82540EP/EM, 82541xx, 82544GC/EI, 82545GM/EM, 82546GB/EB,
Software Developer’s Manual
Initial Public Release
Date Version Comments
Software Developer’s Manual
Contents
TCP Segmentation Use of Multiple Data Descriptors
Software Developer’s Manual Vii
Power Management 129 Introduction to Power Management
10.1.3
203
13.4.25
13.7.10
Appendix 82540EP/EM and 82545GM/EM Differences
Xiv
Overview
Scope
PCI Features
Ethernet Controller Features
CSA Features 82547GI/EI Only
Network Side Features
Host Offloading Features
Additional Performance Features
Technology Features
Additional Ethernet Controller Features
Related Documents
Conventions
Memory Alignment Terminology
Register and Bit References
Introduction
Architectural Overview
External Architecture
PHY
LAN a LAN B
Eeprom Flash
ECHO, Next Fext
AGC, A/D
1 PCI/PCI-X Core Interface
Microarchitecture
DMA Engine and Data Fifo
2 82547GI/EI CSA Interface
5 MII/GMII/TBI/Internal SerDes Interface Block
4 10/100/1000 Mb/s Receive and Transmit MAC Blocks
Eeprom Interface
6 10/100/1000 Ethernet Transceiver PHY
Flash Memory Interface
DMA Addressing
Example 2-1. Byte Ordering
Little Endian Data Ordering
Ethernet Addressing
Intel Architecture Byte Ordering
IA Byte # LSB MSB
Interrupts
Buffer and Descriptor Structure
Hardware Acceleration Capability
Checksum Offloading
TCP Segmentation
Architectural Overview
Introduction
Packet Reception
Packet Address Filtering
Receive Data Storage
Receive Descriptor Format
Receive Descriptor Rdesc Layout
Receive Status RDESC.STATUS Layout
Receive Descriptor Status Field
PIF Ipcs Tcpcs RSV Ixsm EOP
Receive
Receive Descriptor Errors Field
RXE IPE Tcpe RSV
Receive Errors RDESC.ERRORS Layout
RSV SEQ
CXE
Special Descriptor Field Layout
Receive Descriptor Special Field
PRI CFI Vlan
PRI
Receive Descriptor Fetching Algorithm
Receive Descriptor Fetching
Receive Descriptor Queue Structure
Receive Descriptor Write-Back
Receive Descriptor Packing
Null Descriptor Padding
Receive Descriptor Ring Structure
Receive Timer Interrupt
Receive Interrupt Delay Timer / Packet Timer Rdtr
Receive Interrupts
Packet Delay Timer Operation State Diagram
Receive Interrupt Absolute Delay Timer Radv
Small Receive Packet Detect
Receive Packet Checksum Offloading
8 82544GC/EI Receive Interrupts
Receive Descriptor Minimum Threshold ICR.RXDMT
Receiver Fifo Overrun
Packet Type HW IP Checksum HW TCP/UDP Checksum Calculation
Supported Receive Checksum Capabilities
GC/EI Supported Receive Checksum Capabilities
MAC Address Filter
Packet Type HW IP Checksum HW TCP/UDP Checksum
Packet Type HW IP Checksum
SNAP/VLAN Filter
Packet Transmission
9.3 IPv4 Filter
9.4 IPv6 Filter
Transmit Descriptors
Transmit Data Storage
Legacy Transmit Descriptor Format
Transmit Descriptor Tdesc Layout Legacy Mode
Transmit Descriptor Tdesc Layout
Transmit Descriptor Legacy Descriptions
CMD
Transmit Descriptor Description Legacy
STA
CSS
10. Transmit Command TDESC.CMD Layout
Transmit Descriptor Command Field Format
IDE VLE Dext RSV
Ifcs EOP
11. Transmit Status Layout
Transmit Descriptor Status Field Format
12. Special Field TDESC.SPECIAL Layout
Transmit Descriptor Special Field Format
5 TCP/IP Context Transmit Descriptor Format
13. Transmit Descriptor Tdesc Layout Type = 0000b
6 TCP/IP Context Descriptor Layout
Transmit Description Descriptor Offload
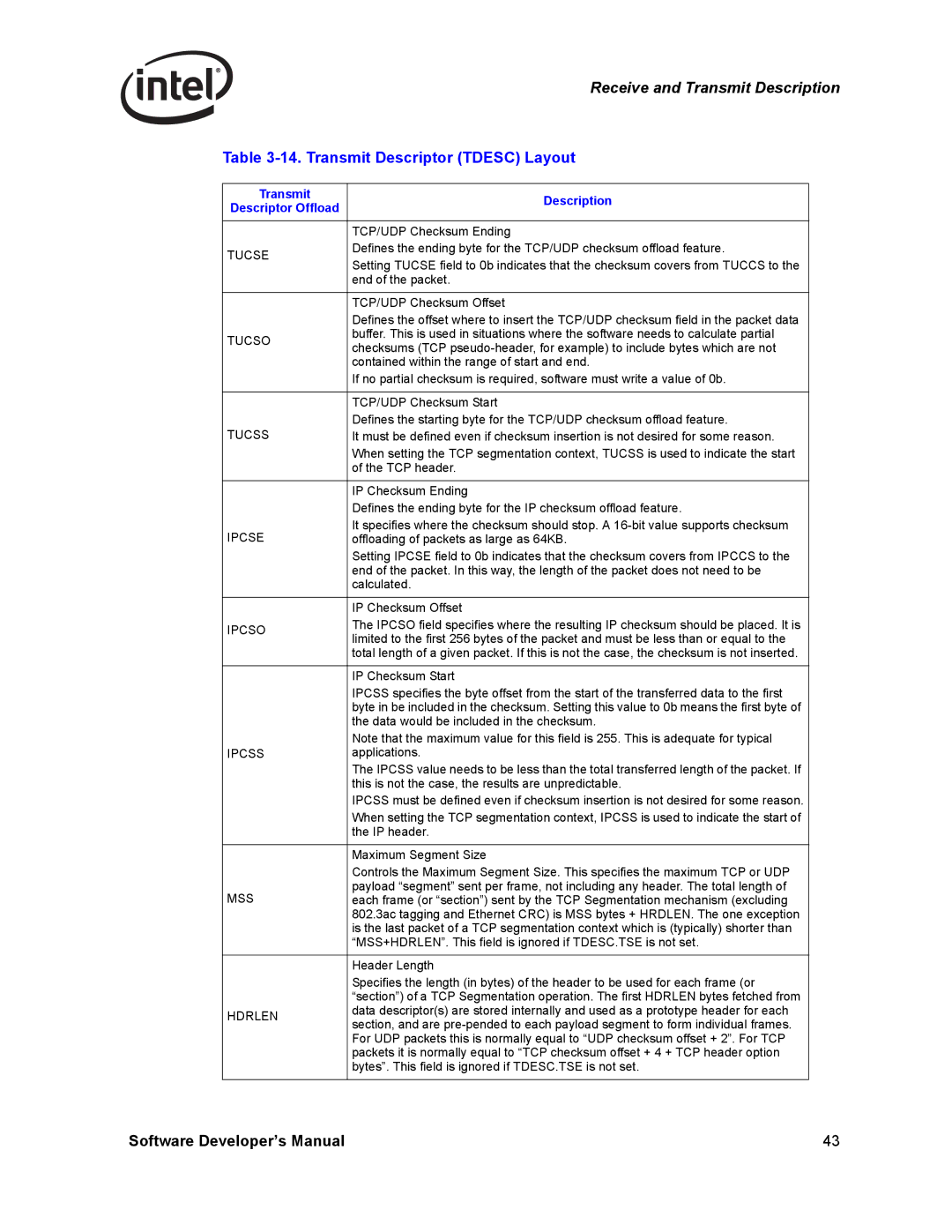
14. Transmit Descriptor Tdesc Layout
Transmit Description
6.1 TCP/UDP Offload Transmit Descriptor Command Field
Tucmd
Dtyp
15. Command Field TDESC.TUCMD Layout
IDE RSV Dext TSE TCP
82544GC/EI only
7 TCP/IP Data Descriptor Format
6.2 TCP/UDP Offload Transmit Descriptor Status Field
16. Transmit Status Layout
17. Transmit Descriptor Tdesc Layout Type = 0001b
Popts RSV STA Dcmd Dtyp Dtalen
Popts
18. Command Field TDESC.DCMD Layout
7.1 TCP/IP Data Descriptor Command Field
IDE VLE Dext
TSE Ifcs EOP
7.2 TCP/IP Data Descriptor Status Field
19. Transmit Status Layout
Reserved
7.4 TCP/IP Data Descriptor Special Field
7.3 TCP/IP Data Descriptor Option Field
20. Packet Options Field TDESC.POPTS Layout
RSV Txsm Ixsm
21. Special Field TDESC.SPECIAL Layout
Transmit Descriptor Ring Structure
Transmit Descriptor Ring Structure
Transmit Descriptor Write-back
Transmit Descriptor Fetching
Transmit Interrupts
Delayed Transmit Interrupts
Transmission Process
Assumptions
Packet Format
TCP Segmentation Performance
TCP Segmentation Data Fetch Control
TCP/UDP Data FCS
3936
TCP Segmentation Indication
TCP Partial Pseudo-Header Checksum
TCP Segmentation Use of Multiple Data Descriptors
IP and TCP/UDP Headers
Version IP Hdr
Options
Type of service Version IP Hdr Length Fragment
Fragment Offset Low
Offset High Header Checksum
TCP Header
Destination Port Sequence Number
Length Checksum Urgent Pointer Options
Byte1 Byte0 Destination Port
Byte3 Byte2 Byte1 Byte0
Source Port Destination Port Length Checksum
Transmit Checksum Offloading with TCP Segmentation
17. UDP Pseudo Header Diagram for IPv4
9 IP/TCP/UDP Header Updating
19. Overall Data Flow
9.2 TCP/IP/UDP Header for the Subsequent Frames
9.1 TCP/IP/UDP Header for the First Frame
9.3 TCP/IP/UDP Header for the Last Frame
IP/TCP/UDP Transmit Checksum Offloading
Ipcss
Receive and Transmit Description
Mandatory PCI Registers
PCI Configuration
Address Description
PCI
Specification Update for the latest stepping information
Addr
Base Address Registers
Field Bits Read Initial Description Write Value
All base address registers have the following fields
Offset Space
Expansion ROM Base Address
Address Next Pointer
Capabilities Linked List
Bits Initial Value Description
PCI definition for more details
82547GI/EI
Status Register Layout
PCI-X Capability ID
PCI-X Configuration Registers
Next Capability
Byte Offset
Bits Read Initial
PCI-X Command
Write Value
Maximum Memory Read Byte Count. This register sets
PCI-X Status
USC SCD
Bits Read Intial Description Write Value
Reserved and Undefined Addresses
Command Register as follows
Message Signaled Interrupt Configuration Registers
Message Signaled Interrupts1
MSI Capability ID
Bits Read Initial Description Write Value 05h
Message Control
3.1.4 Message Address
Commands
3.1.5 Message Upper Address
3.1.6
PCI Commands Abr PCI-X Commands
Accepted PCI/PCI-X Command as a Target
Transaction Target PCI Commands PCI-X Commands
Transaction Cause PCI Commands PCI-X Commands
Memory Write Operations
PCI/PCI-X Command Usage
MWI Bursts
Master Write Command Usage Algorithm
Memory Read Operations
PCI-X Command Usage
MW Bursts
Rules for Memory Read Operations
Outstanding Memory Read
Cache Line Information1
LAN Disable
Interrupt Assignment 82547GI/EI Only
Target Transaction Termination
CardBus Application 82541PI/GI/EI Only
General Overview
Eeprom Interface
Component Identification Via Programming Interface
Component Identification
Stepping Vendor ID Device ID Description
Eeprom Device and Interface
Signature and CRC Fields
Software Access
Command Line Parameters
Eeupdate Utility
Ethernet Controller Address Map
Eeprom Address Map1
Word Used Bit Image
For the 82541xx and 82547GI
82545GM 82540EP
LAN a
82541xx and 82547GI/EI only
82546GB/EB only
82545GM
82541xx
ASF
82540EP/EM
Word Description Default HW Access
GC/EI and 82541ER Eeprom Address Map
Address Hi Byte Low Byte
Software Compatibility Word Word 03h
Ethernet Address Words 00h-02h
Software Compatibility Word Word 03h
Bit Name Description
Eeprom Image Version Word 05h
SerDes Configuration Word 04h
Compatibility Fields Word 05h 07h
PBA Number Word 08h, 09h
Initialization Control Word 1 Word 0Ah
Initialization Control Word 1 Word 0Ah
Subsystem Vendor ID Word 0Ch
Subsystem ID Word 0Bh
Vendor ID Word 0Eh
Device ID Word 0Dh, 11h1
Initialization Control Word 2 Word 0Fh
Initialization Control Word 2 Word 0Fh
82541PI/GI Only
Software Defined Pins Control Word 10h1, 20h
Common Power Word 12h
PHY Register Address Data Words 10h, 11h, and 13h 1Eh
OEM Reserved Words Words 10h, 11h, 13h 1Fh
Software Defined Pins Control Word 10h, 20h
CSA Port Configuration 2 Word 21h
CSA Port Configuration 2 Word 21h
Bit Description Default
21 D3 Power Word 22h low byte
20 D0 Power Word 22h high byte
Circuit Control Word 21h
Reserved Words 23h 2Eh
10. Initial Management Control Register Settings
Management Control Word 13h1, 23h2
82541PI/GI/EI and 82547GI/EI Only
11. SMBus Slave Address
SMBus Slave Address Word 14h1 low byte, 24h low byte
12. Initialization Control
Initialization Control 3 Word 14h1 high byte, 24h high byte
82546GB/EB uses INTB#
For Address 24h High Byte / LAN a
Boot Agent Main Setup Options Word 30h
LED Configuration Defaults Word 2Fh2
27 IPv4 Address Words 15h 16h1 and 25h 26h
28 IPv6 Address words 17h 1Eh1 and 27h 2Eh
15. Boot Agent Main Setup Options
Boot Agent Configuration Customization Options Word 31h
DBS
BBS
SIG
16. Boot Agent Configuration Customization Options Word 31h
Mode
DFU
17. Boot Agent Configuration Customization Options Word 32h
Boot Agent Configuration Customization Options Word 32h
IBA Secondary Port Configuration Words 34h-35h
IBA Capabilities Word 33h
18. IBA Capabilities
20. WOL Mode and Functionality Word 20h
19. WOL Mode and Functionality Word 0Ah
Checksum Word Calculation Word 3Fh
Eeprom Images
21. Flash Memory Manufacturers
Parallel Flash Memory
Manufacturer
Number
124
Flash Interface Operation
Flash Control and Accesses
Write Accesses
Read Accesses
Flash Buffer Write Cycle
128
Assumptions
Introduction to Power Management
D3cold support
Power States
1.2 D0u State
Dr State
Timing
1.3 D0a D0 active
1.4 D3
Diagram #
Power Up Off to Dr to D0u to D0a
Transition from D0a to D3 and Back Without PCI Reset
Transition From D0a to D3 and Back Without PCI Reset
RST#
Transition From D0a to D3 and Back with PCI Reset
PCI Reset Sequence
PCI Reset Without Transition to D3
Bits Default Description
PCI Power Management Registers
Capability ID Byte Offset = 0 RO
Next Item Pointer Byte Offset = 1 RO
Power Management Capabilities PMC 2 Bytes Offset = 2 RO
Reserved
Eeprom
Software Developer’s Manual 139
3.6 Data Register
Pmcsrbse Bridge Support Extensions
Byte Offset = 6 RO
Byte Offset = 7 RO
Wakeup
Advanced Power Management Wakeup
Acpi Power Management Wakeup
Wakeup Packets
Pre-Defined Filters
Directed Exact Packet
Directed Multicast Packet
3.1.3 Broadcast
3.1.4 Magic Packet*1
Offset Field Value Action Comment
Offset Field Value Action Comment Bytes
+ S a
3.1.5 ARP/IPv4 Request Packet1
+ D + S a
ARP
Offset # of bytes Field Value Action Comment
Directed IPv4 Packet1
Directed IPv6 Packet1
Flexible Filter
IPX Diagnostic Responder Request Packet Example1
+ S
+ D + S
3.4 IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Filter1
Directed IPX Packet Example
CRC
Wakeup Packet Storage
152
Link Interfaces Overview
Ethernet Interface
1.2 8B10B Encoding/Decoding
Internal SerDes Interface/TBI Mode- 1Gb/s1
Code Groups and Ordered Sets
Gmii 1 Gb/s
Code Group and Ordered Set Usage
Code OrderedSet
Internal Interface1
Duplex Operation
MII 10/100 Mb/s
Half Duplex
Full Duplex
Packet Bursting
Carrier Extension 1000 Mb/s Only
Auto-Negotiation and Link Setup2
Auto-Negotiation and Link Setup1
Link Configuration in Internal Serdes/TBI Mode1
Link Speed
Auto-Negotiation
Hardware Auto-Negotiation
TXCW.txConfigWord
Bit Description
Software Auto-Negotiation
Forcing Link
Internal GMII/MII Mode
Forcing Speed
Using Auto-Speed Detection ASD
Duplex
Automatic Detection of Link Speed using SPD-IND
MII Management Registers
Comments Regarding Forcing Link
Internal Serdes Mode1 Hardware Enabled
Internal SerDes Mode1 Control Bit Resolution
Internal Serdes1 Mode Software Enabled
Control Bit Effect on Control Bits
Internal PHY Mode Control Bit Resolution
GMII/MII Mode PHY Speed Indication
Internal Serdes Mode1 Auto-Negotiation Skipped
GMII/MII Mode Force Speed
GMII/MII Mode Auto-Speed Detection
Internal Serdes Mode
Loss of Signal/Link Status Indication
Internal PHY Mode
GMII/MII Mode Force Link
Adaptive IFS1
10/100 Mb/s Specific Performance Enhancements
MAC Control Frames & Reception of Flow Control Packets
Flow Control
10. Flow Control Registers
Register Name Description
3x MAC Control Frame Format
Transmission of Pause Frames
Discard Pause Frames and Pass MAC Control Frames
External Control of Flow Control Operation1
Software Initiated Pause Frame Transmission
1 802.1q Tagged Frames
802.1q Vlan Packet Format
Vlan Packet Format Comparison
Packet #Octets
802.1q Vlan Packet Filtering
Transmitting and Receiving 802.1q Packets
Adding 802.1q Tags on Transmits
Stripping 802.1q Tags on Receives
VFE
Packet Reception Decision Table
178
Selecting an LED Output Source
Configurable LED Outputs1
Blink Control
Polarity Inversion
Blink Control
182
Auto-Negotiation
PHY Functionality and Features
Next Page Exchanges
Register Update
Status
11.2 MDI/MDI-X Crossover copper only
Pin
1000BASE-T
11.2.2 10/100 Downshift 82540EP/EM Only
Polarity Correction copper only
PHY Power Management copper only
Cable Length Detection copper only
Link Down Energy Detect copper only
11.4.3 D3 Link-Up, Speed-Management Enabled copper only
11.4.4 D3 Link-Up, Speed-Management Disabled copper only
11.4.2 D3 State, No Link Required copper only
Initialization
Mdio Control Mode
Overview of Link Establishment
Determining Link State
False Link
Configuration Result
Forced Operation
Determining Duplex State Via Parallel Detection
Auto Negotiation
Link Criteria
Parallel Detection
11.7.1 1000BASE-T
Link Enhancements
Using SmartSpeed
11.7.3 10BASE-T
SmartSpeed
Pause And Asymmetric Pause Settings
Low Power Operation
Asmdir Settings Pause Setting
Management Data Interface
Powerdown via the PHY Register
Smart Power-Down
11.11 1000 Mbps Operation
DSP ECHO, Next 4DPAM5
Transmit Fifo
Transmit Functions
Low-Pass Filter
Spectral Shaper
Line Driver
Transmit/Receive Flow
Receive Functions
11.13 10 Mbps Operation
11.12 100 Mbps Operation
Descrambler
Viterbi Decoder/Decision Feedback Equalizer DFE
PHY Line Length Indication
202
Features of Each MAC
Introduction1
12.2.1 PCI/PCI-X interface
204
MAC Configuration Register Space
12.2.3 SDP, LED, INT# output
IO BAR
Shared Eeprom
Eeprom Map
Eeprom Arbitration
Shared Flash
Flash Access Contention
Pin sampled LAN device controlled Enable/Disable
Values Sampled on Reset
Power Reporting
Multi-Function Advertisement
Interrupt Use
Summary
Enabled
Interrupt Line Used
INTA#
Register Conventions
Register Descriptions
Memory-Mapped Access to Flash
Memory-Mapped Access to Internal Registers and Memories
Memory-Mapped Access to Expansion ROM
Memory and I/O Address Decoding
Iodata
Ioaddr
Offset Abbreviation Name Size
Ioaddr
AD C/BE#30 Bits
Iodata Register Configurations
Category Offset Abbreviation Name
Ethernet Controller Register Summary
82544GC/EI
82547GI/EI only
Ipat 82544GC
Fcruc
Xofftxc
PRC64
Gprc
Abbreviation Name Register
Category
82544GC/EI , 82541xx , or 82547GI/EI
To the 82544GC/EI , 82541xx , or 82547GI
PCI-X Register Access Split1
Main Register Descriptions
Device Control Register
Ctrl 00000h R/W
Field Bits Initial Description Value
Ctrl Register Bit Description
SLU
Ilos
Speed
SDP0DATA
Frcdplx
SDP1DATA
ADVD3WUC
Field Bits Initial Description
Device Status Register
BEM = 0 64-bit mode Little-Endian
Status 00008h R
Little-Endian Data Ordering
Status Register Bit Description
Txoff
Tbimode
PCI66
Asdv
Pcixmode
Pcixspd
Eecd 00010h R/W
EEPROM/Flash Control & Data Register
Eecd Register Bit Description
82544GC/EI Only
Eegnt
Eereq
Eepres
Eesize
Eeprom Read Register1
Eerd 00014h RW
Eeprom Read Register Bit Description
Done Start
Eeprom Read Register Bit Description 82541xx and 82547GI/EI
Flash Access1
Flash Access FLA
FLA 0001Ch R/W
Ctrlext 00018h, R/W
Extended Device Control Register
10. Ctrlext Register Bit Description
23 16
SDP2IODIR
SDP6IODIR
SDP7IODIR
Asdchk
11. GPI to SDP Bit Mappings
Vreg Power
Down
Linkmode
12 GC/EI Ctrlext Register Bit Description
Swdpinshi
Swdpiohi
CTRL.RST
13 GC/EI GPI to SDP Bit Mapping
Mdic 00020h R/W
MDI Control Register
RSV PHY REG Data
14. MDI Control Register Bit Description
Regadd
Phyadd
15. PHY Register Bit Mode Definitions
Register Mode Description
PHY Registers
MSB
Field Bits Description Mode HW Rst SW Rst
242
LSB
Enaxc
RO,L
Software Developer’s Manual 245
246
For the 82541xx and 82547GI/EI
Pause
82544GC/EI only 82541xx
82541xx 82547GI/EI 82541xx and 82547GI/EI only
ANEG3
82544GC/EI Only
ANEG2
RF1
Software Developer’s Manual 251
23. Link Partner Ability Register Base Page Bit Description1
24. PHY Link Page Ability Bit Description1
82541xx and 82547GI/EI Only
10BASE-T
100BASE-TX
1b 82541xx
Software Developer’s Manual 255
Bits Field Description Mode HW Rst SW Rst
ANEG0
Master
MASTER/SLAVE
ANEG1
258
Software Developer’s Manual 259
DIS
NLP
SFD
Preen
Software Developer’s Manual 263
264
Software Developer’s Manual 265
266
82541/GI/ER and 82547GI B1
82541EI/82547GI B0 stepping
268
HCD
NOK
Software Developer’s Manual 271
272
Field Bits Description Mode HW Rst
Ledactled
SPEED1000LED
SPEED100LED
276
Software Developer’s Manual 277
Documented MDI Register 30 Operations1
51. MDI Register 30 Operations
To Perform Operation MDI Read/Write Sequence
Flow Control Address High
Flow Control Address Low
Fcal 00028h R/W
Fcah 0002Ch R/W
Vlan Ether Type
Flow Control Type
FCT 00030h R/W
VET 00038h R/W
Fcttv 00170h R/W
Flow Control Transmit Timer Value
56. VET Register Bit Description
57. Fcttv Register Bit Description
Transmit Configuration Word Register1
Txcw 00178h R/W
58. Txcw Register Bit Description
Rxcw 00180h R
Receive Configuration Word Register1
59. Rxcw Register Bit Description
Ledctl 00E00h RW
LED Control1
ANC
LED1 ACTIVITY# LED0 LINKUP#
60. LED Control Bit Description1
Mode Encodings for LED Outputs1
Mode Pneumonic State / Event Indicated
61. Mode Encodings for LED Outputs
PBA 01000H R/W
Packet Buffer Allocation
62. PBA Register Bit Description
Field Bits Initial Value Description
Interrupt Cause Read Register
ICR 000C0H R
63. ICR Register Bit Description
Mdac
RXT0
Rxcfg
GPISDP6
Interrupt Throttling Register1
ITR 000C4h R/W
Interval
Interrupt Cause Set Register
ICS 000C8h W
64. ICS Register Bit Description
IMS 000D0h R/W
Interrupt Mask Set/Read Register
65. IMS Register Bit Description
To the 82544GC/EI
IMC 000D8h W
Interrupt Mask Clear Register
66. IMC Register Bit Description
Rctl 00100h R/W
Receive Control Register
67. Rctl Register Bit Description
SBP
LPE
MPE
LBM
Rdmts
Bsize
BAM
VFE
Cfien
Pmcf
Bsex
Secrc
Flow Control Receive Threshold Low
XON Enable 82544GC/EI , 82541xx , and 82547GI/EI only
Fcrtl 02160h R/W
68. Fcrtl Register Bit Description
Flow Control Receive Threshold High
Fcrth 02168h R/W
69. Fcrth Register Bit Description
Receive Descriptor Base Address High
Receive Descriptor Base Address Low
Rdbal 02800hR/W
Rdbah 02804h R/W
Receive Descriptor Head
Receive Descriptor Length
Rdlen 02808h R/W
RDH 02810h R/W
Receive Descriptor Tail
Receive Delay Timer Register
RDT 02818hR/W
Rdtr 02820h R/W
Radv 0282Ch RW
Receive Interrupt Absolute Delay Timer1
Transmit Control Register
Receive Small Packet Detect Interrupt1
Rsrpd 02C00h R/W
Tctl 00400hR/W
Cold
76. Tctl Register Bit Description
PSP
TCTL.COLD
Tipg 00410R/W
Transmit IPG Register
Rtlc
Nrtu
IPGR2 IPGR1 Ipgt
77. Tipg Register Bit Description
Adaptive IFS Throttle AIT
Aifs 00458R/W
IPGR2
Tdbal 03800h R/W
Transmit Descriptor Base Address Low
78. Aifs Register Bit Description
79. Tdbal Register Bit Description
Transmit Descriptor Length
Transmit Descriptor Base Address High
Tdbah 03804h R/W
Tdlen 03808h R/W
Transmit Descriptor Head
TDH 03810h R/W
82. TDH Register Bit Description
Transmit Descriptor Tail
Transmit Interrupt Delay Value
TDT 03818h R/W
Tidv 03820h R/W
Transmit Descriptor Control
TX DMA Control 82544GC/EI only
Txdmac 03000h R/W
Txdctl 03828h R/W
Lwthresh RSV1 Gran RSV Wthresh Hthresh Pthresh
86. Txdctl Register Bit Description
Tadv 0382Ch RW
Transmit Absolute Interrupt Delay Value1
Gran
Lwthresh
TCP Segmentation Pad And Minimum Threshold Tspmt 03830h RW
Tspbp Tsmt
Tspbp
Software Developer’s Manual 319
Rxdctl 02828h R/W
Receive Descriptor Control
87. Rxdctl Register Bit Description
Wthresh RSV Hthresh Pthresh
Rxcsum 05000h R/W
Receive Checksum Control
88. Rxcsum Register Bit Description
3111
Ipofld
Tuofld
IPV6OFL
Multicast Table Array
Filter Registers
MTA1270 05200h-053FCh R/W
89. MTA Register Bit Description
Destination Address
Receive Address High
Receive Address Low
RAL 05400h + 8*n R/W
RAH 05404h + 8∗n R/W
VFTA1270 05600h 057FCh R/W
Vlan Filter Table Array1
91. RAH Register Bit Description
RAH
Wakeup Control Register
Wakeup Registers
WUC 05800h R/W
92. VFTA1270 Bit Description
Wufc 05808h R/W
Wakeup Filter Control Register
Apmpme
SPM
WUS 05810h R
Wakeup Status Register
330
Ipav 5838h R/W
IP Address Valid
IP4AT 05840h 05858h R/W2
13.6.5 IPv4 Address
Address
Field Dword # Address Bits Initial Value Description
IP6AT 05880h 0588Ch R/W
13.6.6 IPv6 Address
IPV6ADDR0
Dword # Address Bits Initial Value Description
Wakeup Packet Length
Wakeup Packet Memory 128 Bytes
Flexible Filter Length Table
LEN0
Flexible Filter Mask Table Ffmt 09000h 093F8h R/W
LEN1
LEN2
Statistics Registers
Flexible Filter Value Table
Ffvt 09800h 09BF8h R/W
Alignment Error Count
CRC Error Count
Crcerrs 04000h R
Algnerrc 04004h R
RX Error Count
Symbol Error Count
Symerrs 04008h R
Rxerrc 0400Ch R
Single Collision Count
Missed Packets Count
MPC 04010h R
SCC 04014h R
Multiple Collision Count
Excessive Collisions Count
Ecol 04018h R
MCC 0401Ch R
Collision Count
Late Collisions Count
Latecol 04020h R
Colc 04028h R
Transmit with No CRS
Defer Count
DC 04030h R
Tncrs 04034h R
Carrier Extension Error Count
Sequence Error Count
SEC 04038h R
Cexterr 0403Ch R
XON Received Count
Receive Length Error Count
Rlec 04040h R
Xonrxc 04048h R
XON Transmitted Count
Xoff Received Count
Xoff Transmitted Count
Packets Received 64 Bytes Count
FC Received Unsupported Count
Fcruc 04058h R
PRC64 0405Ch R
Packets Received 128-255 Bytes Count
Packets Received 65-127 Bytes Count
PRC127 04060h R
PRC255 04064h R
Packets Received 512-1023 Bytes Count
Packets Received 256-511 Bytes Count
PRC511 04068h R
PRC1023 0406Ch R
Good Packets Received Count
Packets Received 1024 to Max Bytes Count
PRC1522 04070h R
Gprc 04074h R
Multicast Packets Received Count
Broadcast Packets Received Count
Bprc 04078h R
Mprc 0407Ch R
Good Octets Received Count
Good Packets Transmitted Count
Gptc 04080h R
Gorcl 04088h R/GORCH 0408Ch R
Receive No Buffers Count
Good Octets Transmitted Count
Gotcl 04090h R/ Gotch 04094 R
Rnbc 040A0h R
Receive Fragment Count
Receive Undersize Count
RUC 040A4h R
RFC 040A8h R
Receive Jabber Count
Receive Oversize Count
ROC 040ACh R
RJC 040B0h R
Management Packets Received Count1
Mgtprc 040B4h R
129. RJC Register Bit Description
Management Packets Dropped Count1
Management Pkts Transmitted Count1
Total Octets Received
Totl 040C8h R/W / Toth 040CCh R
Total Octets Transmitted
130. Torl and Torh Register Bit Descriptions
131. Totl and Toth Register Bit Descriptions
Total Packets Transmitted
Total Packets Received
TPR 040D0h R
TPT 040D4h R
Packets Transmitted 65-127 Bytes Count
Packets Transmitted 64 Bytes Count
PTC64 040D8h R
PTC127 040DCh R
Packets Transmitted 256-511 Bytes Count
Packets Transmitted 128-255 Bytes Count
PTC255 040E0h R
PTC511 040E4h R
Packets Transmitted 1024 Bytes or Greater Count
Packets Transmitted 512-1023 Bytes Count
PTC1023 040E8h R
PTC1522 040ECh R
Broadcast Packets Transmitted Count
Multicast Packets Transmitted Count
Mptc 040F0h R
Bptc 040F4h R
TCP Segmentation Context Transmit Fail Count
TCP Segmentation Context Transmitted Count
Tsctc 040F8h R
Tsctfc 040FCh R
Receive Data Fifo Head Register
Diagnostics Registers
Receive Data Fifo Tail Register
Rdfh 02410h R/W
Receive Data Fifo Tail Saved Register
Receive Data Fifo Head Saved Register
Rdfhs 02420h R/W
Rdfts 02428h R/W
Transmit Data Fifo Head Register
Receive Data Fifo Packet Count
Rdfpc 02430h R/W
Tdfh 03410h R/W
Transmit Data Fifo Head Saved Register
Transmit Data Fifo Tail Register
Tdft 03418h R/W
Tdfhs 03420h R/W
Transmit Data Fifo Packet Count
Transmit Data Fifo Tail Saved Register
Tdfts 03428h R/W
Tdfpc 03430h R/W
PBM 10000h 1FFFCh R/W
Packet Buffer Memory
151. Tdfpc Register Bit Description
152. PBM Bit Description
370
General Configuration
Power Up State
Receive Initialization
General Initialization and Reset Operation
Transmit Initialization
Ipgt IPGR1 IPGR2
Fiber Copper 82544GC/EI
Signal Ball Name and Function
Signal Descriptions
Carrier Sense
Signal Interface
Receive Data
Receive Clock
Signal Functions
GMII/MII Features not Supported
Signal Function Pin Gmii 1000 Mbps Operations
MII 10/100 Mbps Differences
Avoiding Gmii Test Modes MAC Configuration
Signal Functions Not Supported
Direct PHY Indications to MAC
CTRL.FD
Link Setup
CTRL.RFCE
PHY Initialization 10/100/1000 Mb/s Copper Media
Lanpwrgood
Reset Operation
382
Software Developer’s Manual 383
Initialization of Statistics
Fifo State
Diagnostics
Fifo Data
Loopback
Internal Loopback
Testability
SAMPLE/PRELOAD Instruction
Extest Instruction
Idcode Instruction
Bypass Instruction
388
Appendix Changes From 82544EI/82544GC
New Features
Table A-1. Register Changes
Register Changes
Register Offset
EEC
Serial Flash Interface
82540EP/EM Differences
No TBI/Internal SerDes Interface
Single-Port Functionality
4 32-Bit PCI Support