E6581381
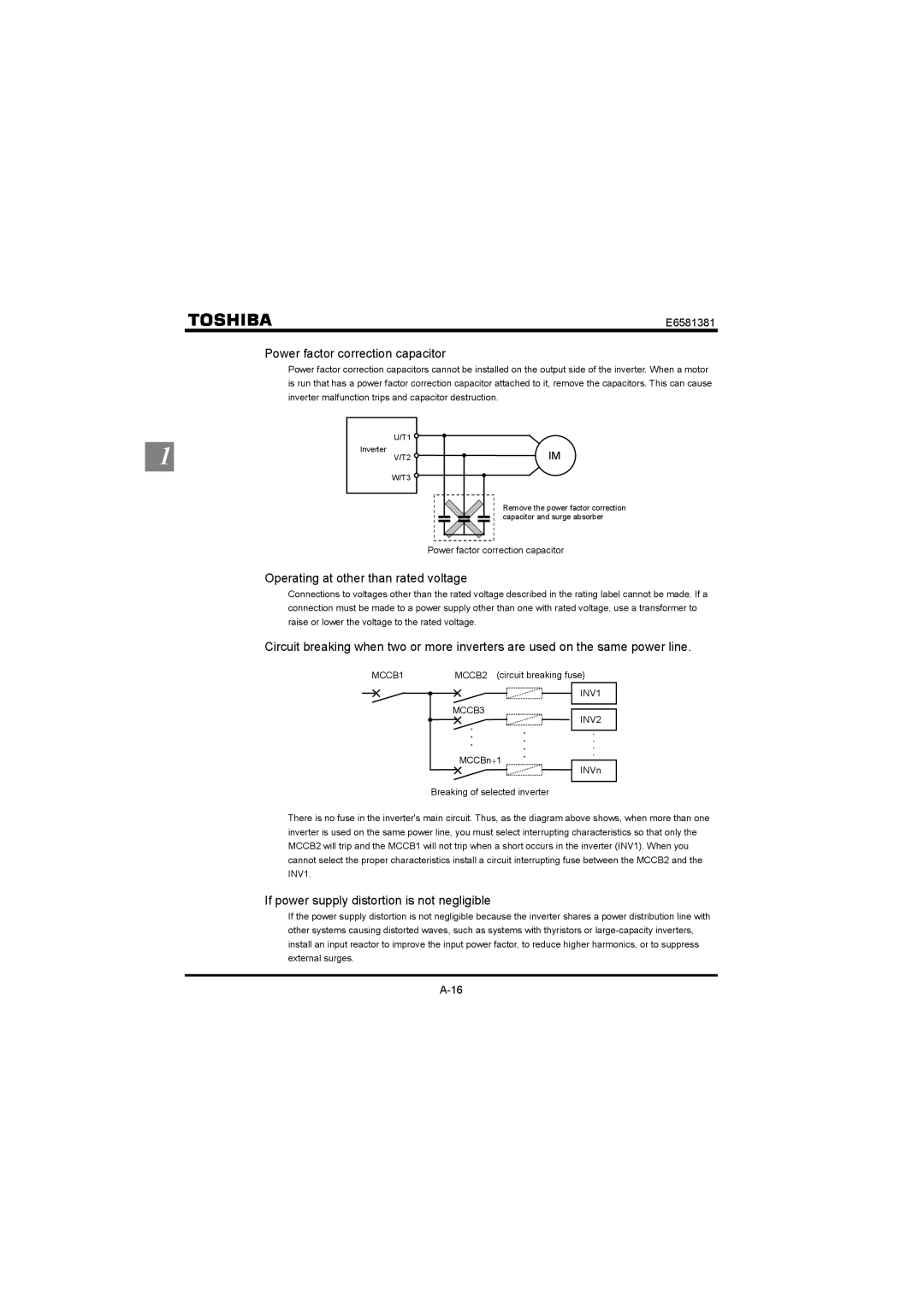
Power factor correction capacitor
Power factor correction capacitors cannot be installed on the output side of the inverter. When a motor is run that has a power factor correction capacitor attached to it, remove the capacitors. This can cause inverter malfunction trips and capacitor destruction.
1
U/T1 ![]()
Inverter
V/T2 ![]()
W/T3 ![]()
IM
Remove the power factor correction capacitor and surge absorber
Power factor correction capacitor
Operating at other than rated voltage
Connections to voltages other than the rated voltage described in the rating label cannot be made. If a connection must be made to a power supply other than one with rated voltage, use a transformer to raise or lower the voltage to the rated voltage.
Circuit breaking when two or more inverters are used on the same power line.
MCCB1 | MCCB2 (circuit breaking fuse) |
INV1
MCCB3
INV2
MCCBn+1
INVn
Breaking of selected inverter
There is no fuse in the inverter's main circuit. Thus, as the diagram above shows, when more than one inverter is used on the same power line, you must select interrupting characteristics so that only the MCCB2 will trip and the MCCB1 will not trip when a short occurs in the inverter (INV1). When you cannot select the proper characteristics install a circuit interrupting fuse between the MCCB2 and the INV1.
If power supply distortion is not negligible
If the power supply distortion is not negligible because the inverter shares a power distribution line with other systems causing distorted waves, such as systems with thyristors or