MEMORY MANAGEMENT AND VIRTUAL ADDRESSING
VIRTUAL ADDRESS |
|
| ||
I SELECTOR | I |
| I | TARGET |
OFFSET | SEGMENT | |||
| ||||
TI |
| 0- |
|
|
|
| PHYSICAL | DATUM | |
|
|
| ||
DESCRIPTOR | ADDRESS |
| ||
I TABLE |
| I |
|
|
SEGMENT
BASE
SEGMENT
DESCRIPTOR
INDEX
G3010B
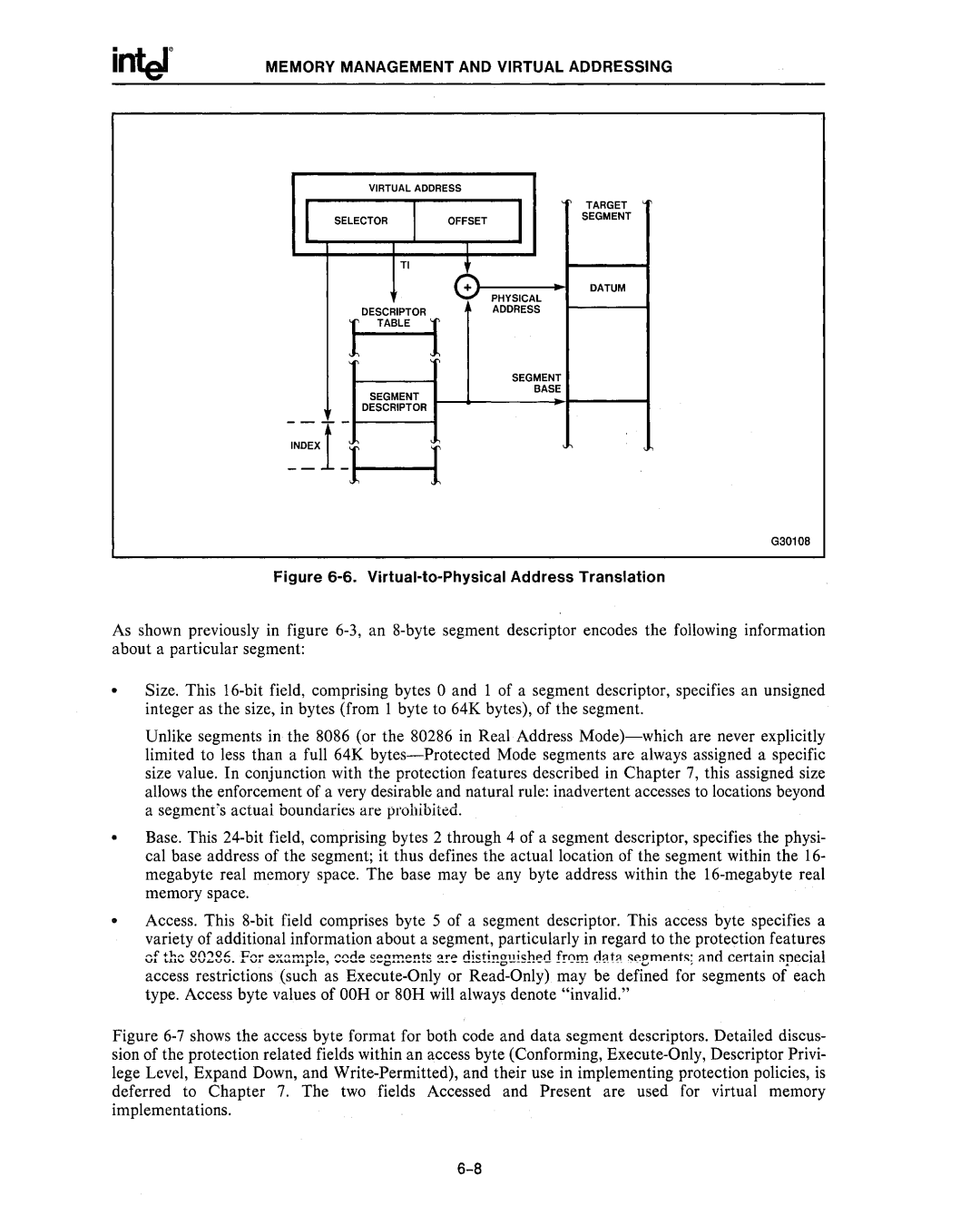
Figure 6-6. Virtual-to-Physical Address Translation
As shown previously in figure
Size. This
Unlike segments in the 8086 (or the 80286 in Real Address
Base. This
Access. This