Ultra ATA Drive Guidelines and Features
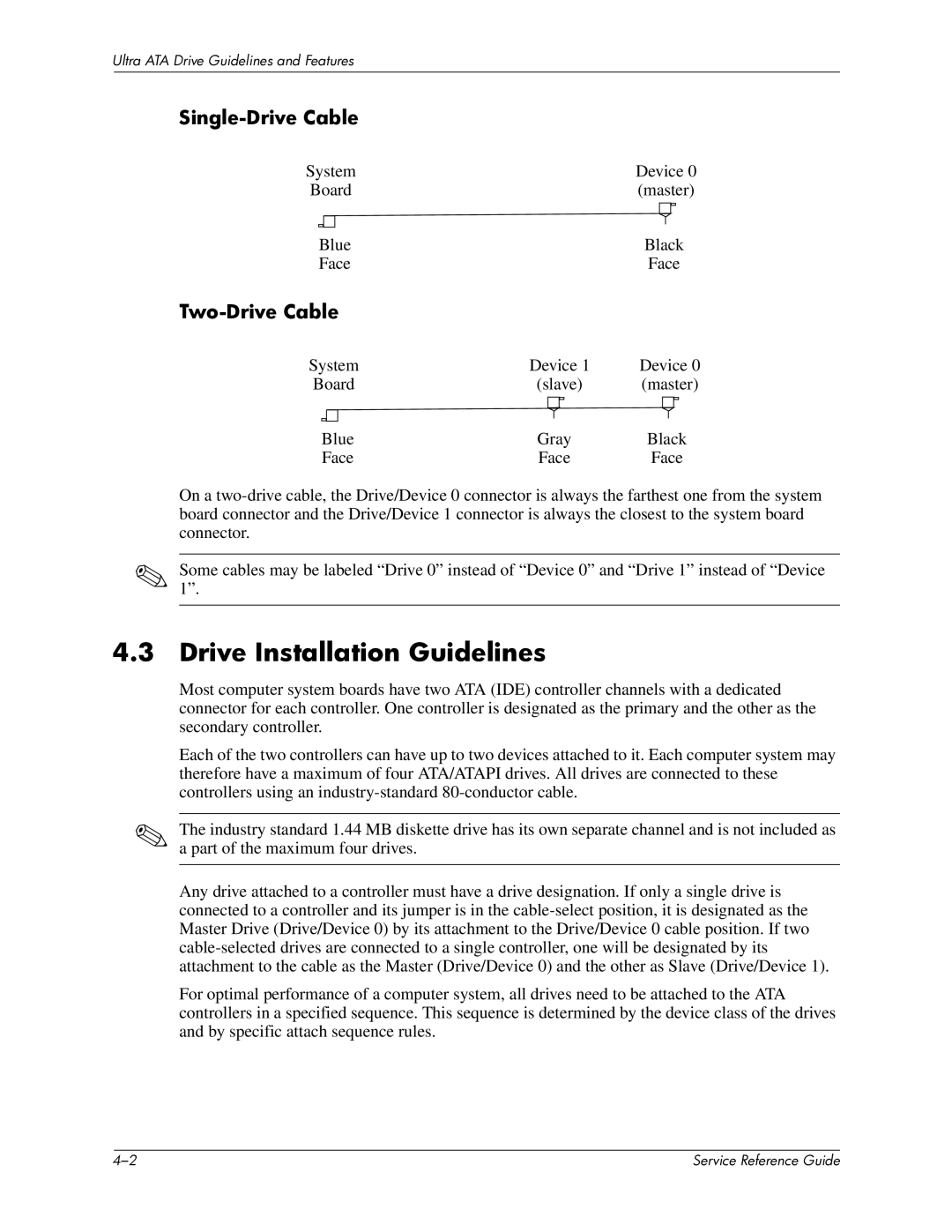
Single-Drive Cable
System | Device 0 | |||||||
Board | (master) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Blue | Black | ||||||
| Face | Face | ||||||
Two-Drive Cable
System | Device 1 | Device 0 | |||||||||||
Board | (slave) | (master) | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Blue | Gray | Black | ||||||||||
| Face | Face | Face | ||||||||||
On a
✎Some1”. cables may be labeled “Drive 0” instead of “Device 0” and “Drive 1” instead of “Device
4.3Drive Installation Guidelines
Most computer system boards have two ATA (IDE) controller channels with a dedicated connector for each controller. One controller is designated as the primary and the other as the secondary controller.
Each of the two controllers can have up to two devices attached to it. Each computer system may therefore have a maximum of four ATA/ATAPI drives. All drives are connected to these controllers using an
✎The industry standard 1.44 MB diskette drive has its own separate channel and is not included as a part of the maximum four drives.
Any drive attached to a controller must have a drive designation. If only a single drive is connected to a controller and its jumper is in the
For optimal performance of a computer system, all drives need to be attached to the ATA controllers in a specified sequence. This sequence is determined by the device class of the drives and by specific attach sequence rules.
| Service Reference Guide |