April
Retain for future use
Please Note
Class a FCC Statement
Contents
Wire Pulse Initiator
Running the Diagnostics Wiring Error Test
Power Factor Min/Max Conventions VAR Sign Conventions
Analog Input Example
Waveform and Event Capture
Alarms
Logging
Appendix B-USING the Command Interface
Disturbance Monitoring
Glossary Index
Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
List of Figures
Figure A-1 Bits in a register 128
List of Figures 63230-300-212 April Viii
List of Tables
Summary of Circuit Monitor Instrumentation
List of Tables 63230-300-212 April
Chapter Contents
Introduction
From the display or remotely using software. -1summarizes
What is the Circuit MONITOR?
Advanced features
Readings available from the circuit monitor
63230-300-212 Introduction April
Accessories and Options for the Circuit Monitor
Circuit Monitor Parts, Accessories, and Custom Cables
Description Part Number Document Number
This Bulletin
Features
Topics not Covered
Firmware
Introduction FirmwAre
Introduction 63230-300-212 FirmwAre April
Safety Precautions
Safety Precautions 63230-300-212 April
Advanced features not accessible from the display
Operation
Main Menu
Meters Resets Min/Max Setup View Alarms Diagnostics
Operating the Display
How the Buttons Work
Language English Date
Display Menu Conventions
Display
MM/DD/YYYY
Main Menu Overview
Operation 63230-300-212 Main Menu Overview April
63230-300-212 Operation April
Configuring the Circuit Monitor Using the Setup Menu
Setting Up the Display
Factory Defaults for the Display Settings
Setting Up the Communications
Infrared Port
Options for Communications Setup
Communications
Meter
Setting Up the Metering Functions of the Circuit Monitor
Ethernet Communications Card ECC Setup
3Ø4W3CT
Options for Meter Setup
3Ø4W4CT2PT
Operation 63230-300-212
Setting Up Alarms
Alarm from the display
Performing two steps
Create the custom alarm
Setup and enable the new alarm
Create Custom
Lbl Over THD Vbc Type Val Qty
Alarm Parameters
Options for Creating an Alarm
THD
Dropout setpoints
Follow these instructions to set up or edit an alarm
From the Main Menu, select Setup Alarm Edit Parameters
Options for Editing an Alarm
Date & Time Display Communications Meter Alarm Passwords
Setting Up I/Os
Setup
KYZ
Custom
Extender Setup
IOX Select Modules
DI120AC
Outputs for the I/O module you selected
Configuring I/O Modules
Descriptions
Name Description
Input/Output Capabilities on
I/O Extender Setup selection menu displays
IOX Custom Setup
Setup Diagnostics Engy/Dmd Reset Min/Max Reset
Setting Up Passwords
Passwords
Advanced Setup Features
Creating Custom Quantities to be Displayed
Select a custom quantity
Select Display Display Setup menu displays
Custom Quant Setup
Option Available Values Default
Options for Custom Quantities
28 for instructions
Select Custom Screen Custom Screen Setup screen displays
Custom Screen Setup
Monthly Energy Cost Blank Line
Screen
Screen Blank Line
Screen Monthly Energy Cost Blank Line
Available Default Quantities
Quantity Type Q Label Q
Viewing Custom Screens Advanced Meter Setup
Monthly Energy Cost Dollars
Select Meter Meter Setup screen displays
Advanced Meter Setup
10 Options for Advanced Meter Setup
ABC
Reset Energy Reset Demand Reset MIN/MAX
Resetting MIN/MAX, DEMAND, and Energy Values
Main Menu Resets
Accumulated Power Demand Min/Max Amp Demand
Operation 63230-300-212 Viewing Metered Data April
Menus where you can view metered data in real time
Viewing Metered Data
MIN/MAX
Current Voltage Frequency Power Power Factor
Viewing Minimum and Maximum Values from the Min/Max Menu
Current a
Mn 01/22/2000159A Mx 01/22/2000815A
View Alarms
Viewing Alarms
Meters Min/Max View Alarms Display Resets Setup Diagnostics
Active Alarms List High Priority Log
View and Acknowledging High Priority Alarms
Viewing Active Alarms
Active Alarms List 1/1
High Priority Alarms
Digital Outputs Kyzoff
Viewing I/O Status
Digital Inputs Analog Inputs Digital Outputs Analog Outputs
READ/WRITE Regs
Diagnostics
Reading and Writing Registers
Reg Hex Dec 1003 000A
Performing a Wiring Error Test
10 Wiring Error Test option on the Diagnostics menu
Running the Diagnostics Wiring Error Test
Meter Information
Perform Test
12 Wiring Error Messages
Message Description
I2 load current less than 1% CT
Operation 63230-300-212 Performing a Wiring Check April
Metering Capabilities
Circuit monitor
Readings
REAL-TIME Readings
More
One-Second, Real-Time Readings Samples
63230-300-212 Metering Capabilities April
MIN/MAX Values for REAL-TIME Readings
100 ms Real-Time Readings
To +0 on the same scale
Power Factor Min/Max Conventions
Included with the software
Positive in this case
Real
Convention, refer to Advanced Meter Setup on
Reactive Power
ALT CM1 VAR Sign Convention IEEE/IEC VAR Sign Convention
Demand Readings
Demand Readings
Demand readings and their reportable ranges
Metering Capabilities 63230-300-212 Demand Readings April
Block Interval Demand
Demand Power Calculation Methods
April Demand Readings
Block Interval Demand Examples
Block Interval Demand on
Demand Current
Demand Voltage
April Demand Readings Synchronized Demand
Interval
Thermal Demand
Minutes for illustration purposes
Peak Demand Generic Demand
Input Pulse Demand Metering
Channel pulse metering example
For all channels
See Appendix A-Abbreviated Register Listing on page 127 for
Energy Readings
Energy Readings
Real Power
April Energy Readings
Harmonic distortion
Power Analysis Values
On page 68 summarizes the power analysis values
100%
Harmonic Power = Overall Power
April Power Analysis Values
Power Analysis Values
Value Reportable Range
INPUT/OUTPUT Capabilities
On page 3 of this bulletin
Input/Output Capabilities 63230-300-212 Options April
Options
I /O Extender Options
Extender Options
Command interface
Digital Inputs
Calculations
Demand Synch Pulse Input
59 in -Metering Capabilities for more about demand
To verify peak demand charges
63230-300-212 Input/Output Capabilities April Analog Inputs
Analog Inputs
Maximum value for each analog input
Sample register readings for analog inputs
Has been configured as follows
Analog Input Example
Input/Output Capabilities 63230-300-212 Analog Inputs April
Latched
Relay Output Operating Modes
Normal
April Relay Output Operating Modes
Absolute kWh Pulse
End Of Power Demand Interval
Timed
Absolute kVARh Pulse
Mechanical Relay Outputs
SOLID-STATE KYZ Pulse Output
Setpoint-controlled Relay Functions
Wire Pulse Initiator
Application
Calculating the KILOWATTHOUR-PER-PULSE Value
Analog Outputs
Register Reading kW Output Current mA
Analog Output Example
Sample register readings for analog output
Alarms
Alarms 63230-300-212 About Alarms April
About Alarms
Alarms Groups
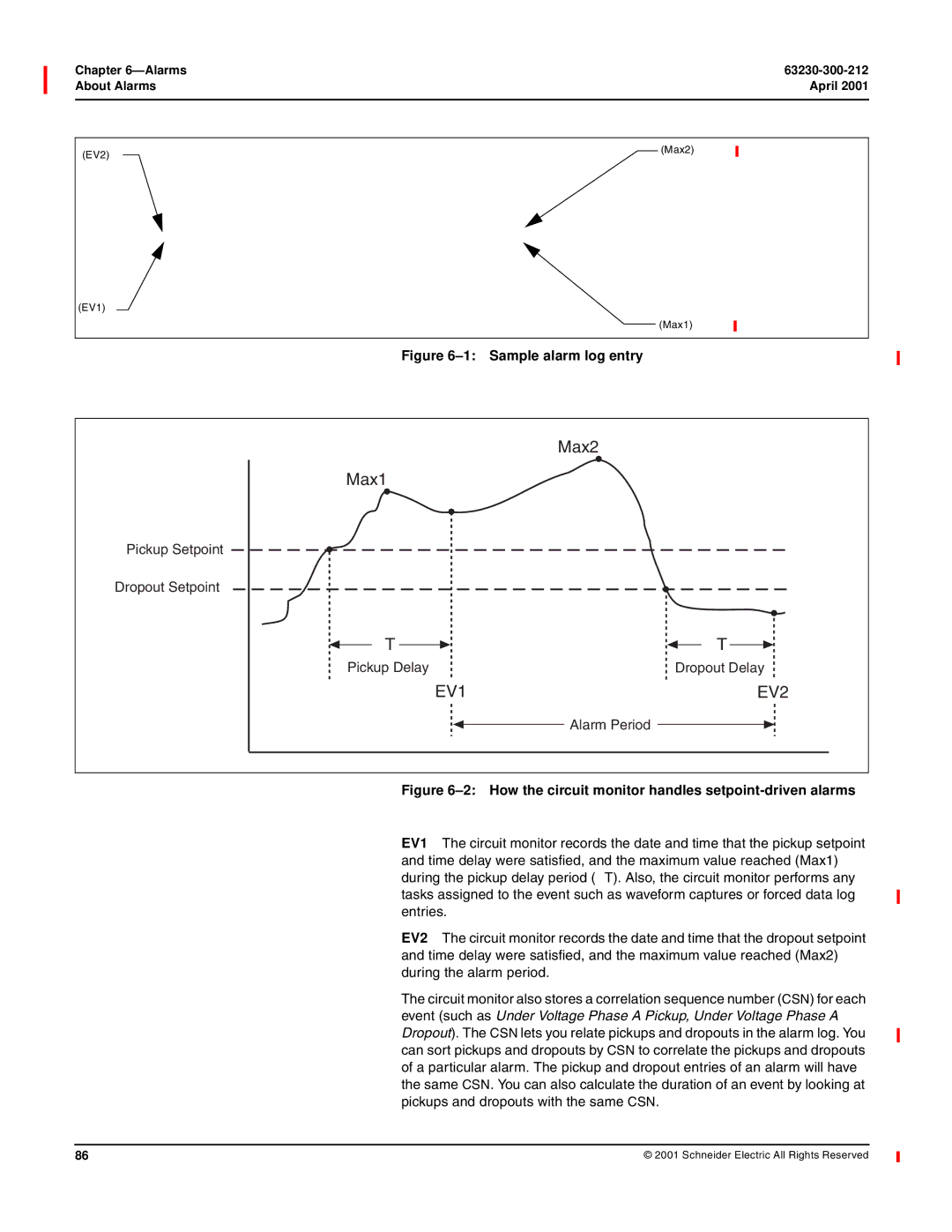
Pickup Setpoint
Setpoint-Driven Alarms
Define the following information
Seconds, 100 ms increments, or cycles
Pickup Setpoint Dropout Setpoint
Pickup Delay Dropout Delay
Alarm Period
Priorities Alarm Levels
Alarms About Alarms
Custom Alarms SETPOINT-CONTROLLED Relay Functions
Alarms 63230-300-212 Custom Alarms April
Undervoltage
63230-300-212 Alarms April
Types of Setpoint-Controlled Relay Functions
Overvoltage
Reverse Power
Phase Loss-Current
Phase Loss-Voltage
Phase Reversal
Scale Factors
Settings
Scale Factors on page 191 in Appendix B-Using the Command
Setpoint
Scale groups and their register numbers
Scaling Alarm Setpoints
Alarms 63230-300-212 Scaling Alarm Setpoints April
Scale Group Register Numbers
Alarm Conditions and Alarm Numbers
Standard Speed Alarms 1 Second
List of Default Alarms by Alarm Number
Alarm Alarm Description Abbreviated Test Units Scale
Display Name Register
Disturbance Monitoring 1/2 Cycle
High Speed Alarms 100 ms
Display Name
Type Description Operation Standard Speed
Alarm Types
Digital
Type Description Operation
High Speed
Disturbance
Boolean
102
See Factory Defaults on page 11 of the installation manual
Alarm Log Storage 100
Data Logs
Alarm LOG
Alarm Log Storage
April Data Logs
101
Logging 63230-300-212 Min/Max Logs April
MIN/MAX Logs
Min/Max Log Interval Min/Max/Average Log
102
April Maintenance Log Interval Min/Max/Average Log Storage
Maintenance LOG
Values Stored in Maintenance Log
Value Stored Description
104
Memory Allocation
Logging Memory Allocation
Memory allocation in SMS
105
Logging 63230-300-212 Memory Allocation April 106
107
107
Steady-state Waveform Capture
Available Resolutions for Disturbance Waveform Captures
Types of Waveform Captures
Disturbance Waveform Capture
Adaptive Waveform Capture
Available Resolutions for Adaptive Waveform Captures
Samples per Cycle Max. Duration Resolution
109
110
100ms rms Event Recording
100ms rms Quantities
63230-300-212 Waveform and Event Capture April
Setting UP the Circuit Monitor for Automatic Event Capture
Waveform Storage
111
HOW the Circuit Monitor Captures AN Event
112
114
Using SMS to gather data when a disturbance event occurs
113
113
About Disturbance Monitoring
April About Disturbance Monitoring
115
116
63230-300-212 Disturbance Monitoring April
Operate any output relays when the event is detected
Capabilities of the Circuit Monitor During AN Event
Categories CM-4000
Onboard Alarms/Events tab
Onboard Files tab
119
Understanding the Alarm LOG
April Understanding the Alarm Log
Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Upgrading Memory in the Circuit Monitor 123
Monitor
121
124
122
April Circuit Monitor Memory
Circuit Monitor Memory
Upgrading Memory in the Circuit Monitor
123
Xxxxxxxx
Identifying the Firmware Version
Meter Information
DOM
Representative for assistance
Troubleshooting
Information in -1 describes potential problems and their
Maintenance and Troubleshooting 63230-300-212 April
126
127
April Contents
About Registers
Currents and voltages
HOW Power Factor is Stored in the Register
128
Table A-2Date and Time Byte Example
HOW Date and Time are Stored in the Register
Table A-1Date and Time Format
Register Listing
Table A-3Abbreviated Register List
Second Real-Time Readings
April Register Listing
Register Description Scale Units Register Range Number
131
132
133
134
Real to Time Minimum Metered Values
135
136
137
138
Real to Time Maximum Metered Values
139
140
To 32,767 See How Power Factor is Stored in the Register on
141
142
143
Accumulated Energy
144
Demand
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
Phase Extremes
System Configuration
Current and Voltage Module Configuration
157
= Cvmt
158
Metering Configuration
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
Table A-4Abbreviated Register List for I/O Status
Register Name Units Range Description Number
167
Digital Input Template
Digital Output Template
169
KWH
171
Analog Input Template
Analog Output Template
First digit 4 indicates point is analog output
Table A-5Registers for Alarm Position Counters
173
174
175
176
177
Template
Table A-6Spectral Components
Register Description Units Range Number
178
179
180
181
Issuing Commands 183 Point Numbers
Various operations
181
182
Overview of the Command Interface
Table B- 1 Location of the command interface
Table B- 2 Command Codes
Issuing Commands
Write the command code to command interface register
8001-15
Resets
Files
April Overview of the Command Interface
Setup
185
Point Numbers
186
63230-300-212 Appendix B-Using the Command Interface April
187
188
Command Interface Control Digital Input Control
Conditional Energy
April Incremental Energy
Using Incremental Energy
Incremental Energy
189
190
Setting UP Individual Harmonic Calculations
Table B- 3 Registers for Harmonic Calculations
Changing Scale Factors
Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Glossary
193
194
Potential transformer PT-also known as a
Glossary 63230-300-212 April
195
True power factor-seepower factor
Voltage transformer VT-seepotential
Glossary 63230-300-212 April 196
INDEXNumerics
197
Index 63230-300-212 April
198
PLC
199
SMS
200
201
Index 63230-300-212 April 202
Page
PBG 1M 4/2001