After read this manual Keep it handy for future reference
Hazardous High Voltage
Safety Messages
General Precautions Read These First
Iii
Index to Warnings and Cautions in This Manual
Page
Wiring Cautions for Electrical Practice
Vii
Powerup Test Caution Messages
Viii
Page
General Warnings and Cautions
Inverter
Remote
Xii
Xiii
Xiv
Terminal Tightening Torque and Wire Size
Wire Connectors
Motor Overload Protection
Circuit Breaker and Fuse Sizes
Table of Contents
Xvii
Revision History Table
Xviii
Revisions
Contact Information
Xix
Getting Started
Introduction
Main Features
Operator Interface Options
040
Inverter Specification Label
Model-specific tables for 200V and 400V class inverters
X200 Inverter Specifications
Derating Curve
X200 Inverter Specifications, …
004HFEF 007HFEF 015HFEF 022HFEF
030HFEF 040HFEF
−10
General Specifications
−11
Signal Ratings
Purpose of Motor Speed Control for Industry
What is an Inverter
−12
Introduction to Variable-Frequency Drives
Torque and Constant Volts/Hertz Operation
Inverter Input and Three-phase Power
−13
Inverter Output to the Motor
−14
Braking
−15
Intelligent Functions and Parameters
Velocity Profiles
−16
−17
Frequently Asked Questions
−18
−19
This Chapter… Orientation to Inverter Features
Inverter Mounting Installation
Unpacking and Inspection
Orientation to Inverter Features
Main Physical Features
Front Housing Cover
Logic Connector Introduction
DIP Switch Introduction
Power Wiring Access First, ensure no power
Inverter
Basic System Description
Step Activity
Step-by-Step Basic Installation
Choosing a Mounting Location
Keep Debris Out of Inverter Vents
Ensure Adequate Ventilation
Check Inverter Dimensions
X200-005SFEF,007SFEF, -007NFU
X200-011SFEF~022SFEF, -015NFU~022NFU, -037LFU
X200-004HFEF, -004HFU
X200-007HFEF, -007HFU
X200-015HFEF~040HFEF, -015HFU~040HFU
This page is left intentionally blank…
Prepare for Wiring
Inverter Model
Determining Wire and Fuse Sizes
Signal Lines
Applicable
−20
Terminal Dimensions and Torque Specs
Wire the Inverter Input to a Supply
−21
−22
−23
Wire the Inverter Output to Motor
Logic Control Wiring
Uncover the Inverter Vents
Powerup Test
Goals for the Powerup Test
−24
−25
Pre-test and Operational Precautions
Powering the Inverter
−26
Using the Front Panel Keypad
Key and Indicator Legend
Keys, Modes, and Parameters
−27
Keypad Navigation Map
−28
Selecting Functions and Editing Parameters
−29
−30
−31
−32
−33
Running the Motor
−34
Monitoring Parameters with the Display
−35
Powerup Test Observations and Summary
Configuring 3 Drive Parameters
Introduction of Inverter Programming
Choosing a Programming Device
Using the Keypad Devices
Monitor Mode Programming Mode
Control Algorithms
Run Mode Edit
Operational Modes
OUT-TM
Group Monitoring Functions
Stop
IN-TM Lhlhl
Trip Event and History Monitoring
Local Monitoring During Network Operation
DIG-RUN FWD
Group Main Profile Parameters
ACC
DEC
OPE-Mode
Group Standard Functions
COM
2F-COM
A002 Run Command Setting Method Refer to page…
Code Run Command Source
A001 Frequency Source Setting Method Refer to page…
MAX
Basic Parameter Settings
Base
2F-BASE
Analog Input Settings
EX%E
EXS
EXE
EX%S
FRS
Multi-speed and Jog Frequency Setting
Manual Torque Boost The Constant
Torque Control Algorithms
2CTRL TRQ
Ctrl TRQ
Normal DC braking performance⎯ The DC
DC Braking DB Settings
DCB T
OFF
DCB F
DCB
Lim L 0000.0Hz
Frequency-related Functions
Lim H 0000.0Hz
2Lim H 0000.0Hz
Jump W1
Jump F1
Jump F2
Jump F3
PID Control
00230V
AVR Mode
Automatic Voltage Regulation AVR Function
AVR AC
ECO Adj 0050.0%
Energy Savings Mode / Optional Accel/Decel
RUN Mode NOR
ACC CHG
Second Acceleration and Deceleration Functions
2ACC2
2DEC2
2DECCHfr 0000.0Hz
ACC CHfr 0000.0Hz
2ACCCHfr 0000.0Hz
DEC CHfr 0000.0Hz
DEC Line
Accel/Decel
ACC Line
Additional Analog Input Settings
Calc Smbl
Calc Slct1
POT
Calc Slct2
ADD DIR Plus
ST-PNT
Potentiometer Settings
Automatic Restart Mode
Group Fine Tuning Functions
Cutoff
IPS Powr ALM
IPS Trip OFF
IPS Retry
THM Char CRT
Electronic Thermal Overload Alarm Setting
THM LVL
2ETHM LVL
Frequency Pull-in Restart
Overload Restriction
Lock
Software Lock Mode
Mode Input
−36
LockMD1
−37
−38
Non Stop Operation at Power OFF
−39
−40
Miscellaneous Settings
TRP
−41
FRS
−42
Stop DEC
−43
RUN FRS ZST
FAN-CTRL OFF
−44
Panel
D001
Ladst LVL
B130, B131 Over-voltage LAD Stop Enable
−45
Ovladstop OFF
−46
DC Bus AVR for deceleration Settings
−47
Miscellaneous Settings ~continuation~
RDY-FUNC OFF
SUP Mode
−48
Cr-DEC
Group Intelligent Terminal Functions
Input Terminal Configuration
−49
Intelligent Input Terminal Overview
−50
Function Name Description
−51
Input Function Summary Table Option
Anlg
−52
RDY
−53
OUT-TM RY
Output Terminal Configuration
−54
FA1
Output Function Summary Table Option
−55
−56
LOC LVL
LOC Mode CRT
−57
Low Load Detection Parameters
−58
Output Function Adjustment Parameters
−59
−60
Network Communications Settings
OI-ADJ
Analog Signal Calibration Settings
−61
ADJ
UP/DWN NO-STR
−62
Miscellaneous Functions
DBG Slct
LogicOut2
−63
Output Logic and Timing
LogicOut1
Dlay RY
−64
Dlay
Hold
Group Motor Constants Functions
−65
This Chapter…
Operations Monitoring
Operations and Monitoring
Operations and Monitoring
Connecting to PLCs and Other Devices
Optional
Example Wiring Diagram
AL2 AL1 AL0
Control Logic Signal Specifications
Intelligent Outputs
Input Function Summary Table Symbol Code Function Name
Intelligent Terminal Listing
Intelligent Inputs
Using Intelligent Input Terminals
Sinking Inputs, Internal Supply
Sinking Inputs, External Supply
A002 =
Forward Run/Stop and Reverse Run/Stop Commands
Terminal Function Name State Description
Valid for inputs C001~C005
Valid for inputs
Multi-Speed Select
Function Name State Description
−13
Option Terminal Function Name State Description
Jogging Command
A053, A054
External Signal for DC Braking
Option Code Terminal Symbol Function Name State Description
None
Set Second Motor, Special Set
Option Terminal Function Name State
A092, A093, A094=00
Two Stage Acceleration and Deceleration
Option Terminal Function Name
B003, B088, C011 to C015
Free-run Stop
Terminal Function Name
External Trip
Unattended Start Protection
B031 excluded from lock
Software Lock
A001 =
Analog Input Current/Voltage Select
Terminal Function Name State Description Code
Reset Inverter
Valid for inputs C005 only
Thermistor Thermal Protection
Three-wire Interface Operation
PID ON/OFF and PID Clear
Remote Control Up and Down Functions
Remote Control Data Clears the Up/Down frequency memory
Force Operation from Digital Operator
A001, A145, A146
Add Frequency Enable
Inverter Ready
Force Terminal Mode
Safe Stop
Required settings
Sinking Outputs, Open Collector
Using Intelligent Output Terminals
Relay shown with inverter power ON, Run Signal OFF
Output Signals
Output Signal ON/OFF Delay Function
Option Terminal Function Name State Description Code
Run Signal
Frequency Arrival Signals
FA2
FM terminal see Analog Output Operation
Overload Advance Notice Signal
Output Deviation for PID Control
Or the relay outputs
Alarm Signal
Power Run Mode AL0-AL1 AL0-AL2
Analog Input Disconnect Detect
PID Second Stage Output
Terminal FBV configuration table is on the following
Transitions to OFF when the PID Feedback
Watchdog time-out period with C077
Network Detection Signal Integrated ModBus
Logic Output Function
Logical 0 result
Set P044=00.00 sec
Network Detection Signal FieldBus Option
C038, C039
Low Load Detection Signal
Analog Input Operation
Other Analog Input-related topics
Analog Output Operation
AM output offset adjustment AM output gain adjustment
GND
PID Loop Operation
Other PID-related topics
PID Loop Configuration
Simultaneous Connections
Configuring the Inverter for Multiple Motors
Inverter Configuration for Two Motor Types
Manual torque boost frequency adjustment
Inverter System Accessories
USA
Example calculation
Component Descriptions
AC Reactors, Input Side
AC Reactors, Output Side
RF Noise Filter Capacitive
Zero-phase Reactor RF Noise Filter
EMI Filter
Dynamic Braking Usage
Dynamic Braking
DC Link Choke
Troubleshooting Maintenance
Inspection Items
Troubleshooting
Safety Messages
General Precautions and Notes
Symptom/condition Probable Cause Solution
Troubleshooting Tips
Reduces output as needed
Monitoring Trip Events, History, & Conditions
Fault Detection and Clearing
Error Codes
Error Name Causes Code
Error Name Causes
Trip Conditions
Trip History and Inverter Status
Action Display Func./Parameter
Restoring Factory Default Settings
Monthly and Yearly Inspection Chart
Maintenance and Inspection
X200
Megger test
Capacitor Life Curves
Spare parts
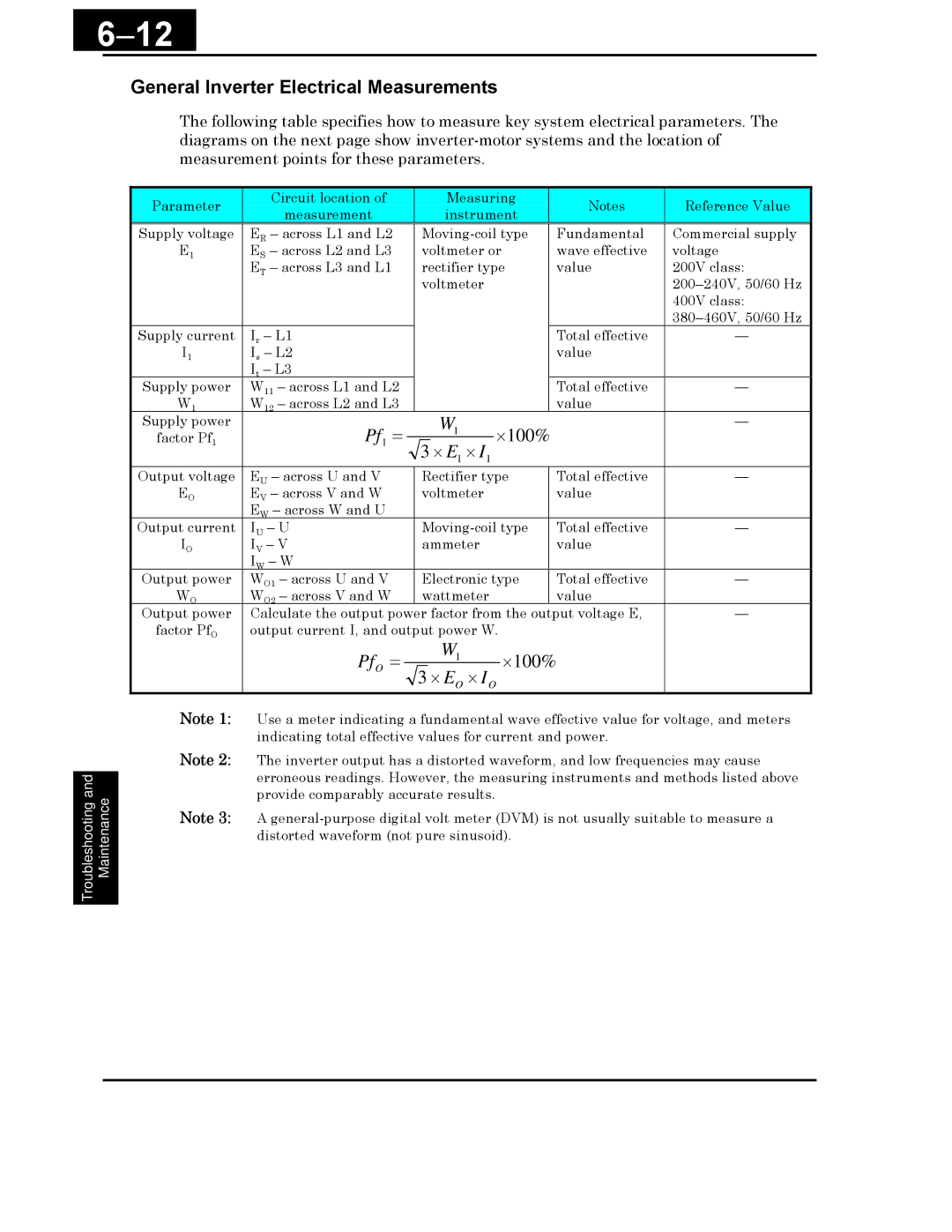
Pf1 =
General Inverter Electrical Measurements
−13
Inverter Output Voltage Measurement Techniques
Igbt Test Method
Warranty Terms
Warranty
This Appendix…
Glossary Bibliography
Glossary
Temperature
EMI
Insulated Gate Bipolar TransistorIGBT a semiconductor
Free-run Stop
NEC
PWM
Squirrel Cage
Torque
Bibliography
ModBus Network Communications
Specifications
Connecting the Inverter to ModBus
SP SN
03… ModBus network input
Settings
Func Name
03…ModBus network input
Slave address
Transmission procedure
Message Configuration Query
Network Protocol Reference
Header and trailer silent interval
Error check
Data
Function code
Normal response
Message Configuration Response
Response when an error occurs
Transmission time required
No response occurs
Field Name
Explanation of function codes
Read Coil Status 01h
Data
Frequency
Read Holding Register 03h
X200 D081
Data Coil Status
Write in Coil 05h
10-11
Write in Holding Register 06h
Loopback Test 08h
Write in Coils 0Fh
Write in Holding Registers 10h
Code Description
Exception Response
Function Code
Exception Code
Submitting an Enter Command
Store New Register Data Enter command
List of Coil Numbers Name Description
ModBus Data Listing
ModBus Coil List
…OFF
Res
ModBus Holding Registers
Output frequency Real-time display of output
Description Network Data Code Reg
List of Holding Registers Func
Acceleration 1 time Standard default acceleration
Frequency source Five options select codes
4000 A024 Multi-speed 4 setting
Code Reg
List of Holding Registers Func Name Description
PID enable Enables PID function
Acceleration 2 time Duration of 2nd segment
OI-L input active Ending point offset for
Selection of automatic Select inverter restart method
Overload restriction Select the operation mode during
Deceleration time Range is 0.01 to
Restart mode after Selects how the inverter resumes 10D7h
B133 DC bus AVR Two option codes
See Input Terminal Configuration
Communication Settings on
See Output Logic and Timing on
Motor capacity …0.20kW
Drive Parameter Setting Tables
Name
Parameter Settings for Keypad Entry
Group Parameters Default Setting
Main Profile Parameters
Code
Standard Functions
Func Name
Name =10
Appendix
Func Name =10
Fine Tuning Functions
Group Parameters
Group Parameters Default Setting
Intelligent Terminal Functions
Expansion Card Functions
Motor Constants Functions
CE-EMC
CE-EMC Installation Guidelines
Integrated EMC Filter
Installation for X200 series example of Sfef models
Hitachi EMC Recommendations
Index
EMI A-3
Index−2
LEDs 2-26,2-27,2-39,3-3 Line reactor A-5
Index−3
Index−4
Non stop operation at power OFF 3-38 AC reactor
Safe stop 2-5
Index−5
Index−6