FVS318N
Trademarks
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
Technical Support
Statement of Conditions
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
Contents
LAN Configuration
Firewall Protection
Virtual Private Networking Using SSL Connections
Network and System Management
Appendix a Default Settings and Technical Specifications
Introduction
Wireless Features
Key Features and Capabilities
Introduction
Powerful, True Firewall
Advanced VPN Support for Both IPSec and SSL
Autosensing Ethernet Connections with Auto Uplink
Security Features
Extensive Protocol Support
Easy Installation and Management
Package Contents
Hardware Features
Green, one for each port
Power Left LAN LEDs
Wireless LED Right LAN LEDs Right WAN LED
Active WAN LED
DMZ LED
Activity Description LAN Ports
WAN Port
Rear Panel
Choose a Location for the Wireless VPN Firewall
Bottom Panel with Product Label
Log In to the Wireless VPN Firewall
To log in to the wireless VPN firewall
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
Web Management Interface Menu Layout
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
IPv4
Requirements for Entering IP Addresses
IPv6
Tasks to Set Up an IPv4 Internet Connection to Your ISP
Internet and WAN Configuration Tasks
Complete these four tasks
Tasks to Set Up an IPv6 Internet Connection to Your ISP
Configure the IPv4 Internet Connection and WAN Settings
IPv4 and IPv6 Internet and Broadband Settings
To configure the IPv4 routing mode
Configure the IPv4 WAN Mode
Configure the IPv4 Routing Mode
Network Address Translation
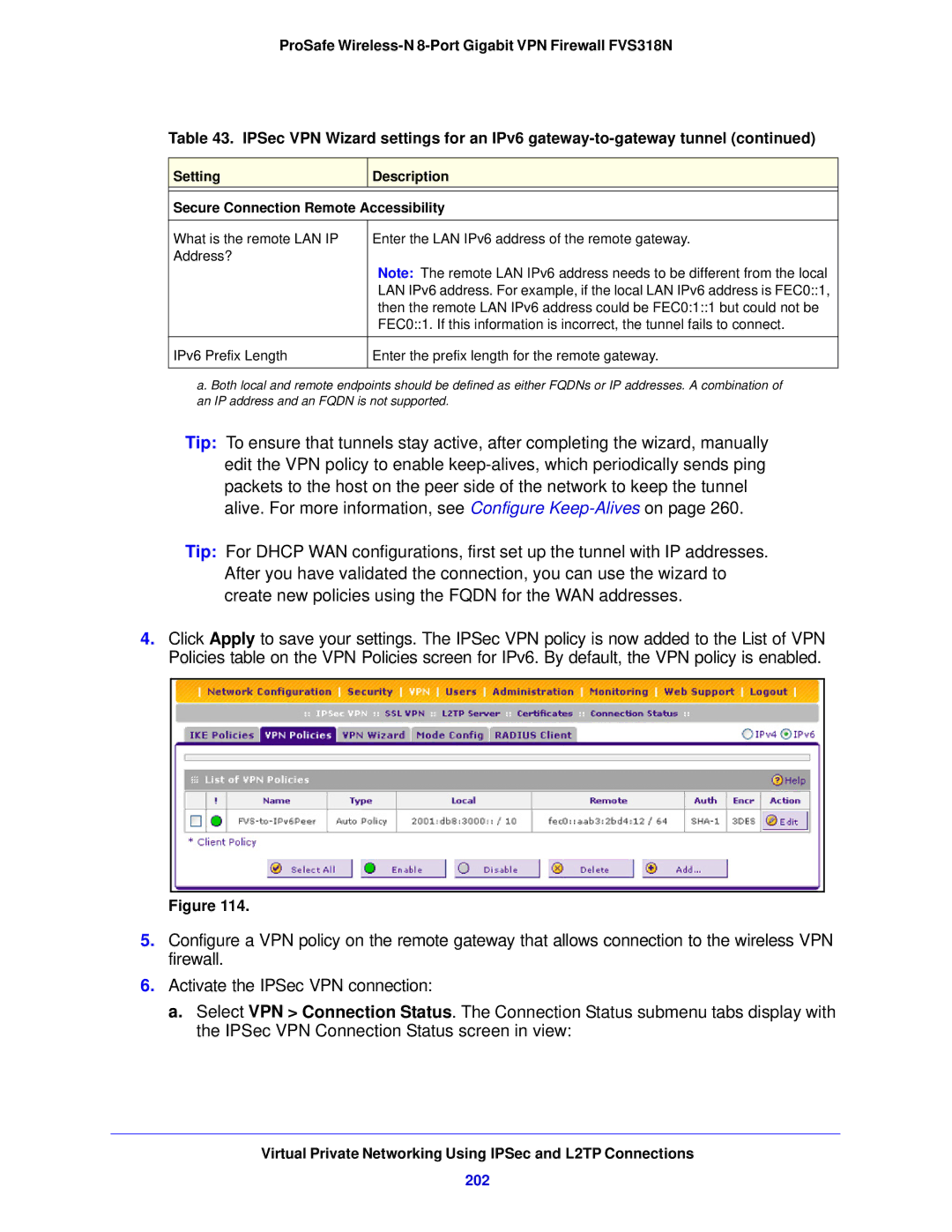
Click Apply to save your settings
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
Connection Method Manual Data Input Required
Pptp
Manually Configure an IPv4 Internet Connection
To manually configure the IPv4 broadband ISP settings
Setting Description
Pptp and PPPoE settings
Step
Has assigned one. You can leave this field blank
Identifier check box
DNS server settings
Get Automatically from ISP radio button
Configure Dynamic DNS
To configure Ddns
Configure the IPv6 Internet Connection and WAN Settings
Ddns service settings
Configure the IPv6 Routing Mode
To configure the IPv6 routing mode
Use a DHCPv6 Server to Configure an IPv6 Internet Connection
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
Configure a Static IPv6 Internet Connection
Setting Description
Configure a PPPoE IPv6 Internet Connection
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
WAN Port Status on Options and Other Tasks on
Stateless DHCPv6 Server With Prefix Delegation on
Configure 6to4 Automatic Tunneling
Select the Enable Automatic Tunneling check box
Configure Isatap Automatic Tunneling
To configure an Isatap tunnel
Add Isatap Tunnel screen settings
To edit an Isatap tunnel
To delete one or more tunnels
Configure Stateless IP/ICMP Translation
View the Tunnel Status and IPv6 Addresses
To view the status of the tunnels and IPv6 addresses
To configure Siit
Configure Advanced WAN Options and Other Tasks
To configure advanced WAN options
Broadband Advanced Options screen settings
Setting Description MTU Size
Default Address radio button
Setting Speed Description
Router’s MAC Address
What to Do Next
Additional WAN-Related Configuration Tasks
Verify the Connection
LAN Configuration
Manage IPv4 Virtual LANs and Dhcp Options
LAN Configuration
Port-Based VLANs
Explained in Configure the IPv4 Internet Connection and WAN
Assign and Manage Vlan Profiles
Vlan Dhcp Options
Dhcp Relay
Dhcp Server
DNS Proxy
Ldap Server
Configure a Vlan Profile
To add a Vlan profile
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
IP Setup
Add Vlan Profile screen settings
Setting Description Vlan Profile
Port Membership
VLAN, the default start IP address is
DNS Proxy
Inter Vlan Routing
To configure a Vlan to have a unique MAC address
Configure Vlan MAC Addresses and LAN Advanced Settings
To enable, disable, or delete one or more Vlan profiles
To edit a Vlan profile
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
To add a secondary LAN IPv4 address
To edit a secondary LAN IP address
Manage IPv4 Groups and Hosts IPv4 LAN Groups
To delete one or more secondary LAN IP addresses
Manage the Network Database
Also Set Up Dhcp Address Reservation on
Add Known PCs and Devices section settings
Add Computers or Devices to the Network Database
Edit Computers or Devices in the Network Database
Deleting Computers or Devices from the Network Database
Change Group Names in the Network Database
To edit the names of any of the eight available groups
Set Up Dhcp Address Reservation
DHCPv6 Server Options
Manage the IPv6 LAN
Stateless DHCPv6 Server
Stateless DHCPv6 Server With Prefix Delegation
Stateful DHCPv6 Server
Configure the IPv6 LAN
DHCPv6
LAN Setup screen settings for IPv6
Setting Description IPv6 LAN Setup
Prefix delegation check box is selected. The stateless
IPv6 LAN Address Pools
IPv6 screen see Configure a Static IPv6 Internet Connection
Settings IPv6 screen see Configure a Static IPv6 Internet
To add an IPv6 LAN address pool
To edit an IPv6 LAN address pool
LAN IPv6 Config screen settings
To delete one or more IPv6 LAN address pools
To edit a prefix
IPv6 LAN Prefixes for Prefix Delegation
To add an IPv6 prefix
To delete one or more prefixes
DHCPv6 and Radvd interaction in the LAN
Flags in the Radvd DHCPv6 Server Provides Radvd Provides
Radvd screen settings for the LAN
To add an advertisement prefix for the LAN
Advertisement Prefixes for the LAN
MTU
To edit an advertisement prefix
Add Advertisement Prefix screen settings for the LAN
SLA ID
To delete one or more advertisement prefixes
Enable and Configure the DMZ Port for IPv4 and IPv6 Traffic
DMZ
To enable and configure the DMZ port for IPv4 traffic
DMZ Port for IPv4 Traffic
DMZ Setup screen settings for IPv4
Setting Description DMZ Port Setup
Dhcp for DMZ Connected Computers
DMZ Port for IPv6 Traffic
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
DHCPv6 for DMZ Connected Computers
DMZ Setup screen settings for IPv6
Configure the IPv6 Router Advertisement Daemon
Advertisement Prefixes for the DMZ on
IPv6 DMZ Address Pools
IPv6 screen see Configure a Static IPv6 Internet
To add an IPv6 DMZ address pool
To edit an IPv6 DMZ address pool
DMZ IPv6 Config screen settings
To delete one or more IPv6 DMZ address pools
DHCPv6 and Radvd interaction in the DMZ
Radvd screen settings for the DMZ
Advertisement Prefixes for the DMZ
To add an advertisement prefix for the DMZ
Add Advertisement Prefix screen settings for the DMZ
Manage Static IPv4 Routing
Configure Static IPv4 Routes
To add an IPv4 static route to the Static Route table
Add Static Route screen settings for IPv4
To edit an IPv4 static route
Configure the Routing Information Protocol
To enable and configure RIP
To delete one or more routes
RIP Configuration screen settings
101
Authentication for RIP-2B/2M
102
IPv4 Static Route Example
Manage Static IPv6 Routing
103
Add IPv6 Static Routing screen settings
104
To edit an IPv6 static route
105
Overview of the Wireless Features
106
Wireless Configuration and Security
Wireless Equipment Placement and Range Guidelines
107
Radio Settings screen settings
Configure the Basic Radio Settings
To configure the basic radio settings
Setting Descriptions
109
Physical and Technical Specifications on
Channel Guidelines following this table
Operating Frequency Channel Guidelines
110
Wireless Data Security Options
111
Wireless Security Profiles
112
Data encryption
Network authentication
113
WPA2 Radius settings
Before You Change the SSID, WEP, and WPA Settings
WPA Radius settings
114
Wireless Profiles screen settings
Configure and Enable Wireless Profiles
To add a wireless profile
115
Setting Description Wireless Profile Configuration
Add Wireless Profiles screen settings
116
117
Security Options on
118
Vlan Profile on
Setting Description WEP Index and Keys
119
To delete one or more wireless profiles
Restrict Wireless Access by MAC Address
To edit a wireless profile
To enable or disable one or more wireless profiles
To allow or restrict access based on MAC addresses
121
To view the status of a specific wireless profile
View the Status of a Wireless Profile
122
123
Configure Wi-Fi Protected Setup
Wireless Profile Statistics
Connected Clients
124
To configure advanced radio settings
Configure Advanced Radio Settings
125
Advanced Wireless screen settings
126
To test for wireless connectivity
Test Basic Wireless Connectivity
127
About Firewall Protection
128
Firewall Protection
Administrator Tips
129
Number of supported firewall rule configurations
Outbound Rules Service Blocking
130
131
Setting Description Outbound Rules
Outbound rules overview
Set a Schedule to Block or Allow Specific Traffic on
132
133
Inbound Rules Port Forwarding
NAT IP
134
Setting Description Inbound Rules
135
136
Manage the Network Database on page 68. Groups are
Order of Precedence for Rules
137
Configure LAN WAN Rules
138
139
To create a new IPv4 LAN WAN outbound rule
Create LAN WAN Outbound Service Rules
IPv4 LAN WAN Outbound Rules
140
141
To create a new IPv6 LAN WAN outbound rule
IPv6 LAN WAN Outbound Rules
142
To create a new IPv4 LAN WAN inbound rule
Create LAN WAN Inbound Service Rules
IPv4 LAN WAN Inbound Service Rules
143
To create a new IPv6 LAN WAN inbound rule
IPv6 LAN WAN Inbound Rules
144
Configure DMZ WAN Rules
145
146
147
To create a new IPv4 DMZ WAN outbound rule
Create DMZ WAN Outbound Service Rules
IPv4 DMZ WAN Outbound Service Rules
148
To create a new IPv6 DMZ WAN outbound rule
IPv6 DMZ WAN Outbound Service Rules
149
To create a new IPv4 DMZ WAN inbound rule
Create DMZ WAN Inbound Service Rules
IPv4 DMZ WAN Inbound Service Rules
150
151
To create a new IPv6 DMZ WAN inbound rule
IPv6 DMZ WAN Inbound Service Rules
152
Configure LAN DMZ Rules
153
154
To create a new IPv4 LAN DMZ outbound rule
Create LAN DMZ Outbound Service Rules
IPv4 LAN DMZ Outbound Service Rules
155
To create a new IPv6 LAN DMZ outbound rule
IPv6 LAN DMZ Outbound Service Rules
156
To create a new IPv4 LAN DMZ inbound rule
Create LAN DMZ Inbound Service Rules
IPv4 LAN DMZ Inbound Service Rules
157
To create a new IPv6 LAN DMZ inbound rule
IPv6 LAN DMZ Inbound Service Rules
158
IPv4 LAN WAN Inbound Rule Host a Local Public Web Server
Examples of Firewall Rules
Examples of Inbound Firewall Rules
159
160
161
162
163
IPv4 LAN WAN Outbound Rule Block Instant Messenger
Examples of Outbound Firewall Rules
164
165
Attack Checks
Configure Other Firewall Features
166
Setting Description WAN Security Checks
To enable IPv4 attack checks for your network environment
Attack Checks screen settings for IPv4
IPv4 Attack Checks
VPN Pass through
Setting Description LAN Security Checks
168
Pptp L2TP
IPv6 Attack Checks
Setting Description Jumbo Frames
169
Setting Description Session Limit
To enable and configure session limits
Session Limit screen settings
Set Limits for IPv4 Sessions
Manage the Application Level Gateway for SIP Sessions
To enable ALG for SIP
Session Timeout
171
Add Customized Services
Services, Bandwidth Profiles, and QoS Profiles
172
173
To add a customized service
Services screen settings
ICMPv6
Service Profiles on
To edit a service
To delete one or more services
174
Create Bandwidth Profiles
To add and enable a bandwidth profile
175
Add Bandwidth Profile screen settings
176
To delete one or more bandwidth profiles
Preconfigured Quality of Service Profiles
To edit a bandwidth profile
177
Configure Content Filtering
178
To enable and configure content filtering
179
180
To build your list of trusted domains
To apply keyword blocking to LAN groups
181
To set a schedule
Set a Schedule to Block or Allow Specific Traffic
182
Enable Source MAC Filtering
183
Set Up IP/MAC Bindings
184
IPv4/MAC Bindings
185
IP/MAC Binding screen settings for IPv4
186
To remove one or more IP/MAC bindings from the table
IPv6/MAC Bindings
To edit an IP/MAC binding
187
IP/MAC Binding screen settings for IPv6
188
189
To add a port triggering rule
Configure Port Triggering
190
To edit a port triggering rule
Port Triggering screen settings
191
To display the status of the port triggering rules
Configure Universal Plug and Play
To configure UPnP
192
193
Virtual Private Networking Using IPSec and L2TP Connections
194
Virtual Private Networking Using IPSec and L2TP Connections
195
196
Connection Name and Remote IP Type
Setting Description About VPN Wizard
197
End Point Information a
Setting Description Secure Connection Remote Accessibility
198
Create an IPv6 Gateway-to-Gateway VPN Tunnel with the Wizard
199
200
201
202
Create an IPv4 Client-to-Gateway VPN Tunnel with the Wizard
203
204
IPSec VPN Wizard settings for a client-to-gateway tunnel
205
206
Information required to configure the VPN client
Component Enter the information that you collected Example
207
208
209
210
VPN client advanced authentication settings
Setting Description Advanced features
NAT-T
211
Type vpnclient
To create new authentication settings
212
Enter
VPN client authentication settings
213
IKE
214
Type netgearplatform
To create an IPSec configuration
215
216
VPN client IPSec configuration settings
ESP
To specify the global parameters
217
Test the Netgear VPN Client Connection
218
Click Gateway-Tunnel, and press Ctrl+O
219
Netgear VPN Client Status and Log Information
View the Wireless VPN Firewall IPSec VPN Connection Status
220
IPSec VPN Connection Status screen information
View the Wireless VPN Firewall IPSec VPN Log
To display the IPSec VPN log
221
Manage IKE Policies
Manage IPSec VPN Policies
222
IKE Policies screen information for IPv4 and IPv6
To access the IKE Policies screen
IKE Policies Screen
223
To manually add an IKE policy for IPv4 or IPv6
Manually Add or Edit an IKE Policy
To delete one or more IKE polices
224
225
226
Add IKE Policy screen settings
Setting Description Mode Config Record
General
Remote
Setting Description Local
227
IKE SA Parameters
Group 5 1536 bit
228
Group 1 768 bit
Dead Peer
To edit an IKE policy
Setting Description Extended Authentication
229
VPN Policies Screen
Manage VPN Policies
230
VPN Policies screen information for IPv4 and IPv6
231
To delete one or more VPN polices
To enable or disable one or more VPN policies
Manually Add or Edit a VPN Policy
To manually add a VPN policy
233
234
Configure Keep-Alives
Add New VPN Policy screen settings for IPv4 and IPv6
Setting Description General
235
236
Setting Description Traffic Selection
Manual Policy Parameters
237
Auto Policy Parameters
To edit a VPN policy
Configure Extended Authentication Xauth
238
To enable and configure Xauth
Configure Xauth for VPN Clients
239
Extended authentication settings for IPv4 and IPv6
User Database Configuration
Radius Client and Server Configuration
240
Setting Description Primary Radius Server
To configure primary and backup Radius servers
Radius Client screen settings
241
Connection Configuration
Backup Radius Server
242
Mode Config Operation
Assign IPv4 Addresses to Remote Users Mode Config
243
To configure Mode Config on the wireless VPN firewall
244
Setting Description Client Pool
Add Mode Config Record screen settings
245
246
Traffic Tunnel Security Level
247
248
249
250
Setting Description IKE SA Parameters
Select Group 2 1024 bit
251
Configure the ProSafe VPN Client for Mode Config Operation
Screen see User Database Configuration on
Radius Chap
252
Type GWModeConfig
253
VPN client authentication settings Mode Config
254
VPN client advanced authentication settings Mode Config
Type TunnelModeConfig
255
256
VPN client IPSec configuration settings Mode Config
192.168.1.1
Configure the Mode Config Global Parameters
257
Test the Mode Config Connection
258
To edit a Mode Config record
Configure Keep-Alives and Dead Peer Detection
Modify or Delete a Mode Config Record
To delete one or more Mode Config records
Configure Keep-Alives
260
Keep-alive settings
Configure Dead Peer Detection
To configure DPD on a configured IKE policy
261
Dead Peer Detection settings
Configure NetBIOS Bridging with IPSec VPN
262
To enable NetBIOS bridging on a configured VPN tunnel
Configure the L2TP Server
263
L2TP Server screen settings
264
265
View the Active L2TP Users
L2TP Active Users screen information
L2TP IP
SSL VPN Portal Options
266
Virtual Private Networking Using SSL Connections
Overview of the SSL Configuration Process
267
Create the Portal Layout
268
To create a new SSL VPN portal layout
269
Portal URL
270
Setting Description Portal Layout and Theme Name
Add Portal Layout screen settings
271
To delete one or more portal layouts
Configure Domains, Groups, and Users
To edit a portal layout
272
To add a server and a port number
Configure Applications for Port Forwarding
Add Servers and Port Numbers
273
274
Add a New Host Name
Port forwarding applications/TCP port numbers
TCP Application Port Number
Fully Qualified Domain Name. The full server name
Configure the SSL VPN Client
To add servers and host names for client name resolution
275
To define the client IP address range
Configure the Client IP Address Range
276
277
SSL VPN Client screen settings for IPv4 and IPv6
Setting Description Client IP Address Range
Routes for VPN Tunnel Clients on
To add an SSL VPN tunnel client route
Add Routes for VPN Tunnel Clients
278
To define a network resource
Use Network Resource Objects to Simplify Policies
Add New Network Resources
279
To edit network resources
Edit Network Resources to Specify Addresses
To delete one or more network resources
280
Setting Description Add Resource Addresses
Resources screen settings to edit a resource
281
Configure User, Group, and Global Policies
282
To view the existing SSL VPN policies
View Policies
283
To add an SSL VPN policy
Add an IPv4 or IPv6 SSL VPN Policy
284
Add SSL VPN Policy screen for IPv4
285
286
Add SSL VPN Policy screen settings
Setting Description Policy For
Add SSL VPN Policies
287
To delete one or more SSL VPN policies
Access the New SSL Portal Login Screen
To edit an SSL VPN policy
288
Portal Layouts screen for IPv6
289
290
291
To display the SSL VPN log
View the SSL VPN Connection Status and SSL VPN Log
To view the status of current SSL VPN tunnels
292
293
Wireless VPN Firewall’s Authentication Process and Options
294
Authentication Description Protocol or Method
External authentication protocols and methods
Manage Users, Authentication, and VPN Certificates
295
Create Domains
Configure Authentication Domains, Groups, and Users
Configure Domains
To create a domain
Add Domain screen settings
297
298
Server Configuration
Radius Client
299
Windows login account name in email format . For example
To delete one or more domains
Display name in the DN format . For example
To edit a domain
Configure Groups
Edit Domains
300
To create a VPN group
Create Groups
301
To delete one or more groups
Add Group screen settings
302
To edit a VPN group
Configure User Accounts
Edit Groups
303
To create a user account
304
Configure Extended Authentication Xauth on
Add Users screen settings
305
To configure user login policies
Set User Login Policies
Configure Login Policies
To delete one or more user accounts
To restrict logging in based on IPv4 addresses
Configure Login Restrictions Based on IPv4 Addresses
307
To delete one or more IPv4 addresses
Configure Login Restrictions Based on IPv6 Addresses
Defined addresses settings for IPv4
To restrict logging in based on IPv6 addresses
Defined addresses settings for IPv6
309
To restrict logging in based on the user’s browser
Configure Login Restrictions Based on Web Browser
To delete one or more IPv6 addresses
310
To delete one or more browsers
Change Passwords and Other User Settings
Internet Explorer Opera Netscape Navigator
311
Edit User screen settings
To modify user settings, including passwords
312
Manage Digital Certificates for VPN Connections
313
VPN Certificates Screen
314
To view and upload trusted certificates
Manage VPN CA Certificates
315
To delete one or more digital certificates
Manage VPN Self-Signed Certificates
316
317
318
Generate self-signed certificate request settings
512 1024 2048
319
To delete one or more SCRs
Manage the VPN Certificate Revocation List
View and Manage Self-Signed Certificates
To delete one or more self-signed certificates
To delete one or more CRLs
321
Bandwidth Capacity
Performance Management
322
Network and System Management
Features That Reduce Traffic
323
Content Filtering
324
Source MAC Filtering
Features That Increase Traffic
325
326
Exposed Hosts
Port Triggering
DMZ Port
VPN and L2TP Tunnels
Set QoS Priorities
Use QoS and Bandwidth Assignment to Shift the Traffic Mix
Monitoring Tools for Traffic Management
Assign Bandwidth Profiles
System Management
Change Passwords and Administrator and Guest Settings
329
330
Configure Remote Management Access
331
Remote Management screen for IPv4
332
Setting Description Secure Http Management
Remote Management screen settings for IPv4 and IPv6
333
334
About Remote Access
Telnet Management
Use a Simple Network Management Protocol Manager
Use the Command-Line Interface
To access the CLI
335
To configure the Snmp settings
336
Snmp screen settings
To edit an Snmp configuration
337
Edit User screen settings for SNMPv3 users
To delete one or more Snmp configurations
To edit the SNMPv3 default users
338
Snmp SysConfiguration screen settings
To configure the Snmp system information
339
Default name is FVS318N
Manage the Configuration File
Setting Description SysName
340
To back up settings
Back Up Settings
Restore Settings
341
Revert to Factory Default Settings
342
To download a firmware version and upgrade the firmware
Update the Firmware
343
To set time, date, and NTP servers
Configure Date and Time Service
Time Zone screen settings
344
345
Http//support.ntp.org/bin/view/Servers/WebHome
To configure and monitor traffic limits on the WAN port
Enable the WAN Traffic Meter
346
Monitor System Access and Performance
347
Traffic Counter
Setting Description Enable Traffic Meter
348
Alerts, and Event Notifications on
Setting Description When Limit is reached
Configure Logging, Alerts, and Event Notifications
To configure and activate logs
349
350
351
Firewall Logs & E-mail screen settings
Setting Description Log Options
Routing Logs
352
Setting Description Enable E-mail Logs
Send e-mail logs by Schedule
Setting Description Enable SysLogs
How to Send Syslogs over a VPN Tunnel between Sites
353
354
Configure Gateway 1 at Site
To change the remote IP address in the VPN policy
Type of Address Gateway 1 at Site Gateway 2 at Site
To specify the syslog server that is connected to Gateway
Configure Gateway 2 at Site
To change the local IP address in the VPN policy
355
Router Status Screen
View Status Screens
View the System Status
To view the Router Status screen
Router Status screen information
357
To view the Router Statistics screen
Router Statistics Screen
358
359
Detailed Status Screen
Router Statistics screen information
Router Statistics
360
WAN Settings on
LAN Port Configuration
WAN Configuration
Detailed Status screen information
Wireless Configuration
362
Tunnel Status Screen
Description Wireless Profile Information
Enable Wireless Profiles on
363
To view the active SSL VPN connections
View the VPN Connection Status and L2TP Users
To view the active IPSec VPN connections
364
To view the active L2TP tunnel users
View the VPN Logs
365
View the Port Triggering Status
To view the status of the port triggering feature
366
To view the IPv4 status of the WAN port
View the WAN Port Status
IPv4 WAN Port Status
Port Triggering Status screen information
368
Connection Status screen information for an IPv4 connection
IPv4 Internet Connection on
Connection Status screen information for an IPv6 connection
IPv6 WAN Port Status
To view the IPv6 status of the WAN port
369
To view the attached devices on the LAN Groups screen
View the Attached Devices and the Dhcp Log
View the Attached Devices
370
To review the most recent entries in the Dhcp log
View the Dhcp Log
371
372
To display the Diagnostics screen
Diagnostics Utilities
373
374
Trace a Route
Send a Ping Packet
Look Up a DNS Address
To display the routing table
Display the Routing Tables
Capture Packets in Real Time
To capture packets in real time
To reboot the wireless VPN firewall
Reboot the Wireless VPN Firewall Remotely
377
Troubleshooting
378
Basic Functioning
Power LED Not On
Troubleshooting
Test LED Never Turns Off
LAN or WAN Port LEDs Not On
Troubleshoot the Web Management Interface
380
When You Enter a URL or IP Address, a Time-Out Error Occurs
381
To check the WAN IP address
Troubleshoot the ISP Connection
382
Troubleshooting the IPv6 Connection
383
MAC OS
384
385
Ping
Troubleshoot a TCP/IP Network Using a Ping Utility
Test the LAN Path to Your Wireless VPN Firewall
386
Ping -n 10 IP address
Test the Path from Your Computer to a Remote Device
387
Restore the Default Configuration and Password
388
Access the Knowledge Base and Documentation
Address Problems with Date and Time
389
WAN settings
Factory Default Settings
Feature Login settings Default Behavior
390
IPv4 LAN, DMZ, and routing settings
Default Settings and Technical Specifications
Feature Default Behavior
IPv6 LAN and DMZ settings
392
Firewall and security settings
SIP ALG
Wireless radio and access point settings
393
3DES
394
SHA-1
User, group, and domain settings
Radius settings
SSL VPN settings
395
Administrative and monitoring settings
Physical and Technical Specifications
Wireless VPN firewall physical and technical specifications
396
397
Setting Specification
Wireless VPN firewall IPSec VPN specifications
Wireless VPN firewall SSL VPN specifications
398
Wireless VPN firewall wireless specifications
399
What Are the Benefits of Two-Factor Authentication?
Why Do I Need Two-Factor Authentication?
400
Two-Factor Authentication
Netgear Two-Factor Authentication Solutions
What Is Two-Factor Authentication?
To use WiKID for end users
402
403
FCC Requirements for Operation in the United States
Regulatory Compliance Information
404
European Union
Notification of Compliance Wired
405
AES
Additional Copyrights
406
Terms
407
MD5
408
Edoc in Languages of the European Community
Language Statement
Notification of Compliance Wireless
409
FCC Caution
410
Interference Reduction Table
Industry Canada
Important Note Radiation Exposure Statement
411
Index
412
413
295
DMZ Radvd
414
DMZ Dhcp
415
227
416
417
SSL VPN
418
419
420
421
422
423
164
424
IKE policies
425