IR2200/iR2800 IR3300
Copyright 2001 Canon INC
Symbols Used
Symbol Description
Outline of the Manual
System Unit
Reader Unit
Printer Unit
Troubleshooting
Introduction
System Unit
Contents
Installation
Chapter General Description
Specifications
Main Body
Type
Systems
Functions
T01-101-03
Ltrr
Single-sided copying mode
T01-101-04
T01-101-05
6GB
DADF-H1
Others
T01-101-06
T01-101-07
A4R
B5R
A5R
T01-101-08
Side Paper Deck-L1
T01-102-01
Names of Parts
External View
ADF
F01-201-01
F01-201-02 10 S
Cross Section
F01-202-01
T01-202-01 12 S
System Configuration
Functional Construction
F01-301-01
Outline of the Electrical Circuitry
Construction of the Electrical Circuit
F01-302-01 14 S
Wiring Diagram of the Major PCBs
Inputs to and Outputs from the Major PCBs
F01-303-01
Configuration with Accessories
Accessories for Original/Paper Feeding
DADF-H1
F01-304-01 16 S
Accessory Boards
F01-304-02
Chapter Main Controller
Basic Construction
F02-101-01
Outline
Main Controller PCB
HDD
T02-102-01
F02-102-01
Start-Up Sequence
F02-103-01
Start-Up Sequence
F02-103-02
F02-103-03
Digital Image Processing
Outline
F02-201-01
Input Image Processing
Binary Processing error diffusion method T-BIC
Image Memory Control
Binary dither screen method
Sdram
When Generating Read Images
When Generating Printer PDL Images
Output Image Processing
Smoothing
Soft Counters
T02-301-01
PS19S
PS21S
F02-301-01
F02-301-02 12 S
T02-301-02
T02-301-03
OFF
OPTIONUSERCOUNTER1
OPTIONUSERCOUNTER2
OPTIONUSERCOUNTER3
OPTIONUSERCOUNTER4
Controlling the Power Supply
Power Supply Modes
Standby Mode normal operation
Sleep Mode
Shift from Standby Mode to Sleep Mode
Shift from Sleep Mode 1 to Standby Mode
Turning Off the Power
Shift from Sleep Mode 2 to Standby Mode
Shift from Sleep Mode 2 to Sleep Mode
New Functions
Hard Disk Spool
Network PCB
F02-501-01 18 S
SMB Printing
F02-502-01
LPD Banner
F02-503-01 20 S
Chapter Installation
Selecting the Site of Installation
F03-100-01
F03-100-02
Unpacking and Installation
Before Starting the Work
Unpacking and Removing the Fixing Materials
Installation
Mounting the Scanner
Removing the Dummy Drum
Supplying the Toner
Installation
Installation
Mounting the Drum Unit
11 S
Stirring the Toner
Setting the Cassette
Set the dial as indicated
LTR
Checking the Images/Operations
17 S
Connecting to the Network
Using the Ping Function
Checking the Network Connection
Copiertestpingnetwork
Troubleshooting the Network
Making a Check Using a Remote Host Address
Checking the Connection of the Network Cable
Making a Check Using a Loop-Back Address
Making a Check Using a Local Host Address
Relocating the Machine
Preparing for Relocation
Lifting the Machine Off the Pedestal
22 S
Installing the Card Reader-C1
Copierfunctioninstallcard
24 S
25 S
Installing the Document Tray-D2
26 S
Replacing the Drum Unit
28 S
29 S
Copierfunctiondpcd Gamma
30 S
Reader Unit
Basic Operation
Image Processing System
Chapter Basic Operation
Outline of Electrical Circuitry
Reader Controller PCB
CPU
RAM
Basic Sequence of Operations at Power-On
Basic Sequence of Operations in Book Mode
Basic Sequence of Operations
F01-202-02
Wiring of Major PCBs
Inputs to and Outputs from the Major PCBs
Chapter Original Exposure System
Outline of Operations
F02-101-01 F02-101-02
LAMP1
Sequence of Operations original exposure
Book Mode, 1 Original, Copyboard Closed
F02-102-02
Book Mode, 1 Original, Copyboard Cover Open
F02-102-03
F02-102-04
Enlargement/Reduction zoom
Changing the Reproduction Ratio in Main Scanning Direction
Changing the Reproduction Ratio in Sub Scanning Direction
Scanner Drive System
Controlling the Motor When Scanning an Image
Controlling the Scanner Motor
F02-202-01
F02-202-02
E202 HP detection error
E204 image leading edge detection error
COPIERFUNCTIONCCDSHDG-POS shading position adjust- ment
F02-202-03
Controlling the Scanning Lamp LA2
Scanning Lamp
Turning On/Off the Lamp
F02-302-01
Detecting an Error
E220
E225
10 R
Detecting the Size of Originals
Points of Detection
Outline of Detection
F02-402-01
Outline of Detection Operation
F02-404-01
12 R
Book Mode, 1 Original, Copyboard Cover Close
T02-404-01
F02-404-02
T02-404-02 14 R
Disassembly and Assembly
Exposure Lamp
Removing the Exposure Lamp
F02-501-01 F02-501-02 16 R
After Replacing the Scanning Lamp
Copierfunction CCDCCD-ADJ
F02-501-03 F02-501-04
Scanner Drive Assembly
Removing the Scanner Motor
F02-502-02 F02-502-03 18 R
Mounting the Motor Unit
F02-502-04 F02-502-05
Removing the Scanner Drive Cable
F02-502-06 20 R
Routing the Scanner Drive Cable
F02-502-07
Adjusting the Position of the No /No Mirror Base
Front Side F marking Rear Side R marking
F02-502-10 F02-502-11
Sensors
Removing the Original Detection Unit
Removing the HP Sensor
F02-503-01
Removing the Original Cover Sensor
F02-503-04
F02-503-05
PCBs
Removing the Inverter PCB
26 R
F02-504-01 F02-504-02 F02-504-03 F02-504-04
Chapter Image Processing System
Outline
CCD CCD PCB
F03-202-01 CCD Block Diagram
Analog Image Processing
Driving the CCD
F03-201-01
Gain Correction and Offset Correction of the CCD Output
A/D Conversion of the CCD Output
F03-205-01
Shading Correction
F03-301-01
Shading Adjustment
Shading Correction
F03-302-01
Edge Gain Correction ADF in use
F03-302-02
Auto Density Adjustment AE
ABC Circuit
F03-303-01
Related Service Mode
COPIERFUNCTIONCCDCCD-ADJ shading auto adjustment
F03-304-01
Disassembly and Assembly
External Covers
External Covers
Removing the Reader Right Cover
F03-401-01
Removing the Copyboard Glass
After Mounting the Copyboard Glass
Copierfunctionccd SH-PS-ST
F03-401-03
CCDs
Removing the CCD Unit
F03-402-01
F03-402-02 12 R
Points to Note When Replacing the CCD Unit
Copierfunction CCDEGGN-POS
Frames
Removing the Left ADF Base Unit
Removing the Reader Upper Frame
F03-403-01
Mounting the Reader Upper Frame
F03-403-03
When Replacing the Reader Controller PCB
Removing the Reader Controller PCB
Printer Unit
Introduction
Controlling the Transfer Charging Roller Bias
PICKUP/FEEDING System
Fixing System
Externals and Controls
PCB
Paper DECK-L1
Cassette Feeding UNIT-W1
Inner 2WAY TRAY-A1
Chapter Introduction
Safety
Safety of Laser Light
Cdrh Ordinances
F01-102-01 Cdrh Label
Handling the Laser System
F01-103-01 Laser Warning Label
Safety of Toner
Image Formation System
F01-201-01 Construction of the Machine
F01-201-02
Chapter Sequence of Operations
Basic Operations
Outline for the Electrical Circuitry
DC Controller PCB
T02-102-01 Control Functions
Dimm ROM
Basic Sequence of Operations at Power-On
Basic Sequence of Operations
T02-103-01
Increase in temperature for each specific period of time
F02-104-01 Control Circuit Block Diagram
Controlling the Main Motor M2
T02-104-01
F02-105-01
Chapter Laser Exposure System
Part 2Chapter 41.1 Outline of Laser Exposure System
T03-101-01
F03-101-01
T03-101-02
Generating Sync Signals
Part 2Chapter 42 Generating the BD Signal
Sequence of Operations laser exposure system
F03-102-01
Flow of Sync signals
F03-202-01
Laser Driver Circuit
Controlling the Laser Unit
ADJUSTLASERPVE-OFST
ADJUSTLASERLA-OFF
Controlling the Laser Scanner Motor
Part 2 4.1 Outline
Disassembly and Assembly
Laser Scanner Assembly
Removing the Laser Unit
F03-501-01
F03-501-02
Chapter Image Formation System
Outline of Processes
T04-101-01
F04-101-01
Basic Sequence of Operations image formation system
F04-102-01
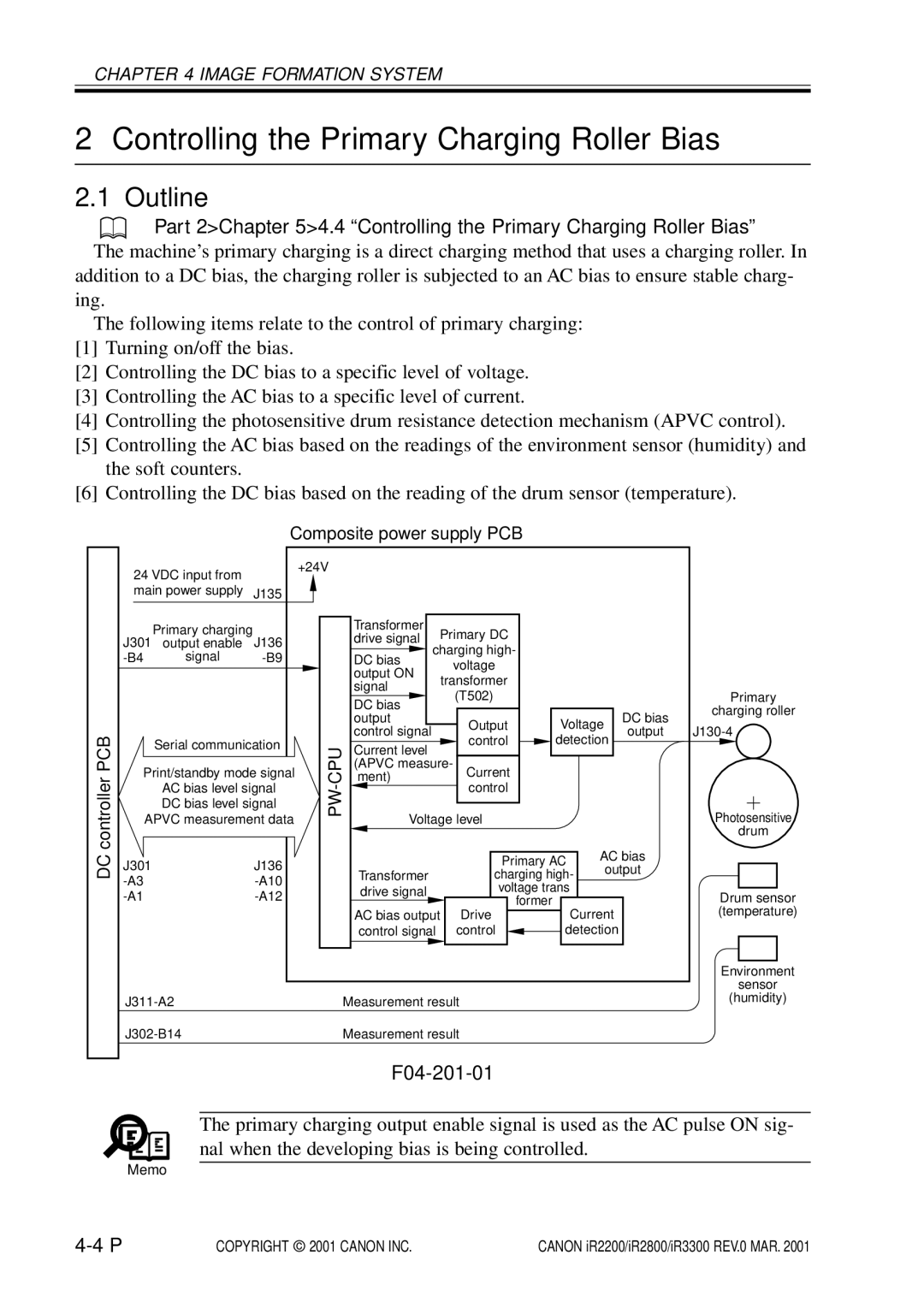
Controlling the Primary Charging Roller Bias
F04-201-01
Turning On/Off the Bias
Controlling the Current Voltage/Current to a Specific Level
Temperature Correction of the DC Bias
Humidity Correction of the AC Bias
F04-204-01
F04-205-01
Image Formation System
COPIERADJUSTHV-PRIP-AC
COPIERADJUSTHV-PRIAGS-GAIN
COPIERADJUSTHV-PRIAGS-OFST
COPIERADJUSTHV-PRIOFST1-AC
Controlling the Transfer Charging Roller Bias
F04-301-01
10 P
Controlling the Output by Operating Mode
Types of Modes
Turning On/Off the Cleaning Bias
F04-304-01
12 P
Controlling the Output
Controlling the Separation Static Eliminator Bias
Part 2Chapter 58.3 Static Eliminator Separation Method
F04-401-01 14 P
Controlling the Bias to a Specific Voltage Level
Controlling the Transfer Guide Bias
Transfer Guide Bias
Part 2Chapter 57.2 Transfer Guide Type
F04-501-01 16 P
Primary Charging Roller Cleaning Mechanism
Part 2Chapter 510.1.5 Cleaning the Primary Charging Roller
F04-601-01
Developing Assembly
F04-701-01 18 P
Controlling the Developing Bias
F04-702-01
Controlling the DC Developing Bias
Controlling the AC Developing Bias
Controlling the Level of the DC Developing Bias
20 P
Detecting the Level of Toner
F04-703-01
Drum Cleaner
F04-801-01 22 P
F04-801-02
Monitoring the Waste Toner Case
F04-802-01 24 P
Locking of the Waste Toner Feedscrew
26 P
Pre-Exposure Lamp Unit
Removing the Pre-Exposure Lamp Unit
F04-901-01
Photosensitive Drum
Removing the Drum Unit
F04-902-01
F04-902-02
Cleaning the Photosensitive Drum
Transfer Charging Roller
Removing the Transfer Charging Roller
F04-903-01
F04-903-02 30 P
Charging Roller Solenoid
Removing the Charging Roller Solenoid SL6
F04-904-01 F04-904-02
F04-904-03 F04-904-04 F04-904-05 32 P
Developing Assembly
Removing the Developing Assembly
F04-905-01
Removing the Grip Assembly
Removing the Developing Assembly Upper Cover
Removing the Toner Sensor
F04-905-02 F04-905-03
Removing the Blade Base Unit
Removing the Developing Cylinder
F04-905-05 F04-905-06
F04-905-07
F04-905-08
F04-905-09
F04-905-10 36 P
F04-905-11
F04-905-12
F04-905-13
Positioning the Developing Assembly Magnetic Seal
Mounting the Developing Assembly Blade
F04-905-14
F04-905-15
When Removing the Paper Lint
Removing the Paper Lint
Removing the Paper Lint
F04-906-01
Waste Toner Case
Replacing the Waste Toner Case
F04-907-01 F04-907-02 F04-907-03 40 P
Cleaning the Waste Toner Case
F04-907-04 F04-907-05 F04-907-06
Chapter PICK-UP/FEEDING System
Specifications and Construction
T05-101-01
Arrangement of Rollers
F05-101-01
Arrangement of Motors, Clutches, and Solenoids
F05-102-01
Arrangement of Sensors
F05-103-01
T05-102-01
Delay Jam
Cassette Pickup Assembly cassette 1
Detecting Jams
Sequence of Operations jam detection
Other Delay Jams
F05-201-02
T05-201-02
F05-201-03 Power-On Stationary Jam
Stationary Jam
Jam History
Common Stationary Jam
Pickup Assembly
Pickup Control System
F05-301-01
Outline
Sequence of Operations pickup
Cassette
F05-303-01 10 P
Operation of the Cassette Lifter
Operation of the Lifter During Printing
F05-304-01
Releasing the Lifter
Switching the Pickup Roller Drive
Cassette Pickup Operation
Rotating the Pickup Roller
Pickup Roller Shaft Reference
F05-305-02
F05-305-03 14 P
Moving Up/Down the Pickup Roller
F05-306-01
F05-306-02
Conditions for Detecting a Delay
Pickup Retry Operation
F05-307-01 Retry Operation 16 P
Paper Retraction
F05-307-02
Operation Other Than Cassette Pickup standby
F05-308-01 18 P
F05-308-02
F05-308-03 20 P
F05-308-04 Releasing the Lifter
Detecting the Level of Paper
F05-309-01
T05-309-01 22 P
Detecting the Presence/Absence of Paper Inside the Cassette
F05-310-01
AB-/Inch-Setting Switch
Identifying the Size of Paper
Identifying the Size
F05-402-01 24 P
Paper Size
A4R
F05-403-01 Rotary Label
Paper Size List
T05-403-01 List of Paper Sizes 26 P
Multifeeder
F05-501-01
Identifying the Size of Paper in the Multifeeder
Detecting the Width of Paper
Rear/Front Registration
Identifying the Length of Paper
COPIERADJUSTFEED-ADJREGIST
Controlling the Registration Roller
Control System
COPIERADJUSTFEED-ADJADJ-REFE
Double-Sided Printing
Through-Path Operation
Outline of Operations
F05-703-01
F05-703-02 32 P
Detecting the Horizontal Registration Position
T05-703-01
Operation
F05-703-02
Controlling the Pickup Assembly Motor
Pickup Assembly Motor
T05-801-01
F05-801-01
Disassembly and Assembly
Pickup Assembly
Removing the Pickup Assembly
F05-901-01
F05-901-02
Removing the Pickup/Feeding/Separation Rollers
F05-901-04
F05-901-05 38 P
Removing the Frame Lid
F05-901-06
F05-901-07 F05-901-08
Removing the Pickup Motor
Remove the Vertical Path Cultch
F05-901-09 F05-901-10 F05-901-11 40 P
Removing the Horizontal Registration Sensor Shift Motor
F05-901-12
F05-901-13
F05-901-14
Adjusting the Cassette Rear Front Registration
Checking the Image Rear Front Position
F05-901-15
COPIERFUNCTIONC1- ADJ-Y/C2-ADJ-Y/C3-ADJ-Y/ C4-ADJ-Y
F05-901-16
F05-901-17
Multifeeder Tray Assembly
Removing the Multifeeder Tray Assembly
F05-902-01
F05-902-02
Removing the Pickup Cover
Removing the Multifeeder Tray Pickup Roller
F05-902-03
F05-902-04
Removing the Separation Pad
F05-902-05
F05-902-06
F05-902-07 46 P
Adjusting the Registration for the Multifeeder Rear Front
Attaching the Timing Belt of the Multifeeder Tray
F05-902-08
F05-902-09
F05-902-10 48 P
Feeding Assembly
Removing the Feeding Assembly
F05-903-01
F05-903-02
Mounting the Feeding Assembly
F05-903-04 50 P
Registration Roller Assembly
Removing the Registration Roller
F05-904-01 F05-904-02 F05-904-03
F05-904-04
F05-904-05
F05-904-06 52 P
F05-904-07
Chapter Fixing System
Fixing system has the following major functions
T06-101-01
F06-101-01
F06-101-02
T06-101-02
Fixing Drive System
Controlling the Fixing Roller Drive
F06-202-01
COPIERADJUSTFIXINGFX-FL-SP COPIERADJUSTFIXINGFX-FL-TH
Controlling the Fixing Film Speed
F06-202-02
Controlling the Fixing Temperature
F06-301-01
Temperature Control
T06-302-01
Copieroptionbody
FIX-TEMP
Fixing Temperature Control
F06-302-01
Detecting Errors
F06-303-01
10 P
Disassembly and Assembly
Fixing Assembly
Removing the Delivery Cover
Removing the Riser Guide
F06-401-01
Removing the Fixing Assembly
Removing the Fixing Stepped Gear
Removing the Fixing Film Unit
F06-401-04 F06-401-05 F06-401-06
F06-401-07 F06-401-08
F06-401-09
F06-401-10 F06-401-11 F06-401-12
Removing the Cleaning Roller Unit
Removing the Lower Guide Ribs
F06-401-13 F06-401-14 16 P
Removing the Fixing Drive Unit
Mounting the Locking Cam Unit
F06-401-15
F06-401-16 F06-401-17
Chapter Externals and Controls
Control Panel
F07-101-01
COPIERFUNCTIONPANELLED-CHK
COPIERFUNCTIONPANELLED-OFF
Arrangement, Functions, and Error Codes
Fans
T07-201-01
F07-201-01
Operation
1 2-Speed Control
Sequence of Operations
F07-202-01
Power Supply
Power Supply
T07-301-01
Machine distributes power as follows
F07-301-01
Power Outputs
T07-301-02
F07-301-02
PCB
Rated Outputs of the Main Power Supply PCB
Rated Output of the Composite Power Supply PCB
T07-302-01
T07-303-01
Rated Outputs of the Accessories Power Supply PCB
T07-304-01
Protective Functions
Silent Mode
Others
Disassembly and Assembly
F07-501-01
Removing the Front Cover
Removing the Inside Cover
F07-501-02 F07-501-03 14 P
Removing the Support Cover
F07-501-04
Control Panel
Removing the Control Panel
F07-502-01
F07-502-02 16 P
Points to Note When Replacing the DC Controller PCB
Removing the DC Controller PCB
Removing the Controller Cover
F07-503-01
Removing the HDD
F07-503-03
F07-503-04 18 P
Removing the HDD Unit
Removing the Controller Box Unit
F07-503-05
F07-503-06
Removing the Main Controller PCB
F07-503-07
F07-503-08 20 P
10When Replacing the Main Controller PCB
11Removing the Composite Power Supply
12Removing the Accessories Power Supply
F07-503-09
13Removing the Main Power Supply
F07-503-11 22 P
Chapter Paper DECK-L1
Pickup
Pickup Operation
F08-101-01
Sequence of Pickup Operations deck
F08-101-02
Switching the Deck Paper Size
Detecting Paper in the Deck
Detecting the Presence/Absence of Paper
F08-102-01 F08-102-02
Detecting the Level of Paper in the Deck
T08-102-01
PS2D PS8D PS7D
Deck Lifter
F08-103-01
Indicating the Level of Paper deck front cover
F08-103-02
Opening/Closing of the Compartment
Opening/Closing of the Compartment
F08-104-01
Sequence of Operations opening/closing of the compartment
F08-104-02 10 P
Controlling the Deck Motor
Controlling the Deck Main Motor M1D
Turning On/Off the Motor
F08-105-01
Controlling the Deck Lifter Motor M2D
F08-105-02
M2D
F08-201-01
T08-201-01 14 P
PS1D
PS6D
F08-201-02
Intr Scan Print
Disassembly and Assembly
Sliding Out the Compartment
F08-301-01 F08-301-02
F08-301-03
F08-301-04 18 P
Adjusting the Paper Level Indicator
F08-301-05
F08-301-06-A
Removing the Rear Cover
Moving the Deck Lifter
F08-301-06-B
F08-301-07 20 P
Removing the Right Cover
Removing the Front Upper Cover
F08-301-08 F08-301-10
Removing the Upper Cover
F08-301-11 22 P
Paper Deck Body
F08-302-01
F08-302-02-A
F08-302-02-B
F08-302-03 24 P
Removing the Compartment
F08-302-04 F08-302-05
F08-302-06 F08-302-07 26 P
Changing the Deck Paper Size
After Changing the Deck Paper Size
Copieroptionaccdk
F08-302-08
F08-302-09
COPIERFUNCTIONDK- ADJ-Y
Adjusting the Registration for the Deck
Adjusting the Position of the Support Member
F08-302-10
F08-302-11
Drive System
Removing the Deck Pickup Clutch CL2D
Removing the Deck Feeding Clutch CL1D
F08-303-01-A
Removing the Deck Main Motor M1D
Removing the Deck Lifter Motor M2D
F08-303-02
F08-303-03
Removing the Lifter Cable deck front
F08-303-04
F08-303-05a F08-303-05b 32 P
F08-303-06
F08-303-07
Removing the Lifter Cable deck rear
F08-303-08 F08-303-09 34 P
F08-303-10 F08-303-11
Routing the Lifter Cable
F08-303-12 36 P
Feeding Mechanism
Removing the Deck Pickup Unit
Removing the Deck Pickup Roller
F08-304-01
Mounting the Deck Pickup Roller
Removing the Deck Pickup/Feeding Roller
F08-304-04 F08-304-05
F08-304-06 38 P
Orientation of the Deck Pickup/Feeding Roller
Removing the Deck Separation Roller
F08-304-07 F08-304-08
F08-304-09
Adjusting the Deck Separation Roller Pressure
F08-304-10 40 P
Position of the Deck Pickup Roller Releasing Solenoid SL1D
F08-304-11
Removing the Open Switch PCB
Electrical Mechanisms
Removing the Deck Drive PCB
F08-305-01
Chapter Cassette Feeding UNIT-W1
T09-101-01
Following rollers are used to move paper inside the machine
F09-103-01
M1C
M2C
CL1C
F09-104-01
PS2C
PS3C
Delay Jams
Sequence of Jam Detection
Stationary Jams
F09-301-01
Detecting the Presence/Absence of Paper Inside the Cas Sette
AB/Inch-Setting Switch
Disassembly and Assembly
F09-501-01
F09-501-02
F09-501-03 F09-501-04
F09-502-01 F09-502-02 12 P
Adjusting the Registration for the Cassette Rear Front
Removing the Pickup/Feeding/Separation Roller
Removing the Pickup Soleroid
Removing the Vertical Path Clutch
Removing the Cassette Size Detection Unit
F09-503-01 F09-503-02 14 P
Removing the Pedestal Controller PCB
F09-503-03
Drive Mechanisms
Removing the Main Motor Drive Unit
Removing the Pedestal Main Motor
F09-504-01 F09-504-02 16 P
Mounting the Pedestal Main Motor
F09-504-03
Chapter Inner 2 WAY TRAY-A1
Type
T10-101-01
F10-101-01
10-1 P
F10-102-01
10-2 P
Arrangement of Rollers and Sensors
F10-201-01
10-3 P
Delivery to the No Delivery Slot
F10-202-01
F10-202-02 10-4 P
F10-203-01
F10-203-02
10-5 P
F10-203-03
F10-203-04 10-6 P
Detecting Jams
Arrangement of Sensors
F10-204-01
10-7 P
F10-204-02
10-8 P
PS20B
Stationary Jam at Power-On
Door Open Jam
F10-204-03
10-9 P
10-10 P
Removing the Inner 2-Way Delivery Unit
F10-301-01
F10-301-02
F10-201-03
F10-201-04
F10-201-05 10-12 P
F10-201-06
F10-201-07
F10-201-08 10-14 P
Chapter Envelope Feeder ATTACHMENT-B1
Envelope Feeder Attachment-B1
Host Machine
Names of Parts
Specifications
Envelope Cassette
T11-102-01 11-2 P
Envelopes
T11-102-02
F11-102-01
11-3 P
Guaranteed Image Area
F11-102-02
F11-102-03
F11-102-04 11-4 P
Pickup Operations
11-5 P
Error Codes
Service Mode
Making Selections
Option Envsw
Making Adjustments
Replacing the Spring
Envelopes and Type of Spring
Replacing the Spring
Changing the Size
Changing the Size
F11-502-03 F11-503-01 11-8 P
ISO-C5
COM10, Youkei ISO-B5
11-9 P
Troubleshooting
Maintenance and Inspection
Troubleshooting Image FAULTS/ Malfunctions
Registration roller fails to Rotate
DC-CON
CON
MN-CON
Feeder
Board
DIMM/ROM
Chapter Maintenance and Inspection
Periodically Replaced Parts
Checking the Time of Replacement
Consumables and Durables
COPIERCOUNTERDRBL-2
T01-203-01
Inner 2-Way Tray-A1
T01-203-03
Periodical Servicing Procedure
Work Procedure
Maintenance and Inspection
Scheduled Servicing Chart
T01-401-01
Upon replace
Points to Note for Scheduled Servicing
F01-500-01
Cleaning the Bottom of the Developing Assembly
Cleaning the Bottom of the Developing Assembly
F01-601-01
Chapter Image Adjustment Basic Procedure
Image Adjustment Basic Procedure
YES DISPLAYHV-STS
Chapter Standards and Adjustments
Image Adjustments
Standards of Image Position
F03-101-01 Image Leading Edge Margin
F03-101-03 Leading Edge Non-Image
Checking the Image Position
Adjusting Left/Right lamge Margin
F03-103-01
F03-103-02
COPIERFUNCTIONMF- ADJ
Copierfunctiondk ADJ-Y
F03-103-04
Adjusting the Image Leading Edge Margin
Adjusting the Left/Right Non-Image Width
Duplex Feeding Unit
F03-104-01
Adjusting the Leading Edge Non-Image Width
Copieradjustccd
Scanning System
After Replacing the Scanning Lamp
Mounting the Motor Unit
F03-202-01 F03-202-02
Routing the Scanner Drive Cable
F02-203-01
Adjusting the Position of the No /No Mirror Base
F03-204-01
F03-204-02
F03-204-03 F03-204-04 10 T
Mounting the Copyboard Glass
Points to Note When Replacing the CCD Unit
When Replacing the Reader Controller PCB
Mounting the Reader Upper Frame
F03-206-01
Positioning the Developing Assembly Magnetic Seal
Mounting the Developing Assembly Blade
F03-303-02 14 T
Cleaning the Waste Toner Case
F03-304-02
F03-304-03
Fixing System
Mounting the Locking Cam Unit
F03-401-01 16 T
Paper Deck
Mounting the Front Cover
F03-501-01 F03-501-02
Adjusting the Paper Level Indicator
Adjusting the Position of the Support Member
F03-502-01
F03-503-01 18 T
Mounting the Deck Pickup Roller
Removing the Deck Pickup/Feeding Roller
F03-504-01 F03-504-02
F03-505-01
Adjusting the Deck Separation Roller Pressure
Orientation of the Deck Pickup/Feeding Roller
F03-506-01
F03-507-01 20 T
Position of the Deck Pickup Roller Releasing Solenoid SL1D
F03-508-01
Adjusting the Height of the Side Member
Before Making Adjustments
Making Adjustments
F03-509-01 22 T
Cassette Feeding Unit-W1
Mounting the Pedestal Main Motor
F03-601-01
Envelope Feeder Attachment
Envelopes and Type of Spring
F03-702-01
F03-702-02 24 T
F03-702-03 F03-703-01
26 T
Chapter Troubleshooting Image Faults Malfunctions
Checking the Site of Installation
Making Initial Checks
Checking the Originals
Checking the Developing Assembly
Image Adjustment Basic Procedure
Charging Roller and Static Eliminator
Checking the Paper
Others
Blank
Samples of Image Faults
Troubleshooting Image Faults
Copy is too light halftone area only
Copy is too light including solid black
Resistance of the high-voltage cord white is about 10 k Ω
Copy is too light entire face, considerable
11 T
12 T
Copy is foggy entire face
14 T
Copy has a black line vertical, fine
16 T
Copy has a white spot horizontal
Back of the copy is soiled/Soiled edge
Copy has a fixing fault
Regist
Copy is blurred
YES
Copy is foggy horizontal
Copy has inadequate sharpness
Copy is completely blank
25 T
Copy is completely black
Copy has a black line stream reading
Troubleshooting Malfunctions
Power Supply System
AC power is absent
28 T
DC power is absent
3VB
Pickup fails
30 T
Lifter fails to move up pickup from the cassette
Vertical path roller fails to rotate
Registration roller fails to rotate
32 T
33 T
Photosensitive drum fails to rotate
Pre-exposure lamp fails to go on
34 T
No mirror base fails to move
Scanning lamp fails to go on
36 T
Message Indication
Add Toner message fails to go OFF
Add Paper message fails to go OFF
Close the Front Cover message fails to go OFF
38 T
Paper Deck
Deck lifter fails to move up
40 T
Troubleshooting Feeding Faults
Paper Jams
F04-501-01
Pickup Assembly
42 T
Separation/Feeding Assembly
Fixing/Delivery Assembly, Duplex Reversing Assembly
Duplex Feeding Assembly
44 T
Faulty Feeding
Double Feeding
Wrinkles
Outline of Electrical Components
Introduction
Guide to the List
46 T
Checking the Photointerrupters
Paper Sensor
Open/Closed Sensor
Position Sensor, Presence/Absence Sensor
Clutches Solenoids, Switches
E201 reader unit/printer unit
F04-602-01 48 T
Clutches
Motors 1/2
F04-602-02 50 T
M1 DC-CON
M2 Feed
M3 DC-CON
M4 DC-CON
Motors 2/2
F04-602-02 52 T
M6 DC-CON
M9 DC-CON
Fans
F04-602-03 54 T
FM1 DC-CON
FM2 DC-CON
FM3 MN-CON
FM4 DC-CON
Sensors 1/3
F04-602-04 56 T
SD1 R-CON
BD DC-CON
PS1 DC-CON
PS2 DC-CON
Sensors 2/3
F04-602-04 58 T
PS8 DC-CON
PS9 DC-CON
PS10 DC-CON
PS11 DC-CON
Sensors 3/3
F04-602-04 60 T
S4 DC-CON
S5 DC-CON
VR1 DC-CON
Lamps, Heaters, and Others
F04-602-05 62 T
H4 Mpws
H5 Mpws
LAMP1 R-CON
CB1 Mpws
PCBs
F04-602-06 64 T
CCD PCB
Clutches Solenoids, and Switches Motors
F04-603-01
66 T
Solenoids and Switches
Sensors PCBs
F04-603-02 68 T
Sensors
Clutches Solenoids and Switches Motors
2-Cassette Feeding Unit-W1
F04-604-01 70 T
CL1C PEDE-FEED
SL1C PEDE-FEED
S1C PEDE-CON
S2C PEDE-CON
F04-604-02 72 T
PS1C PEDE-CON
PS2C PEDE-FEED
PS3C PEDE-FEED
Q1604 PEDE-FEED
Solenoids Motors Sensor
F04-605-01 74 T
Solenoids
Super G3 FAX Board-J1
Others PCBs
F04-606-01 76 T
SP1 FAX-CON
NCU PCB
Dimm
78 T
F04-607-01
Sdram
Protect the back-up data as follows
Reader Controller PCB
F04-607-02
F04-607-03 80 T
Composite Power Supply PCB
Fixing Film Sensor PCB
F04-607-04
F04-607-05
Chapter Service Mode
Outline of Service Mode
Starting Service Mode and Making Selections
F05-101-02
Ending Service Mode
Backing Up Service Mode
F05-104-01
Using Service Mode
Initial Screen
Level 1/Level 2 Item Screen
F05-105-01
Version Ready
FF.D9
ADJ-X
Display Control Display Mode
Copier
F05-201-01
Version
Punch
LANG-EN
LANG-FR
LANG-DE
LANG-NO
LANG-PL
LANG-PT
LANG-RU
User
ACC-STS
Analog
CST-STS
WIDTH-MF
JAM
ERR
FF Types of Jams Source of Paper
FFff Sensor/Type jams in feeder
Ff Jam Sensors
FFff Sensor/Type Jams in Saddle Finisher-G1
FFff Sensor/Type Jams in Finisher-J1
T05-201-05
T05-201-06
ERR
FFff
Eeee
HV-STS
Sensor
ALARM-2
ALARM-2 Ready
F05-201-04
Feeder
Feedsize
O, I/O Display mode
MN-CON
DC-CON
DC-CON 1/7
DC-CON 2/7
DC-CON 3/7
M7B
DC-CON 4/7
DC-CON 5/7
DC-CON 6/7
VR1
DC-CON 7/7
CON
CON 1/3
SD1
CON 2/3
FL1N
CON 3/3
MN-CON
MN-CON 1/2
MN-CON 2/2
Feeder 1/2
LED
SL2
Feeder 2/2
Sorter
Finisher-J1
Sorter 1/8
Sorter 2/8
CCW on
SW1
Sorter 3/8
Saddle Finisher-G1
Sorter 4/8
Full
Sorter 5/8
PI1P
MS3
MS1
Sorter 6/8
Puncher Unit Saddle Finisher-G1
Sorter 7/8
Sorter 8/8
M2P
M1P
T05-301-01
Adjust Adjustment Mode
F05-401-01 44 T
AE-TBL
F05-401-02
ADJ-XY
ADJ-Y
F05-401-03
F05-401-04 46 T
ADJ-S
F05-401-06
CCD
Laser
Develop
DE-DC
DE-OFST
Dens
Blank
DENS-ADJ
BLANK-T
HV-PRI
AGS-GAIN
AGS-OFST
OFST1-DC
HV-TR
TR-N1
TR-N2
TR-OFST
FEED-ADJ
CST-ADJ
Fixing
MF-A4
FX-FL-TH
FX-FL-SP
Misc
C1-ADJ-Y
DK-ADJ-Y
FRAME-X
FRAME-Y
IMG-DLY
Docst
LA-SPEED
F05-402-01
PNCH-HLE
F05-403-01
PNCH-Y
F05-403-02 60 T
Function Operation/Inspection Mode
Install
TONER-S
STRD-POS
CCD-ADJ
F05-501-02
SHDG-POS
240 to 320 a multiple of 8 causes a shift of about 0.17 mm
SH-PS-ST
EGGN-POS
F05-501-04 66 T
WHITE-ME
PD-DENS
F05-501-05
PD-ME
F05-501-06 68 T
DPC
CST
Gamma
MF-A4R MF-A6R MF-A4
NIP-CHK
F05-501-07
Panel
PART-CHK
Input Keys/Indications
CL-ON
MTR
MTR-ON
SL-ON
Codes and Clutches
T05-501-02
Codes and Motors
Codes and Solenoids
T05-501-03
T05-501-04 74 T
Service
Clear
ERR
JAM-HIST
Alarm
PWD-CLR
ADRS-BK
CNT-MCON
MISC-R
Scanlamp
MISC-P
Print
KEY-HIST
HIST-PRT
USER-PRT
C1-ADJ-Y
C2-ADJ-Y
MF-ADJ-Y
LBL-PRNT
PRE-EXP
System
Download
CHK-TYPE
HD-CHECK
Option Machine Settings Mode
F05-601-01 82 T
Body
MODEL-SZ
Scanslct
TRANS-SW
PRIAC-SW
SENS-CNF
Config
Sharp
COTDPC-D
DF-BLINE
DECRL-FN
TR-CLN
FAN-EXTN
COPY-LIM
COUNTER2
COUNTER3
COUNTER4
COUNTER5
TRY-STP
88 T
Soft Counter Specifications
T05-601-01a
T05-601-01b 90 T
T05-601-01c
CST-U1
CST-U2 CST-U3 CST-U4 CST-U5 CST-U6 CST-U7 CST-U8
92 T
Codes and Paper Names
T05-601-02
ACC
INT-FACE
Coin
DK-P
SIZE-SW
BLNK-SW
MD-SPRTN
F05-603-01
Board
96 T
Test Test Print Mode
F05-701-01
Type Input Numbers and Test Prints
T05-701-01 98 T
Network
Ping
Network
F05-701-02
100 T
Counter Counter Mode
Clearing the Counter Readings
Dividing Papers Between Small-Size and Large-Size
List of Counter Items
102 T
Copiercounterfeeder
Level 2 DRBL-1
104 T
Chapter Self Diagnosis
Self Diagnosis
ADF
E000
Detail Codes copier
Copierfunctionclearerr
E001
E002
E003
Copierfunctionfclearerr
E007
E010
E014
E019
E032
E051
E064
E100
BD PCB
E110
E202
E204
E220
E225
E240
E243
E248
E261
E302
E315
E601
E602
E604
E605
E606
E674
E677
E710
E711
E712
E713
E716
E717
E719
E732
E733
E737
E740
E741
E743
E744
E803
E805
E901
ADF Error Codes
E420
E421
E422
Saddle Finisher-G1 Error Codes
Error Code of the Finisher Unit
E501
E505
E514
E530
E531
E532
E537
E540
E577
E590
E592
E593
E5F1
Finisher-J1 Error Codes
E500
Return roller is faulty
E580
E585
Chapter Upgrading
Download Mode
Downloading in Download Mode
Bootdev ALL
Upgrading
Downloading in Service Mode
Making Pre-Checks
Pdldev Fstdev Dosdev
F07-101-02
Memo
Data Control
F07-102-01
F07-102-02
F07-102-03
F07-102-04
Downloading the System Software, RUI, and Language Module
Making Connections
Downloading
F07-103-01
F07-103-02
F07-103-03
F07-103-04 10 T
F07-103-05
F07-103-06
F07-103-07
F07-103-08 12 T
F07-103-09
Upgrading the Boot ROM
After Downloading
Making Preparations
HDD COPIERDISPLAYVERSIONMN-CONT
Preparing Boot ROM
Connection
F07-104-01
F07-104-02
F07-104-03 16 T
F07-104-04
F07-104-05
F07-104-06
F07-104-07 18 T
Boot ROM COPIERDISPLAYVERSIONBOOT-ROM
F07-104-08
Formatting the HDD
Starting Formatting
F07-105-01 20 T
F07-105-02
F07-105-03
F07-105-04
F07-105-05 22 T
F07-105-06
F07-105-07
F07-105-08
F07-105-09 24 T
F07-105-10
07-105-11
Points to Note When Formatting the Hard Disk
F07-105-12
Downloader PCB
Purpose
Downloader PCB Components
T07-106-01
Download Procedure a. Connecting to the option
Finisher -J1
DADF-H1
F07-106-02
Downloading
F07-106-03
F07-106-04
F07-106-05
F07-106-06 30 T
F07-106-07
F07-106-08
Disconnecting
F07-106-09
Upgrading by Replacing the DIMM/ROM
F07-107-01
Backing Up Data
Backing Up Data
Backing Up Data
F07-202-02 36 T
F07-202-03
F07-202-04
F07-202-05
F07-202-06 38 T
F07-202-07
F07-202-08
F07-202-09
F07-202-10 40 T
Downloading Backup Data
F07-202-11
F07-202-12
F07-202-13
F07-202-14 42 T
F07-202-15
F07-202-16
F07-202-17
Managing Backup Data
F07-202-18
F07-202-19
F07-202-20
F07-202-21 46 T
F07-202-22
Appendix
General Timing Chart
General Timing Chart printer unit
General Timing Chart reader unit w/ ADF
A4, 2 sheets, Signal-sided, Direct
General Circuit Diagram
From FAX Unit
Side Paper Deck-L1 General Circuit Diagram
Side deck drier PCB
Cassette Feeding Unit-W1 General Circuit Diagram
Cassette pickup PCB
Inner 2-Way Tray-A1 General Circuit Diagram
List of Special Tools
Appendix
List of Solvents/Oils
Canon INC
This publication is printed on 100% recycled paper