Register Description
R
At the time that a hub interface or AGP accesses to the PAM region may occur, the targeted PAM segment must be programmed to be both readable and writeable.
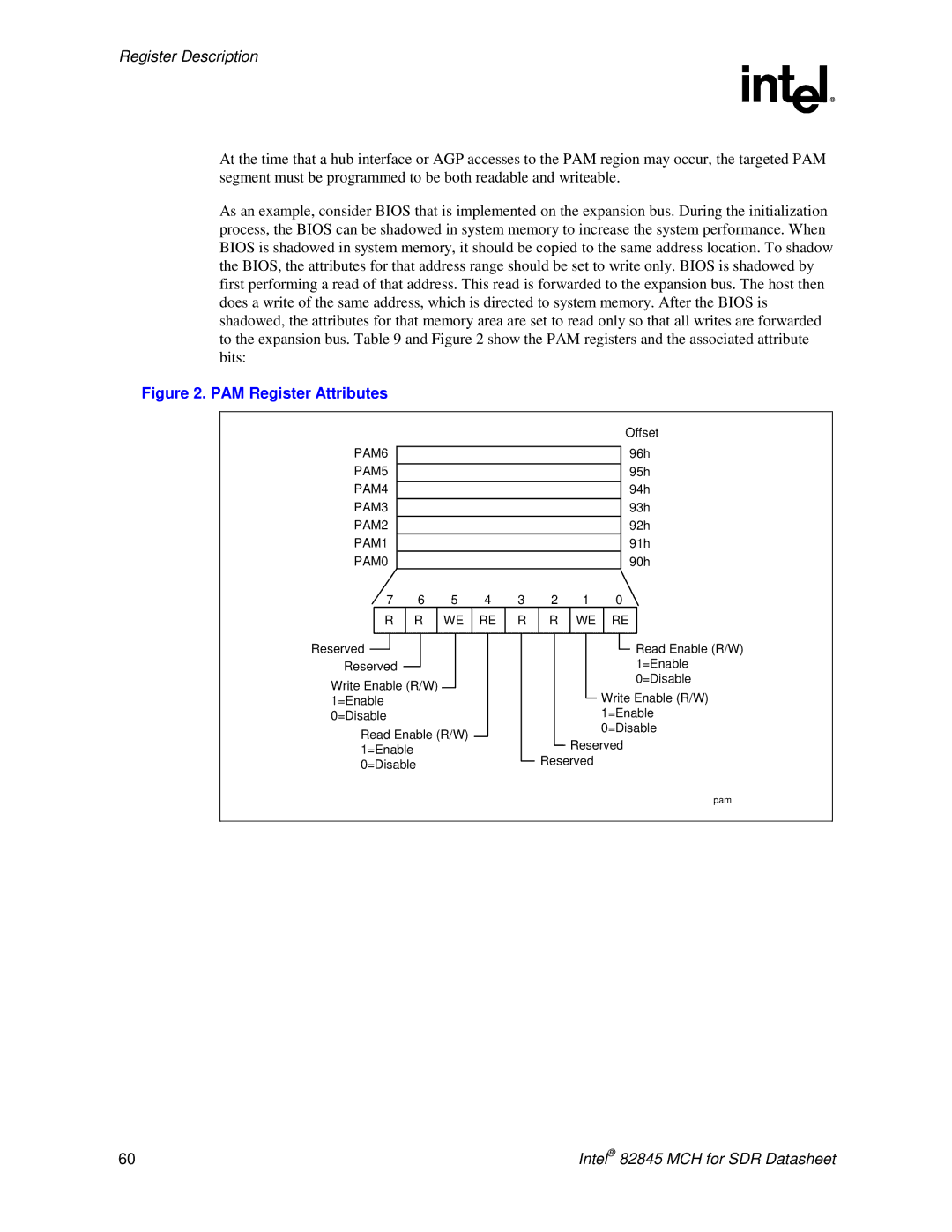
As an example, consider BIOS that is implemented on the expansion bus. During the initialization process, the BIOS can be shadowed in system memory to increase the system performance. When BIOS is shadowed in system memory, it should be copied to the same address location. To shadow the BIOS, the attributes for that address range should be set to write only. BIOS is shadowed by first performing a read of that address. This read is forwarded to the expansion bus. The host then does a write of the same address, which is directed to system memory. After the BIOS is shadowed, the attributes for that memory area are set to read only so that all writes are forwarded to the expansion bus. Table 9 and Figure 2 show the PAM registers and the associated attribute bits:
Figure 2. PAM Register Attributes
PAM6
PAM5
PAM4
PAM3
PAM2
PAM1
PAM0
Offset 96h 95h 94h 93h 92h 91h 90h
7 |
| 6 |
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| ||
| R |
| R |
| WE | RE | R | R | WE |
| RE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reserved |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Read Enable (R/W) | |||
Reserved |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1=Enable | |||
Write Enable (R/W) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 0=Disable | |||||
|
|
|
|
| Write Enable (R/W) | |||||||
1=Enable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
0=Disable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1=Enable | ||||
Read Enable (R/W) |
|
|
|
| 0=Disable | |||||||
|
|
| Reserved | |||||||||
1=Enable |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
| Reserved |
|
|
| ||||
0=Disable |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
pam
60 | Intel® 82845 MCH for SDR Datasheet |