User’s Guide
HP Rut No -90367 Supersedes October Printed iu USA February
@ Copyright Hewlett-Packard Company 1998
Certification
Wmanty
Clean the cabinet, using a damp cloth only
Maintenance
Shipment for Service
Assistance
‘Iktble O-1. Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service OfEces
JspaJp Fb@me
Safety Symbols
Instrument Markings
General Safety Considerations
Acoustic Noise Emission/Geraeuschemission
Compliance with German FTZ Emissions Requirements
Compliance with German Noise Requirements
LpA70 dB Lpa70 dD
User’s Guide Overview
Network Analyzer Documentation Set
Page
Declaration of Conformity
Contents
Page
Making Mixer Measurements
LO to RF Isolation RF Feedthrough
Printing, Plotting, and Saving Measurement Results
Optimizing
Application and Operation Concepts
Uncoupling StimuIus Values Between Primary Channels
Contents-ll
C0ti0ntr-8
Calibrated Power Level
TRL* Error Model Isolation Source match and load match
TRL Calibration Procedure Requirements for TRL Standards
Loss of Power Meter Calibration Data
Locking onto a signal with a frequency modulation component
Transforming CW Time Measurements Into the Frequency Domain
Specifications and Measurement Uncertainties
Compatible Peripherals
Error Messages
Menu Maps Key Definitions
11-l 11-2 11-3 11-4 11-5 11-6 11-7 11-8 11-9
Preset State and Memory Allocation
CITIfUe Data Format and Keyword Reference
Determining System Measurement Uncertainties
Index
Display
Example of Searching for a Bandwidth Using Markers
Results
Gate Shape
Measurement Setup Diagram Shown on Analyzer Display
Time Domain Transmission Example Measurement
Measurement
Contents-19
Reflection Measurement of Two Cables 128
Range Resolution of a Siie Discontinuity
Combined Effects of Amplitude and Phase Modulation
Response 134
Range of a Forward Transform Measurement
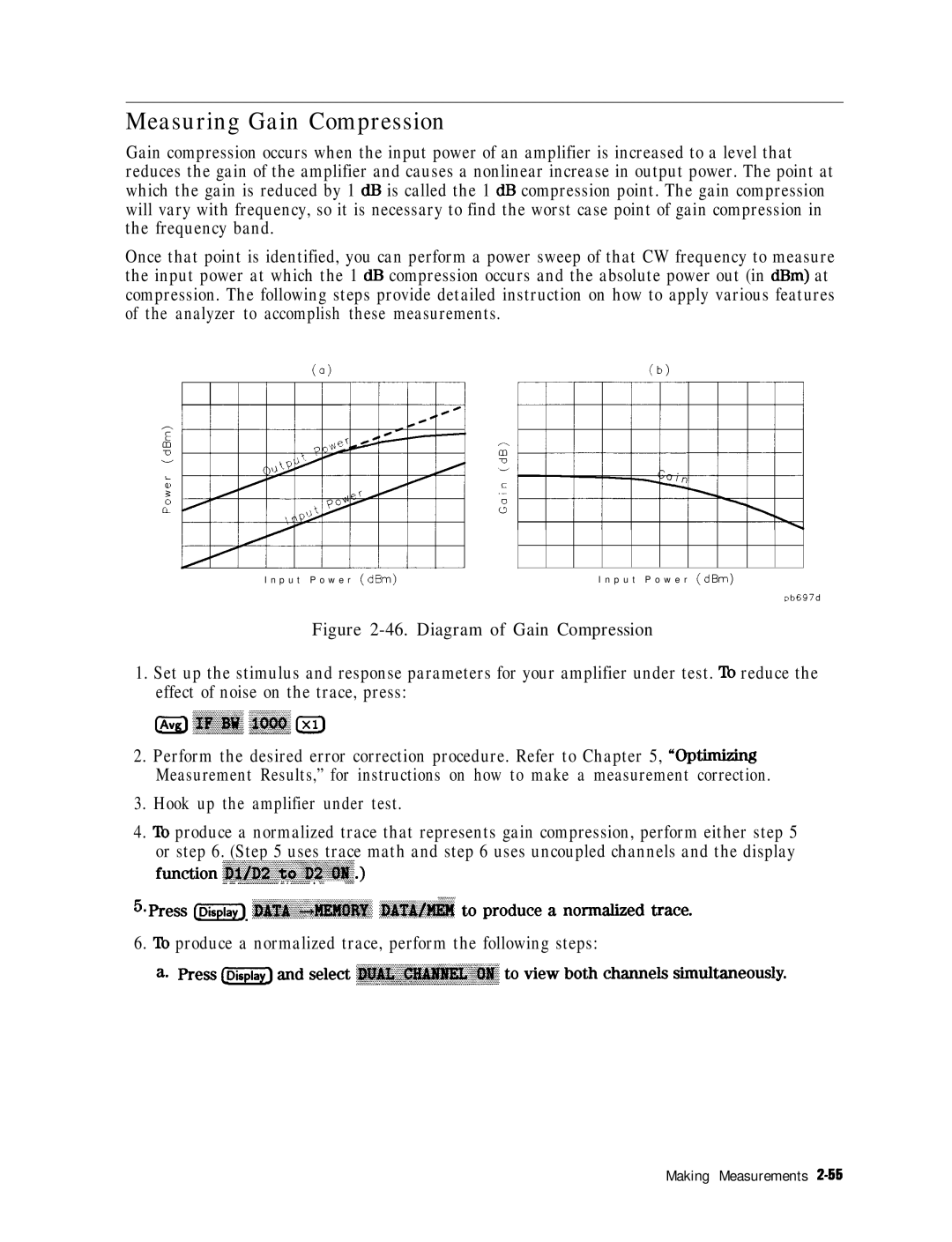
Diagram of Gain Compression
Modulation
Amplifier Parameters
Bles
Results of Power Loss to Non-Volatile Memory 12-12
Sufhx Character Definitions 12-5 Preset Conditions 1 12-8
Power-on Conditions versus Preset 12-11
12-3
Where to Look for More Information
HP 87533 Description and Options
Control
Analyzer Description
Performance
Accuracy
Printin& Plotting, and Saving
Front Panel Features
Disk eject button
HP 5753E Dessription and Options l-5
HP-IB Status indicators are also included in this block
Analyzer Display
Analyzer Display Single Channel, Cartesian Format
Application and Operation Concepts
See J%I@ in , Key Definitions
From inactive channels
10 HP 8753E Description and Options
Rear Panel Features and Connectors
%.n. This fan provides forced-air cooling for the analyzer
Pass TTLhigh
Fail ITLlow
Analyzer Options Available
Service and Support Options
Option lCP, Rack Mount Flange Kit With Handles
Differences among the HP 8753 Network Analyzers
Lhble l-l. Comparing the J3P 8753AIBKYD
‘able 1-2. Comparing the HP 8753D and HP 8753E
Making Measurements
Principles of Microwave Connector Care
‘lhble 2-l. Connector Care Quick Reference
Basic Measurement Sequence
Setting the Frequency Range
Basic Measurement Sequence and Example
Basic Measurement Example
Setting the Measurement
Setting the Source Power
Lb change the power level to -5 dRm, press
‘lb set the span to 30 MHz, press &gziJm
Measure the device under test
Using the Display Functions
Example Dua.l Channel With Split Display On
Lb View the Measurement Data and Memory Trace
To Save a Data Trace to the Display Memory
I............s..........i
‘RI Ratio Measurements in Channel 1
To Divide Measurement Data by the Memory Trace
Analyzer performs a vector subtraction on the complex data
To Title the Active Channel Display
Example of a Display Title
Page
Channel Display
To Activate and Co&lgure the Auxilkry Channels
Duplexer’s three ports are
Smith chart by pressing @GZ $#$Z~B&KX
Characterizing a Duplexer
Transmit TX
Press=
Procedure for Characterizing a Duplexer
Required Equipment
Port an unlit LED indicates no connection
D. F%ess @G-T to activate channel 4, press $%$.‘
Duplexer Measurement
Using Analyzer Display Markers
To Use Continuous and Discrete Markers
To Activate Display Markers
‘Ib switch off all of the markers, press ~~~
Or ~~~~~7
Tb Move Marker Information off of the Grids
PRnl
Lb Use Delta a Markers
Rlllllllllll
Press jj ~~~~~~~~ ‘~~~~, to m&e marker 1 a reference maker
Lb Activate a Fixed Marker
‘Ib change the reference marker to marker 2, press
Log Fiag 10 dfl, REF -50 d6 16 415 dB
To move the reference position, press
Or enter a value from the front panel keypad
To Use Polar Format Markers
To access the polar markers, press
‘lb Couple and Uncouple Display Markers
For the display channels
~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~
To Use Smith Chart Markers
Sin 0, where M=magnitude
‘j3JU
‘lb Set Measurement Parameters Using Markers
17. Example of Impedance Smith Chart Markers
Setting the Start Frequency
Setting the Center Frequency
Fl i t-11I
22. Example of Setting the Reference Value Using a Marker
Value. .... ... y
Setting the CW Frequency
23. Example of Setting the Electrical Delay Using a Marker
‘lb Search for a Specific Amplitude
Searching for the Maximum Amplitude
Searching for the Minimum Amplitude
Searching for a ‘beget Amplitude
Example of Searching for a Beget Amplitude Using a Marker
~~~~~ ad
Press ~~~~~~ MarkerFctn‘~~~~~~~
Bandpass or band reject shape on the measurement trace
To Calculate the Statistics of the Measurement Data
Figure Z-28. Example Statistics of Measurement Data
Measuring the Magnitude Response
Measuring Magnitude and Insertion Phase Response
Connect your test device as shown in Figure
Measuring Insertion Phase Response
30. Example Magnitude Response Measurement Results
32. Phase Samples
Measuring Electrical Length
Measuring Electrical Length and Phase Distortion
Phase Distortion
Electrical Length
34. Linearly changing Phase
Measuring Phase Distortion
Deviation From Linear Phase
Group Delay
36. Deviation From Linear Phase Example Measurement
37. Group Delay Example Measurement
III 11 I 11 11 MHZ
Setting Up the Measurement Parameters
Lksting a Device with Limit Lines
Creating Flat Limit Lines
41. Example Flat Limit Line
Creating a Sloping Limit Line
42. Example Flat Limit Lines
~9~~~~~~
~~@#g
This example procedure, the following limits are set
Creating Single Point Limits
Editing Limit Segments
Deleting Limit Segments
Reviewing the Limit Line Segments
Bnnning a Limit Tkst
Activating the Limit Test
Offsetting Limit Lines
Making Measurements
Measuring Gain Compression
Lb produce a normalized trace, perform the following steps
@ @ to change the scale to 1 dB per division
Lb place the marker eax.ct& on a measurement point, press
Press LMenu ~~~~~~~~~~ gaw,, $
Enter the start and stop power levels for the sweep
~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~
~~~ ~~~ Mif Rress cmJ j-1 ~~~~~~~~~.~~~ ~~~..~~~~,~~~
48. Gain Compression Using Power Sweep
Tiess c~isplay ~~~~,~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~
Measuring Gain and Reverse Isolation Simultaneously
Press *F p#~~~.p~~~~6~~~~’
To channel 1 and channel
49. Gain and Reverse Isolation
Connect the Device Under Test
Measurements Using the Swept List Mode
Set the following measurement parameters
To set up the swept list measurement, press
Observe the Characteristics of the Filter
Choose the Measurement Parameters
~~~~~~~~~~ m Lxl
~~~~~~~~~ l-loJ Ixl
Gp&g ~~~
KG&’
Calibrate and Measure
Press iJk&~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~h
53. Filter Measurement Using Swept List Mode
Typical test setup
Measurements Using the Tuned Receiver Mode
Tuned receiver mode in-depth description
External Source Requirements
Tkst Sequencing
Creating a Sequence
55. ‘l&t Sequencing Help Instructions
Running a Sequence
Stopping a Sequence
‘Ib delete the selected command, press =J backspace key
Inserting a Command
Editing a Sequence
Modifying a Command
Clearing a Sequence from Memory
You stop at each character
Naming Files Generated by a Sequence
Changing the Sequence Title
Lb complete the titling, press %@@
Storing a Sequence on a Disk
Purging a Sequence from Disk
Procedure and then follow the printing sequence
Loading a Sequence from Disk
Printing a Sequence
Cascading Multiple Example Sequences
To run both sequences, press
MKR Fctn
Loop Counter Example Sequence
Start of Sequence Trans FWD s21 B/R
To run the loop sequence, press
Generating Files in a Loop Counter Example Sequence
Plot llle names generated by this sequence will be
Limit Test Example Sequence
Data file names generated by this sequence will be
‘lb nm the sequence, press
This will create a displayed list for sequence 1, as shown
Recall FlEG
Fundamental frequencies
Measuring Swept Harmonics Option 002 Only
Set the start frequency to a value greater than 16 MHz
57 nd Harmonic Power Level in dBc
Gating
Measuring a Device in the Time Domain Option 010 Only
Transmission Response in Time Domain
Connect the device as shown in Figure
59. Time Domain Transmission Example Measurement
Gating in a Time Domain Transmission Example Measurement
‘able 2-2. Gate Characteristics
Fiiure 2-61. Gate Shape
Gating Effects in a Frequency Domain Example Measurement
Reflection Response in Time Domain
64. Device Response in the Frequency Domain
Front panel keypad after each key press
65. Device Response in the Time Domain
Non-coaxial Measurements
Where to Look for More Information
Making Mixer Measurements
Minimizing Source and Load Mismatches
Eliminating Unwanted Mixing and Leakage Signals
Measurement Considerations
Reducing the Effect of Spurious Responses
Down Converter Port Connections
Differences Between Internal and External R Channel Inputs
Frequency Offset Mode Operation
Jfqyw
B Channel External Connection
Power Meter Calibration
Conversion Loss Using the Frequency Offset Mode
Page
Network Analyzer Power Meter POW-N&OR
~~/...~ . . . . T.,, .. L? Jal~.i
To view the measurement trace, press
Conversion Loss Example Measurement
High Dynamic Range Swept RF/IF Conversion Loss
10. Connections for Broad Band Power Meter Calibration
11. Connections for Eeceiver Calibration
Filter External LO Source
13. Example of Swept if Conversion Loss Measurement
Sequence 1 Setup
Tuned Receiver Mode
Fixed if Mixer Measurements
Press the following keys on the analyzer to create sequence
~~~~~,~~
~ .~~~~~~~~~~~
Im ~~~~
CaUing the Next Measurement Sequence
Done List Freq B
Sequence 2 Setup
Following sequence commands
Measurement Completed
16. Example Fixed if Mixer Measurement
Phase or Group Delay Measurements
17. Counections for a Group Delay Measurement
To make a response error-correction, press
Scale the data for best vertical resolution
Amplitude and Phase Tracking
Conversion Compression Using the Frequency Offset Mode
Pg634e
Make the connections as shown in Figure
Mixer Under Test External LO Source
Measurements setup diagram is shown in Figure
~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~,~~
Example Swept Power Conversion Compression Measurement
Isolation Example Measurements
LO to RF Isolation
Refer to , Optinking Measurement Results
26. Connections for a Mixer Isolation Measurement
RF Feedthrough
27. Example Mixer ID to RF Isolation Measurement
28. Connections for a Response Calibration
30. Example Mixer RF Feedthrough Measurement
Printing, Plotting, and Saving Measurement Results
Printinfl, Plotting, and Saving Measurement Results
Printing or Plotting Your Measurement Results
Conf@uring a Print Function
~.~.~.~.~.~..~.~ ....ii.........i..~~~
Defining a Print Function
Black and white from a color printer
To Reset the Printing Parameters to Default Values
If Yim Are Using a Color Printer
Printing One Measurement Per
I i i
Printing Multiple Measurements Per
Page
~............../i
If Yim Are Plotting to a Pen Plotter Then @ii. &g. Mti
Plot function as follows ~,~,~
If You Are Plotting to a Disk Drive
S K E J E C T T T O N L
Choosing Display Elements
Defining a Plot Function
Selecting Auto-Feed
Selecting Pen Numbers and Colors
Corresponding Key
Selecting Line Types
Channel
Choosing Scale
Press ~&&&&& mtd the selection appears that you want
Plotting One Measurement Per Page Using a Pen Plotter
To Reset the Plotting Parameters to Default Values
Plotting Multiple Measurements Per Page Using a Pen Plotter
Plot Quadrants
8 Printing, Plotting, and Saving Measurement Results
Plotting a Measurement to Disk
Automatic File Naming Convention for LIF Format
To View Plot Files on a PC
To Output the Plot Files
Using AmiPro
Using Freelance
Outputting Plot Files from a PC to a Plotter
Store the Hpgl initialization sequence
Outputting Single Page Plots Using a Printer
Store the exit Hpgl mode and form feed sequence
Outputting Multiple Plots to a Single Page Using a Printer
PLOTOO.RL PLUTOO.RU
Plotting Multiple Measurements Per Page From Disk
‘lb Plot Multiple Measurements on a Full
PL0TOOFPD
To Plot Measurements in Page Quadrants
11. Plot Quadrants
Titling the Displayed Measurement
Aborting a Print or Plot Process
Confqjuring the Analyzer to Produce a Time Stamp
If Ibu Want a Single Page of Values
If You Want the Entire List of Values
Solving Problems with Printing or Plotting
What You Can Save to the Analyzer’s Internal Memory
Places Where Ybu Can Save
Saving and Recalling Instrument States
What You Can Save to a Floppy Disk
What You Can Save to a Computer
Peripheral Access
Saving an Instrument State
Saving Measurement Results
Deline Save ModificationFlexibility II Dnring
Ad enter the &-ive where your &Sk is located
See Ascii Data Formats. ’
Ascii Data Formats
S2P Data Format
Template for component data fiIes is as follows Comment line
Re-Saving an Instrument State
‘lb Delete an Instrument State File
Renaming a File
~~~~.~~~~~
If Yim Are Using an External Disk Drive
Solving Problems with Saving or Recalling Files
Formatting a Disk
Optimizing Measurement Results
Temperature Drift
Connector Repeatability
Interconnecting Cables
Increasing Measurement Accuracy
Performance Verification
Frequency Drift
Reference Plane and Port Extensions
Conditions Where Error-Correction is Suggested
Measurement Error-Correction
Types of Error-Correction
Error-Correction Stimulus State
When to Use Interpolated Error-Correction
Calibration Standards
~~~~~~~~~~
Procedures for Error-Correcting Your Measurements
Frequency Response Error-Corrections
Response Error-Correction for Reflection Measurements
Network Analyzer
Response Error-Correction for Transmission Measurements
2J. $!B
Receiver Calibration
Standard Connections for Receiver Calibration
Results chapter for procedures
Frequency Response and Isolation Error-Corrections
Pg612e
Optimizing Measurement Results
Ad enter at leaf, four times more
One-Port Reflection Error-Correction
Connect your device under test
Open Short Loag Open Short Load For S
Optimizing Measurement Results
Full Two-Port Error-Correction
For Reflection For Transmission For Isolation
To pORT 2, ad use the ~~~~~~~~~., ~~~~~~~~~~
Page
T&M* Error-Correction
TRL Error-Correction
TRMError-Correction
Come& the lOad to Port 2 a& press ~~~~~.,~~~~~
Page
~~~~~ Or ~~~~
Modifying !L’RL Standards
@ Lxl ~~~~~~~~~~~
Modifying TRM Standards
Assign the Stadards to the Various TRM Classes
Iabel the Classes
Page
Editing Frequency Segments
Entering the Power Sensor Calibration Data
Press ~,~~ and enter the segment number followed by xl
Compensating for Directional Coupler Response
Deleting Frequency Segments
Using Sample-and-Sweep Correction Mode
Sample-and-Sweep Mode for Power Meter Calibration
Using Continuous Correction Mode
KGE
To Calibrate the Analyzer Receiver to Measure Absolute Power
Calibrating for Noninsertable Devices
10. Noninsertable Device
Adapter Removal
11. Adapters Needed
12. ‘lko-Port Cal Set
Remove the Adapter
14. Cklibrated Measurement Verify the Results
Example Program
MAtched Adapters
NON-INSERTABLE Dewce
Modify the Cal Kit Thru Deilnition
To Improve Measurement Results
Cause of Measurement Problems
Making Accurate Measurements of Electrically Long Devices
Decreasing the Sweep Rate
Decreasing the Time Delay
Detecting if Delay
To Use Swept List Mode
Increasing Sweep Speed
Option
Lb Set the Auto Sweep Time Mode
Ib Decrease the Frequency Span
Option 006
‘lb Reduce the Averaging Fktor
Lb Widen the System Bandwidth
‘Ib Reduce the Number of Measurement Points
Select the sweep type
Lb Set the Sweep Type
Lb View a Single Measurement Channel
Points are of interest
‘lb Use Fast a-Port Calibration
To Activate Chop Sweep Mode
To Use External Calibration
Lb activate the continuous mode, press
‘lb enter the number of sweeps, press
To Reduce the Receiver Noise Floor
To Increase the Test Port Input Power
Increasing Dynamic Range
Changing System Bandwidth
To Activate Averaging
Reducing Trace Noise
Reducing Receiver Crosstalk
To Change System Bandwidth
Reducing Recall Time
~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~.. f#jy %&ig ~~$fj& , /.. P
Understanding Spur Avoidance
Where to Look for More Information
Application and Operation Concepts
HP 8753E System Operation
Signal-separation devices Receiver Display
Built-In Synthesized Source
Microprocessor
Built-In ‘I&t Set
Receiver Block
Required Peripheral Equipment
Data Processing Flow Diagram
Data Processing
Processing Details
Pre-Raw Data Arrays
~...... .A....u.........s....i
Transform Option 010 Only
Auxiliary Channels and Two-Port Calibration
Active Channel Keys
Channel 3 without pressing chanj twice
Multiple Channel Displays
Entry Block Keys
Enabling Auxiliary Channels
Uncoupling Stimulus Values Between Primary Channels
Knob
Units Terminator
Step Keys
Modifyiug or Deleting Entries
Stimulus Functions
Defining Ranges with Stimulus Keys
Stimulus Menu
Power Menu
Understanding the Power Ranges
Power Range Transitions in the Automatic Mode
Channel coupling
Power Coupling Options
Test port collpling
Sweep Time
Manual Sweep Time Mode
Auto Sweep Time Mode
Minimum Sweep Time
‘12l.ble 6-1. Minimum Cycle Time in seconds
Continuously and the trace is updated with each sweep
Trigger Menu
Feature
Source Attenuator Switch Protection
Allowing Repetitive Switching of the Attenuator
Specified number of sweeps is completed.
Channel Stimulus Coupling ‘. . . . . . . .,‘....’
Sweep Type Menu
Segment Menu
Logarithmic Frequency Sweep Hz
Stepped List Frequency Sweep Hz
Loss of calibration
Stepped Edit Subsweep Menu
Parameters can also be saved with an instrument state
Power
Ii ,.,,,, ....i,..... ...c .i i
Selecting Sweep Modes
Power Sweep dBm
CW Time Sweep Seconds
Calibration section
Auxihary channel is enabled
Response Functions
Parameters
Understanding S-Parameters
S-parameter menu contains the following softkeys
Deilnition
Conversions, as these formats are not easily interpreted
Log Magnitude Format ~......, .~
Format Menu
Are available by means of which softkeys / .‘~ ~~~.,..~~~
Phase Format
Group Delay Format
Smith Chart Format
13. Group Delay Format
14. Standard and Inverse Smith Chart Formats
Polar Format
Linear Magnitude Format
SWR Format
Real Format
Ima@naryFormat
Group Delay Principles
19. Constant Group Delay
21. Rate of Phase Change Versus Frequency
Application and Operation Concepts
Or ~~~~~~~~~~
Electrical Delay
Scale Reference Menu
Assuming a relative permeability
Display Menu
Dual Channel Mode
Single graticule see -23a
4 Application and Operation Concepts
Chapter for more information on this condition
Four-Parameter Display Functions
Customizing the Display
Ble
Provides a quick way to set up a four-parameter display
Is sele&ed ~~~~6~~~~~ @ves you two choices for a
Yellow, indicating that the keys in yellow apply to channel
PRRI=IMETER Shortcut Keys
Memory Math F’unctions
Setting Display Intensity
Two trace math operations are implemented
Setting Default Colors
\/ii
Yellow 100
Numeric keypad, until the desired color appears
Red 100
Green 100
Averaging
Averaging Menu
Following softkeys are located within the averaging menu
Smoothing
If Bandwidth Reduction
27. if Bandwidth Reduction
Markers
28. Bbkers on Trace
IMarker Menu
Marker type
Marker Function Menu
Is displayed
What Is Accuracy Enhancement?
Measurement Calibration
What Causes Measurement Errors?
Directivity
Source Match
Isolation crosstalk
Frequency Response Tracking
Characterizing Microwave Systematic Errors
One-Port Error Model
34. Effective Directivity EDF
36. Reflection Tracking Em
38. Measured Effective Directivity
40. Open Circuit ?Lkrmina.tion
Device Measurement
42. Bhjor Sources of Error
+ !T + I Reverse S,2M
44. Load Match Em
45. Isolation Em
46. Full Two-Port Error Model
47. Full Two-Port Emor Model Equations
Device Measurements
Calibration Considerations
Measurement Parameters
Omitting Isolation Calibration
Calibration Standards
Frequency Response of Calibration Standards
Electrical Offset
Open W Ql.7~J
How Effective Is Accuracy Enhancement?
50. Response versus S 11 l-Port CMibration on Smith Chart
Ensuring a Valid Calibration
Correcting for Measurement Errors
Following softkeys are located within the correction menu
Interpolated Error-correction
~or-co~e&on is on or off Press I- j~~~~~~~~~~
Response and Isolation Calibration
Calibrate Menu
Response Calibration
S11 and S22 One-Port Calibration
TRL*/LRM* Two-Port Calibration
Cal Kit Menu
Restarting a Calibration
Select Cal Kit Menu
Definitions
Procedure
Modifying Calibration Kits
Following are definitions of terms
Modify Calibration Kit Menu
Detie Standard Menus
TIhble 6-5. Standard DelInitions
Application and Operation Concepts
Described next
Impedance different from system ZO
Characters
~~,~~~~~~~
Label Standard Menu
‘Ihble 6-6. Slamlard Class Assignments
Calibration. For default calibration kits, this is the thru
Calibration
Verify performance
Verification procedure may be used
Cal kit menu. It will be saved with calibration sets
TRL%RM* Calibration
Why Use TRL Calibration?
TRL lkrminology
TRL* Error Model
How !CRL*/LRM* Calibration Works
IsoIation
Same during the isolation calibration and the measurement
Source match and load match
Frequencies is often times physically impossible
54. Typical Measurement Set up
Length
No loss. Characteristic impedance ZO need not be known
Requirements
Where = frequency l=lengthofline
Let Fl = 1000 MHz
Application and Operation Concepts
Or match &n&d ~~~~~~~~ .gQ or to the system
Where
Selections under this menu
Menu and ~~~~~~~~. with the defie timdad menu me ignored
Is used to set the reference plane ~~~~~~~..~~~
Associated with power meter calibration
Power Meter Calibration
Calibrated Power Level
Primary Applications
Interpolation in Power Meter Calibration
Loss of Power Meter Calibration Data
Power Meter Calibration Modes of Operation
55. ‘I&t Setup for Continuous Sample Mode
Power Sensor Calibration Factor List
Network Analyzer Power Meter Power Sensor
Number of Beadings Sweep Time Characteristic
SpeedandAccuracy
Corrected
Alternate and Chop Sweep Modes
57. Alternate and Chop Sweeps Overlaid
Matched Adapters
Modify the Cal Kit Thru Definition
Using the Instrument State Functions
58. Instrument State Function Block
HP-IB Menu
= talk mode = service request SRQ asserted by the analyzer
HP-IB Status Indicators
System Controller Mode
~.&.. .?....bLi.... ...l
Gpio Mode
Using the Parallel Port
Copy Mode
Instrument
Limits Menu
~~~~~..~~~~~ provides access to the instrument mode menu
System Menu
Ikmi% tiih
Edit Limits Menu
Offset Limits Menu
External Source Mode
Knowing the Instrument Modes
Page
CW=e Bange
‘lhble 6-8. External Source Capture Ranges
If you press @KJ ~~~~~~~~~~
Pical Test Setup
60. Typical ‘l&t Setup for a Frequency Offset Measurement
Application and Operation Concepts
61. Typical Harmonic Mode ‘I&t Setup
To OFF to allow alternating sweeps
Bhximum Fundamental Frequency
Time Domain Operation Option
Transform Menu
General Theory
Time Domain Bandpass
63. a Reflection Measurement of Two Cables
Transmission Measurements Using Bandpass Mode
‘I&ble 6-10. Time Domain Reflection Formats
Setting frequency range for time domain low pass
Fault Location Measurements Using Low Pass
Reflection Measurements In Time Domain Low Pass
E M E N T E P R E S P O N S E P U L S E R E S P O N S E
Transmission Measurements In Time Domain Low Pass
PgBlQ6-c
69. Transmission Measurements Using Low Pass Impulse Mode
Time Domain Concepts Masking
70. Masking Example
Sidelobes
10 90%
= 100 x lo-’ seconds
Where AF’ is the spacing between frequency data points
Example
= 100 x lo-’ 6 x 3 x l$ m/s
Resolution
\I I
75. Sequence of Steps in Gating Operation
‘able 6-13. Gate Characteristics
Transforming CW Time Measurements Into the Frequency Domain
I i iiiii t
Forward Transform Measurements
78. Combined Effects of Amplitude and Phase Modulation
~~~~~~
80. Range of a Forward Transform Measurement
Wst Sequencing
Active entry command 1 per digit
Type of Command Size in Bytes
ZoF the ~~~~~~~~
Results for each input power level applied to the amplifier
Sequencing Menu
Parallel in ETS OUT Bits
Sequence Decision Making Menu
Commands require you to enter the destination sequence
Sequencing Special Functions Menu
Decision Making Functions
HP-GLConsiderations Entering HP-GL Commands
Naming Files Generated by a Sequence
Plot absolute HP-GL command PA
Label HP-GL comman& Ia
Amplifier Tksting
Amplifier parameters
Gain Compression
85. Diagram of Gain Compression
Metering the power level
Frequency Offset
Mixer Testing
Difficulty selecting the correct signal to measure
Tuned Receiver
Mixer Parameters That You Can Measure
Accuracy Considerations
Attenuation at Mixer Ports
Filtering
J j j i
92.Examples of Up Converters and Down Converters
You a s&& either ~~~~~,~~~~~ or ~~~~,~~~~,~
93. Down Converter Port Connections
94. Up Converter Port Connections
Isolation
Conversion Loss
LOFeedthru/LOtoRFLedage
SWR / Return Loss
Phase Measurements
Conversion Compression
Amplitude and Phase Tracking
Phase Linearity and Group Delay
Applicationmd OperationConcepts
Adapters
Reflected Signal
Connection Considerations
Worst Case System DiBtiVity 28d.B 17dEI 14 dE3
Fixtures
If You Want to Design Your Own Fixture
General Measurement and Calibration Techniques
Reference Documents
Fixtures and Non-Coaxial Measurements
On-Wafer Measurements
Specifkations and Measurement Uncertainties
Dynamic Range
HP 8753E Measurement Port Specifications
HP 8763E 6OQ with 7-mm Test Ports
Frequency Range
HP 8763E SO@ with Type-N Test Ports
HP8753E Wiih HP85032B Calibration Kit
HP 8763E SO@W with 3.6~mm Test Ports
HP8753E Wiih HP85033D Calibration Kit
HP 8763E 76Q with Type-N Test Ports
GHz to 3 GHz
Applies at 26 f6 C t Typical Performance 15dB,30kHzto6OkHz
HP 8763E 7612 with Type-F Test Ports
Instrument Spectications
‘lhble 7-12. HP 8753E Instrument Specifications 1
‘Ihble 7-12. HP 8753E Instrument Specifkations 2
‘lhble 7-12. HP 8753E Instrument Specifications 3
‘Ihble 7-12. HP 8753E Instrument Specifhtions 4
‘Ihble 7-12. EP 8753E Instrument Speciikations 5
‘Ihble 7-12. EIP 8753E Instrument Specifications 6
HP 8763E Network Analyzer General Characteristics
Measurement Throughput Summary
Rear Panel Connectors
Front Panel Connectors
Probe Power
Remote Programming
External Auxilhry Input AUX Input
Video Output VGA OUT
Parallel Port
Line Power
Display Pixel Integrity
232
Environmental Characteristics
General Conditions
Cabinet Dimensions
Weight
Internal Memory
Page
Menu Maps
Page
Menu Maps
IrCOPY
Page
Format Menu LOG MAG DELA,’ Smith Chart Polar LIN MAG SWR
MAX
+ RefIFWD
MenuMaps
SAVE/RECALL MEN + Save State Recall
MenuYaps
Page
MenuMaps
Pg657e
Key Definitions
Guide Tkrms and Conventions
Analyzer Functions
Set to the current adive -ker position, using the ~~~
Key Definitions
At the St& of the averaging or following ~~~~~~~~~~
Ad for specifying the calibration s-d=& used. me ~~~
Key Dsfinitions
Key Definitions
Mo&fication.\ ~~~~~~~~lt~\brings up the printer color
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ the preset condition, both channels have
Key Definitions 8-l
2 Key Definitions
Sequence position Sequence 1 through 6. ~~~~~~~~
Key Definitions
S21
~~~~~~~
Key Definitions
8 Key Definitions
Key Definitions 9-l
With the &@&ElV &3 softkey, if it is to be used later
Turns limit. .I lines on or off. lb define limits, use
Key Definitions B-21
Stimulus menu
Switched on. Thirty lines of data are listed on each
Lxm
Edit subsweep menu. Up to 30 frequency subsweeps
Ldab AlO Wfset ILocal
Let G .m4
LWX $%QXlXl% Sequence Filenaming
#F$
F4MEt + ,START
Couples the marker stimulus values for the two display
Stimulus settings
Hold mode for one measurement
Allows the marker stimulus values to be controlled
Moves the active marker to the minimum point on the trace
Completes the selection in the Offset Load Menu
Selects the calibration standard load as being offset
Is used to omit the isolation portion of the calibration
Drn SB
When editing a sequence, False Tg .&ZLlZGT appears when you
With the plotter
Configures the analyzer for a plotter that has a parallel
Is used to set the same power levels at each port
Directs plots to the selected disk internal or external
Allows you to set different power levels at each port
Frequency and power loss value
FRXif Hii tXWR
Key Definitions
Key Definitions
RsE#kswa, Value
KRSPti#SE
Measures the reverse isolation of the calibration standard
Gggs&fi
’F7
Key is disabled if ‘~~~~~~~ is set to ~~~
~~~~~~~~~~ menu
Key Definitions
Kay Definitions
To temate the smdwd definition
Key Definitions
Key Definitions
Is used to specify the arbitrary impedance of the standard,
~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Men ~~~~~~~~ or ~~~~~~~~ is pressed, a
Key Definitions B-61
~~~~~~~~~~ above
Key Definitions
Cross Reference of Key Function to Programming Command
Anab
Menucal
M4HEH
DEFAULT,. i?RXllT f%KtVP
?lZAXJ.LT CXtLUH
MARKF-AUV
OFFlPon #iv
Harmoff
Lintdata
Markmidd
Ofls
Titp
Pric
‘fhble Cross Reference of Key Function to Programm ingbmmand
Resd
Labesbba
Stop
Limtsl
Seatarg
Trackoff
Yellow
Softkey Locations
‘Ittble 9-2. Softkey Locations SoftkeyFront-Panel Access Key
‘Ihble 9-2. Softkey Locations
Key Definitions
Key Definitions
~~~ ~~~~~~~~~
Able 9-2. Softkey Locations SoftkeyFront-Panel Access Key
Key Definitions
Lhble 9-2. Softkey Lacations SoftkeyFront-Panel Access Key
$84 Iey Definitions
‘lhble 9-2. Softkey Locations SoftkeyFront-Panel Access Key
‘lhble 9-2. Softkey Locations SoftkeyFFont-Panel Access Key
Ble 9-2. Softkey Locations SoftkeyFront-Panel Access Key
‘lhble 9-2. Softkey Locations SoftkeyFront-Fanel Access Key
’hble 9-2. Softkey Locations
‘lhble 9-2. Softkey Locations SoftkeyFront-Rmel Access Key
‘Ihble 9-2. Softkey Locations SoftkeyFront-Panel Access Key
‘able 9-2. Softkey Locations
Able 9-2. Softkey Locations SoftkeyFront-Panel Access Key
7hble 9-2. Softkey Locations ISoftkeyFront-Panel Access Key
‘Ihble 9-2. Softkey Locations
Error Messages
Error Messages in Alphabetical Order
Analog BUS Disabled IN6KHZ if BW
Ascii Missing ‘VAR’ Statement
Blockinputlengthehhor
CANTSTORE/LOADSEQUENCE, Insufficientmemory
Correction and Domain Reset
Deadlock
Diskis Writeprotected
Duplicating to this Sequence not Allowed
File not Found
~ ..~~~.. .. .., .,~~,~
IFBWKEYDISABLED, Editlistmodetbl
Error Number You pressed an undefined softkey
9in progress. Start a new calibration
Order to use the ~~~~,~~~ softkey function
Error Number See error number
Error Number See error number 57
Plot Aborted
Error Number The parallel port printer is not accepting data
PRINT/PLOTINPROGRESS, Abortwithlocal
Probepowershut Down
Selectedsequenceisenpty
Slides Aborted Memoryreallocation
Sweep, pres LMenu ~~~~~~ ~~~~~~, or ~~~~~~~~~
TOO Manynested SEQUENCES. SEQ Aborted
WAITINGFORHP-IB Control
Error Messages in Numerical Order
Error
Error Messages 1O-28
IN-zErl
Device not on, not connect, wrong addrs
No Memory Available for Sequencing
List Mode OFF Invalid with LO Freq
Error Number
Analog BUS Disabled in 6 KHZ if BW
Compatible Peripherals
Calibration Kits
Test Port Return Cables
Verification Kit
Adapter Kits
Power Limiters
Transistor Test Fixtures
System Cabinet
System Testmobile
HP-IB Cables
Mass Storage
Interface Cables
Analyzer Function
Keyboards
‘Ihble 1 l-l. Keyboard ‘lkmplate Definition
Keyboaxd Analyzer Function Kety Name
External Monitors
Controller
Sample Software
Commended Color Monitors
Connecting the Peripheral Device
Peripheral Connections to the Analyzer
Cotiguring the Analyzer for the Peripheral
If the Peripheral is a Printer
=.~~~~~.........~.......~
Until the correct function appears
Print function as follows
Appears
Z...... iizz......ii.w.....A........w..i.i
‘.’ .~
HP 436A HP 437B or 438A
Enter the HP-IB address of the power meter, followed by @
Enter the volume number
Press Local and select one of the following
Configuring the Analyzer to Produce a Time Stamp
Press $m$&& ad enter the au-rent year, fdlowed by Ixl
HP-IB Programming Overview
HP-IB Operation
Device Types
HP-IB Bus Structure
Unaddress and revert to an idle state
Data lines carry device-dependent instructions or data
SRQ Service Request
REN Remote Enable
EOI End or Identify
Complete device clear
Full-acceptor handshake
Does not respond to parallel poll
No extended listener capabilities
HP-II3 Status Indicators
= ‘IU mode = Service request SRQ asserted by the analyzer
System-Controller Mode
Next lower address
Analyzer Command Syntax
Code Naming Convention
Valid Characters
KHz Kilohertz US Microseconds MHz Megahertz
HP-II3 Debug Mode
User Graphics
GHz Gigahertz
Preset State and Memory Allocation
Types of Memory and Data Storage
Non-Volatile Memory
Preset State and Memory Allocation
Storing Data to Disk
‘&ble 12-2. SuiIix Character Definitions
Using Saved Calibration Sets
Conserving Memory
Preset State
Register in which it is stored
‘Ihble 12-3. Preset Conditions 1
‘lhble 12-3. Preset Conditions 2
Able 12-3. Preset Conditions 3
An instrument state are cleared
Default color values
Taker/listener
Sequence 1 through 5 are erased
9600
HP-IB Addresses are set to the following defaults HP 8753E
Power Meter Type is set to HP 438A/437
Xon-Xoff
CITIfile Data Format
CITIllle Keyword Reference
Data part
This section will dehne the following terms Package Header
Header part CITIFILEA.0190
23491E-3,-1.39883E-3 00382E-3,-1.40022E-3
CITIfile Keyword
#NA VERSIONHP8510B.05.00
Data Sl,l RI
Example 4,861O S-Term Frequency List Cal Set F’ile
Conclusion
CITINe Keyword Reference
Variable
Don’t change when the independent variable changes
Is supported in revision A.O1.OO
Commonly used array names include the following
Sources of Measurement Errors
Determining System Measurement Uncertainties
Sources of Random Errors
Abl, Ab2 = dynamic accuracy = frequency
Sources of Additional Measurement Errors
Measurement Uncertainty Equations
Reflection Phase Uncertainty Erp
Transmission Uncertainty Equations
Efnf = effective noise floor
Transmission Phase Uncertainty Etp
Dynamic Accuracy
Procedures
Determining Expected System Performance
Characteristic Vdues ‘lhble
Measurement Uncertainty Worksheet 1
Page
Page
Page
75Q Impedance option Mm test ports
Specifications
GHz operation option
Active
Enabling
Allowing repetitive switching Switch protection ~~~~~~ 4
Format, 419 auto sweep time mode
Key
To key cross reference, 9-54 compatible
Group delay measurement
Connecting peripherals, 1 l-8 connections, 6 Adapters
Mode Down converter port
Conhguring
Deviation from linear phase measurement
Definition Calibration standards, 5-27 delay
Electrical Delete display option, 1-13 deleting
DTl responds to a group execute trigger
Linear magnitude, 6-36 log magnitude, 6-32 phase
Display functions, 6-42 color
Increasing Limitations, 7-l E2 W-state drivers, 11-19 edit
Swept if conversion loss measurement
ESD precautions Exammmg calibration constants, 5-27 example
Signal flow in a mixer
Fan location, l-11
Frequency domain concepts, 6-125-145 transform from CW time
Area of display, l-10 arrays Menu, 6-32 giizj zkzz
Receiver and source requirements, 6-122 receiver frequency
Measure electrical length and phase distortion
Calibrate the analyzer receiver to measure absolute power
Isolation, 5-14 error-correct for full two-port
Define the print
Domain
Set auto sweep time mode
Set frequency span with markers, 2-29 set source power
Print a sequence Print multiple measurements per
Hpgl
LIF Input ports menu
InstAent state, 6-110-116 &iJ
6-51 It, 6-11 @J, 6-78 0, 6-11 @jiiJ, 6-42 entry, 6-9-l
List values
Softkey labels, l-10 softkeys
Low pass mode
Magnitude and insertion phase response measurement
LOG MKR, 2-25 Loop counter sequence
Parameters set with markers, 2-26 sequence
Measurement frequencies, diagram, 3-10 measurement points
Using swept list mode
75Q type-F test ports 75Q type-N test ports
Iavp
Accuracy Amplitude and phase tracking, 6-167 attenuation
Tuned receiver mode Up conversion
@g$, 8-6 @iii,8 68-7
Multiple sequence cascading
New features to the analyzer, l-2 ~~~~
CaI kit thru definition, 5-47 modifying Sequence
Printing or plotting, 4-30 operation
Peripheral
Points Datahow to reduce
Parameters set with markers, 2-26 center frequency
~~~~.~~~ 4
Polar or Smith format markers, 2-22 port 1 and port2, l-6
Multiple measurements per Solving problems ‘amji$J& use
Configuration, 4-4, 49, 11-9 mode
Printing or plotting list values or operating parameters
Values Resetting the printing parameters to default values
Error-correction for one-port reflection measurements
Modifying Trmm calibration standards Offsetting limit lines
Response error-correction for reflection measurements
Using ~~~~~ to .&jvate a tied
Setting center frequency with markers
Using delta a markers
Viewing the measurement data and memory trace Procedures
Running
Relative velocity for time domain, 2-90 remote control
Retention, 4-33 Re/Im MKR, 2-25, 2-26 relative
Searching for values with markers, 2-32 bandwidth
Service request asserted by the analyzer S
@iG
Specify
Spectral purity characteristics, 7-10 spurious signals
Stop frequency Setting with markers Stopping
Standarddehnitions Entering
Testing with Iimit lines, 2-46 testmobile
Test set
Forward transform mode, 6-126 gating
Test set switch, controlling the, 5-54 test using limits
Active channel display, 2-9 titling
Type-N calibration standard sex, 5-6 type-N test ports
How to set
Weight Widen system bandwidth, 5-52 windowing Time domain
Understanding S-parameters, 6-29 units

![]() :..: .A... .::.:.:.i..;;.;;.;;..;;;;; ii i ii.i..::: . i. .z..:..
:..: .A... .::.:.:.i..;;.;;.;;..;;;;; ii i ii.i..::: . i. .z..:..