THE 80286 INSTRUCTION SET
Table
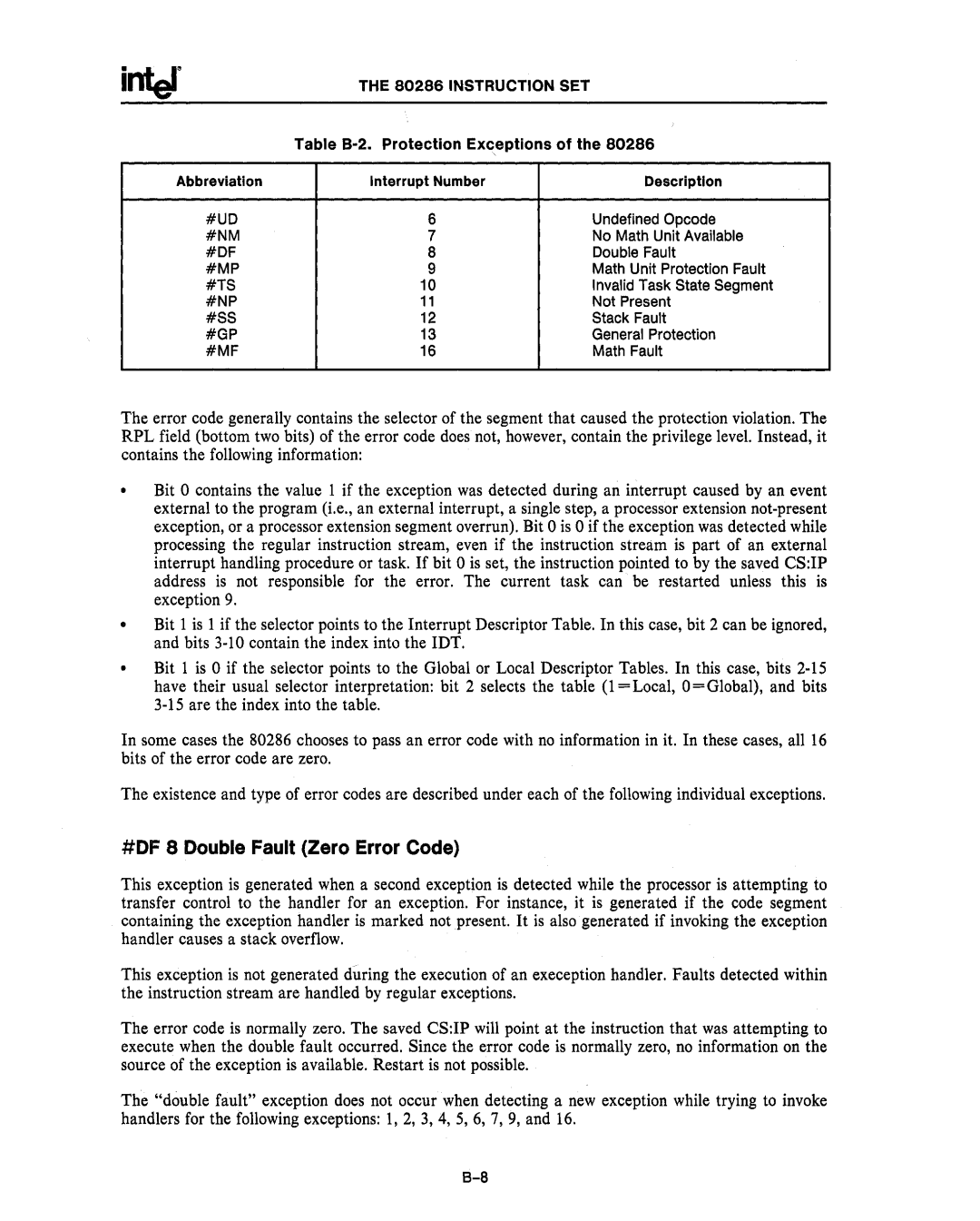
Abbreviation | Interrupt Number | Description |
#UD | 6 | Undefined Opcode |
#NM | 7 | No Math Unit Available |
#DF | 8 | Double Fault |
#MP | 9 | Math Unit Protection Fault |
#TS | 10 | Invalid Task State Segment |
#NP | 11 | Not Present |
#SS | 12 | Stack Fault |
#GP | 13 | General Protection |
#MF | 16 | Math Fault |
The error code generally contains the selector of the segment that caused the protection violation. The RPL field (bottom two bits) of the error code does not, however, contain the privilege level. Instead, it contains the following information:
Bit 0 contains the value 1 if the exception was detected during an interrupt caused by an event external to the program (i.e., an external interrupt, a single step, a processor extension
•Bit 1 is 1 if the selector points to the Interrupt Descriptor Table. In this case, bit 2 can be ignored, and bits
Bit 1 is 0 if the selector points to the Global or Local Descriptor Tables. In this case, bits
In some cases the 80286 chooses to pass an error code with no information in it. In these cases, all 16 bits of the error code are zero.
The existence and type of error codes are described under each of the following individual exceptions.
#DF 8 Double Fault (Zero Error Code)
This exception is generated when a second exception is detected while the processor is attempting to transfer control to the handler for an exception. For instance, it is generated if the code segment containing the exception handler is marked not present. It is also generated if invoking the exception handler causes a stack overflow.
This exception is not generated during the execution of an exeception handler. Faults detected within the instruction stream are handled by regular exceptions.
The error code is normally zero. The saved CS:IP will point at the instruction that was attempting to execute when the double fault occurred. Since the error code is normally zero, no information on the source of the exception is available. Restart is not possible.
The "double fault" exception does not occur when detecting a new exception while trying to invoke handlers for the following exceptions: 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,9, and 16.