aggregated links. For example, an aggregated link consisting of two 1000 Mbit/sec ports can support an aggregate bandwidth of 4 Gbit/sec when operating at full duplex.
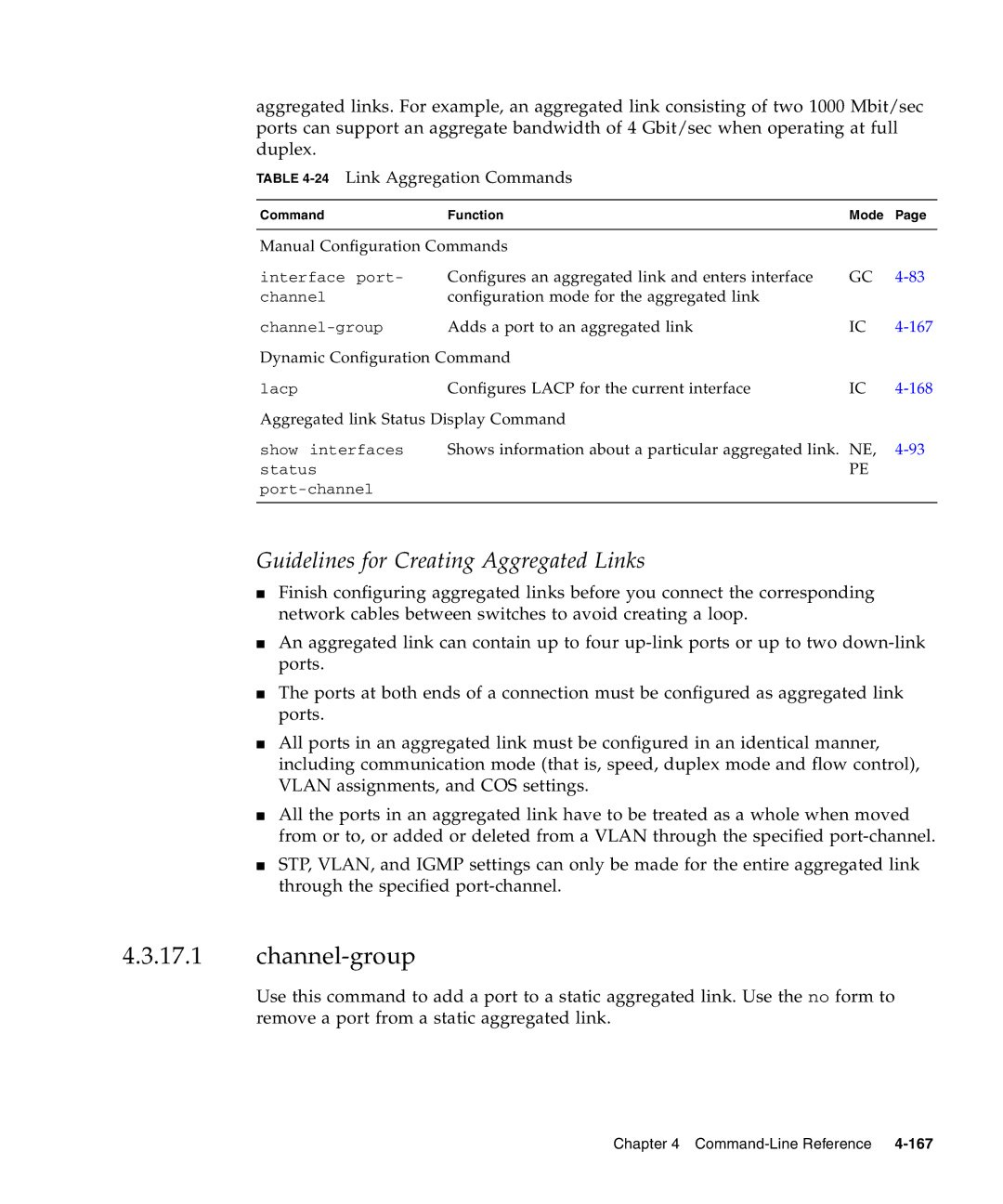
TABLE 4-24 Link Aggregation Commands
Command | Function | Mode | Page |
|
|
| |
Manual Configuration Commands |
|
| |
interface port- | Configures an aggregated link and enters interface | GC | |
channel | configuration mode for the aggregated link |
|
|
Adds a port to an aggregated link | IC | ||
Dynamic Configuration Command |
|
| |
lacp | Configures LACP for the current interface | IC |
|
Aggregated link Status Display Command |
|
| |
show interfaces | Shows information about a particular aggregated link. NE, | ||
status |
| PE |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
Guidelines for Creating Aggregated Links
■Finish configuring aggregated links before you connect the corresponding network cables between switches to avoid creating a loop.
■An aggregated link can contain up to four
■The ports at both ends of a connection must be configured as aggregated link ports.
■All ports in an aggregated link must be configured in an identical manner, including communication mode (that is, speed, duplex mode and flow control), VLAN assignments, and COS settings.
■All the ports in an aggregated link have to be treated as a whole when moved from or to, or added or deleted from a VLAN through the specified
■STP, VLAN, and IGMP settings can only be made for the entire aggregated link through the specified
4.3.17.1channel-group
Use this command to add a port to a static aggregated link. Use the no form to remove a port from a static aggregated link.
Chapter 4