ADVANCED TOPICS
If a conforming segment is readable, it can be read from any privilege level without restriction. This is the only exception to the protection rules. This allows constants to be stored with conforming code. For example, a
11.2.2 Expand-Down Data Segments
\
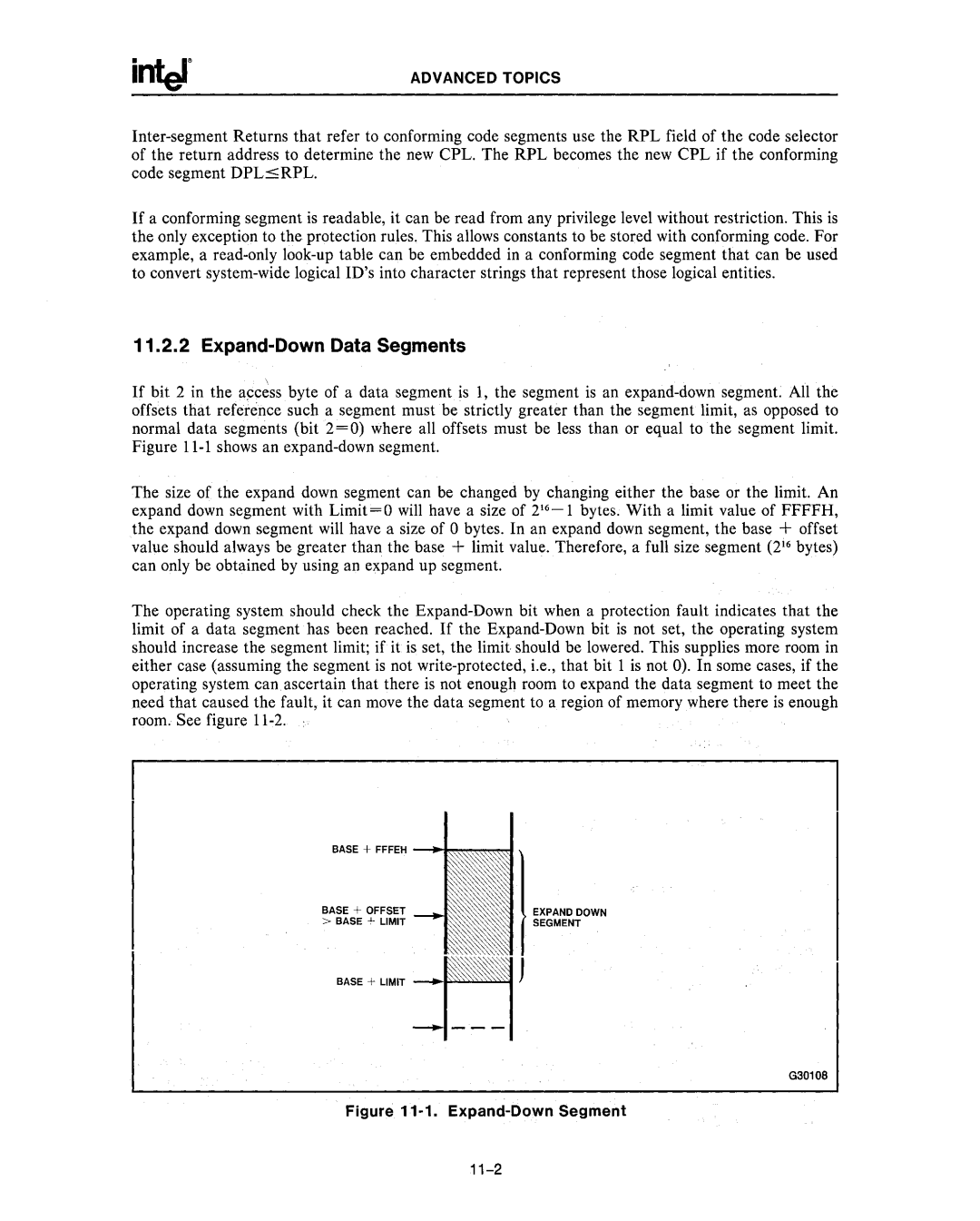
If bit 2 in the a~cess byte of a data segment is 1, the segment is an
The size of the expand down segment can be changed by changing either the base or the limit. An expand down segment with Limit=O will have a size of 216
The operating system should check the
room. See figure | . |
BASE + FFFEH
BASE + OFFSET | 1 |
EXPAND DOWN | |
> BASE + LIMIT | SEGMENT |
BASE + LIMIT
G30108