User Guide
Legal Notice
Copyright Information
Open Source Code
Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
490
477
485
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Contents
Contents Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
About this Guide
Feature Description
What’s New In ArubaOS
Issued
Users using them in a given network
Spectrum enhancements
Spectrum recording information
WebUI
Fundamentals
Type Style Description
Related Documents
Conventions
Page
Deployment Scenario #1 Controller and APs on Same Subnet
Understanding Basic Deployment and Configuration Tasks
Basic User-Centric Networks
APs All on One Subnet Different from Controller Subnets
APs on Multiple Different Subnets from Controllers
Running Initial Setup
Configuring the Controller
Connecting to the Controller after Initial Setup
Using the LCD Screen
Dell W-7200 Series Controller
New Port Numbering Scheme
Displays
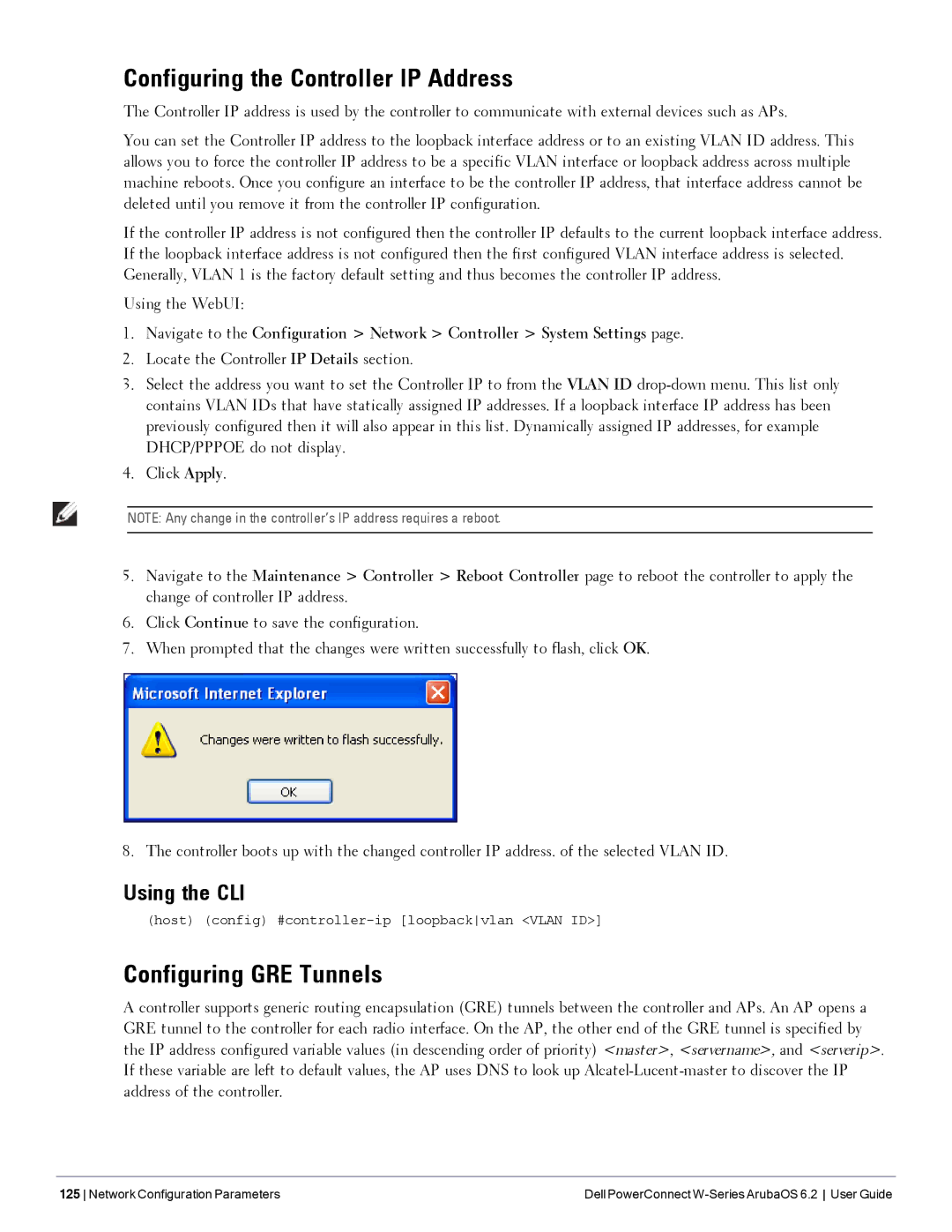
Upgrading an Image
Using the LCD and USB Drive
Uploading a Pre-saved Configuration
Disabling LCD Menu Functions
Configuring a Vlan to Connect to the Network
Creating, Updating, and Deleting Vlan Pools
Assigning and Configuring the Trunk Port
Creating, Updating, and Viewing VLANs and Associated IDs
Configuring the Loopback IP Address for the Controller
Configuring the Default Gateway
To confirm the port assignments, use the show vlan command
WebUI
Controller returns the following messages
Configuring the System Clock
Enter y to reboot the controller or n to cancel
Configuring Your User-Centric Network
Enabling Wireless Connectivity
Installing Licenses
Connecting the Controller to the Network
Must explicitly enable Telnet on the controller
Control Plane Security
Configure the following control plane security parameters
Configuring Control Plane Security
Control Plane Security Overview
Parameter Description
Example
CLI
Adding APs to the Campus and Remote AP Whitelists
Managing AP Whitelists
Status Entry
Viewing Whitelist Status
Address as a name
Control Plane Security Campus AP Whitelist status only
Status Entry Description
Click the Campus AP Whitelist tab
Command Description
Modifying an AP in the Campus AP Whitelist
Purging the Campus AP Whitelist
Revoking an AP via the Campus AP Whitelist
Deleting an AP Entry from the Campus AP Whitelist
With local Dell
Campus AP whitelist contains Master switch
Managing Whitelists on Master and Local Controllers
Viewing the Master or Local Switch Whitelist
Viewing and Managing the Master or Local Switch Whitelists
Campus AP Whitelist Synchronization
Data Column Description
Deleting an Entry from the Master or Local Switch Whitelist
Configuring Networks with Clusters of Master Controllers
Configuring Networks with a Backup Master Controller
Purging the Master or Local Switch Whitelist
Working in Environments with Multiple Master Controllers
Creating a Cluster Root
Click the Cluster Setting tab
Creating a Cluster Member
Viewing Controller Cluster Settings
To view your current cluster configuration via the WebUI
Replacing a Local Controller
Replacing a Controller on a Multi-Controller Network
Replacing Controllers in a Single Master Network
Replacing a Redundant Master Controller
Replacing a Master Controllerwith No Backup
Replacing Controllers in a Multi-Master Network
Replacing a Cluster Member Controller with no Backup
Replacing a Local Controller in a Multi-Master Network
Replacing a Redundant Cluster Member Controller
Replacing a Redundant Cluster Root Controller
Troubleshooting Control Plane Security
Configuring Control Plane Security after Upgrading
Identifying Certificate Problems
Manually Certify Campus APs
Verifying Whitelist Synchronization
Verifying Certificates
Disabling Control Plane Security
Rogue APs
Supported APs
Software Licenses
Understanding License Terminology
Working with Licenses
Working with Licenses on a Multiple Controller Network
Using Licenses
License
Basis What Consumes One License
Controller Total AP Count Campus APs Remote APs
Understanding License Interaction
Enabling a new license on your controller
License Installation Best Practices and Exceptions
Installing a License
Locating the System Serial Number
Requesting a Software License in Email
Obtaining a Software License Key
Creating a Software License Key
Deleting a License
Resetting the Controller
Moving Licenses
Applying the Software License Key in the WebUI
Page
Network Configuration Parameters
Configuring VLANs
You can create and update a single Vlan or bulk VLANs
Navigate to the Configuration Network VLANs
Creating Named VLANs
Navigate to Configuration Network VLANs
Creating a Named Vlan not in a Pool
Creating Bulk VLANs In the WebUI
Creating a Vlan Pool
Using the WebUI
This example assigns a name to an existing Vlan ID
This example assigns a Vlan name in a virtual AP
Creating a Vlan Pool
Distinguishing Between Even and Hash Assignment Types
Viewing and Adding Vlan IDs Using the CLI
Creating a Vlan Pool Using the CLI
Following example shows how to view Vlan IDs to a Vlan pool
Updating a Vlan Pool
Optimizing Vlan Broadcast and Multicast Traffic
Adding a Bandwidth Contract to the Vlan
Using the CLI
Configuring Ports
Proxy Arp is disabled for the Interface
Navigate to Configuration Network IP
Classifying Traffic as Trusted or Untrusted
Configuring Trusted/Untrusted Ports and VLANs
About Trusted and Untrusted Physical Ports
About Trusted and Untrusted VLANs
This example
For Port Mode select Trunk
Assigning a Static Address to a Vlan
Understanding Vlan Assignments
How a Vlan Obtains an IP Address
Configuring Multiple Wired Uplink Interfaces Active-Standby
Configuring a Vlan to Receive a Dynamic Address
Navigate to the Configuration Network IP IP Interfaces
Enabling the Dhcp Client
Select Obtain an IP address with PPPoE
Enabling the PPPoE Client
Select Apply
Default Gateway from DHCP/PPPoE
Configuring DNS/WINS Server from DHPC/PPPoE
Configuring Source NAT for Vlan Interfaces
Configuring Source NAT to Dynamic Vlan Address
Inter-VLAN Routing
Example Configuration
Navigate to the Configuration Network IP IP Interface
Configuring Static Routes
Using the WebUI to restrict Vlan routing
Apply
Configuring the Loopback IP Address
Modify the IP Address as required Click
Using the CLI
Configuring the Controller IP Address
Configuring GRE Tunnels
Creating a Tunnel Interface
Navigate to the Configuration Network IP GRE Tunnels
Directing Traffic into the Tunnel
Static Routes
CLI
Tunnel Keepalives
WebUI
Understanding IPv6 Notation
This chapter describes ArubaOS support for IPv6 features
Understanding IPv6 Topology
IPv6 Support
Enabling IPv6 Support for Controller and APs
Enabling IPv6
Features Supported on IPv6 APs?
To Configure Link Local Address
Configuring IPv6 Addresses
To Configure Global Unicast Address
Yes Limited
To Configure Loopback Interface Address
Configuring IPv6 Static Neighbors
To Configure IPv6 Default Gateway
Configuring IPv6 Default Gateway and Static IPv6 Routes
To Configure Static IPv6 Routes
Managing Controller IP Addresses
To Modify IPv6 MLD Parameters
Configuring Multicast Listener Discovery MLD
Provisioning an IPv6 AP
Debugging an IPv6 Controller
Filtering an IPv6 Extension Header EH
Configuring a Captive Portal over IPv6
Working with IPv6 Router Advertisements RAs
To view the EH types denied
You can use the WebUI or CLI to configure IPv6 RA on a Vlan
Configuring an IPv6 RA on a Vlan
Using WebUI
Using CLI
Configuring Optional Parameters for RAs
To configure neighbor discovery retransmit time
Navigate to the ConfigurationNetworkIP
To configure IPv6 recursive DNS server
To configure RA hop-limit
Viewing IPv6 RA Status
Supported Network Configuration
XSec No not tested MAC-based Yes
Understanding Authentication
Authentication Method Supported for IPv6 Clients?
Authentication Description Method
Working with Firewall Features
Understanding Firewall Policies
Field Description
Creating an IPv6 Firewall Policy
To assign an IPv6 policy using the WebUI
Assigning an IPv6 Policy to a User Role
For Host IP, enter 2002d81ff9f01000
Understanding IPv6 Exceptions and Best Practices
Managing IPv6 User Addresses
Host config #ipv6 enable
Link Aggregation Control Protocol Lacp
Understanding Lacp Best Practices and Exceptions
Set the port priority
Configuring Lacp
Lacp Sample Configuration
151
OSPFv2
Understanding Ospf Deployment Best Practices and Exceptions
Wlan Topology
Understanding OSPFv2 by Example using a Wlan Scenario
Wlan Routing Table
Below is the routing table for Router
Branch Office Ospf Topology
Branch Office Topology
Branch Office Routing Table
Configuring Ospf
Routing table of the Central office controller is below
Routing table for Router 1 is below
Select the Add button to add an area see Figure
General Ospf Configuration
Remote Branch
Sample Topology and Configuration
Remote Branch
Central Office Controller-Active
Central Office Controller-Backup
OSPFv2 Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide OSPFv2
Tunneled Nodes
Understanding Tunneled Node Configuration
Navigate to ConfigurationAdvanced ServicesWired Access
Configuring a Wired Tunneled Node Client
For example
WebUI
Configuring a Trunk Port as a Tunneled Node Port
Configuring an Access Port as a Tunneled Node Port
Locate the Wired Access Concentration Configuration section
Verify the configuration
On the tunneled node client
Sample Output
Page
Understanding Servers and Server Groups
Authentication Servers
Describes the parameters you configure for a Radius server
Configuring Servers
Configuring a Radius Server
Default 5 seconds
Timeout
Override the global configuration
NAS IP address to send in Radius packets
Radius Server Authentication Codes
Configuring an RFC-3576 Radius Server
Radius Server Fully Qualified Domain Names
Set a DNS Query Interval
Host IP address of the Ldap server Default N/A Admin-DN
Configuring an Ldap Server
Describes the parameters you configure for an Ldap server
Enter parameters as described in Table
Configuring a TACACS+ Server
Defines the TACACS+ server parameters
Type Connection type is Ldap-s Start-tls Clear-text
Configuring a Windows Server
Parameters
Configuring the Internal Database
Managing the Internal Database
Managing Internal Database Files
Enter the following command in enable mode
Exporting Files in the WebUI
Parameters Description
Working with Internal Database Utilities
Configuring Server Groups
Configuring Server List Order and Fail-Through
Configuring Server Groups
Select Fail Through
Configuring Dynamic Server Selection
Scroll to the right and click Add Server Click Apply
Click Add Rule
Trimming Domain Information from Requests
Configuring Match Fqdn Option
Configuring Server-Derivation Rules
Top
Controller when the rule is applied
Default bottom
Management Authentication
User Authentication
Navigate to the Configuration Management Administration
Assigning Server Groups
Radius Accounting
Accounting
Select AAA Profile, then select the AAA profile instance
TACACS+ Accounting
Configuring Authentication Timers
Timer Description
Default 5 minutes
Setting an Authentication Timer
Logon User Lifetime
Range
MAC-based Authentication
Configuring MAC-Based Authentication
Configuring the MAC Authentication Profile
Parameter
Using the WebUI to configure a MAC authentication profile
Configuring Clients
Using the CLI to configure a MAC authentication profile
Disables blacklisting
CLI
802.1X Authentication
Understanding 802.1X Authentication
Supported EAP Types
Configuring Authentication with a Radius Server
802.1X Authentication with Radius Server
Configuring Authentication Terminated on Controller
Configuring 802.1X Authentication
Default User Role Guest role Reauthentication
Failures, and the default value is 0 failures
Timer per role overrides this setting
This option is disabled by default
Default value is
Interval Seconds, and the default value is 30 seconds
Count
Requests
Disable this feature
Key Exchange Delay between WPA/WPA2
Authentication takes place
Option is disabled by default
Use to authenticate itself to the client
For the cached information. The default value is 24 hours
Disabled by default
Negotiation Disabled by default WPA-Fast-Handover
Configuring and Using Certificates with AAA FastConnect
Machine User Auth Description Role Assigned Status
Configuring User and Machine Authentication
Enabling 802.1x Supplicant Support on an AP
Authenticated Vlan configured Virtual AP profile
Machine Auth User Auth Description Vlan Assigned Status
Virtual AP profile
Provisioning an AP as a 802.1X Supplicant
To view the 802.1x authentication details on the controller
Prerequisites
Configuring Authentication with an 802.1X Radius Server
Sample Configurations
Configuring Roles and Policies
Creating the Student Role and Policy
Can use the alias for other rules and policies
Creating the Guest Role and Policy
Using the WebUI
Creating the Faculty Role and Policy
Under Time Range, select working-hours
Creating Roles and Policies for Sysadmin and Computer
Configuring the Radius Authentication Server
Creating an Alias for the Internal Network Using the CLI
Using the WebUI to create the computer role
Select Enforce Machine Authentication
Configuring 802.1X Authentication
Configuring VLANs
Navigate to the Configuration Wireless AP Configuration
Configuring the WLANs
Configuring the Guest Wlan
AP Group list, click Edit for the first-floor
Configuring the Non-Guest WLANs
CLI
Configuring a Server Rule Using the CLI
Configuring a Server Rule Using the WebUI
Select Termination
Configuring WLANs
Configuring the Guest Wlan
Configuring the Non-Guest WLANs
Authentication
Configuring Mixed Authentication Modes
Describes the different authentication possibilities
802.1x Logon
Configuring Reauthentication with Unicast Key Rotation
Performing Advanced Configuration Options for
Stateful and WISPr Authentication
Working With Stateful Authentication
Configuring Stateful 802.1x Authentication
Working With WISPr Authentication
Understanding Stateful Authentication Best Practices
Configuring Stateful Ntlm Authentication
Configuring Stateful Kerberos Authentication
Configuring WISPr Authentication
Profiles list, expand the WISPr Authentication Profile
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide 227
Configuring an Ocsp Controller as a Responder
Configuring a Controller as Ocsp and CRL Clients
Understanding Ocsp and CRL
Certificate Revocation
Navigate to the Configuration Management Certificates Upload
Configuring the Controller as an Ocsp Client
Select the Revocation Checkpoint tab
Configuring the Controller as a CRL Client
Configuring the Controller as an Ocsp Responder
Select Enable next to Enable Ocsp Responder
Understanding Captive Portal
Captive Portal Authentication
Navigate to the Configuration Management General
Configuring Captive Portal in the Base Operating System
Policy Enforcement Firewall Next Generation Pefng License
Controller Server Certificate
WebUI
CLI
Using Captive Portal with a Pefng License
To configure captive portal with Pefng license via the WebUI
Configuring Captive Portal in the WebUI
Creating a Guest User Role
Sample Authentication with Captive Portal
Configuring Captive Portal in the CLI
Select Add to add the guest-logon-access policy
Configuring Policies and Roles in the WebUI
Creating an Auth-guest User Role
Creating a Time Range
Creating Aliases
Creating an Auth-Guest-Access Policy
To configure the auth-guest-access policy via the WebUI
To create the block-internal-access policy via the WebUI
Creating an Block-Internal-Access Policy
Creating a Guest Role
Creating a Drop-and-Log Policy
To create the drop-and-log policy via the WebUI
To create a guest role via the WebUI
Creating an Auth-Guest Role
Configuring Policies and Roles in the CLI
Defining a Time Range
To create the guest-logon role via the WebUI
Creating a Guest-Logon-Access Policy
Configuring Guest VLANs
Creating a Block-Internal-Access Policy
Creating a Guest-Logon Role
Click Add For Vlan ID, enter Click Apply
Configuring Captive Portal Authentication Profiles
Modifying the Initial User Role
Configuring the AAA Profile
Managing User Accounts
Configuring the Wlan
Unauthenticated that a guest cannot access
Configuring Captive Portal Configuration Parameters
Utilization Logon Threshold Default 60% Logon wait
Role
Following are optional captive portal configurations
Enabling Optional Captive Portal Configurations
Changing the Protocol to Http
Uploading Captive Portal Pages by Ssid Association
Entity Engineering Business Faculty
Specify the fac-logon user
Security Access Control Policies
Configuring Redirection to a Proxy Server
L3 Authentication
For captive portal with Pefng license
For captive portal with role-based access
Redirecting Clients on Different VLANs
Personalizing the Captive Portal
Web Client Configuration with Proxy Script
Select the Your Custom Background
To customize the page background
Creating a New Internal Web
Creating and Installing an Internal Captive Portal
Username Example
Password Example
Fqdn Example
Variable
Basic Html Example
Installing a New Captive Portal
Displaying Authentication Error Messages
Configuring Localization
Reverting to the Default Captive Portal
This should be replaced with a link like this
Insert javascript to handle error cases
This should be replaced with a link like the following
Div id=errorbox style=display none /div
Sample Translated
Customizing the Welcome
Customizing the Pop-Up box
Customizing the Logged Out Box
Navigate to Advanced Services Stateful Firewall Destination
Creating Walled Garden Access
Enabling Captive Portal Enhancements
Configuring the Redirect-URL
Configuring the Login URL
Configuring the Netdestination for a Whitelist
Configuring a Whitelist
Defining Netdestination Descriptions
Associating a Whitelist to Captive Portal Profile
Use the following commands to verify the whitelist alias
Verifying a Whitelist Configuration
Verifying a Captive Portal Profile Linked to a Whitelist
Verifying Dynamic ACLs for a Whitelist
TOS
Verifying DNS Resolved IP Addresses for Whitelisted URLs
Example
Virtual Private Networks
Planning a VPN Configuration
Understanding Suite-B Encryption Licensing
Selecting an IKE protocol
IKE Policies Suite-B for IPsec tunnels
384 Suite-B certificates ECDSA-256, ECDSA-384
Understanding Supported VPN AAA Deployments
Working with IKEv2 Clients
Parameter Default Default-rap Default-cap
Working with VPN Authentication Profiles
Working with Certificate Groups
VPN Client
Configuring a Basic VPN for L2TP/IPsec in the WebUI
Navigate to Configuration IP NAT Pools
Defining Authentication Method and Server Addresses
Defining Address Pools
Enabling Source NAT
Defining IKEv1 Shared Keys
Configuring IKE Policies
Finalizing WebUI changes
Setting the IPsec Dynamic Map
Enable authentication methods for IKEv1 clients
Configuring a VPN for L2TP/IPsec with IKEv2 in the WebUI
Configure source NAT
Create address pools
Defining Address Pools
PRF-HMAC-MD5 PRF-HMAC-SHA1 PRF-HMAC-SHA256
PRF-HMAC-SHA384
Working with Smart Card clients using IKEv2
Configuring a VPN for Smart Card Clients
Enable authentication methods for IKEv2 clients
Define IKEv2 Policies
Select Enable L2TP
Configuring a VPN for Clients with User Passwords
Working with Smart Card Clients using IKEv1
Click Add User
Configuring Remote Access VPNs for XAuth
Configuring VPNs for XAuth Clients using Smart Cards
Certificates or Common Name as it appears on the certificate
Working with Remote Access VPNs for Pptp
Working with Third-Party Devices
Working with Site-to-Site VPNs
Understanding VPN Topologies
Configuring Site-to-Site VPNs
Working with Site-to-Site VPNs with Dynamic IP Addresses
Show crypto-local pki servercert certname subject
Click Doneto activate the changes Click Apply
For certificate authentication
Detecting Dead Peers
For preshared key authentication
For the Pre-shared-key
For the Pre-shared-key for All FQDNs
Working with VPN Dialer
Understanding Default IKE policies
Assigning a Dialer to a User Role
Configuring VPN Dialer
Host config #user-role role dialer name
Roles and Policies
Configuring Firewall Policies
Creating a Firewall Policy
Working With Access Control Lists ACLs
Support for Desktop Virtualization Protocols
This can be one of the following
Configure the NAT pool in the controller
IP address of the host
Queue in which a packet matching this rule should be placed
When it leaves the controller
Pause ARM
White List
Creating an ACL White List
Creating a Network Service Alias
Configuring the White List Bandwidth Contract in the CLI
Configuring the ACL White List in the WebUI
Configuring the ACL White List in the CLI
Use the following CLI command to create ACL White Lists
Creating User Roles
Click the Delete button against the role you want to delete
Creating a User Role
Bandwidth Contracts
Configuring and Assigning Bandwidth Contracts in the CLI
Configuring a Bandwidth Contract in the WebUI
Bandwidth Contract Exceptions
Assigning a Bandwidth Contract to a User Role in the WebUI
Assigning User Roles
Configuring Bandwidth Contract Exceptions
Assigning User Roles in AAA Profiles
Viewing the Current Exceptions List
Rule Type Condition Value
Working with User-Derived VLANs
Equals String
Dhcp server
Dhcp Option Description Hexadecimal Equivalent
Configuring a User-derived Vlan in the WebUI
Understanding Device Identification
See for descriptions of these parameters
Configuring a User-derived Role or Vlan in the CLI
User-Derived Role Example
Controller’s log files
Configuring a Default Role for Authentication Method
Navigate to the Configuration Security Authentication
Configuring a VSA-Derived Role
Configuring a Server-Derived Role
Understanding Global Firewall Parameters
Monitor TCP SYN Attack rate
Log Icmp Errors
Or disabled
Default Disabled stateful SIP processing is enabled
Portal configuration
Default 15 seconds
Session Idle Timeout sec
Disable FTP Server
Default Disabled FTP server is enabled
Mbps Default 1 Mbps Rate limit CP auth process traffic
Session-tunnel FIB Enable session,tunnel based forwarding
Mbps Is 1-200 Mbps Default 1 Mbps
Session mirror Ipsec
Page
Virtual APs
Configuring Virtual AP Profiles
Wlan Profiles Default AP Group Toronto AP Group
Excluding a Virtual AP Profile From an AP in the CLI
Configuring a Virtual AP
Excluding a Virtual AP Profile From an AP in the WebUI
Building3-lobby Guest
Configuring the User Role
Deny Time Range
Ssid profile guest
Done
Configuring Authentication Servers
Configuring Authentication
MAC Authentication Default Role
Users. The default role for unauthenticated users is logon
Wired to Wireless Roaming
Side of the network. This feature is enabled by default
Select Wireless LAN under Profiles, then select Virtual AP
Click Edit for the default AP group
Applying the Virtual AP
Enforce Dhcp
Can be configured in tunnel mode
Forward mode
Campus APs in decrypt-tunnel forward mode
Enforcement, 802.11k and station blacklisting
Click the Global Setting tab
Enable this setting
Setting on each individual local controller
Band Steering
Default 3600 seconds 1 hour
Default 6 stations
Authentication Failure
APs. Default Disabled
Creating a new Ssid Profile
Select Wireless LAN underProfiles, then select Virtual AP
Dtim Interval
Keys
XSec license in each controller
Default value is 2333 bytes
Other wireless clients are transmitting
Powersave WMM Tspec Min
Period to receive broadcasts
Battery Boost
Frames is disabled
Lengthening battery life
At the lowest configured rate
Configuring an Ssid for Suite-B Cryptography
Configuring a Guest Role
Configuring a Guest Wlan
Configuring a Vlan
Select Virtual AP
Configuring a Guest Virtual AP
Enabling bSec Ssid Support
Sample Configuration
To enable bSec Ssid using bSec-128 or bSec-256
Enabling 802.11k Support
Measurement Report Mode field
Measurement Mode for Beacon Reports
Default Mode beacon-table
Advertise 802.11K Capability
Handover of Voice Clients’ feature
Handover Trigger Feature Settings Profile
Beacon Report Request Settings Profile
TSM Report Request Settings Profile
Working with Radio Resource Management Information Elements
Working with Beacon Report Requests
Measurement Mode for
Con when Measurement Mode is set to Active-Channel Report
Range from 0 to 255. The default value is
Randomization Interval
Request frame. The default value is enabled
Gered. When the triggered option is selected,
Working with a Traffic Stream Measurement Report
Number of repetitions
Range 0, 65535. The default value is
Configuring a High-Throughput Virtual AP
Range 0, 255. The default value is
Bin 0 Range
40MHz intolerance
Select the 802.11a radio profile
Select the 802.11g radio profile
Capabilities
Maximum number of spatial
Streams usable for Stbc
Transmission
Short guard interval in 20 MHz
Mode Is enabled by default
Short guard interval in 40 MHz
Supported MCS set
Managing High-Throughput Profiles
Adaptive Radio Management ARM
Understanding ARM
ARM Support for 802.11n
Configuring ARM Scanning
Monitoring Your Network with ARM
Understanding ARM Application Awareness
Creating a New ARM Profile
Configuring ARM Profiles
ARM Profiles Example Wlan Description
Select RF Management to expand the RF Management section
Copying an Existing Profile
Configuring ARM Settings
Deleting a Profile
Select Adaptive Radio Management ARM Profile
Setting Description
Power Save
That Scanning is also enabled
Aware Scan Mode Default disabled Video Aware
Default 8 scans
Scan That Scanning is also enabled
Default 9 dBm
Enabled, that device will ignore this setting
Client Aware setting is disabled
Error Rate
Default 240 seconds
Threshold Change Default 50% Error Rate Wait
Time Channel change Default 30 seconds Noise Threshold
Mode Aware
Default 1250000 Bps
Load Aware
Scanning if the load for the AP gets too high
Assigning an ARM Profile to an AP Group
Select Configuration AP Configuration
Steering Modes
Using Multi-Band ARM for 802.11a/802.11g Traffic
Enabling Band Steering
Enabling Band Steering
Select Wireless LAN to expand the Wireless LAN section
To disable band steering, include the no parameter
Enabling Traffic Shaping
To configure traffic shaping via the WebUI
Enabling Traffic Shaping
Select QoS to expand the QoS section
Enabling Spectrum Load Balancing
To disable traffic shaping, use the default-accessparameter
Configuring Non-802.11 for Noise Interference Immunity
Reusing Channels to Control RX Sensitivity Tuning
ARM Metrics
Wireless Clients Report a Low Signal Level
Troubleshooting ARM
Transmission Power Levels Change Too Often
Too many APs on the Same Channel
APs Don’t Change Channels Due to Channel Noise
APs Detect Errors but Do Not Change Channels
This chapter contains the following sections
Wireless Intrusion Prevention
Working with the Reusable Wizard
Understanding Wizard Intrusion Detection
Protection features for Wlan clients
Protecting Your Clients
Understanding Wizard Intrusion Protection
Protecting Your Infrastructure
WIP Wizard Intrusion Protection
Monitoring the Dashboard
Understanding Classification Terminology
Detecting Rogue APs
Understanding Classification Methodology
Classification Description
Understanding Suspected Rogue Confidence Level
Understanding Match Methods
Understanding Match Types
Understanding Rule Matching
Understanding AP Classification Rules
Understanding Infrastructure Intrusion Detection
Feature Command Trap Syslog ID
Working with Intrusion Detection
Detect-bad-wep WlsxStaRepeatWEPIVViolation 126016
Ids impersonation-profile WlsxAPSpoofingDetected 126069
Ids impersonation-profile
126086
Ids unauthorized-device-profile WlsxWirelessBridge 126036
Require-wpa WlsxChannelMisconfiguration 127028
Detect-wireless-bridge Wireless-bridge-quiet-time
Detect-malformed-large-duration Detected
Detecting Active 802.11n Greenfield Mode
Detecting an 802.11n 40MHz Intolerance Setting
Detecting an Ad hoc Network Using a Valid Ssid
Detecting Ad hoc Networks
Detecting a Beacon Frame Spoofing Attack
Detecting Bad WEP Initialization
Detecting a Client Flood Attack
Detecting an RTS Rate Anomaly
Detecting a Wireless Bridge
Detecting a Misconfigured AP
Detecting Broadcast Deauthentication
Detecting Malformed Frame-Auth
Detecting Wellenreiter
Understanding Client Intrusion Detection
Detect-power-save-dos-attack
Ids dos-profile WlsxPowerSaveDoSAttack 126109
Detect-hotspotter-attack Hotspotter-quiet-time
Ids dos-profile WlsxOmertaAttack 126071
Detecting a Block ACK DoS
Detecting a Meiners Power Save DoS Attack
Detecting a ChopChop Attack
Detecting a Disconnect Station Attack
Detecting Rate Anomalies
Detecting an Omerta Attack
Detecting a Tkip Replay Attack
Detecting Unencrypted Valid Clients
Understanding Infrastructure Intrusion Protection
Configuring Intrusion Protection
Understanding Client Intrusion Protection
Navigate to the Configuration Advanced Services Wireless
Configuring the Wlan Management System WMS
Protecting Valid Stations
Protecting Windows Bridge
Not configured
Configuring Local WMS Settings
Managing the WMS Database
Station Ageout Interval
Blacklisting Manually
Understanding Client Blacklisting
Methods of Blacklisting
Enter a value in the Max Authentication failures field
Blacklisting by Authentication Failure
Enabling Attack Blacklisting
Captive portal
Setting Blacklist Duration
Working with WIP Advanced Features
Removing a Client from Blacklisting
Profiles list, expand the IDS menu, then select IDS profile
Understanding TotalWatch Channel Types and Qualifiers
Configuring TotalWatch
Understanding TotalWatch Scanning Spectrum Features
Understanding TotalWatch Monitoring Features
Understanding TotalWatch Channel Dwell Time
Frequency Channel
Configuring Per Radio Settings
Administering TotalWatch
Configuring Per AP Setting
Understanding TotalWatch Channel Visiting
DOS
Understanding Tarpit Shielding Licensing CLI Commands
Configuring Tarpit Shielding
Working with Tarpit Shielding
Licensing
Access Points APs
Basic Functions and Features
Function
Following topics are included in this chapter
Naming and Grouping APs
Creating an AP group
Use the following command to create an AP group
Assigning APs to an AP Group
You can use the WebUI or the CLI to create a new AP group
Click Apply and Reboot
Understanding AP Configuration Profiles
Working with Wireless LAN Profiles
Page
Page
Working with QoS Profiles
Working with AP Profiles
Provisioning Mesh Profiles
Working with RF Management Profiles
Other Profiles
Viewing Profile Errors
Profile Hierarchy
AP Specific and AP Group Profile Hierarchies
Other Profile Hierarchies
Deploying APs
Configuring Firewall Settings
Running the RF Plan
Verifying that APs Can Connect to the Controller
Enabling Controller Discovery
Configuring DNS Resolution
Configuring Dhcp Server Communication with APs
Verifying that APs Are Receiving IP Addresses
Using the Aruba Discovery Protocol ADP
Navigate to the Configuration Network IP Dhcp Server window
Provisioning 802.11n APs for Single-Chain Transmission
Provisioning APs for Mesh
AP Model Freqency Band Antenna Port
AP92 4GHz or 5GHz
AP Model Freqency Band
Installing APs on the Network
5GHz
AP134 4GHz or 5GHz
Updating the RF Plan
Provisioning Installed APs
Designation an AP as Remote RAP versus Campus CAP
Working with the AP Provisioning Wizard
Provisioning an Individual AP
AP Provisioning Window
Page
AP is associated
Provisioning Multiple APs using a Provisioning Profile
LMS or backup LMS values
Assigning Provisioning Profiles
Troubleshooting
Configuring a Provisioned AP
AP Installation Modes
Renaming an AP
Clear gap-db wired-mac
Optimize APs Over Low-Speed Links
Configuring the Bootstrap Threshold
To configure the bootstrap threshold using the WebUI
Configuring split-tunnel forwarding
RF Band for AM Mode scanning
Backup LMS IP
LMS IPv6 Backup LMS IPv6 LMS Preemption
From a wireless client that is connected to a tunneled Ssid
Bootstrap threshold
Wireless frame is only encapsulated inside the IPsec tunnel
When an AP process crashes
Prioritizing AP heartbeats
AP Redundancy
AP Maintenance Mode
Energy Efficient Ethernet
To enable AP maintenance mode
AP130 Series only
Managing AP LEDs
802.11a and 802.11g RF Management Profiles
RF Management
Enable CSA
Managing 802.11a/802.11g Profiles Using the WebUI
Creating or Editing a Profile
Radio
Reuse feature
Level 5 disable PHY reporting
Balancing mode Select one of the following options
MHz and 40 MHz modes
Channel. The default CSA count is 4 announcements
Load-balancing mode
Balancing threshold
Radio Management ARM scanning and channel assignment
RX sensitivity tuning based channel reuse threshold, in dBm
RX Sensitivity Tuning
Signal strength
Default, allowing 40 MHz operation
Assigning a High-throughput Profile
Assigning an 802.11a/802.11g Profile
Profile Spectrum monitor radio
AM Scanning Profile
Assigning an ARM Profile
Creating or Modifying a Profile
Managing 802.11a/802.11g Profiles Using the CLI
Deleting a Profile
To view the settings of a specific RF management profile
Viewing RF Management Settings
RF Optimization
Assigning a 802.11a/802.11g Profile
Default value 0 seconds
RF Event Configuration
Is sent to the client
Maximum value 8 seconds
Frame Error Rate Low
Frame Error Rate High
Detect Frame Rate Anomalies
Recommended value is 85%
Select the Regulatory Domain profile named default
Configuring AP Channel Assignments
Frame Retry Rate High
Frame Retry Rate Low
Channel Switch Announcement CSA
Automatic Channel and Transmit Power Selection
Managing AP Console Settings
Domain name used by the AP
IP address of the AP’s master controller
IP address of the DNS server used by the AP
Secure Enterprise Mesh
Understanding Mesh Access Points
Mesh Points
Mesh Portals
Mesh Clusters
Understanding Mesh Links
Component Description
Link Metrics
Optimizing Links
Mesh Cluster Profile
Understanding Mesh Profiles
Mesh Radio Profile
RF Management 802.11a and 802.11g Profiles
High-Throughput Profiles
Mesh High-Throughput Ssid Profile
Adaptive Radio Management Profiles
Mesh Recovery Profile
Understanding Mesh Solutions
Wired AP Profile
Point-to-Multipoint Deployment
Thin AP Services with Wireless Backhaul Deployment
Point-to-Point Deployment
Sample Point-to-Multipoint Deployment
High-Availability Deployment
Collecting Required Information
Planning a Wlan According to Your Specifications
Task Overview
AP Desired Rates 2.4 GHz Radio Properties
Building Dimensions
Managing Mesh Profiles In the WebUI
Working with Mesh Radio Profiles
Creating a New Profile
AM Desired Rates
Indicates the transmit rates for the 802.11a radio
Threshold Nodes Default 10 missed heartbeats. The range is
Rates
AP goes through the list and uses the next highest rate
Default distributed-tree-rssi
Range 0-4094. Default 0 disabled
Recommends using this default startup-subthresholdvalue
Used for user traffic
Assigning a Profile to a Mesh AP or AP Group
Default 2,333 bytes. The range is 256- 2,346
Editing a Profile
Link quality
Managing Mesh Profiles In the CLI
Viewing Profile Settings
To view the settings of a specific mesh radio profile
Managing Profiles In the WebUI
Working with Mesh High Throughput Ssid Profiles
Assigning a Profile to an AP Group
Deleting a Mesh Radio Profile
Enabled legacy stations are allowed
Temporal Diversity Enable
Configured value adjusts based on AP capabilities
Launch then software retries
Μsec, 2 µsec, 4 µsec
Mode Enabled by default
Degrade throughput
Different values, separate each value with a comma
Managing Profiles In the CLI
To view the settings of a specific high-throughput profile
Viewing High-throughput Ssid Settings
Understanding Mesh Cluster Profiles
Deployments with Multiple Mesh Cluster Profiles
Managing Mesh Cluster Profiles In the WebUI
Associating a Profile to Mesh APs
Deleting a Mesh Cluster Profile
Managing Mesh Cluster Profiles In the CLI
Associating Mesh Cluster Profiles
Viewing Mesh Cluster Profile Settings
To view the settings of a specific mesh cluster profile
Configuring Bridging on the Ethernet Port
Configuring Ethernet Ports for Mesh
Excluding a Mesh Cluster Profile from a Mesh Node
To exclude a specific mesh cluster profile from an AP
Configuring Ethernet Ports for Secure Jack Operation
Extending the Life of a Mesh Network
Outdoor AP Parameters
Provisioning Mesh Nodes
IP settings section, select Obtain IP Address Using Dhcp
Under Port Selection, click the port to configure
Provisioning Caveats
Provisioning Mesh Nodes
Booting the Mesh Point
Understanding the AP Boot Sequence
Booting the Mesh Portal
Air Monitoring and Mesh
Verification Checklist
Verifying the Network
CLI Examples
Configuring Remote Mesh Portals RMPs
Creating a Remote Mesh Portal In the WebUI
How RMP Works
Defining the Mesh Private Vlan
Provisioning the AP
Adding a Mesh Cluster Profile
Selecting a Mesh Radio Profile
Selecting an RF Management Profile
Profile Details window
Configuring a Dhcp Pool
Configuring the Vlan ID of the Virtual AP Profile
Additional Information
Provisioning a Remote Mesh Portal In the CLI
Configuring Redundancy Parameters
Configuring the Local Controller for Redundancy
On the master controller
Configuring the LMS IP
Configuring the Master Controller for Redundancy
Enter the master-redundancy context
Command Explanation
Router ID of the Vrrp instance
Controllers. Specify a key of up to 64 characters
This config mode command includes RF plan data when
Configuring Database Synchronization
Configuring Master-Local Controller Redundancy
Enabling Incremental Configuration Synchronization CLI Only
Redundant Topology Master-Local Redundancy
Vrrp Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide
Working with Rapid Convergence
Disabled Discarding Blocking
Understanding Rstp Migration and Interoperability
Rstp 802.1w Description Port Role
Edge Port and Point-to-Point
Configuring Rstp
Feature Default Value/Range
Change the default configurations via the command line
Troubleshooting Rstp
Monitoring Rstp
Port Fast
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 User Guide Rstp
Enabling PVST+ in the CLI
Understanding PVST+ Interoperability and Best Practices
Enabling PVST+ in the WebUI
From the WebUI, add a Vlan instance and enable PVST+
IP Mobility
Understanding Dell Mobility Architecture
Enable mobility disabled by default
Configuring Mobility Domains
On a master controller
On all Dell controllers in the mobility domain
Configuring a Mobility Domain
Joining a Mobility Domain
Example Configuration
Navigate to the Configuration Advanced Services IP Mobility
Subnetwork Mask
Configuring Mobility using the WebUI
Home Agent Address or Vrip
On controller a the master controller
Viewing mobile client status using the WebUI
Configuring Mobility using the CLI
Viewing mobile client status using the CLI
Tracking Mobile Users
Viewing specific client information using the CLI
Viewing user roaming status using the CLI
Roaming Description Status Type
Status Type Description
Setting up mobility association Using the CLI
Configuring Advanced Mobility Functions
Mobile Client Roaming Locations
HA Discovery on Association
Default setting is 3 attempts
Is 0-5000 visitors. The default setting is 5000 visitors
Seconds. The default setting is 5000 seconds
Enable standalone AP
Click Apply after setting the parameter
Proxy Dhcp
Proxy Mobile IP
Revocations
Understanding Bridge Mode Mobility Deployments
Working with Inter controller Mobility
Enabling Mobility Multicast
Working with Proxy Igmp and Proxy Remote Subscription
Inter-controller Mobility
Configuring Mobility Multicast
Enable Igmp snooping
Enable Igmp proxy on the FastEthernet Ieee 802.3 interface
Example
Start at 0 from the left-most position
External Firewall Configuration
Understanding Firewall Port Configuration Among Dell Devices
Configuring Ports to Allow Other Traffic Types
Enabling Network Access
Ports Used for Virtual Internet Access VIA
Page
Remote Access Points
About Remote Access Points
Remote AP with a Private Network
Configure a Public IP Address for the Controller
Configuring the Secure Remote Access Point Service
Using the WebUI to create a DMZ address
Configure the NAT Device
Chap Authentication Support over PPPoE
Configure the VPN Server
Using the WebUI to configure Chap
You can use the CLI or the WebUI to configure Chap
Creating a Remote AP Whitelist
Configuring Certificate RAP
Using the CLI to configure the Chap
Using WebUI
Configuring PSK RAP
Using CLI
RAP Static Inner IP Address
IP-Address parameter in the local database
Provision the AP
Deployment Scenario Master IP Address Value
Deploying a Branch Office/Home Office Solution
Troubleshooting Remote AP
Configuring the Branch Office AP
Provisioning the Branch Office AP
Local Debugging
Basic View Information Advanced View Information Name
Remote AP Connectivity
Seamless failover from backup link to primary link on RAP
Multihoming on remote AP RAP
Data Description
Enabling Remote AP Advanced Configuration Options
Remote AP Diagnostics
Understanding Remote AP Modes of Operation
Remote Oper Forward Mode Setting Ation
Only Ssid configuration Stored in flash on
Working in Fallback Mode
Essid is up when Same behavior as Not supported AP contacts
SSIDs
Configuring the AAA Profile for Fallback Mode in the WebUI
Configuring Fallback Mode
Backup Configuration Behavior for Wired Ports
Configuring the AAA Profile for Fallback Mode in the CLI
Configuring the Dhcp Server on the Remote AP
Using the WebUI
Configuring the Session ACL in the WebUI
Configuring Advanced Backup Options
Configuring the AAA Profile in the WebUI
Configuring the Session ACL in the CLI
Defining the Backup Configuration in the WebUI
Configure the Remote-AP Dhcp Server fields
Route src-nat
Using the CLI to configure the AAA profile
Specifying the DNS Controller Setting
Defining the Backup Configuration in the CLI
You can define other parameters as needed
Backup Controller List
Configuring the LMS and backup LMS IP addresses in the CLI
Configuring Remote AP Failback
Configuring Remote AP Authorization Profiles
Enabling RAP Local Network Access
To enable, enter
To disable, enter
Understanding Split Tunneling
Working with Access Control Lists and Firewall Policies
Adding or Editing a Remote AP Authorization Profile
Sample Split Tunnel Environment
Configuring Split Tunneling
Configuring the Session ACL Allowing Tunneling
Configuring an ACL to Restrict Local Debug Homepage Access
Enable Restricted Access to LD Homepage
Configuring the AAA Profile for Tunneling
Inthe CLI
Configuring the Tunneling Virtual AP Profile
Defining Corporate DNS Servers
Provisioning Wi-Fi Multimedia
Navigate to Configuration Wireless AP Configuration
To configure bandwidth reservation
Configuring Bandwidth Reservation
Navigate to Configuration Advanced Services All Profiles
Reserving Uplink Bandwidth
Navigate to Configuration Wireless AP Installation
Provisioning 4G USB Modems on Remote Access Points
4G USB Modem Provisioning Best Practices and Exceptions
Provisioning RAP for USB Modems
RAP 3G/4G Backhaul Link Quality Monitoring
Pantech
Configuring W-IAP3WN Access Points
Converting an IAP to CAP
Converting an IAP to RAP or CAP
Converting IAP to RAP
Enabling Bandwidth Contract Support for RAPs
Configuring Bandwidth Contracts for RAP
Defining Bandwidth Contracts
Applying Contracts
Verifying Contracts Applied to Users
Verifying Contracts on AP
Verifying Bandwidth Contracts During Data Transfer
Following is a sample output for a per-user configuration
Page
How it Works
Virtual Intranet Access
Understanding VIA Connection Manager
On Microsoft Windows Computers
Installing the VIA Connection Manager
On Apple MacBooks
User action / environment VIA’s behavior
Upgrade Workflow
Configuring the VIA Controller
Minimal Upgrade
Complete Upgrade
Authentication mechanisms supported in VIA
Supported Authentication Mechanisms
Other authentication methods
Before you Begin
Suite-B
Configuring VIA Settings
Enable VPN Server Module
Using the WebUI to Configure VIA
Create VIA Authentication Profile
Create VIA User Roles
To create VIA connection profile
Create VIA Connection Profile
Enter a name for the server group
Configuration Option Description
List of all IKEv2 authentication methods
To the support email-address for troubleshooting
Default None
Client Auto-Login
Enable Fips Module
Enable Supplicant
VIA Authentication Name\username instead of just username
Use Windows Credentials
To configure VIA web authentication profile
Configure VIA Web Authentication
To configure a VIA client Wlan profile
Configure VIA Client Wlan Profiles
Associate VIA Connection Profile to User Role
To associate a VIA connection profile to a user role
Cryptobinding TLV
Option Description
Servers or trusted certification authorities
Mschapv2-use-windows-credentials
To download the VIA installer and version file
Rebranding VIA and Downloading the Installer
Download VIA Installer and Version File
Create VIA authentication profiles
Using the CLI to Configure VIA
Create VIA roles
Create VIA connection profiles
Downloading VIA
Customize VIA logo, landing page and downloading installer
Pre-requisites
Requires the following Microsoft KB on the end-user systems
Downloading VIA
Login to Download VIA
Connection Details Tab
Installing VIA
Using VIA
Settings Tab
Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Tab
Spectrum Analysis
Understanding Spectrum Analysis
Device
AP104 Yes
Graph Title
Device Configurable as a
Hybrid AP?
Graph Title Description Update Interval
Spectrogram
Spectrum Analysis Clients
Real-Time FFT
Swept
Hybrid AP Channel Changes
Hybrid APs Using Mode-Aware ARM
Creating Spectrum Monitors and Hybrid APs
Converting an Individual AP to a Spectrum Monitor
Converting APs to Hybrid APs
Select AP to expand the AP profiles section
Converting a Group of APs to Spectrum Monitors
Connecting Spectrum Devices to the Spectrum Analysis Client
View Connected Spectrum Analysis Devices
Disconnecting a Spectrum Device
Table Column Description
To manually disconnect a spectrum monitor or hybrid AP
Click the Spectrum Dashboards tab
Configuring the Spectrum Analysis Dashboards
Selecting a Spectrum Monitor
Click theSpectrum Dashboards tab
Changing Graphs within a Spectrum View
Select Rename
Renaming a Spectrum Analysis Dashboard View
Saving a Dashboard View
Resizing an Individual Graph
Customizing Spectrum Analysis Graphs
Active Devices
Spectrum Analysis Graph Configuration Options
Show
Channel Range
Active Devices Table
Service set identifier of the device’s 802.11 wireless LAN
Device Type
Column may display any of the following values
Radio band or channel
Select the button by the symbol
Column heading
Select the button by the Less than drop down list
Detects on the radio channel
Active Devices Trend
Center Frequency
MHz
Channel Metrics
Wi-Fi data as non-Wi-Fi data
Show lines for these
Select one of the following device types
Radio band displayed in this graph
Channel Metrics Graph
Channel Metrics Trend
Minutes
Drop-down list and select one of the following options
Hour
Unselect the checkbox to hide that information
Monitor
Channel Summary Table
Band Radio band displayed in this graph
Device Duty Cycle
Following device types
Channel Utilization Trend
Numbering Identify a channel numbering scheme for the graph
Devices vs Channel
As non-Wi-Fi data
Intervals
Uncheck the checkbox by that channel number
Devices vs Channel Options
FFT Duty Cycle
FFT Duty Cycle
Interference Power
Interference Power Options
Device types
Quality Spectrogram
Data
Real-Time FFT
Frequencies for the graph
Axis
Swept Spectrogram
Frequency Center of the x-axis of this chart Span
Center
Right field, and the higher value in the left field
Simple Line Graph of FFT Power Data
Swept Spectrogram Options
Working with Non-Wi-Fi Interferers
Device vs Channel Interference Power
Non-Wi-Fi Description Interferer
Viewing Spectrum Analysis Data
Understanding the Spectrum Analysis Session Log
To record spectrum analysis data for later analysis
Recording Spectrum Analysis Data
Creating a Spectrum Analysis Record
Playing a Spectrum Analysis Recording
Saving the Recording
Playing a Recording in the Spectrum Dashboard
To save the recording file
Click Load File For Playback
Playing a Recording Using the RFPlayback Tool
Click the Recording View/Play link at the top of the window
Troubleshooting Browser Issues
Troubleshooting Spectrum Analysis
Converting a Spectrum Monitor Back to an AP or Air Monitor
Loading a Spectrum View
Understanding Device Ageout Times
Understanding Spectrum Analysis Syslog Messages
Playing a Recording in the RFPlayback Tool
Age Out Generic Frequency Hopper
Age Out Generic Fixed Frequency
Hopper Seconds
Dashboard Monitoring
Monitoring Performance
Clients
APs
Monitoring Usage
Using Dashboard Histograms
Monitoring WLANs
Monitoring Potential Issues
Monitoring Security
Monitoring Clients
Monitoring Access Points
Monitoring Firewalls
To disable this setting, include the no parameter
Element View
Element
Bytes Tx Bytes Rx Bytes
Element Description
Column
Element Tab
Details View
Element Summary View
User Bytes Packets Device Destination
Application
Usage Breakdown
Usage Breakdown
Aggregated Sessions
Destination Alias
Column Description
Source IP
Management Access
Configuring Certificate Authentication for WebUI Access
Enabling Public Key Authentication for SSH Access
Select the client certificate Click Apply
Enabling Radius Server Authentication
Configuring Radius Server Authentication with VSA
Configuring a set-value server-derivation rule
Resetting the Admin or Enable Password
Disabling Authentication of Local Management User Accounts
Verifying the configuration
User admin Password
Bypassing the Enable Password Prompt
Setting an Administrator Session Timeout
Implementing a Specific Management Password Policy
Defining a Management Password Policy
Configure the settings described in Table
Allowed Characters Disallowed Characters
Allowed Characters
Management Authentication Profile Parameters
Colon
Period Pipe Plus sign + Tilde ~ Comma Accent mark `
About Digital Certificates
Managing Certificates
Obtaining a Server Certificate
Navigate to the Configuration Management Certificates CSR
Parameter Description Range
Enter the following information
Obtaining a Client Certificate
Run the following command
Importing Certificates
PKCS7 encrypted PKCS12 encrypted
Viewing Certificate Information
Use the following command to import CSR certificates
Imported Certificate Locations
Location Description
Snmp Parameters for the Controller
Configuring Snmp
Checking CRLs
Configuring Logging
Category/Subcategory Description
802.1x messages Radius Radius user messages
Category/Subcategory
Logging Level Description
Enabling Guest Provisioning
Configuring the Guest Provisioning
Configuring the Guest Fields
Guestcategory
Guest Field
Guest Field Description
Configuring the Page Design
Provisioning page for the sponsor information
Fields that follow
Navigate to the Configuration Management SMTPpage
Configuring the Smtp Server and Port in the WebUI
Configuring Email Messages
Creating Email Messages in the WebUI
Configuring an Smtp server and port in the CLI
Click Apply and then Save Configuration
Username and Password Authentication Method
Configuring a Guest Provisioning User
Static Authentication Method
Management Users section, click Add
Smart Card Authentication Method
Customizing the Guest Access Pass
Username and Password Method
Click Apply and Save Configuration
Customized Guest Account Information Window
Creating Guest Accounts
Creating a Guest Account-New Guest Window
Guest Provisioning User Tasks
Creating Multiple Guest Entries in a CSV File
Importing Multiple Guest Entries
CVS File Format-Guest Entries Information
Importing the CSV File into the Database
Importing a CSV file that contains Guest Entries
Displaying the Guest Entries Log File
Printing Guest Account Information
Optional Configurations
Restricting one Captive Portal Session for each Guest
Using the WebUI to set the maximum time for guest accounts
Setting the Maximum Time for Guest Accounts
Using the CLI to set the maximum time for guest accounts
Managing Files on the Controller
Navigate to the Maintenance Controller Image Management
Server Type Configuration
Transferring ArubaOS Image Files
Username to log into server
Copying Log Files
Backing Up and Restoring the Flash File System
Manually Setting the Clock
Setting the System Clock
Navigate to the Configuration Management Clock
Copying Other Files
Clock Synchronization
Configuring NTP Authentication
Threshold Description
Enabling Capacity Alerts
Timestamps in CLI Output
User-capacity
Sent. The default threshold for this parameter is 80%
Examples
Adding Local Controllers
Configuring Local Controllers
Using the Initial Setup
Configuring Trusted Ports
Configuring Layer-2/Layer-3 Settings
Configuring Local Controller Settings
Using the Web UI
Using the WebUI to configure the LMS IP
Configuring APs
Using the CLI to configure the LMS IP
Moving to a Multi-Controller Environment
Configuring a Preshared Key
Using the WebUI to configure a Local Controller PSK
Configuring a Controller Certificate
Using the WebUI to configure a Master Controller PSK
Using the CLI to configure a PSK
Using the CLI to configure the Master Controller Certificate
Advanced Security
Securing Client Traffic
Wireless xSec Client Example
Securing Wireless Clients
Securing Wired Clients
Navigate to the Configuration Advanced Services Wired Access
Securing Wireless Clients Through Non-Dell APs
Securing Clients on an AP Wired Port
Succeed
Time to wait for authentication to
For Controller
Configuring Controllers for xSec
Securing Controller-to-Controller Communication
Installing the Odyssey Client
Configuring the Odyssey Client on Client Machines
Modifying a regedit Policy
Certificate Information
Page
Setting up Net Services
Configuring Voice and Video
Using Default Net Services
Voice and Video License Requirements
Creating Custom Net Services
Configuring User Roles
Using the Default User Role
Net Service Name Protocol Port
Service Name
Using the WebUI to configure user roles
Navigate to the Configuration Security Access Control
Creating or Modifying Voice User Roles
Click Done Click Apply
Using the CLI to configure a user role
Using the WebUI to derive the role based on Ssid
Using the User-Derivation Roles
Using the CLI to derive the role based on Ssid
Using the WebUI to derive the role based on MAC OUI
Configuring Video over Wlan enhancements
Configuring Firewall Settings for Voice and Video ALGs
Additional Video Configurations
Pre-requisites
To enable Igmp snooping
To add the ACL to a user role
Configure multicast rate optimization for video traffic
Set a bandwidth percentage for the following categories
Configure and apply a bandwidth management profile
Enable Igmp Proxy
Enable multicast shaping on the firewall
Enable Igmp Snooping
Configure ARM scanning for video traffic
Configure multicast rate optimization for the video traffic
This step is optional
Configure and apply bandwidth management profile
Working with QoS for Voice and Video
Understanding VoIP Call Admission Control Profile
Voip Tspec Enforcement
Understanding Wi-Fi Multimedia
To enable call admission control in this profile
Priority 802.1p Priority WMM Access Category
Configuring WMM AC Mapping
Enabling WMM
Lowest Background Best effort Video Voice Highest
Background Best effort Video Voice
Dscp Decimal Value WMM Access Category
Using the WebUI to map between WMM AC and Dscp
Using the CLI to map between WMM AC and Dscp
Configuring Dscp Priorities
WMM Access Category Description 802.1p Tag
Configuring Dynamic WMM Queue Management
Enhanced Distributed Channel Access
Disables this option
Using the WebUI to configure Edca parameters
1. a value of 4 computes to 2 4-1 = 15. Possible values are
Microseconds, enter 94 3008/32. Possible values are
To associate the Edca profile instance to a Ssid profile
Enabling WMM Queue Content Enforcement
Using the CLI to configure Edca parameters
Microsoft OCS
Understanding Extended Voice and Video Features
Apple Facetime
Port Packet Type
Scanning for VoIP-Aware ARM
Enabling WPA Fast Handover
Enabling Mobile IP Home Agent Assignment
Disabling Voice-Aware
Configuring SIP Authentication Tracking
Enabling Real Time Call Quality Analysis
To configure Real Time analysis on voice calls
Web UI
Viewing Real Time Call Quality Reports
SIP session timer is implemented in the SIP ALG as per RFC
Enabling SIP Session Timer
Click the Policies tab
To configure the session timer and the timeout value
To view the SIP settings on the controller
Select the Classify Media check box
Enabling Wi-Fi Edge Detection and Handover for Voice Clients
Click the Apply button to save the configuration
Expand Handover Trigger under Wireless Lan
Working with Dial Plan for SIP Calls
Understanding Dial Plan Format
Action Description
Configuring Dial Plans
Dialplan Profile displays the dial plan details
Dialplan Profile
To create a voice dial plan profile
Enabling Enhanced 911 Support
To associate the dial plan with SIP ALG
To view the SIP dial plan profile
Working with Voice over Remote Access Point
Enabling Lldp
Understanding Battery Boost
Configure the Lldp profile parameters as desired then click
Lldp PDUs. The AP will send all 802.1 TLVs by default
Lldp PDUs. The AP will send all optional TLVs by default
Lldp PDUs. The AP will send all 803.2 TLVs by default
Show the power support capabilities of the AP interface
LLDP-MED Profile Configuration Parameters
Apply to save your settings
Viewing Troubleshooting Details on Voice Client Status
Advanced Voice Troubleshooting
Connected
To view the details of a completed call based on the CDR Id
Viewing Troubleshooting Details on Voice Call CDRs
Enabling Logging for a Specific Client
Navigate to the Configuration Management Logging
Enabling Voice Logs
Viewing Voice Traces
To view the voice signaling message traces
To set the voice logging level to debugging
To debug voice logs for a specific client
To view the voice configuration details on your controller
Viewing Voice Configurations
SIP settings Value Parameter
Overview
L2/L3 network mode support
Instant AP VPN Support
Termination of Instant AP VPN tunnels
Whitelist DB Configuration
VPN Configuration
Controller Whitelist DB
External Whitelist DB
VPN Profile Configuration
VPN Local Pool Configuration
Viewing Branch Status
Radius proxy for VPN connected IAPs
Output of this command includes the following parameters
Series Controllers
Understanding W-600 Series Best Practices and Exceptions
Controller
USB Ports
Finding USB Modem Commands
Connecting with a USB Cellular Modems
Switching Modes
Cellular Profile
Uplink Manager
Cellular Profile from the WebUI
Dialer Group
Verify the modem is registered with the Uplink Manager
Configuring a Supported USB Modem
If you get entries similar to the example below
Configuring a New USB Modem
Configuring the Profile and Modem Driver
Driver=none
Configuring the TTY Port
Selecting the Dialer Profile
Testing the TTY Port
Linux Support
Setting Up NAS Network-Attached Storage Devices
NAS Device Setup
View list of shares in a disk
Configuring in the CLI
Managing NAS Devices
Controller wake-up Green-solid Button
Mounting and Unmounting Devices
NAS Media Green-solid Press and hold media
Printer Setup Using the CLI
Connecting to a Print Server
Additional Commands for Managing Printers
To view a list of printers mounted on the controller, type
Remote Branch 1-W-650 Controller
Series Sample Topology and Configuration
Remote Branch 2-W-650 Controller
Central Office Controller-Active
Central Office Controller-Backup
Page
Sample ESI Topology
External Services Interface
ESI-Fortinet Topology
ESI Parser Domains
Understanding the ESI Syslog Parser
Syslog Parser Rules
Peer Controllers
User Pattern Matching
Configuring ESI
Condition Pattern Matching
Enter a Profile Name
Configuring Health-Check Method, Groups, and Servers
Defining the ESI Server
Defining the ESI Server Group
To configure an ESI server group on the controller
Server Name
Enter a Group Name
Redirection Policies and User Role
Managing Syslog Parser Domains in the WebUI
ESI Syslog Parser Domains and Rules
Adding a new syslog parser domain
Deleting an existing syslog parser domain
Managing Syslog Parser Domains in the CLI
Use these CLI commands to manage syslog parser domains
Managing Syslog Parser Rules
Editing an existing syslog parser domain
Editing an existing syslog parser rule
Adding a new parser rule
Deleting a syslog parser rule
Use these CLI commands to manage syslog parser rules
Testing a Parser Rule
Showing ESI syslog parser rule information
Sample Route-mode ESI Topology
Monitoring Syslog Parser Statistics
IP routing configuration on Fortinet gateway
Configuring the Example Routed ESI Topology
ESI server configuration on controller
Defining the Ping Health-Check Method
Health-Check Method, Groups, and Servers
Enter a Group Name. Enter fortinet
Trusted IP Address. Enter Untrusted IP Address. Enter
Redirection Policies and User Role
Add a New Syslog Parser Domain in the WebUI
Syslog Parser Domain and Rules
Adding a New Parser Rule in the WebUI
To add a new syslog parser domain for the routed example
Example NAT-Mode Topology
Sample NAT-mode ESI Topology
ESI server configuration on the controller
Configuring the NAT-mode ESI Example in the WebUI
Configuring the Example NAT-mode ESI Topology
Configuring the ESI Group in the WebUI
Profile Name. This example uses externalcpping
Configure the ESI Servers in the WebUI
Configuring the Example NAT-mode Topology in the CLI
Configuring the Redirection Filter in the WebUI
Policy Name. This example uses cpredirectacl
Configuring ESI Servers
Configuring a Health-Check Ping
Using the ESI Group in a Session Access Control List
CLI Configuration Example
Character-Matching Operators
Understanding Basic Regular Expression BRE Syntax
Description Sample Result
Regular Expression Repetition Operators
Regular Expression Anchors
References
External User Management
Working with the ArubaOS XML API Works
Creating an XML Request
Authenticating a User
Adding a User
Deleting a User
Format of a default XML response from the controller is
Default Response Format
XML Response
Blacklisting a User
Code Reason message
Response Codes
Code Reason message Description
Query Command Response Format
Configuring the XML API Server
Using the XML API Server
Verify the XML API server configuration
Associating the XML API Server to a AAA profile
Vlan
Associating the Captive Portal Profile to an Initial Role
Set up Captive Portal profile
Options Description Range / Defaults
Authentication Command Description
This command deletes the user from the controller
Dell controllers configuration
Monitoring External Captive Portal Usage Statistics
Sample Code
Using XML API in C Language
Page
Page
List all parameter that you can use in a request
Understanding Request and Response
Understanding XML API Request Parameters
Understanding XMl API Response
This command will add a client on your network
Adding a Client
Response from the controller
Deleting a Client
Authenticating a Client
View the updated details of the client on the controller
Status of the client after authentication
Status of the client before authentication
Sending the authentication command
Querying for Client Details
Blacklisting a Client-request and response
Blacklisting a Client
RF Plan
Supported Planning
Planning Deployment
Configuration Considerations
Pre-Deployment Considerations
Outdoor-Specific Deployment Considerations
Dual-Port AP Considerations
Post-Deployment Considerations
Buttons Description
Launching the RF Plan
Campus List
Edit a campus from the building list pane
Building List Pane
Buttons
Building Dimension
Building Specifications Overview
AP Modeling Parameters
Radio Type
Radio Description Button
Design Model
Overlap Factor
Radio Properties Desired Rates and HT Support Options
Users/AP
Overlap Description Factor
Radio Property Description
Valid values are 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9, 6, 11, 5.5, 2
AM Modeling
Number of available channels
Design Models
Planning Floors
Monitor Rates
Radio Button Description
Zoom
You can select or adjust the features as described in Table
Floor Editor Dialog Box
Approximate Coverage Map
Level
Naming
Background Images
Area Editor Dialog Box
Area Types
Location and Dimensions
Fixed
Access Point Editor Dialog Box
802.11n Features
Power Levels
Radio Types
Y Coordinates
Initialize
AP Plan
Optimize
Memo
Viewing the Results
AM Plan
Fix All Suggested AP/AMs
Exporting and Importing Files
Export Buildings
Export Campus
Import Campus
Import Buildings
Locate
Property Description
Fqln Mapper
Search Results
Using the Fqln Mapper in the AP Provision
RF Plan Example
Using the WebUI
Sample Building
Height
Create a Building
Text Box
Model the Access Points
Information
Campus Name
Add and Edit a Floor
Model the Air Monitors
Adding the background image and naming the first floor
Adding the background image and naming the second floor
Running the AP Plan
Creating a Don’t Deploy Area
Click Initialize
Running the AM Plan
Click Optimize
Click Initialize then Optimize
Forwarding Mode Feature Not Supported
Understanding Mode Support
Behavior and Defaults
Name Protocol
Understanding Basic System Defaults
Network Services
Name Protocol Ports
Following are predefined policies
Policies
Predefined Policy Description
Access the controllers administrative
Used to enable the captive portal logout
Be modified. It permits APs to boot up
Network access. You can use this rule to
NAT-T UDP 4500. Remove NAT-T if not
Permits all DNS traffic
Needed
This policy can be used to source-NAT all
Following are predefined roles
Roles
Predefined Role Description
Should be disabled if it is not needed
Enables captive portal
Beginning
Profiles with different customization
ArubaOS software includes predefined management user roles
Understanding Default Management User Roles
Predefined Role Permissions
Show aaa authentication-server all
Show aaa state configuration
Show switches summary
Show wlan-ap-count type access-points
Monitoring Controller Clients Packet CaptureMonitoring
Port Protocol Where Used Description Number
Understanding Default Open Ports
Testing
Controller Remote wired MAC lookup 4343
Port is not exposed to wireless users
Exposed to wireless users
Configuring Option
Configuring a Windows-Based Dhcp Server
To configure option 60 on the Windows Dhcp server
Dhcp with Vendor-Specific Options
Field Information
To configure option 43 on the Windows Dhcp server
Scope Options Dialog Box
Enabling Linux Dhcp Servers
Navigate to Configuration Network IP IP Interfaces
Enabling Dhcp Relay Agent Information Option Option
Range 10.200.10.200
Radius Client Configuration
Configuring Microsoft IAS
802.1X Configuration for IAS and Windows Clients
Active Directory Database
Remote Access Policies
Configuring Policies
Click Configure to select additional properties
IAS Remote Access Policies
Policy Configuration Wizard-Authentication Methods
Radius class Attribute Configuration
Configuring Radius Attributes
Next, create a remote policy for your new Radius client
Configuring Management Authentication using IAS
Creating a Remote Policy
Creating a User Entry in Windows Active Directory
Defining Properties for Remote Policy
Configuring a Server Group for IAS Management Authentication
Click Begin Test
Window XP Wireless Client Sample Configuration
Navigate to DiagnosticsAAA Test Server
Wireless Networks
Networks to Access
Wireless Network Association
Wireless Network Authentication
Protected EAP Properties
EAP MSCHAPv2 Properties
Acronyms and Terms
Acronyms
Acronym
Definition
DoS
Acronym
MSCHAPv2
PPPoE
PoE
QoS
RoW
VoFI VoIP
Term
Terms
WISPr
XAuth
Term
Term Definition
Fixed wireless
Encryption authentication
Shops are providing free wireless access for customers
IR wireless
Hills, mountains, and large human-made structures
Optical wireless
Input, multiple output
Near field communicationNFC
Wi-Fi
Access W-CDMA
Facilities offer public access to Wi-Fi networks
Standards for broadband wireless access BWA networks. WiMAX
Wired LAN
Wireless service provider
Kilometers
Yagi antenna