MEMORY MANAGEMENT AND VIRTUAL ADDRESSING
|
| o | 7 |
|
+7 |
| INTEL RESERVED' | ||
| MUST BE 0 |
| ||
|
|
| ||
+5 | pIDPLI~1 | TYPE | I | BASE23'16 |
+3 |
| BASE 15.0 |
| |
+1 |
| LlMIT 15·0 |
| |
| 15 | 8 | 7 |
|
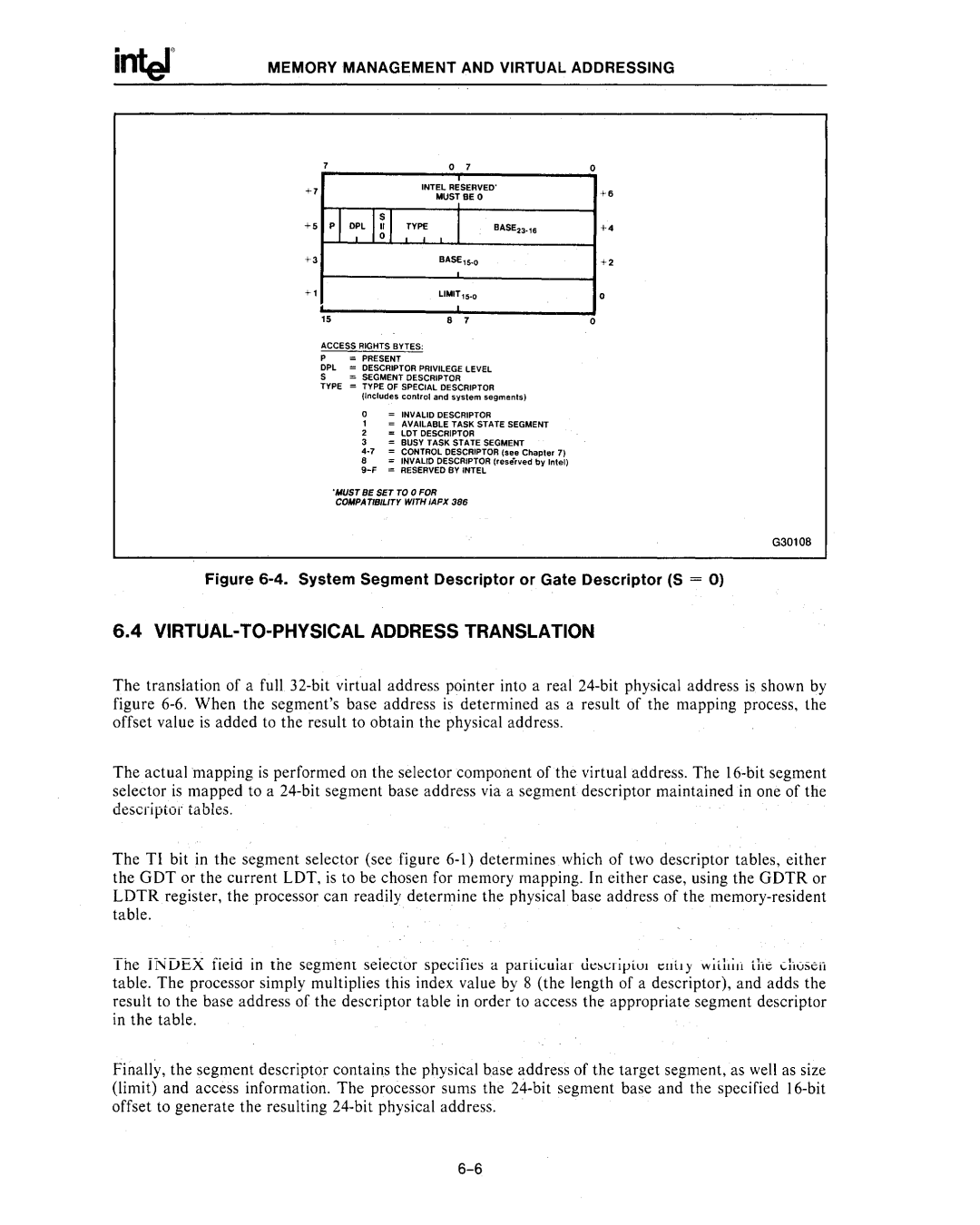
ACCESS RIGHTS BYTES:
P- PRESENT
OPl = DESCRIPTOR PRIVILEGE LEVEL
5:;::. SEGMENT DESCRIPTOR
TYPE = TYPE OF SPECIAL DESCRIPTOR
(Includes control and system segments)
o= INVALID DESCRIPTOR
1= AVAILABLE TASK STATE SEGMENT
2= LOT DESCRIPTOR
3= BUSY TASK STATE SEGMENT
8= INVALID DESCRIPTOR (reserved by Intel)
'",UST BE SET TO 0 FOR COMPATIBILITY WITH IAPX 386
+6
+4
+2
G3010B
Figure 6-4. System Segment Descriptor or Gate Descriptor (S = 0)
6.4 VIRTUAL-TO-PHYSICAL ADDRESS TRANSLATION
The translation of a full
The actual mapping is performed on the selector component of the virtual address. The
descriptor tables.
The TI bit in the segment selector (see figure
table. | . |
1 he INDEX fieici in the segment seiecwr speClIles a parliculaI ue,CIil"UI clIlly wi,llill the Cll0SeH table. The processor simply multiplies this index value by 8 (the length of a descriptor), and adds the result to the base address of the descriptor table in order to access the appropriate segment descriptor in the table.
Finally, the segment descriptor contains the physical base address of the target segment, as well as size (limit) and access information. The processor sums the