Addressing
The base register consists of an
The I/O limit register consists of an
Bits[11:0] of the limit address are assumed to be FFFh, which naturally aligns the limit address to the top of a 4 KB I/O address block. The 16 bits I/O base and limit registers at offsets 30h and 32h are not implemented, since the 41210 supports only
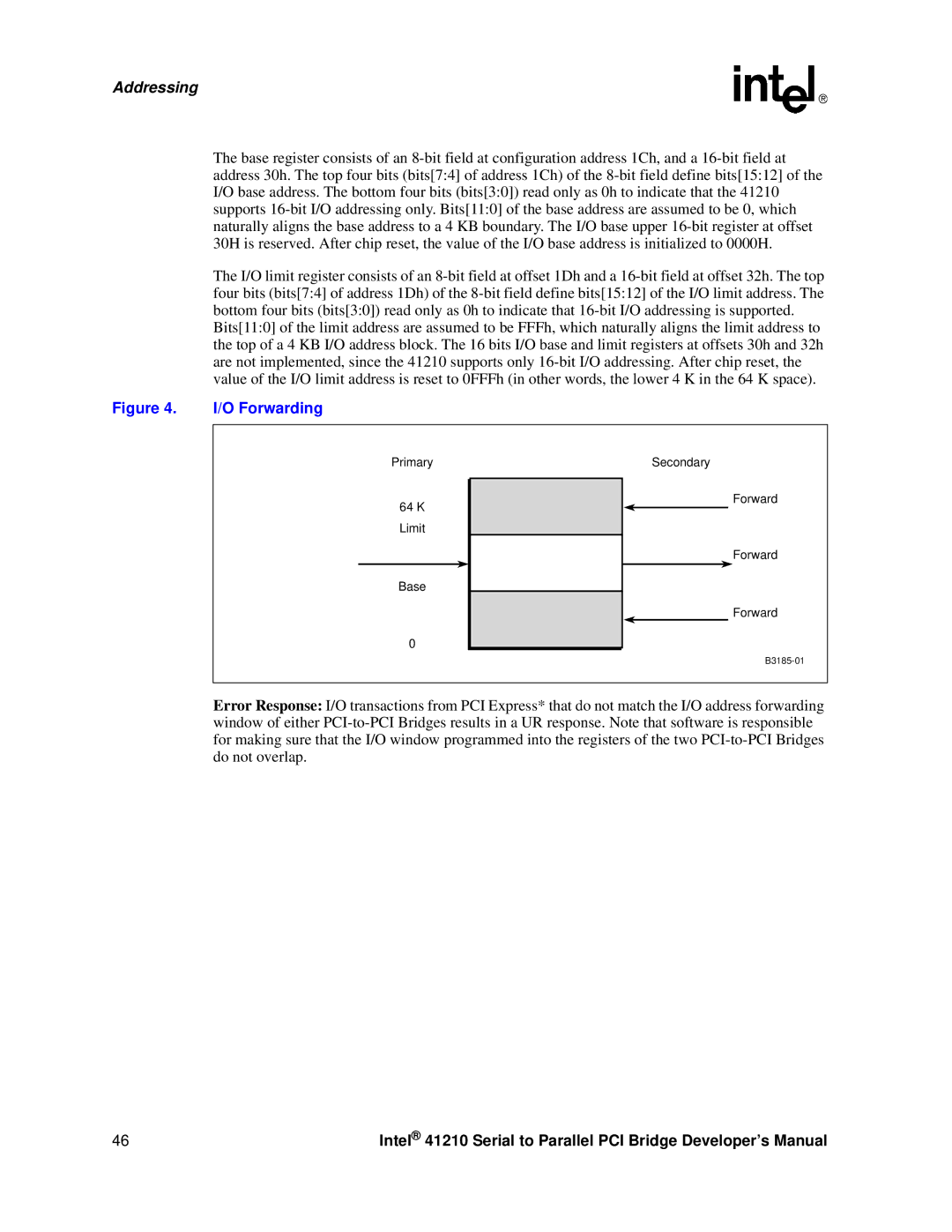
Figure 4. I/O Forwarding
Primary
64K Limit
Base
0
Secondary
Forward
Forward
Forward
Error Response: I/O transactions from PCI Express* that do not match the I/O address forwarding window of either
46 | Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual |