The
Creating a Striped Volume
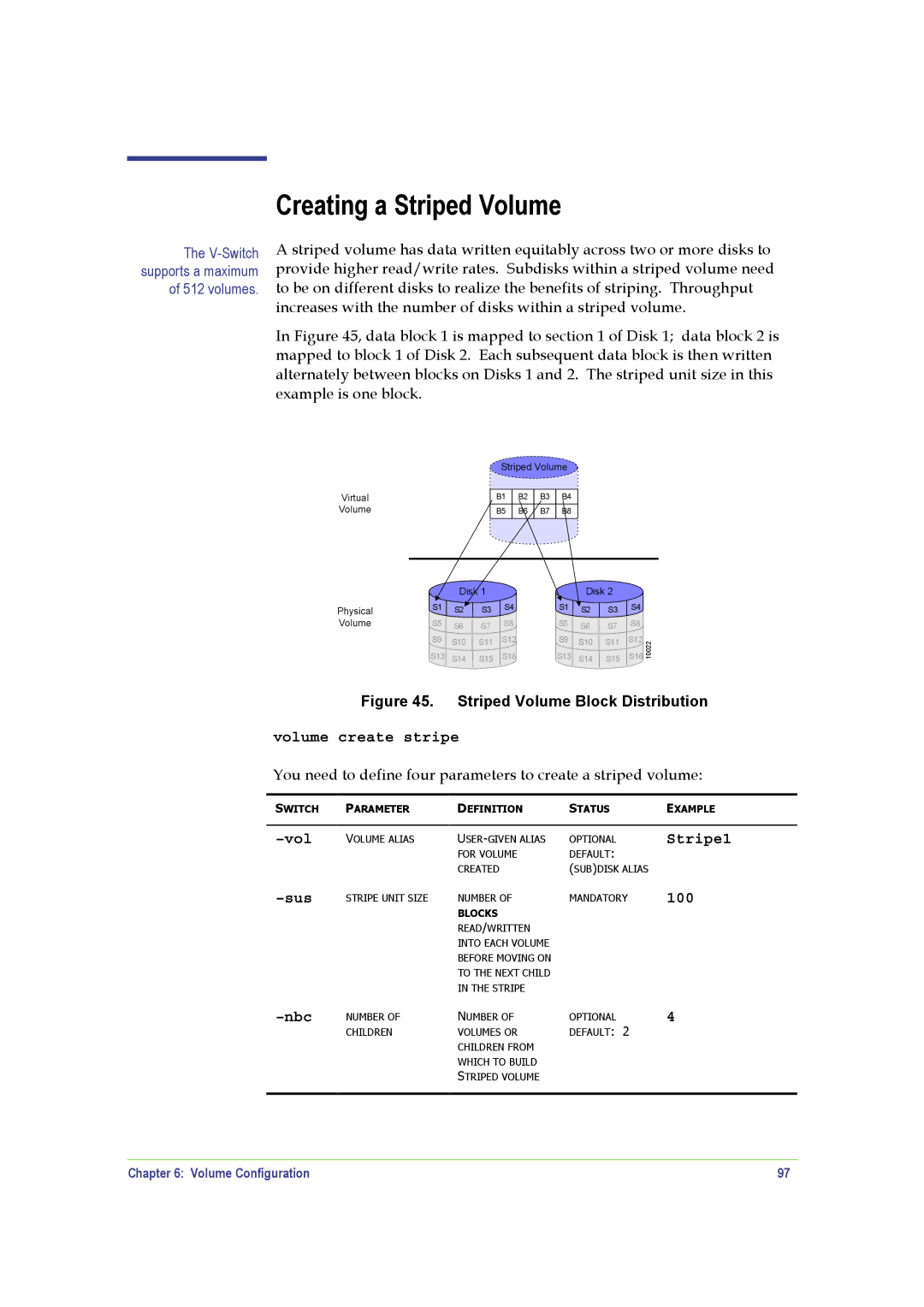
A striped volume has data written equitably across two or more disks to provide higher read/write rates. Subdisks within a striped volume need to be on different disks to realize the benefits of striping. Throughput increases with the number of disks within a striped volume.
In Figure 45, data block 1 is mapped to section 1 of Disk 1; data block 2 is mapped to block 1 of Disk 2. Each subsequent data block is then written alternately between blocks on Disks 1 and 2. The striped unit size in this example is one block.
Virtual
Volume
Striped Volume
B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 |
B5 | B6 | B7 | B8 |
Disk 1 | Disk 2 |
Physical | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 |
Volume | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 |
| S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 |
| S13 | S14 | S15 | S16 |
S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 |
S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 |
|
| ||
S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 |
|
| ||
S13 | S14 | S15 | S16 |
10022
Figure 45. Striped Volume Block Distribution
volume create stripe
You need to define four parameters to create a striped volume:
SWITCH | PARAMETER | DEFINITION | STATUS | EXAMPLE |
|
|
|
|
|
| VOLUME ALIAS | OPTIONAL | Stripe1 | |
|
| FOR VOLUME | DEFAULT: |
|
|
| CREATED | (SUB)DISK ALIAS |
|
| STRIPE UNIT SIZE | NUMBER OF | MANDATORY | 100 |
|
| BLOCKS |
|
|
|
| READ/WRITTEN |
|
|
|
| INTO EACH VOLUME |
|
|
|
| BEFORE MOVING ON |
|
|
|
| TO THE NEXT CHILD |
|
|
|
| IN THE STRIPE |
|
|
NUMBER OF | NUMBER OF | OPTIONAL | 4 | |
| CHILDREN | VOLUMES OR | DEFAULT: 2 |
|
|
| CHILDREN FROM |
|
|
|
| WHICH TO BUILD |
|
|
|
| STRIPED VOLUME |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chapter 6: Volume Configuration | 97 |