003 Toshiba TEC
Laser power comparison circuit Laser driver Circuit Constant
Polygonal motor reference clock signal
Polygonal motor ON/OFF signal
Laser Unit Cooling Fan
Polygonal Motor
Laser optical unit
Laser unit cooling fan
Drive System
Construction
Main Motor
Drive circuit of main motor
Signal level of motor circuit
Transport Motor
Drive circuit of transport motor
Developer Motor
Developer motor rotational direction signal
Developer motor on signal
Developer motor reference clock signal
Normal Out of control Developer motor PLL signal
Developer motor drive unit
Black developer lifting clutch
Developer motor
Remove 2 screws and take off the developer motor
Transport motor drive unit
Setscrew
Transport motor drive unit Connector
Main motor drive unit
Tension plate
Motor
STUDIO3511/4511 Drive System November 2003 Toshiba TEC
General Descriptions
Paper Feeding System
Page
Paper Feeding Section Sectional View Front side
Paper Feeding Section Drive System Rear side
Operation of bypass pickup roller
Operation of drawer pickup roller
Separation of paper
Bypass feeding
General operation From power-ON to ready status
Ready status
Drawer feedingD-1 Lower drawer
Stop
Drive Circuit of Tray-up Motor
IN1 IN2 Brake CCW
Bypass unit A-1 Bypass unit
Bypass tray slide guide width detection PC board
Bypass pickup roller
Bypass transport roller
Bypass paper sensor
Bypass pickup solenoid
Bypass separation roller
Bypass feed roller
Bypass feed sensor
Lower drawer feed sensor/Side cover opening/closing switch
Remove the arbor, shaft and spring
Upper drawer feed sensor/Registration sensor
Registration roller
Feed clutch
Drawer feeding unit E-1 Drawer feeding unit
Separation roller
Remove 1 screw and take off the separation roller holder
CLUTCH-6-L
Pickup roller
Feed roller
Remove the pulley, one-way clutch and 3 E-rings
6Drawer tray-up sensor and Drawer empty sensor
Drawer paper stock sensor
Tray drive unit
Tray drive unit
Registration guide
Lower transport clutch Low/High speed
Middle guide
Drum Related Section
Functions
Page
IC7
Output Control Circuits of High-Voltage Transformer
CPU
Drum Temperature Detection Circuit
Temperature/Humidity Sensor
Operation
Charger Wire Cleaner
Drive circuit
Cleaner unit
Cleaner unit
Main charger grid
Main charger unit B-1 Main charger unit
Remove 1 screw and take off the pad guide
Charger wire
Wire pad
Drum
Remove the base
Drum cleaner brush
Cleaner Drum cleaning blade
Recovery blade
Remove the discharge LED
Drum thermistor
Discharge LED unit F-1 Discharge LED
Charger cleaner detection switch
Charger cleaner motor
Toner bag full detection sensor-2
Ozone exhaust fan
Temperature/Humidity sensor
Ozone filter
Latch
Page
Developer Unit
Color auto-toner sensor Mixer Developer sleeve
Toner motor
Black Toner Cartridge Drive Unit
General descriptions
Functions
Black Developer Unit
Black developer unit drive section
Converter
Black auto-toner sensor circuit
LCA301-1
Magnetic circuit
STUDIO3511/4511 Developer Unit November 2003 Toshiba TEC
Black developer unit lifting mechanism
Color Developer Unit
Gear G21
Color developer unit drive section
Color auto-toner sensor circuit
Page
Color toner supply
CDVDON-0 CDVAON-0
High-Voltage Transformer Output Control Circuit
Developer material
Black developer unit A-1 Black developer unit
Doctor blade
Pour the developer material
Auto-toner sensor
Developer sleeve
Remove 2 screws and take off the doctor blade
Mixer
Color developer unit B-1 Developer material
Take off the mixer from the hole of front side
Discharge the developer material Pour the developer material
Gear assembly
Procedure for replacing an oil seal
Take off the black developer toner supply unit .7 K
Black developer lifting unit
Black toner supply unit
Remove 2 screws and take off the cleaner rail stay
Cartridge switch with the whole bracket
Black toner supply auger unit
Remove 2 screws and take off the toner motor
STUDIO3511/4511 Developer Unit November 2003 Toshiba TEC
Revolver Unit
STUDIO3511/4511 Revolver Unit November 2003 Toshiba TEC
Drive of Revolver Unit
Revolver motor
Revolver Motor Drive Circuit
Home position detection
Operation
Escape position movement
During warming-up
During image quality control
Color developer unit
Color toner cartridge
Rear Front
Color toner cartridge sensor
Remove 1 screw and take off the color toner cartridge sensor
Revolver home position sensor
Revolver unit
Lock lever
Remove 5 screws and take off the bracket
Internal cooling fan
Transfer Unit
STUDIO3511/4511 Transfer Unit November 2003 Toshiba TEC
Page
Outline of 2nd transfer
Outline of 1st transfer
LCA-301-1
High-Voltage Power Supply
1000V
PWA
Transfer belt unit
Loosen 3 screws and take off the bracket
Transfer belt
Stand plate short
1st transfer roller
Transfer belt home position sensor-2
Transfer belt home position sensor-1
Transfer belt cleaning unit
Remove 1 screw and take off the bracket on the front side
Conductive tape
Harness clamp Transfer belt cleaner auger motor
2nd transfer unit
2nd transfer roller
2nd transfer roller contact clutch
Paper clinging detection sensor
2nd transfer roller position detection sensor
Paper clinging detection sensor Bracket
Page
Principle of the Sensor
Image Quality Control
YES
Flow Chart of Control Procedure
Various image forming conditions
Image quality sensor / Image quality sensor Shutter solenoid
Fuser Unit / Paper Exit Section
Functions
Page
Heater Control Circuit
Configuration
Image of Current Flowing form a to B
Book Diagram of High Frequency Power Supply
Heating principle of IH Heater
+5VSW
IH control circuit interface
IH2 on
IH1 on
FAX
For ASD, AUD, CND
OFF
Control of the surface temperature of the fuser belt
Temperature detection section
Energy Saver
Reference
PC4/AN4
Condtion Priority of error checking
Abnormality in the IH control circuit
IH error
Exit Motor Drive
Control Circuit of Exit Motor
Oil roller
Rear side
Cleaning roller
Fuser roller / Fuser belt guide
IH coil
Bearing Fuser belt guide
Fuser belt
Separation finger
Separation finger unit
Thermostat
Pressure roller
Thermistor
Remove 2 screws and take off the thermostat from the bracket
Exit sensor / Exit finger / Transport guide
Exit roller
IH control board cooling fan
IH control PC board IH board
Scraper
Flow
Automatic Duplexing Unit ADU
Description of Operations
Page
Page
Page
Unit msec
Equipment
ADU entrance sensor ADU exit sensor ADU clutch ADU motor
Exit sensor Registration sensor Registration clutch
Drive of ADU
Yes
Command signal
Operation of DC Output Circuits
Power Supply Unit
Output Channel
November 2003 Toshiba TEC STUDIO3511/4511 Power Supply Unit
Fuse
Charger cleaner motor Power supply Power supply cooling fan
Bridge unit +24VD2
F54A Semi time-lag +24VD4
Toshiba
Configuration of Power Supply Unit
PWR-EN
Sequence of Power Supply
PWR-DN
Scanner
AC Wire Harness
STUDIO3511/4511 Power Supply Unit November 2003 Toshiba TEC
PC Boards
PWA-F-LGC
PWA-F-SLG PWA-F-CCD PWA-F-SDV
PWA-F-DRV
PWA-F-ADU
PWA-F-LDR PWA-F-SNS
PWA-F-DSP PWA-F-KEY
PWA-F-FUS ASD/AUD/CND models Standard, MJD model Option
PWA-F-FIL
NAD/SAD/TWD models Standard
STUDIO3511/4511 PC Boards November 2003 Toshiba TEC
Page
Kanda NISHIKI-CHO, CHIYODA-KU, TOKYO, 101-8442 Japan