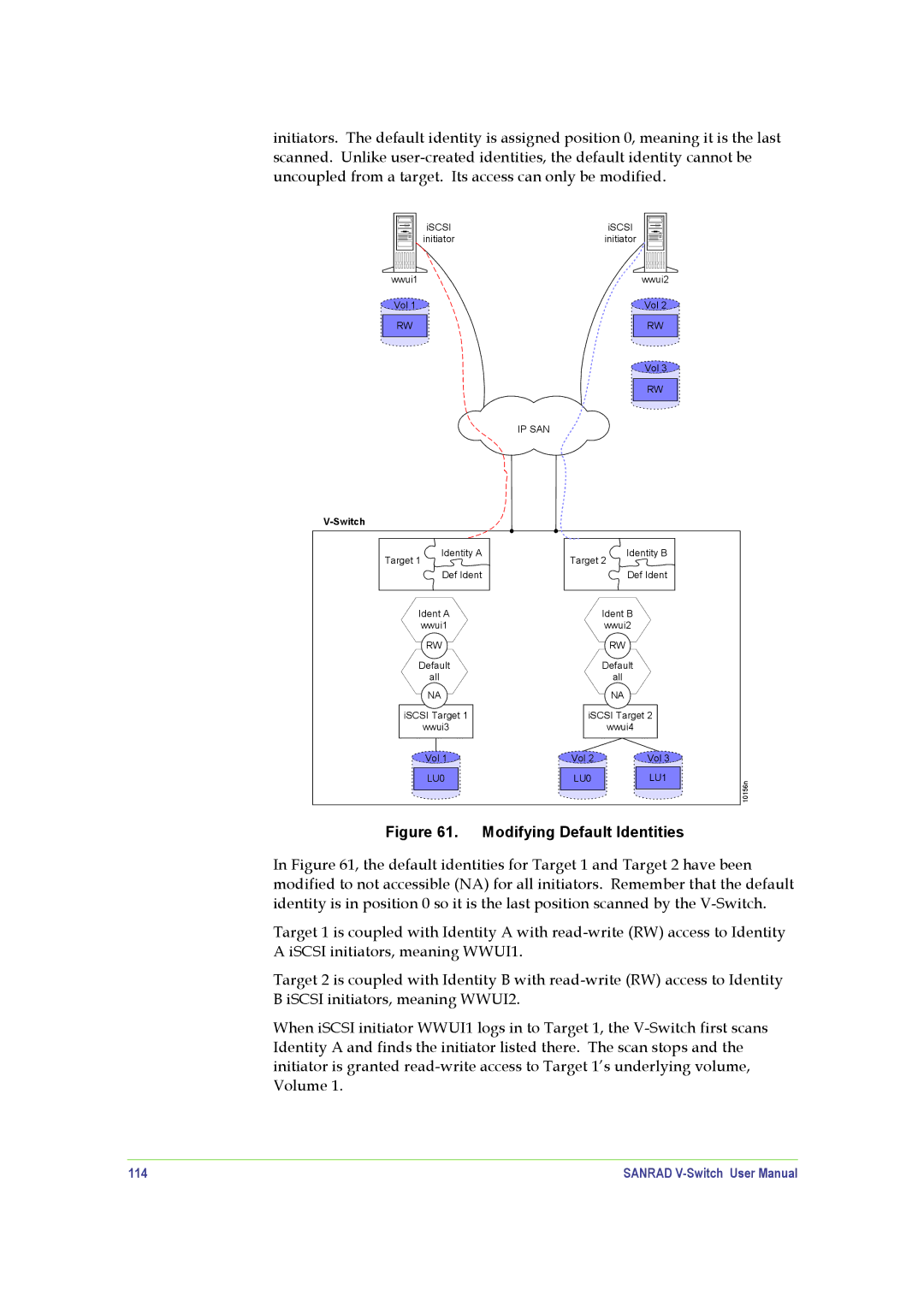
initiators. The default identity is assigned position 0, meaning it is the last scanned. Unlike
iSCSI | iSCSI |
initiator | initiator |
wwui1 | wwui2 |
Vol 1 | Vol 2 |
RW | RW |
| Vol 3 |
| RW |
| IP SAN |
V-Switch
Target 1
Identity A
Def Ident
Target 2 | Identity B |
| |
| Def Ident |
Ident A wwui1
RW
Default
all
NA
iSCSI Target 1
wwui3
Vol 1
LU0
| Ident B |
| wwui2 |
| RW |
| Default |
| all |
| NA |
iSCSI Target 2 | |
| wwui4 |
Vol 2 | Vol 3 |
LU0 | LU1 |
| 10156n |
Figure 61. Modifying Default Identities
In Figure 61, the default identities for Target 1 and Target 2 have been modified to not accessible (NA) for all initiators. Remember that the default identity is in position 0 so it is the last position scanned by the
Target 1 is coupled with Identity A with
Target 2 is coupled with Identity B with
When iSCSI initiator WWUI1 logs in to Target 1, the
114 | SANRAD |