USER’S Guide
Virus Disclaimer
Trademarks
DOC Notice
Contents
Software Overview
Hardware Installation
Cfgedit
Configuration Tools
Security Overview
Configuring System Options and Information
Configuring Off-node Server Information
Configuring Encryption
Configuring Advanced Bridging
Configuring IPX
Central Site Remote Access Switch
Configuring Snmp
Configuring Other Advanced Options
Verifying the Base System
Verifying Routing Protocols
LCD Messages
System Commands
System Statistics
Routine Maintenance
Cfgedit Map
Using this Guide
Cfgedit MAP
Documentation SET
Cfgedit Screens
Guide Conventions
User’s Guide
System Overview
CyberSWITCH
Cyberswitch
Hours of Usage
Unique System Features
USER’S Guide
Central Site Remote Access Switch
Interoperability Overview
Radius
Interoperability Protocols
Interoperability Devices
Encryption Overview
Network Layer
Link Layer
Network Interface Overview
Security Overview
System Components
Isdn
Remote Isdn Devices
Switches Supported
Hardware Overview
System Platforms
Platform Number Main Speed Slots
CSX5500
System Platforms
EMI
To reduce the risk of electrical shock or energy hazards
CSX6000
Cleaning the CSX6000 AIR Filter
To reduce the risk of electrical shock or energy hazards
CSX7000
Disk Drives Number of 1/3 height IDE disk drives supported
Front View
NE 2000-II a Network Express Platform
Platform Characteristics
NE 4000 a Network Express Platform
USER’S Guide
NE 5000 Platform a Network Express Platform
Cleaning the NE 5000 AIR Filter
EMI
Mtbf
Hardware Characteristics
System Adapters
Ethernet Adapters
Basic Rate Adapters
75000hrs
Primary Rate Adapters
PRI-8
PRI-23
Jumper Usage
PRI-23/30
Expander Adapter
PRI-8, PRI-23, and PRI-23/30 Connection
Adapter
35 Pin
Receive Data No Connect
Data Set Ready No Connect Gnd Signal Return
No Connect Ring Indicator
Transmit Clock
With data compression
With error control
With error control and data compression
Digital Modems
DM-24
DM-8
LSI Logic LR33000RISC
Mvip
Encryption Adapter
System Software
Administration Software
Software Overview
Overview
System Files
Configuration Files
Operational Files
User Level Security Files
Accessing the CyberSWITCH
System Installation
Ordering BRI Isdn Lines Using Provisioning Settings
Ordering Isdn Service US only
Ordering NI-1 Lines Using EZ-ISDN Codes
Ordering NI-1 Lines Using NI-1 Isdn Ordering Codes
NI-1 AT&T Custom Point-to-Point
Provisioning Settings for AT&T 5ESS Switches
CSD limit CSD NB limit
AT&T 5ESS NI-1 Service
Unrestricted
CSV limit CSV NB limit
CSD limit
Provision Settings for Northern Telecom DMS-100 Switches
CSV limit
Any
PVC
Number of call Appearances
Version Functional Yes
Basic Information for Ordering PRI Isdn Lines
US Only
Sprint
Type of Switch
Disabled
Option Local Bell Operating Company
Verify system power requirements
Hardware Installation
PRE-INSTALLATION Requirements
Choose a suitable setup location
If you are installing WAN adapters and DM adapters
Verify administration console requirements
Provide a diskette for configuration backup
If you are installing only WAN adapters
If you are installing WAN adapters and an Encryption adapter
Adapter Settings
Configured Slot Interrupt Jumper Address Switch Setting SW1
Adapter Interrupt and I/O Address Settings
DM-24 Adapter Interrupt and I/O Address Settings
SW3
SW2
OFF
Encryption Adapter Settings
Mvip Settings
DES/RSA Adapter
Additional Adapter Settings
Line Type Settings
Top Left Top Pair Right Pair
PRI-23 Clock Settings
Jumper Jumper Setting North American
J10 J11 J12 J13 J14
JP9 Mvip
JP1
JP3
JP6
Inserting the Adapters Into the Cyberswitch
Connecting Multiple Adapters
Connecting Adapter INTER-BOARD Cables
Flat Bus Ribbon Cable
Connecting a WAN Adapter to the LCD
Summary of Guidelines
Accessing the Cyberswitch
Making Connections
Direct Connection
NULL-MODEM Connection to a PC
DCD DTR DSR RCV Xmit GND RTS CTS
Remote Connection Using Telnet
COM1
On the CyberSWITCH side
On the remote administration console side
Remote Connections Modem to Modem
From Cfgedit Options, select Default Async Protocol
Establishing AN Administration Session
Accessing the Release Notes
Upgrading System Software
Installing Software
Couldn’t open the file C\SYSTEM\PLATFORM.NEI
Upgrading System Software
Local Upgrade
Remote Upgrade
Accessing the Release Notes
Configuring Basic Bridging
Basic Configuration
Cfgedit
Configuration Tools
Executing Dynamic Management
Dynamic Management
Executing Cfgedit
Saving Cfgedit Changes
Saving Dynamic Management Changes
Utility Dynamic Management Commands
Using the Configuration Chapters
Using the Network Worksheets
Configuring Resources and Lines
Configuring Resources Using Cfgedit
Resources
Resource Configuration Elements
Resource Background Information
PPP
Lines
Configuring Lines Using Cfgedit
Characteristic PRI/T1 lines E1 line
Multiframe CRC
CommonChannel
Select Change from the Data Lines menu of Physical Resources
Auto TEI
Line Configuration Elements
Switch Type Number of Data Number of SPIDs
Directory Numbers
DMS100 custom NI-1
Directory Numbers
Line Encoding
Line Background Information
Commport Information
Subaddresses Background Information
Configuring a Subaddress Using Cfgedit
Subaddress Configuration Elements
Subaddresses
MAC Layer Bridging Configuration Elements
Configuring Basic Bridging
ENABLING/DISABLING Bridging Using Cfgedit
Select Enable/Disable Bridging
MAC Layer Bridging Background Information
Configuring Basic IP Routing
Enabling IP Using Cfgedit
Internet Protocol IP Option
IP Background Information
IP Operating Mode
IP Option Configuration Elements
Configuring the IP Operating Mode Using Cfgedit
IP Operating Mode Background Information
IP Operating Mode Configuration Elements
IP Network Interfaces
Configuring Interfaces Using Cfgedit
USER’S Guide
Network Interface Configuration Elements
MTU
Transmit Broadcast IP Address
Default switch for numbered WAN interfaces
IP RIP Receive Control
IP Network Interface Background Information
Hdlc Bridge
IP Network Interface Type Associated Remote Device
IP Host RFC1294
WAN Direct Host IP Host RFC1294
USER’S Guide
Example 1 LAN, WAN and WAN Direct Host Interfaces
Example 2 LAN, WAN UnNumbered, WAN Remote LAN Interfaces
IP RIP and the IP Network Interfaces
Isdn
Isdn
IP RIP Over Dedicated Connections
Isdn
Redundant Configurations for Backup
Network Flattening
Proxy ARP
Example IP Host Communications in Flattened Networks
Secondary IP Addressing
Static Routes
Configuring Static Routes
IP address for the destination network or host
Static Route Configuration Elements
Central Site Remote Access Switch
Static Route Background Information
Isdn
Default Routes
Configuring Default Routes
Default Route Configuration Elements
Routing Information Protocol RIP Option
ENABLING/DISABLING IP RIP Using Cfgedit
LAN
IP RIP Configuration Elements
IP RIP Status
IP RIP Background Information
Security and Encryption Options
Configuring Security Level
Security Level
Security Overview
Device Level Databases
System Options and Information
Network Login Information
User Level Databases
OFF-NODE Server Information
Configuring Security Level
On-Node Yes
Database Device Level User Level Administration Security
No Security
Configuring no Security Using Cfgedit
Configuring Device Level Security Using Cfgedit
Device Level Security
Device Level Security Background Information
Configuring User Level Security Using Cfgedit
User Level Security
User Level Security Background Information
User Level Security
Isdn
Making a Telnet Connection
Responding to Login Prompts
ACE
Configuring Device and User Level Security Using Cfgedit
Device and User Level Security
Tacacs
Device and User Level Background Information
Configuring System Options and Information
Configuring System Options Using Cfgedit
System Options
System Options
System Options Configuration Elements
PAP Chap
Bridge MAC Calling Line Id Authentication Address
PAP Chap
System Options Background Information
Optional Calling Line Id
Configuring System Information Using Cfgedit
System Information Configuration Elements
System Information
Administrative Session
Configuring Administrative Sessions Using Cfgedit
System Information Background Information
Administrative Session Configuration Elements
Administrative Session Background Information
Emergency Telnet Server Port Number Background Information
Configuring Device Level Databases
Configuring AN ON-NODE Device Database
ON-NODE Device Database
ON-NODE Device Entries
Configuring ON-NODE Device Entries
On-node Device Entries
No pvc configured for Device DAN
SVC
None
0.0
IP SubNetwork number
ON-NODE Device Database Configuration Elements
Base Data Rate
Frame Relay Access Configuration Elements
Chap Secret
Outbound Authentication
RIP/SAP
Appletalk Information Configuration Elements
Bridge Information Configuration Elements
Bridging with Hdlc Bridge Devices
ON-NODE Device Database Background Information
Security Mode On-node Device Table Configuration Data
IP Routing with Hdlc Bridge Devices
Line Id
IP Routing with PPP IP Devices Using Ipcp
IP Routing with IP Host Devices RFC1294
PAP or Chap
Bridging with PPP Bridge Devices Using BCP
PAP Password or
IP Routing with PPP Bridge Devices Using BCP
OFF-NODE Device Database Location
Configuring OFF-NODE Device Database Location Using Cfgedit
OFF-NODE Device Database Location Background Information
OFF-NODE Device Database Location Configuration Elements
Configuring User Level Databases
User Level Authentication Database Location
Configuring Authentication Database Location Using Cfgedit
Database Telnet Port Number
Type communications server
Configuring OFF-NODE Server Information
Multiple Administration Login Names
Name John Doe Name mynode1 Address Remote Office1
Configuring CSM Authentication Server
CSM Authentication Server
CSM Authentication Server Configuration Elements
CSM Authentication Server Background Information
Configuring a Radius Authentication Server
Is SHAREDSECRET1234
Radius Authentication Server Background Information
Radius Authentication Server Configuration Elements
Select 5 Off-node Server Information
Configuring a Radius Accounting Server
Return to the Off-node Server Information Menu
Radius Accounting Server Background Information
Radius Accounting Server Configuration Elements
Radius RFC2138
Enabling Radius Type Using Cfgedit
Radius Type
Radius Type Configuration Elements
Configuring the Dynamic Device Option Using Cfgedit
Dynamic Device Option
Dynamic Device Configuration Elements
Configuring a Tacacs Authentication Server
Tacacs Authentication Server
Tacacs Authentication Server Background Information
Tacacs Authentication Server Configuration Elements
Configuring AN ACE Authentication Server
ACE Authentication Server
ACE Authentication Server Configuration Elements
ACE Authentication Server Background Information
Configuring Network Login Information
Network Login General Configuration
Configuring General Network Login Information Using Cfgedit
Select the type of authentication desired
Network Login Banners
Network Login General Configuration Background Information
Configuring Network Login Banners Using Cfgedit
Login Configuration Specific to Radius Server
Network Login Banners Background Information
Configuring Radius Server Login Information Using Cfgedit
Login Configuration Specific to Radius Server
Configuring Tacacs Server Login Information Using Cfgedit
Login Configuration Specific to Tacacs Server
Login Configuration Specific to Tacacs Server
USER’S Guide
Select Add a Resource
Configuring Encryption
Configuration
Configuring AN Encryption Adapter Using Cfgedit
Select Add. Respond to the following series of questions
Select IP Security Associations
Select Device Level Databases Select On-node device entries
Configuring Link Layer Encryption PPP Encryption only
Encryption Configuration Elements
Final Destination IP Address
IP Network Layer Encryption
Encryption Background Information
8888CCCC 12345678
12345678 8888CCCC
Isdn
Link Layer Encryption
Interaction with Other Features
For Link Layer encryption
For IP Layer encryption
Configuring Alternate Accesses
Advanced Configuration
Configuring Alternate Accesses
Dedicated Accesses
Configuring a Dedicated Access Using Cfgedit
Dedicated Access Background Information
Dedicated Access Configuration Elements
Configuring AN X.25 Access
Accesses
Accesses
USER’S Guide
Configuration Elements
Lapb Configuration Elements
Timers
Maximum Window Size
Nonstandard Default Transmit Window Size
PVC Configuration Elements
Access Background Information
B1 B2
Frame Relay Accesses
Configuring a Frame Relay Access
Select Access Information
Select Add a PVC
Frame Relay General Configuration Elements
Dlci Value
Frame Relay PVC Configuration Elements
LMI
LMI Format
PVC Name
Frame Relay Access Background Information
Local Management Interface Overview
Allowed
Not Allowed
Bridge Dial OUT
Configuring Advanced Bridging
Under ISDN, select Dial Out Phone Number
Spanning Tree Protocol
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol Using Cfgedit
Spanning Tree Protocol Background Information
Spanning Tree Protocol Configuration Elements
Bridge Mode of Operation Background Information
Bridge Mode of Operation
Configuring the Bridge Mode of Operation Using Cfgedit
Bridge Mode of Operation Configuration Elements
Bridge Filters
Configuring Bridge Filters Using Cfgedit
Source MAC Filter Commands
Protocol Definition Commands
Destination MAC Filter Commands
Protocol Filter Commands
Packet Data Filter Commands
Lsap in HEX
Bridge Filter Configuration Elements
Bridge Filters Background Information
Filter Type Maximum Number of Each
Filter Destination MAC
Source Discard Connect Destination Protocol Packet
Unrestricted Mode Bridge Filters
Central Site Remote Access Switch
Sites connected over the WAN according to
Filter Action Distribution Result List
Packet matching this filter will not be forwarded
On any LAN port. The packet will be sent to remote
On LAN port 2. The packet will be sent to remote
On LAN port 1. The packet will be sent to remote
Sites connected over the WAN and to LAN port
According to the normal learning bridge methods
Restricted Mode Forwarding Action
Restricted Mode Bridge Filters
Central Site Remote Access Switch
Any remote sites connected over the WAN
Filter Distribution Result Action List
Packet matching this filter will only be forward
Ed on the LAN ports. The packet will not be sent to
Ed on LAN port 2. The packet will not be sent to re
Ed on LAN port 1. The packet will not be sent to re
Mote sites connected over the WAN or to LAN
Port
Remote sites connected on the WAN. The packet
Packet matching this filter will be discarded on
LAN ports. The packet will be sent to all
Packet matching this filter will be discarded to
Preliminaries
Configuring a Destination MAC Address Filter
Discard Connect
Known Connect List
Configuring the Known Connect List
Known Connect List Background Information
Known Connect List Configuration Elements
Static ARP Table Entries
Configuring Advanced IP Routing
Select Static ARP Table Entries from the IP menu
Configuring Static ARP Table Entries Using Cfgedit
Static ARP Table Entries Configuration Elements
Static ARP Table Entries
Static Route Lookup VIA Radius
Isolated Mode
IP Address Pool
Static Route VIA Radius Configuration Elements
Configuring AN IP Address Pool Using Cfgedit
IP Address Pool Configuration Elements
IP Address Pool Background Information
IP Filters
Configuring Packet Types Using Cfgedit
Initiating the IP Filter Configuration Using Cfgedit
TCP UDP Icpm
Specify a control value any, established, or not established
Select Icmp Type
Select Add a Forwarding Filter
Configuring Forwarding Filters
Configuring Connection Filters
Configuring Exception Filter
Applying Filters
Select IP Interfaces
Select Apply Global Forwarding Filter
TCP and UDP Ports
IP Filters Configuration Elements
NEQ
Range
IP Filters Background Information
Forwarding Filters
Packet Types
Exception Filters
Connection Filters
Application to Network Interfaces
Limitations
Common Portion
FTP WWW Sfvra
Example of AN IP Filter Configuration
Forward
Dhcp Relay Agent
Configuring a Dhcp Relay Agent Using Cfgedit
Dhcp Background Information
Dhcp Configuration Elements
Router to Bridge Environment
Bridge to Bridge Environment
IP Router to IP Router with Relay Agents on both
USER’S Guide
Remote Bridge to IP Router w/Relay Agent
= WAN Rlan
Configuring the Dhcp Proxy Client
Dhcp Proxy Client
Select Dhcp Proxy Client
Dhcp Proxy Client ENABLE/DISABLE Flag
Sample Configuration IP Router with Dhcp Proxy Client
Configuration for IP Router Chloe
Configuring Security Associations Using Cfgedit
Security Associations
Configuring DNS and Netbios Addresses Using Cfgedit
DNS and Netbios Addresses
DNS/NBNS Background Information
DNS/NBNS Configuration Elements
Configuring IPX
Configuring IPX Information
ENABLING/DISABLING IPX Using Cfgedit
IPX Option Configuration Element
IPX Routing Option
IPX Option Background Information
Configuring the IPX Internal Network Number Using Cfgedit
IPX Internal Network Number Configuration Element
IPX Internal Network Number
Configuring IPX Network Interfaces Using Cfgedit
IPX Network Interfaces
IPX Network Number Background Information
Displays the current IPX network interface data
IPX Network Interface Configuration Elements
SAP IPX Network Interface Configuration Elements
IPX Network Interface Background Information
Configuring IPX Routing Protocols Using Cfgedit
IPX Routing Protocol Configuration Elements
IPX Routing Protocols
SAP
IPX Routing Protocol Background Information
Special Considerations Remote LAN Interface
IPX Static Routes
Configuring IPX Static Routes Using Cfgedit
IPX Static Routes Background Information
IPX Static Routes Configuration Elements
Configuring IPX Netware Static Services Using Cfgedit
IPX Netware Static Services
IPX Netware Static Services Configuration Elements
IPX Netware Static Services Background Information
Configuring IPX Spoofing Using Cfgedit
IPX Spoofing
IPX Spoofing Background Information
IPX Spoofing Configuration Elements
Watchdog Protocol
Configuring IPX Type 20 Packet Handling Using Cfgedit
IPX Type 20 Packet Handling Configuration Elements
IPX Type 20 Packet Handling
IPX Isolated Mode Background Information
IPX Isolated Mode
Configuring IPX Isolated Mode Using Cfgedit
IPX Isolated Mode Configuration Elements
Displaying WAN Peer List
Configuring Triggered RIP/SAP Global Timers Using Cfgedit
Triggered RIP/SAP Background Information
IPX-SPECIFIC Information for Devices
Configuring IPX Devices
IPX-Specific Information for Devices
Remote LAN Devices
IPX Configuration Elements for Devices
Enable Bridging and disable Make calls for bridge data
None
IPX Background Information for Devices
Configuring Snmp
Configuring Snmp
Configuring Snmp
Snmp Configuration Elements
Snmp Background Information
WAN
Central Site Remote Access Switch
CT-CONTAINER-MIB CT-WAN-MIB CTMIB2-EXT-MIB
Using Cabletron NMS Systems
Configuring Appletalk Routing
Enabling Appletalk Routing Using Cfgedit
Appletalk Routing Option
Appletalk Routing Background Information
Appletalk Routing Option Configuration Element
Configuring Appletalk Ports Using Cfgedit
Appletalk Ports
Appletalk Ports Configuration Elements
Appletalk Ports Background Information
Overview
Considerations
Configuration
Configuring Appletalk Static Routes Using Cfgedit
Appletalk Static Routes
Appletalk Capacities
Appletalk Routing Static Routes Configuration Elements
Configuring Appletalk Capacities Using Cfgedit
Appletalk Capacities Configuration Elements
Appletalk Capacities Background Information
Appletalk Isolated Mode
Configuring the Appletalk Isolated Mode Using Cfgedit
Appletalk Isolated Mode Configuration Elements
Call Control Menu
Configuring Call Control
Throughput Monitor
Configuring the Throughput Monitor
Throughput Monitor Background Information
Throughput Monitor Configuration Elements
90%
Condition Trigger Number Window Size Utilization
Underload Condition Monitoring
USER’S Guide
Monthly Call Charge
Call Interval Parameters
Monthly Call Charge Background Information
Monthly Call Charge Configuration Elements
Configuring Call Restrictions Using Cfgedit
Call Restrictions
Call Restriction Configuration Elements
Maximum Calls PER DAY
Maximum Call Minutes PER Month
Configuring Bandwidth Reservation
Bandwidth Reservation
Call Restrictions Background Information
Bandwidth Reservation
Select Bandwidth Reservation
Bandwidth Reservation Configuration Elements
Configuring Semipermanent Connections Using Cfgedit
Semipermanent Connections
Bandwidth Reservation Background Information
Semiperm
Semipermanent Connections Configuration Elements
Call Device Commands
Semipermanent Connections Background Information
Throughput Monitor
Call Restrictions
CSM AS a Call Control Manager
Configuring CSM for Call Control Using Cfgedit
Call Control Management
Configuring D Channel Callback Using Cfgedit
Channel Callback
Select D Channel Callback
Channel Callback Background Information
Channel Callback Configuration Elements
Modem Inactivity Timeout Configuration Elements
Digital Modem Inactivity Timeout
Modem Inactivity Timeout Background Information
For IP routing
Configuring Other Advanced Options
Configuring for a Digital Modem Using Cfgedit
Digital Modem
For IPX routing
For AppleTalk routing
Digital Modem Background Information
Digital Modem
PPP Mode Using Cfgedit
Default Async Protocol
Terminal Mode Using Cfgedit
Call Disconnect Using Cfgedit
Default Async Protocol Configuration Elements
Data Timeout Value
Autosense Feature
PPP Configuration
Configuring PPP
PPP Configuration Elements
PPP Configuration
PPP Background Information
Configuring Default Line Protocol Using Cfgedit
Default Line Protocol
LOG Options
Default Line Protocol Configuration Elements
Default Line Protocol Background Information
Configuring LOG Options Using Cfgedit
From Log Options, select Call Detail Recording
From Log Options, select Authentication Message DA log
LOG Options Configuration Elements
Select Add a Syslog Server
LOG Options Background Information
UDP Port
Central Site Remote Access Switch
System Messages
CDR Log Report
Call Detail Recording Events
Event Report Contents
Record
Disconnect/Term Disconnect Event Report Contents
Connect/Term Connect Event Report Contents
System Up Event Report Contents
Reject Event Report Contents
Term Succ Event Report Contents
Term Fail Event Report Contents
Verify Event Report Contents
Configuring Compression Options Using Cfgedit
Compression Options
Compression Options Configuration Elements
Compression Options Background Information
Central Site Remote Access Switch
Configuring Tftp
Tftp Configuration Elements
Tftp Background Information
Configuring File Attributes
File Attributes Configuration Elements
File Attributes
File Attributes Background Information
ARP
Verification and Diagnosis
Verifying the Base System
Hardware Resources OPERATIONAL?
WAN Adapter INITIALIZED?
LAN Adapter INITIALIZED?
To correct the problem, try the following
Verifying WAN Line Availability
WAN Lines Available for USE?
Dedicated Serial Connections
LAN Connection OPERATIONAL?
Try the following to correct the problem
Bridge INITIALIZED?
IP Router INITIALIZED?
Set-up
Remote Device Connectivity
Security Rejection-Invalid Calling Line Id #
To verify multi-level security
MULTI-LEVEL Security
IP Host INITIALIZED?
IP Host Mode
Disabled
IP Host Mode OPERATIONAL?
Try the following
Dedicated Connections
Alternate Accesses
Frame Relay Connections
Connections
A Terminal Server Menu
Verifying Routing Protocols
IP Routing OPERATIONAL?
IP Routing Over a LAN Interface
IP Routing Over a WAN Interface
Ping 192.100.1.1 return
IP Routing Over a WAN Direct Host Interface
100.0.0.1 100.0.0.0 Host B 100.0.0.3 Host a 100.0.0.2
IP Routing Over a WAN Remote LAN Interface
IP Routing Over a WAN Unnumbered Interface
Ip filter trace discard return
IP Filters
If you are still experiencing problems
Ip filter trace off return
IP RIP INITIALIZED?
IP RIP Output Processing on a LAN Interface
IP RIP Input Processing on a LAN Interface
IP RIP Output Processing on a WAN Interface
IP RIP Input Processing Operational on a WAN Interface
IPX Router INITIALIZED?
IPX
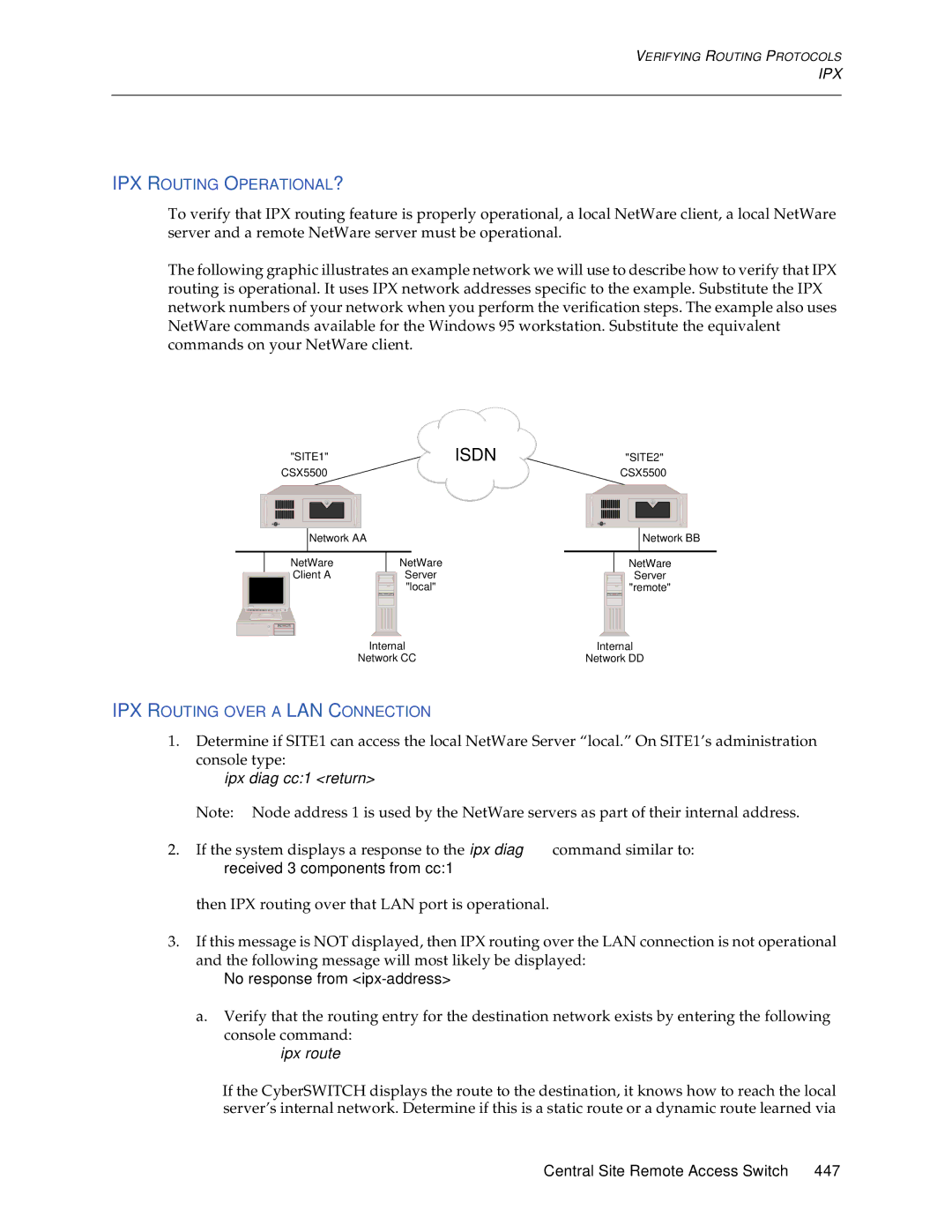
IPX Routing Over a LAN Connection
IPX Routing OPERATIONAL?
IPX Remote LAN Connection
Xxxx
Triggered RIP/SAP
IPX Routing Over a WAN Connection
Ipx trigreq device
Appletalk Routing
Appletalk Routing INITIALIZED?
Appletalk Routing OPERATIONAL?
Appletalk Routing Over the LAN Connection
Atalk port
Appletalk Routing Over a WAN Connection
USER’S Guide
Snmp
Verifying System Options
USER’S Guide
Dial OUT
Set Up
Call Detail Recording
Compression
CyberSWITCH does not have Compression Enabled
Reserved Bandwidth
Peer Protocol-Rejects CCP
Verifying Dhcp Relay Agent Initialization
Verifying the Relay Agent is Enabled
Verifying the Relay Agent is Operational
USER’S Guide
Verifying Dhcp Proxy Client Initialization
Verifying the Proxy Client is Enabled
Verifying the Proxy Client is Operational
Ip addrpool return
Modem Callback
Verifying a Semipermanent Connection
Proxy ARP
Proxy ARP
LCD Messages
Troubleshooting
Normal Operation LCD Messages
LCD Messages
LCD Message Groups
Initialization LCD Message
Error LCD Messages
LCD Message Groups
Auto
Over Max Charge
System Messages
Normal Operation Messages
Error Messages
Informational Messages
Initialization Messages
System Message Summary
Port LAN Adapter, operating in remote mode only
Port LAN Adapter, operating in local and remote mode
Call has exceeded the configured maximum duration
Adapter does not respond adapter #’x’
Acct Warning code Timeout
Adapter #’x’ failed to respond from bootstrap
Activation Failure- Session not active
Auth ACE Could not write service file
Attempting to load FileName for Upgrade
Attempt to initialize unconfigured DM card in slot slot #
Auth ACE Could not create service file
Auth Radius Chap rejected for device device name
Auth ACE Error receiving server log message acknowledgment
Auth ACE Login rejected user user name
Auth ACE Node verification received Client initialized
Auth Radius PAP rejected device device name
Auth Radius Login rejected device device name
Auth Radius IP Host rejected IP Host id IP host Id
Auth Radius IP Resolve rejected IP Address IP address
Auth Warning code 0007 Authentication mode mismatch
Auth Tacacs Login rejected user user name
Auth Warning code 0001 Timeout
Auth Warning code 0004 No authentication node available
Bad auth result in smgrauthaanotify for device device name
Booting System Software
Bootstrap came alive on DM card in slot slot #
Bootstrap came alive on WAN card in slot slot #
CallID in use in Hostcallrequest
Call Restrictions have been disabled by user command
Calculating CRC’s
Callback type call back type ID is not currently supported
Call Restrictions will allow calls to be made this hour
Call Restrictions have been enabled by user command
Call Restriction statistics reset for new day
Call Restriction statistics reset for new month
Central Site Remote Access Switch
CCP Option Negotiation Failure, Non-Convergence detected
Cause cause code received for Dlci dlci index
Cause Code Event
CCP Internal Decompression Failure
Chap Authentication Failure remote device not responding
Channel in use in Hostcallrequest
CNTR-TMRTimed out waiting for TMR number interrupt
Connection disconnected for license violation
Configured adapter # ’x’ type does not exist
Couldn’t find speech service slot #, port #
Current monthly charges reset for new month
DHCP-P Failed to close UDP port x, erc = y
Data link test successful DSL port # , CES
DCE Data Rate is invalid on FrStartPVC
Dedicated connection down slot #, port #
DHCP-P UDP port 67 closed
DHCP-P Proxy Client disabled
DHCP-P Proxy Client enabled
DHCP-P Proxy Client initialization failed
DHCP-R Failed to open UDP port 67, erc =
DHCP-R Relay Agent disabled
DHCP-R Relay Agent enabled
DHCP-R Failed to close UDP port 67, erc =
DM card failed Flash download bad xx Srec
DM card in slot slot # is not usable, could not upgrade
DM card in slot slot # signals it is operational
DM card type configured in slot slot # does not exist
Downloading Bootstrap to DM card in slot slot #
DM card in slot slot # will not come out of reset
DM upgrade started. Board=board #, Modem=modem #
DM upgrade success. Board=board #, Modem=modem #
Error downloading operational software to adapter ’x’
Edrv transmit error error code
Error closing file ’s’
Error downloading bootstrap program to adapter #’x’
Error initializing WAN card WAN card Id
Error during channel initialization Access access index
Error during port initialization Access access index
Error during PVC initialization Access access index
Error reading sdconf.rec file
Error opening file \system\ethernt2.bin
Error programming adapter #’x’ hardware
Error reading file file name, section = section name
Failed to obtain Terminal info in smgrprocterminalauthsess
Failed to get a tone signaling session
Facility not subscribed Slot=slot # Port=port #
Failed to allocate enough memory for Xilinx load file
Failure during read of file ’s’
Failure during Static RAM test on adapter # ’x’
Failure to allocate enough memory for Xilinx load file
Central Site Remote Access Switch
Frame Relay event queue full
File Access Err
Formatting Flash Memory
Frietf detected PPP protocol from NAME, shutting down PVC
Invalid Password password given
Installing File Set into Flash Memory
Interrupt fault on WAN Adapter in Slot slot #
Invalid Cllm received on Access access index
Invalid serial number in SERIAL.001, file is ignored
IP Error from ESP datagram discarded
IP x.x.x.x not added to the pool Unknown error y
Invalid SERIAL.001 file present, file is ignored
IP Failed to de-register with IP Address Pool Manager erc=x
IP Default Route not added, invalid next hop IP address #
IP Invalid configuration for Network Interface dd
IP Cannot stop Proxy Arp for IP address #, no cmd buf avail
IP Network initialized successfully on ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd
IP Invalid Peer IP Address IP address, WAN IP Stream Closed
IP IP host is initialized successfully
IP IP router is initialized successfully
IP Host Call Dropped XID was not received from remote
Ipcp IP Address Pool Out of IP addresses
Ipcp Option Negotiation Failure, Non-Convergence detected
Ipcp Remote device does not negotiate IP address
IP RIP Send queue full
IP RIP All network interfaces used
IP RIP Buffers allocated
IP RIP Initialization failed, unable to allocate buffers
IPX IPX router initialized successfully
IPX Invalid Ipxwc passed
IPX Network initialized successfully on
IPX Network Interface on LAN port port # not initialized
IPX SAP Buffers allocated
IPX SAP Space available in service table
IPX SAP Unable to add service, service table full
Ipxwan IPX Internal Network Number must be configured
LAN Adapter HW upgrade may be required
LAN Adapter Command Timeout
LAN Adapter configuration conflict
LAN Adapter Fatal Error Reported
LAN Init Error
LAN Adapter Reset
LAN Adapter Response Timeout
LAN Adapter System resource error
Manage Mode updates have been successfully committed
LAN Xmit Error
LMI alarm on Access access index
LMI alarm reset Access access index
Max ATI3 retries exceeded on modem modem # of slot slot #
Memory Access Timeout
Mismatch of configured and installed DM card in slot slot #
Manual restart initiated on DM board in slot slot #
Network loop between site1 and site
Modem modem # of DM card in slot slot # is unusable
Modem revision on modem modem # of slot slot # failed
Negotiation Failure with Semipermanent device
No Active List entry available in INM
Network sent Cause Spid not supported slot #, port #
Network sent Status with state = 0, tear down call
No Active Calls Active Sites
Offnode server lookup of Dial Out User failed
Out of LAN Adapter transmit command descriptors
No Sites Connected
Not enough memory for Security module
Out Svc # slot # , port #
Auto For over 5 minutes Report problem to Phone company
PAP Identification timeout on remote device
PAP Invalid password for name given by remote device
Post number, Hdlc #number Internal Loopback Test Failed
PAP Remote device rejected System Information error message
PAP Unknown name name given by remote device
Post number, Hdlc #number External Loopback Test Failed
R2 not capable of Multichannel or Non-circuit calls
PVC for Dlci dlci index not Active
PVC not allocated for dlci index
PVC rcv wait q already full
Rebooting
RBS LIFAddTimer failure
RBSoutSMchannel # Timeout waiting for Wink
Reattempting to Install File Set into Flash Memory
Remote peer ID discrepancy
Replace Lithium Battery Contact your Representative
Reserved signal
Received charge amount charge amount
Security Rejection Caller did not negotiate security
Security Rejection Invalid Password password given
Security Rejection No Password given by caller
Security Rejection Timeout on Startup Complete
Slot #, port # Cfg Error
Semipermanent. Device x disconnected by admin
Semipermanent. Device x reconnected by admin
Signal for unknown CallCmd task task Id
Snmp Unable to obtain an Snmp Trap queue entry buffer
Snmp Authentication failure, unknown community name
Snmp Snmp initialization failure unable to open UDP port
Snmp Snmp initialized successfully
SSB Post 24 i960iointreg Failure
SSB Post 27 i960timer82c54FAILURE
SSB i960 Post number not equal to i386’s
SSB Post 23 i960hostintreg Failure
SSB Post 35 i960hdlc4 Failure
SSB Post 32 i960hdlc1 Failure
SSB Post 33 i960hdlc2 Failure
SSB Post 34 i960hdlc3 Failure
TCP Connection to CSM at IP address is UP
Successfully Loaded Release X.Y Issue Z
Switch could not recognize phone number nnnnnnn
System Clock Fault on Wan Adapter in Slot slot #
Tftp Local error #5 UDP open failed
Tftp Local error #2 Feature not initialized
Tftp Local error #3 Server not initialized
Tftp Local error #4 UDP rejected packet filename
Tftp Local error #19 Disk full filename
Tftp Local error #14 Bad file name
Tftp Local error #15 Bad mode string
Tftp Local error #18 Unable to open file filename
Tftp Remote error # 4 Text from Remote Host
Tftp Remote error # 1 Text from Remote Host
Tftp Remote error # 2 Text from Remote Host
Tftp Remote error # 3 Text from Remote Host
Timeout on Startup Complete
This card does not support R2 Signaling
Timeout detected on connection establishment
Timeout detected on receiving caller’s number
Unable to Decrypt Datagram
Type mismatch of configured & installed adapter # ’x’
Too many digits in TN in Hostcallrequest
Tried to free unallocated buffer sub name, size=size
Unable to get Digital Modem resource to place call
Unable to open \config\devdb.nei file
Unable to open Modem Upgrade file
Unable to restore original ISRs for Interrupt interrupt #
Unknown Calling Bridge MAC address
Unexpected error during transmission of LMI frame
Unmatched Login Task
Updating CyberSWITCH from FileName
X25 facilities error, facilities not allowed in PVC
WAN card in slot slot # signals it is operational
Watchdog timeout detected on DM board in slot slot #
Watchdog timeout detected on WAN board ’x’
X25 facilities error, facility not allowed
X25 facilities error, bad facility length
X25 facilities error, invalid facilities length
X25 facilities error, invalid DTE address
X25 facilities error, Rpoa not available
X25 facilities error, facility not available
X25 facilities error, packet length negotiation not allowed
X25 facilities error, window size negotiation not available
Zone allocation failed, maximum capacity already configured
Trace Messages
Location Causes
Call Trace Messages
Call Trace Message Summary
Configure ack slot #
Inband treatment has been applied
-BRD CFG ACK Slot=slot #
Init data link slot #, port #, ces
Origination call address is non-ISDN
Out configure port #
Interworking unspecified cause
Off-hook warning tone on
Received unknown progress value
Received unknown signal value
Out init data link slot #, port # , ces
Recall dial tone on
IP Filters Trace Messages
PPP Packet Trace Messages
Configure Reject
Configure Request
Configure ACK
Configure NAK
Trace Message Summary
Trace Messages
Echo Reply
Discard Request
X25 DCE RR LCN logical channel number, number of bytes bytes
X25 Data LCN logical channel number, number of bytes bytes
System is sending a call request to the network
Lapb Trace Message Summary
Lapb Trace Messages
Out Lapb DM
Lapb Sabme
Lapb UA
Out Lapb Disc
Remote Management
System Maintenance
Remote Management
SITE.HQ
Usage Instructions
Installation and Configuration
Isdn
Telnet
Earlier Releases
Central Site Remote Access Switch
General tab
Setting UP a NEW Number
Setting UP Server Type
WIN95 DIAL-UP Networking
Dialing OUT
Site HQ Isdn
Users Report Files Statistics Files Config files Other Files
Carbon Copy
Changing Carbon Copy Configuration Parameters
COM1
Modem Type
Baud Rate
Performing a File Transfer Using Carbon Copy
Running Without Carbon Copy
Copy LCNETWORK.NEI HC\CONFIG\NETWORK.NEI
Removing Carbon Copy
Accessing Administration Services
System Commands
Accessing Dynamic Management
Setting the IP Address
Viewing Operational Information
Neif
Connected
Second column is the potential number of connections
Viewing Throughput Information
Throughput Monitor Contents
Clearing Operational Information
Saving Operational Information
CONFIGURATION-RELATED Commands
Terminating and Restarting the Cyberswitch
Setting the Date and Time
Terminating Administration Sessions
Login-Id
Appletalk Routing Commands
State
Type
Physical address
Default zone
Network range
Flags
Zones valid
Distance
Zone
Bridge Commands
Call Control Commands
Indicates that a call request process has been initiated
Call peer phone number data rate device bearer
Calling phone number at data rate, device PPP
Call Restriction Commands
Call Detail Recording Commands
Compression Information Commands
CSM Commands
Dhcp Commands
Digital Modem Commands
Frame Relay Commands
Clears all statistics associated with the fr stat command
IP Routing Commands
Disables the trace
Mask used for the destination
Time since the last update was received
IPX Routing Commands
Ipx diag host ipx address timeout
Isdn Usage Commands
LOG Commands
LAN Commands
Packet Capture Commands
Pkt display
Banyan Vines Packet Detail Screen Bridged Packet
Radius Commands
Radius ipres
Spanning Tree Port Information
Serial Interface Commands
Snmp Commands
Spanning Tree Commands
Spanning Tree Bridge Information
Bridge priority of the root bridge
TCP Commands
Telnet Commands
Possible send parameters are defined as follows
Terminal Commands
Tftp GET
Tftp Commands
Tftp PUT
Trace Commands
User Level Security Commands
UDP Commands
WAN Commands
Commands
Clears the statistics for the default VC
Connectivity Statistics
System Statistics
Call Restriction Statistics
Call Statistics
Throughput Monitoring Statistics
Appletalk Protocol Statistics
Appletalk Statistics
Number of AppleTalk Echo requests received
Count of AppleTalk Echo replies received
Number of NBP LookUp Requests received
Appletalk Port Statistics
Call Detail Recording Statistics
Bridge Statistics
Compression Statistics
Compression Related Statistics
Decompression Related Statistics
Dhcp Statistics
Dhcp Relay Agent statistics and Dhcp Proxy Agent statistics
Common Dhcp Statistics
Dhcp Relay Agent Statistics
Dhcp Proxy Client Statistics
Access Related Statistics
Digital Modem Statistics
Frame Relay Statistics
Init
PVC Related Statistics
LAN Statistics
IP Group Statistics
IP Statistics
Number of IP datagrams successfully reassembled
Icmp Group Statistics
IPX General Statistics
IPX Statistics
Network number portion of the IPX address of this system
IPX RIP Statistics
IPX Route Statistics
IPX Triggered RIP Statistics
IPX Triggered SAP Statistics
IPX SAP Statistics
RIP Interface Statistics
IPX Service Statistics
RIP Statistics
RIP Global Statistics
Snmp Statistics
Serial Interface Statistics
SnmpInBadVersions
SnmpInGetNexts
TCP Statistics
Tftp Statistics
Statistics for Server or Remote Initiated Tftp Activity
Statistics for Local or Client Initiated Tftp Activity
Statistics for ALL Tftp Activity
UDP Statistics
WAN Frietf Statistics
WAN L1P Statistics
Layer 1 PRI Error Statistics
Layer 1 General Statistics
WAN Statistics
Statistics
Maximum number of active VCs allowed at any time
Virtual Circuit VC Related Statistics
USER’S Guide
Making Changes Using Cfgedit
Routine Maintenance
INSTALLING/UPGRADING System Software
Executing Configuration Changes
Configuration Backup and Restore
Making Changes Using Manage Mode
Obtaining System Custom Information
System Worksheets
Appendices
System Adapters
Ethernet Adapter
Ethernet Adapter Side View
Basic Rate Adapter
BRI-4 Adapter Side View
Primary Rate Adapters PRI-8
Front View PRI-8 Adapter Side View
PRI-23 Adapter
PRI-23/30 Adapter
Front View PRI-8 Expander Adapter Side View
Front View Adapter Side View
Front View RS232 Adapter Side View
Digital Modems DM-8
DM-8 Adapter
DM-24 Adapter
OFF
DM-24+/DM-30+
DM-24+ Adapter
DM-24+ Adapter Back view
USA
System Worksheets
Network Topology
System Details
Resources
Lines
Over Isdn
Accesses
Device Information
Authentication Information Frame Relay Information
IP Routing
Bridging and Routing Information
IPX Routing
IP Routing
AppleTalk Routing/Port Information
Appletalk Routing
FR DBU
Main Menu
IPX
Snmp PPP
Physical Resources Menu
SPI
Options Menu
WAN Rlan
Dhcp
Snmp
FR DBU
Security Menu
CSM Radius Tacacs ACE
SVC, PVC
PPP STAC-L25
CSM Radius
CSM
TCP port
Reporting Problems
Getting Assistance
Contacting Cabletron Systems
To Customer Service From
Phone FAX Cabletron Systems System Problem Report
Number of Pages Including this
Administrative Console Commands Table
Displays authentication messages
Command Use Cdr verify
Verifies call detail recording servers are configured
Clears administration screen
Administrative Console Commands Table
Local log file only erases the call detail recording log
Generates a triggered RIP/SAP update request to
Local log file only displays the call detail recording log
Log cdr erase
Changes password for current access level
Displays the current Tftp statistics
Displays system errors and system messages
Specified X.25 access
Writes current authentication messages to disk
Access or the specified access
Sets LCN index default value to m
Manage Mode Commands Table
Address pool
Adds/changes/deletes an IPX address from the IPX
Ipxsvc add/change/delete Adds/changes/deletes an IPX service
Central Site Remote Access Switch
Cause Codes Table
Cause Codes Table
USER’S Guide
Central Site Remote Access Switch
USER’S Guide
Central Site Remote Access Switch
Unknown
Dec Value Hex Value Cause
Index
Atalk
Br stat
Clid 195
Date
Cr stats 596 crossover cable
Ip addrpool
Help 113
Ipcp
Isdn usage commands 607 isolated mode
Netstat -r 443 network flattening
Modem devices
STAC-LZS
Offnode 213, 216
Restart 585 restore
Radius Server configuring
Srcfilt 270 startne
Snmp 352 snmp stats 614 socket number 336 software
Trace lapb
Terminal mode 33, 102, 392, 393
Wan
Wr 72, 584 ws 72