| OVERVIEW OF NUMERIC PROCESSING | ||
| Table | ||
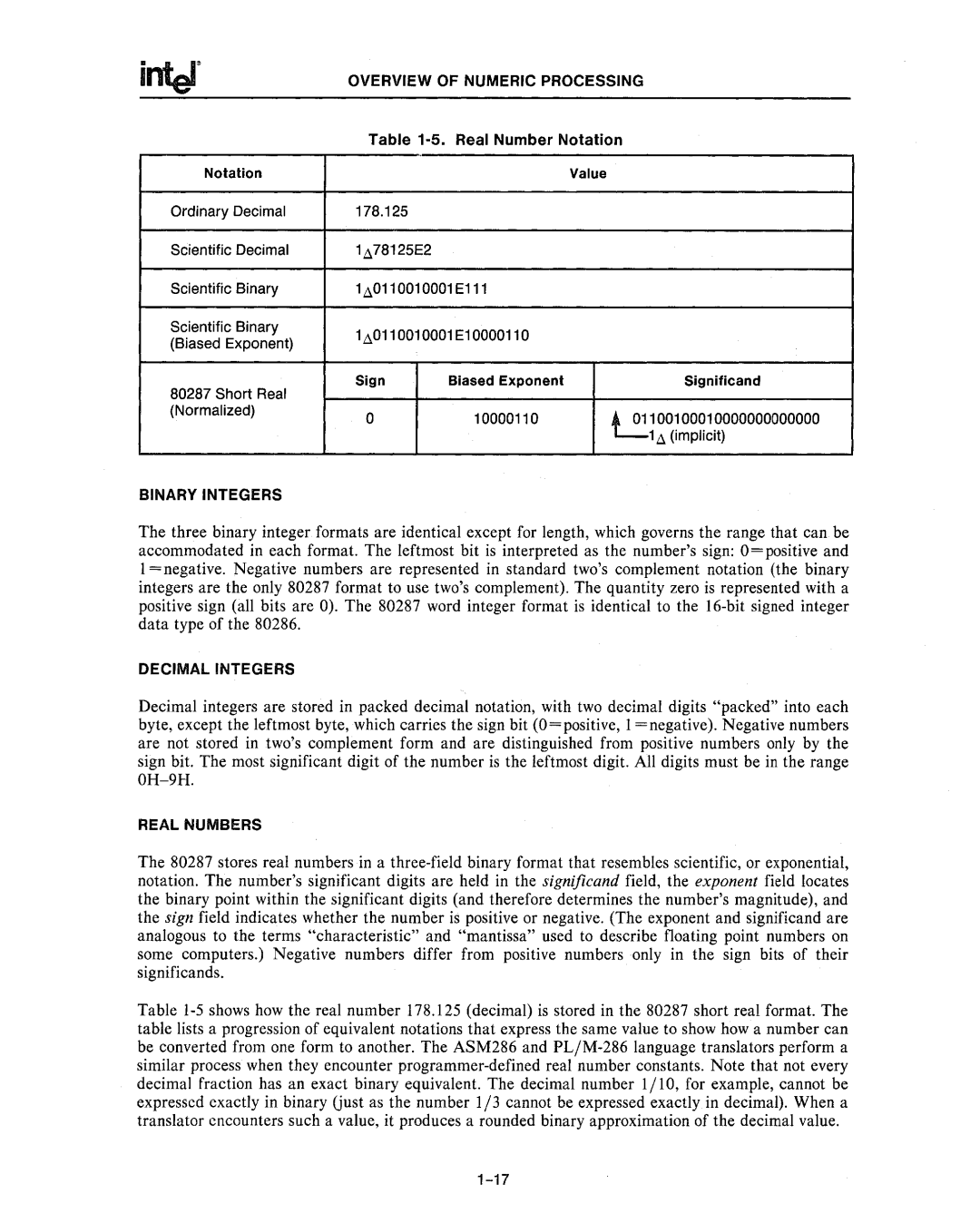
Notation |
|
| Value |
Ordinary Decimal | 178.125 |
|
|
Scientific Decimal | 1A78125E2 |
|
|
Scientific Binary | 1A0110010001E111 |
| |
Scientific Binary | 1A0110010001E10000110 |
| |
(Biased Exponent) |
| ||
|
|
| |
80287 Short Real | Sign | Biased Exponent | Significand |
|
|
| |
(Normalized) | 0 | 10000110 | ~100100010000000000000 |
| |||
1A (implicit)
BINARY INTEGERS
The three binary integer formats are identical except for length, which governs the range that can be accommodated in each format. The leftmost bit is interpreted as the number's sign: O=positive and 1= negative. Negative numbers are represented in standard two's complement notation (the binary integers are the only 80287 format to use two's complement). The quantity zero is represented with a positive sign (all bits are 0). The 80287 word integer format is identical to the
DECIMAL INTEGERS
Decimal integers are stored in packed decimal notation, with two decimal digits "packed" into each byte, except the leftmost byte, which carries the sign bit (O=positive, 1= negative). Negative numbers are not stored in two's complement form and are distinguished from positive numbers only by the sign bit. The most significant digit of the number is the leftmost digit. All digits must be in the range
REAL NUMBERS
The 80287 stores real numbers in a
Table